Topic how to find the perimeter of hexagon: Discover the simple steps to accurately calculate the perimeter of a hexagon, whether it’s regular or irregular. This guide provides clear formulas, examples, and expert tips to ensure you can confidently find the perimeter of any hexagon. Perfect for students, teachers, and geometry enthusiasts alike!
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Hexagon
- Introduction to Hexagons
- Types of Hexagons
- Understanding Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeter
- Using Side Lengths to Find Perimeter
- Formulas for Regular Hexagon Perimeter
- Formulas for Irregular Hexagon Perimeter
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Advanced Tips for Finding Perimeter
- Applications of Hexagon Perimeter Calculations
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE:
How to Find the Perimeter of a Hexagon
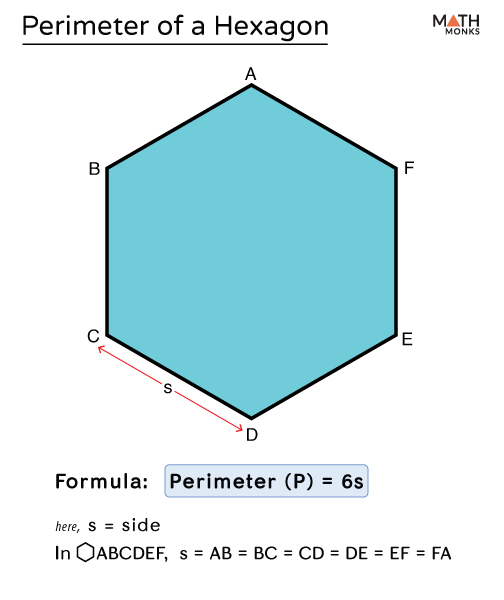
A hexagon is a six-sided polygon. To find the perimeter of a hexagon, you need to know the lengths of its sides. Here, we explore the methods to calculate the perimeter for both regular (all sides equal) and irregular (sides of different lengths) hexagons.
Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon has six equal sides. The formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a regular hexagon is:
\( P = 6 \times s \)
where \( s \) is the length of one side of the hexagon.
Example: If the side length of a regular hexagon is 5 units, then the perimeter is:
\( P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units} \)
Perimeter of an Irregular Hexagon
An irregular hexagon has sides of different lengths. The perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. The formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of an irregular hexagon is:
\( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 \)
where \( s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4, s_5, \) and \( s_6 \) are the lengths of the six sides of the hexagon.
Example: If the sides of an irregular hexagon are 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 units, then the perimeter is:
\( P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 = 33 \text{ units} \)
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Hexagon
- Determine whether the hexagon is regular or irregular.
- If it is a regular hexagon, use the formula \( P = 6 \times s \).
- If it is an irregular hexagon, sum the lengths of all six sides.
Additional Tips
- Ensure that all side lengths are in the same unit before performing the calculations.
- Double-check the side lengths to avoid any errors in your calculation.
- For a regular hexagon, you can often find the side length if you know other properties like the radius or the apothem.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Hexagons
A hexagon is a polygon with six sides and six angles. Hexagons are common in nature and everyday life, found in honeycombs, crystals, and even in the shapes of nuts and bolts. Understanding the properties and characteristics of hexagons is essential for solving various geometric problems, including finding their perimeter.
Hexagons can be classified into two main types:
- Regular Hexagon: All six sides and angles are equal. Each internal angle is \(120^\circ\).
- Irregular Hexagon: The sides and angles are not necessarily equal, leading to a variety of shapes.
The perimeter of a hexagon is the total length of its sides. Calculating the perimeter can be straightforward for regular hexagons but requires more information for irregular hexagons. Here, we will explore the methods to calculate the perimeter for both types.
- Identify the type of hexagon (regular or irregular).
- For a regular hexagon, use the formula \( P = 6s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side.
- For an irregular hexagon, sum the lengths of all six sides: \( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 \).
Understanding these basics will help you approach more complex problems involving hexagons with confidence.
Types of Hexagons
Hexagons are six-sided polygons that can be categorized based on the lengths of their sides and the measures of their internal angles. Understanding the different types of hexagons is crucial for accurately calculating their perimeter.
There are primarily two types of hexagons:
- Regular Hexagon: A regular hexagon has six equal sides and six equal angles. Each internal angle is \(120^\circ\). Regular hexagons are symmetrical and have a high degree of regularity, making them easier to work with in geometric calculations.
- Irregular Hexagon: An irregular hexagon has sides and angles that are not necessarily equal. This type of hexagon can take on a variety of shapes and is less predictable than a regular hexagon. Calculating the perimeter of an irregular hexagon requires knowing the length of each individual side.
Here is a step-by-step comparison between regular and irregular hexagons:
| Feature | Regular Hexagon | Irregular Hexagon |
|---|---|---|
| Sides | All sides are equal | Sides have different lengths |
| Angles | All angles are \(120^\circ\) | Angles vary in measure |
| Symmetry | Highly symmetrical | Asymmetrical |
| Perimeter Calculation | \( P = 6s \) (where \( s \) is the length of one side) | \( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 \) |
Understanding these differences helps in accurately determining the perimeter and other properties of hexagons. Whether dealing with regular or irregular hexagons, knowing their characteristics simplifies many geometric problems.
Understanding Perimeter
The perimeter of a polygon is the total length of its sides. For a hexagon, which has six sides, the perimeter is the sum of these sides. Knowing how to calculate the perimeter is essential for various applications in geometry, engineering, and everyday problems.
To better understand the concept of perimeter, let's break it down:
- Definition: The perimeter is the distance around a two-dimensional shape. For polygons, it is the sum of the lengths of all the sides.
- Calculation: The method to calculate the perimeter varies depending on whether the hexagon is regular or irregular.
For a regular hexagon, where all sides are equal, the formula is straightforward:
\( P = 6 \times s \)
where \( s \) is the length of one side. For example, if each side of a regular hexagon is 4 units long, the perimeter is:
\( P = 6 \times 4 = 24 \text{ units} \)
For an irregular hexagon, the sides have different lengths. The perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all six sides:
\( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 \)
For example, if the side lengths are 3, 5, 4, 6, 7, and 2 units, the perimeter is:
\( P = 3 + 5 + 4 + 6 + 7 + 2 = 27 \text{ units} \)
Here are the steps to find the perimeter of any hexagon:
- Identify whether the hexagon is regular or irregular.
- Measure the length of each side. For a regular hexagon, measure one side.
- Apply the appropriate formula:
- For a regular hexagon, multiply the side length by 6.
- For an irregular hexagon, sum the lengths of all six sides.
- Sum the measurements to find the perimeter.
Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a hexagon enables you to solve various geometric problems and apply these principles in real-world contexts.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a hexagon, whether regular or irregular, involves different steps. This guide will provide a detailed, step-by-step process for both types.
For a Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon has six equal sides, simplifying the calculation of its perimeter. Follow these steps:
- Measure One Side: Determine the length of one side of the hexagon. Let's call this length \( s \).
- Apply the Formula: Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular hexagon:
\( P = 6 \times s \)
- Calculate the Perimeter: Multiply the length of one side by 6 to find the total perimeter.
\( P = 6 \times s \)
- Example: If the side length is 7 units:
\( P = 6 \times 7 = 42 \text{ units} \)
For an Irregular Hexagon
An irregular hexagon has sides of different lengths, requiring a different approach. Follow these steps:
- Measure Each Side: Measure the length of all six sides of the hexagon. Denote these lengths as \( s_1, s_2, s_3, s_4, s_5, \) and \( s_6 \).
- Sum the Lengths: Add the lengths of all six sides together to find the perimeter.
\( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 \)
- Calculate the Perimeter: Perform the addition to get the total perimeter.
\( P = s_1 + s_2 + s_3 + s_4 + s_5 + s_6 \)
- Example: If the side lengths are 3, 5, 4, 6, 7, and 2 units:
\( P = 3 + 5 + 4 + 6 + 7 + 2 = 27 \text{ units} \)
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any hexagon, whether it is regular or irregular. This process is essential for solving various geometric problems and applying these calculations in practical situations.

Using Side Lengths to Find Perimeter
Finding the perimeter of a hexagon is straightforward if you know the lengths of its sides. The perimeter is the total length around the hexagon, which is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. There are two main types of hexagons to consider: regular and irregular.
Regular Hexagon
A regular hexagon has all sides of equal length. To find the perimeter of a regular hexagon, you can use the following formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 6 \times \text{side length} \]
For example, if each side of the hexagon is 5 units long, the perimeter would be:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 6 \times 5 = 30 \text{ units} \]
Irregular Hexagon
An irregular hexagon has sides of different lengths. To find the perimeter of an irregular hexagon, you simply add up the lengths of all the sides. The formula is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e + f \]
where \(a, b, c, d, e,\) and \(f\) are the lengths of the sides of the hexagon. For instance, if the side lengths are 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, and 8 units respectively, the perimeter would be:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7 + 8 = 33 \text{ units} \]
Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify whether the hexagon is regular or irregular.
- If the hexagon is regular, measure one side.
- Use the formula \( \text{Perimeter} = 6 \times \text{side length} \) to find the perimeter of a regular hexagon.
- If the hexagon is irregular, measure all six sides.
- Use the formula \( \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c + d + e + f \) to find the perimeter of an irregular hexagon.
Examples
Here are a few more examples to illustrate the process:
- Regular Hexagon Example: Side length = 10 units
- Irregular Hexagon Example: Side lengths = 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, and 12 units
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 6 \times 10 = 60 \text{ units} \]
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2 + 4 + 6 + 8 + 10 + 12 = 42 \text{ units} \]
Formulas for Regular Hexagon Perimeter
A regular hexagon is a polygon with six equal sides and six equal angles. Calculating the perimeter of a regular hexagon is straightforward due to its symmetrical properties.
The formula for the perimeter P of a regular hexagon is given by:
\[ P = 6a \]
where a is the length of one side of the hexagon.
To find the perimeter of a regular hexagon:
- Measure the length of one side of the hexagon.
- Multiply the length of the side by 6.
For example, if each side of a regular hexagon is 5 units long, the perimeter is calculated as:
\[ P = 6 \times 5 = 30 \, \text{units} \]
Thus, the perimeter of the hexagon is 30 units.
Here are a few more examples to illustrate:
- If the side length a is 7 units, then
\[ P = 6 \times 7 = 42 \, \text{units} \] - If the side length a is 10 units, then
\[ P = 6 \times 10 = 60 \, \text{units} \]
Understanding and applying this simple formula allows for quick and accurate calculations of the perimeter for any regular hexagon.
Formulas for Irregular Hexagon Perimeter
The perimeter of an irregular hexagon is the total distance around the hexagon, which is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. Unlike a regular hexagon, where all sides are equal, an irregular hexagon has sides of different lengths. Here are the steps and formulas to calculate the perimeter of an irregular hexagon:
- Identify the Lengths: Measure the lengths of all six sides of the hexagon. Let's denote these side lengths as \(a_1, a_2, a_3, a_4, a_5,\) and \(a_6\).
- Sum the Lengths: Add the lengths of all the sides to find the perimeter.
The formula to calculate the perimeter (P) is:
Which simplifies to:
Example Calculation
Suppose an irregular hexagon has the following side lengths:
- Side 1: 5 cm
- Side 2: 7 cm
- Side 3: 8 cm
- Side 4: 6 cm
- Side 5: 9 cm
- Side 6: 4 cm
To find the perimeter, we sum these lengths:
Using Coordinates
If the coordinates of the vertices are known, we can use the distance formula to find the lengths of the sides. For example, for two vertices with coordinates \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\), the distance between them is:
Calculate the distances for all adjacent vertices, sum these distances, and you get the perimeter of the irregular hexagon.
Examples and Practice Problems
Let's go through some examples and practice problems to solidify your understanding of how to find the perimeter of a hexagon. We'll start with regular hexagons and then move to irregular hexagons.
Example 1: Regular Hexagon
Given a regular hexagon with a side length of 5 cm, find the perimeter.
- Identify that a regular hexagon has all six sides of equal length.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular hexagon: P = 6s, where s is the side length.
- Substitute the given side length into the formula: P = 6 * 5.
- Calculate the perimeter: P = 30 cm.
Therefore, the perimeter of the regular hexagon is 30 cm.
Example 2: Irregular Hexagon
Given an irregular hexagon with side lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, find the perimeter.
- List all the side lengths of the hexagon: 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm.
- Add the lengths together to find the perimeter: P = 3 + 4 + 5 + 3 + 4 + 5.
- Calculate the perimeter: P = 24 cm.
Therefore, the perimeter of the irregular hexagon is 24 cm.
Practice Problems
- Problem 1: Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon with a side length of 7 cm.
- Problem 2: An irregular hexagon has side lengths of 2 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm. Calculate its perimeter.
- Problem 3: A regular hexagon's perimeter is 42 cm. Determine the length of one side.
- Problem 4: Given an irregular hexagon with sides of lengths 6 cm, 8 cm, 10 cm, 6 cm, 8 cm, and 10 cm, find the perimeter.
Answers to Practice Problems
- Answer to Problem 1:
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a regular hexagon: P = 6s.
- Substitute the given side length: P = 6 * 7.
- Calculate the perimeter: P = 42 cm.
- Answer to Problem 2:
- List all the side lengths: 2 cm, 3 cm, 4 cm, 5 cm, 6 cm, 7 cm.
- Add the lengths together: P = 2 + 3 + 4 + 5 + 6 + 7.
- Calculate the perimeter: P = 27 cm.
- Answer to Problem 3:
- Use the perimeter formula: P = 6s.
- Given P = 42 cm, solve for s: s = P / 6 = 42 / 6.
- Calculate the side length: s = 7 cm.
- Answer to Problem 4:
- List all the side lengths: 6 cm, 8 cm, 10 cm, 6 cm, 8 cm, 10 cm.
- Add the lengths together: P = 6 + 8 + 10 + 6 + 8 + 10.
- Calculate the perimeter: P = 48 cm.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Calculating the perimeter of a hexagon, whether regular or irregular, can sometimes lead to errors. Here are common mistakes and tips on how to avoid them:
- Misidentifying Hexagon Type:
Confusing a regular hexagon with an irregular one can lead to incorrect perimeter calculations. A regular hexagon has all sides of equal length, while an irregular hexagon does not. Ensure you correctly identify the type before proceeding with the calculations.
- Incorrect Formula Application:
For a regular hexagon, use the formula \( P = 6s \), where \( s \) is the side length. For an irregular hexagon, sum the lengths of all six sides. Verify that you are using the correct formula for the given hexagon type.
- Inaccurate Measurements:
Ensure all side lengths are measured accurately. Even small measurement errors can lead to significant discrepancies in the perimeter calculation.
- Unit Conversion Errors:
If side lengths are given in different units, convert them to a common unit before summing. For example, convert all measurements to centimeters or meters before performing the calculation.
- Ignoring Diagonals and Angles:
In some complex problems, especially involving irregular hexagons, ignoring the relationships between diagonals and angles can lead to errors. Be thorough in considering all geometric properties relevant to the problem.
- Arithmetic Mistakes:
Simple addition errors can affect the final perimeter result. Double-check your calculations to ensure accuracy.
By being mindful of these common mistakes and carefully applying the correct methods, you can accurately find the perimeter of any hexagon. Practice with various examples to build confidence and proficiency.
Advanced Tips for Finding Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a hexagon, whether regular or irregular, can be made more efficient and accurate with the following advanced tips:
- Use of Symmetry: For regular hexagons, leverage the symmetry of the shape. Since all sides are equal, simply measure one side and multiply by six:
\[ P = 6s \]
where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( s \) is the side length. - Calculating Perimeter from Area: If the area of a regular hexagon is known, you can find the side length and then the perimeter. The formula for the area \( A \) of a regular hexagon with side length \( s \) is:
Solving for \( s \):
\[ A = \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} s^2 \]
Once you have \( s \), use it to find the perimeter:
\[ s = \sqrt{\frac{2A}{3\sqrt{3}}} \]
\[ P = 6s \] - Coordinate Geometry Method: For irregular hexagons, if the coordinates of the vertices are known, use the distance formula to calculate the length of each side:
Sum the lengths of all six sides to get the perimeter:
\[ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
\[ P = d_1 + d_2 + d_3 + d_4 + d_5 + d_6 \] - Use of Trigonometry: For hexagons inscribed in a circle (circumscribed hexagons), the radius \( R \) can be used to find the side length. For a regular hexagon:
Therefore, the perimeter can be calculated as:
\[ s = R \]
\[ P = 6R \] - Breaking Down into Triangles: Divide the hexagon into six equilateral triangles. For regular hexagons, use the properties of these triangles to find side lengths if only partial information is available.
Each side of the hexagon equals the side of one of these triangles.
By using these advanced methods, you can simplify the process of finding the perimeter of both regular and irregular hexagons, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in your calculations.
Applications of Hexagon Perimeter Calculations
Understanding the perimeter of hexagons has numerous practical applications across various fields. Here are some notable examples:
- Architecture and Design
Hexagonal shapes are often used in architecture for floor tiles, pavements, and building designs due to their aesthetic appeal and structural efficiency. Knowing the perimeter helps in estimating materials and costs.
- Beekeeping
The hexagonal honeycomb structure in beehives is a classic example from nature. Beekeepers use perimeter calculations to estimate the amount of wax needed for artificial hives or to gauge honey production capacity.
- Chemistry
Hexagonal patterns are prevalent in the molecular structures of many compounds, such as graphene. Scientists calculate the perimeter to understand bond lengths and molecular stability.
- Game Design
Many board games and digital games use hexagonal grids for complex playing fields. Knowing the perimeter helps in designing balanced and engaging game mechanics.
- Engineering
Hexagons are employed in engineering for their strength and ease of use, such as in bolts and nuts. Engineers calculate the perimeter to size tools and components accurately.
- Land Surveying
Hexagon-shaped plots of land may need their perimeters calculated for legal or developmental purposes. Land surveyors rely on these measurements for accuracy.
- Urban Planning
Hexagonal grids are used in urban planning to optimize land use and infrastructure design, requiring accurate perimeter calculations for implementation.
These applications highlight the importance of understanding hexagon perimeters in both natural and industrial contexts, demonstrating the wide-ranging utility of this geometric concept.
Conclusion and Summary
Understanding how to find the perimeter of a hexagon is crucial in various mathematical and practical applications. This guide has provided comprehensive insights into different types of hexagons and the methods used to calculate their perimeters.
- Introduction to Hexagons: Hexagons are six-sided polygons commonly found in nature and various man-made structures.
- Types of Hexagons: We explored regular and irregular hexagons, with regular hexagons having equal side lengths and angles, while irregular hexagons do not.
- Understanding Perimeter: The perimeter is the total distance around a hexagon, calculated by summing the lengths of all its sides.
- Perimeter of a Regular Hexagon: The formula
P = 6a(whereais the side length) is used for regular hexagons. - Perimeter of an Irregular Hexagon: For irregular hexagons, the perimeter is the sum of all six side lengths.
- Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating Perimeter: Detailed steps were provided to calculate the perimeter for both regular and irregular hexagons.
- Examples and Practice Problems: Practical examples illustrated how to apply the formulas, enhancing understanding.
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them: We highlighted frequent errors and provided tips to prevent them.
- Advanced Tips for Finding Perimeter: Advanced methods, including using vertices coordinates, were discussed.
- Applications of Hexagon Perimeter Calculations: Various applications in fields like architecture, engineering, and nature were explored.
By mastering these concepts, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any hexagon, whether regular or irregular. This knowledge is not only academically valuable but also practically useful in real-world situations. Keep practicing with different examples to strengthen your understanding and application skills.
Thank you for following this guide. We hope it has been informative and helpful in your learning journey.

GRADE 7: CHU VI HÌNH LỤC GIÁC
READ MORE:
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Lục Giác Đều: Bài Toán Hàng Ngày
