Topic formula of perimeter of square: The formula of the perimeter of a square is essential for anyone studying geometry. This complete guide will help you understand the concept, learn how to calculate it, and apply it in various scenarios. Whether you're a student or just curious, this article will provide you with all the information you need.
Table of Content
- Perimeter of a Square
- Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
- Definition and Basic Concept
- Formula for Calculating Perimeter
- Step-by-Step Calculation Process
- Mathematical Derivation of the Formula
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Applications in Real Life
- Visual Representation and Diagrams
- Advanced Topics and Further Reading
- FAQs about Perimeter of a Square
- Summary and Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi của hình vuông với Thầy J. Video này phù hợp cho những ai muốn nắm vững công thức tính chu vi hình vuông.
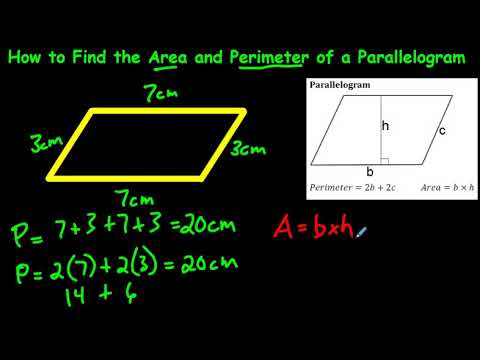
Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is the total length of all four sides of the square. Since all sides of a square are equal in length, the formula to calculate the perimeter is straightforward.
Formula
If s represents the length of one side of the square, then the formula for the perimeter P is:
In LaTeX format:
Example Calculation
Let's say the side length of a square is 5 units. Using the formula:
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Square
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4.
- The result is the perimeter of the square.
By following these simple steps, you can easily find the perimeter of any square.
| Side Length (s) | Perimeter (P) |
|---|---|
| 3 units | |
| 7 units |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Perimeter of a Square
The perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry that measures the total length around the square. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is crucial for various mathematical and real-world applications. The formula for the perimeter of a square is simple and easy to remember.
A square is a four-sided polygon, also known as a quadrilateral, with all sides equal in length and all angles equal to 90 degrees. This unique property of squares makes calculating their perimeter straightforward.
The formula for the perimeter (P) of a square is:
Where s represents the length of one side of the square.
Here’s how to calculate the perimeter step-by-step:
- Measure the length of one side of the square.
- Multiply this length by 4 to account for all four sides.
- The result is the perimeter of the square.
For example, if one side of a square is 5 units long, the perimeter is calculated as:
Understanding the perimeter of a square can help in various applications, such as:
- Planning the amount of material needed for a border around a square garden.
- Determining the fencing required for a square plot of land.
- Calculating the boundary length for square-based projects in construction and design.
The concept of perimeter is not only limited to squares but is also applicable to other polygons. However, the simplicity of the square’s properties makes it an excellent starting point for learning about perimeters.
Definition and Basic Concept
The perimeter of a square is defined as the total distance around the outside of the square. It is a measure of the boundary length of the square and is an essential concept in geometry.
A square is a special type of quadrilateral where all four sides are equal in length and all interior angles are right angles (90 degrees). Due to these properties, calculating the perimeter of a square is straightforward.
The basic formula for the perimeter of a square is:
Where:
- P is the perimeter of the square.
- s is the length of one side of the square.
Let's break down the concept step-by-step:
- Identify the length of one side of the square. Since all sides are equal, you only need to measure one side.
- Multiply the length of this side by 4, as the square has four equal sides.
- The resulting value is the perimeter of the square.
For example, if the length of one side of the square is 6 units, the perimeter can be calculated as:
This formula works because the perimeter of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of all its sides, and for a square, this is simply four times the length of one side.
Understanding the perimeter of a square is not only important in theoretical geometry but also in practical applications such as construction, crafting, and any task that involves creating or enclosing square shapes.
Formula for Calculating Perimeter
The formula for calculating the perimeter of a square is simple and easy to remember due to the unique properties of a square. The perimeter is the total distance around the boundary of the square, which can be calculated using the length of one side.
The basic formula for the perimeter P of a square is:
Where:
- P is the perimeter of the square.
- s is the length of one side of the square.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to using this formula:
- Measure one side of the square: Since all sides of a square are equal, you only need to measure the length of one side.
- Multiply by 4: Multiply the length of one side by 4 to account for all four sides of the square.
- Result: The resulting value is the perimeter of the square.
For example, if the length of one side of the square is 8 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
This formula is derived from the fact that a square has four equal sides. Therefore, multiplying the length of one side by 4 gives the total distance around the square.
Let's look at another example for clarity. If one side of a square is 12 units long, the perimeter calculation would be:
This straightforward calculation demonstrates how the formula works efficiently for any given side length of a square.
Understanding this formula is beneficial for various practical applications, such as determining the amount of material needed for framing a square picture, constructing a square garden, or any project involving square boundaries.
Step-by-Step Calculation Process
Calculating the perimeter of a square involves a straightforward process using the simple formula. Here is a detailed, step-by-step guide to help you understand and perform the calculation accurately.
- Identify the length of one side:
First, measure the length of one side of the square. Since all sides of a square are equal, you only need the measurement of one side.
- Apply the formula:
Use the perimeter formula for a square:
where P is the perimeter and s is the length of one side of the square.
- Perform the multiplication:
Multiply the length of the side by 4. This step accounts for all four equal sides of the square.
For example, if the side length s is 7 units:
- Result:
The result of the multiplication gives you the perimeter of the square. In the above example, the perimeter is 28 units.
Let's look at another example to ensure clarity:
Suppose the side length of a square is 10 units. Using the formula, the calculation is:
Therefore, the perimeter of a square with a side length of 10 units is 40 units.
To summarize, the step-by-step process to calculate the perimeter of a square involves:
- Measuring one side of the square.
- Multiplying the side length by 4.
- Obtaining the result, which is the perimeter.
By following these simple steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any square, making it a useful skill for both academic and practical purposes.

Mathematical Derivation of the Formula
The formula for the perimeter of a square is derived from the basic properties of a square. Understanding this derivation helps in grasping the fundamental concepts of geometry and can be useful in various mathematical contexts.
A square is defined as a quadrilateral with all four sides of equal length and all angles equal to 90 degrees. To derive the formula for its perimeter, follow these steps:
- Understand the structure of a square:
A square has four equal sides. If we denote the length of one side as s, then each of the four sides of the square is s.
- Perimeter definition:
The perimeter of a polygon is the total distance around the polygon, which means adding up the lengths of all its sides.
- Sum the sides:
Since a square has four sides of equal length, we sum these sides:
This can be simplified by combining like terms:
Thus, the formula for the perimeter P of a square with side length s is:
To further illustrate, let's consider a square with a side length of 5 units. Applying the formula:
This derivation shows that the perimeter is simply four times the length of one side, reflecting the symmetry and equal side lengths of a square.
Understanding this derivation is not only important for academic purposes but also enhances problem-solving skills by reinforcing the logical steps needed to arrive at a formula from basic principles.
Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding the perimeter of a square through examples and practice problems helps solidify the concept. Below are some examples and problems to practice.
Example 1
Calculate the perimeter of a square with a side length of 5 cm.
- Identify the side length: \( s = 5 \, \text{cm} \)
- Use the formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Substitute the side length into the formula: \( P = 4 \times 5 \, \text{cm} \)
- Calculate the result: \( P = 20 \, \text{cm} \)
Therefore, the perimeter of the square is 20 cm.
Example 2
Find the perimeter of a square whose side length is 12 inches.
- Identify the side length: \( s = 12 \, \text{in} \)
- Use the formula: \( P = 4s \)
- Substitute the side length into the formula: \( P = 4 \times 12 \, \text{in} \)
- Calculate the result: \( P = 48 \, \text{in} \)
Therefore, the perimeter of the square is 48 inches.
Practice Problems
Try solving these problems on your own to practice:
- 1. What is the perimeter of a square with a side length of 7 m?
- 2. Calculate the perimeter of a square where each side is 15 cm.
- 3. If a square has a side length of 25 mm, find its perimeter.
- 4. Determine the perimeter of a square with a side length of 9 feet.
- 5. Find the perimeter of a square whose side length is 20 yards.
Solutions
Here are the solutions to the practice problems:
- 1. \( P = 4 \times 7 \, \text{m} = 28 \, \text{m} \)
- 2. \( P = 4 \times 15 \, \text{cm} = 60 \, \text{cm} \)
- 3. \( P = 4 \times 25 \, \text{mm} = 100 \, \text{mm} \)
- 4. \( P = 4 \times 9 \, \text{ft} = 36 \, \text{ft} \)
- 5. \( P = 4 \times 20 \, \text{yd} = 80 \, \text{yd} \)
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Calculating the perimeter of a square seems straightforward, but several common mistakes can lead to incorrect results. Here are some pitfalls to watch out for and how to avoid them:
-
Incorrect Formula Usage:
The perimeter of a square is given by the formula \( P = 4s \), where \( s \) is the length of one side. Ensure you use this formula correctly and do not confuse it with formulas for other shapes.
-
Misidentifying the Side Length:
Always identify the correct measurement for the side length of the square. Sometimes, problems may provide the area or the diagonal instead of the side length.
For example, if given the area \( A \), find the side length using \( s = \sqrt{A} \). If given the diagonal \( d \), use \( s = \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} \).
-
Unit Conversion Errors:
Ensure all side lengths are in the same unit before applying the perimeter formula. Convert units where necessary to maintain consistency.
-
Overlooking Equal Side Lengths:
A square has four equal sides. Double-check that the length used for all four sides is the same, as errors here can lead to incorrect perimeter calculations.
-
Arithmetic Mistakes:
Simple arithmetic errors can lead to incorrect results. Carefully perform each multiplication and addition step.
For example, for a square with a side length of 5 units, calculate \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units.
-
Misinterpreting Diagonal as Side Length:
In some problems, the diagonal of the square is given. Do not use the diagonal length directly as the side length in the perimeter formula. Instead, convert it first: \( s = \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} \).
By being aware of these common mistakes and following the correct steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any square.
Applications in Real Life
The perimeter of a square has various practical applications in real life. Here are some common scenarios where understanding and calculating the perimeter of a square is useful:
- Gardening: When designing or laying out a square garden, the perimeter helps in determining the length of fencing needed. For example, if each side of the garden is 5 meters, the total fencing required would be 4 times 5 meters, which equals 20 meters.
- Construction: In construction, the perimeter is used to plan the layout of square rooms, offices, or any square structures. Knowing the perimeter helps in estimating materials like baseboards or trim required for the room.
- Interior Design: When arranging furniture or designing the layout of a room, the perimeter can help in ensuring that all pieces fit well within the space without overcrowding.
- Real Estate: For real estate purposes, the perimeter of a plot is important for legal descriptions and property boundaries, particularly if the plot is square-shaped.
- Farming: Farmers use the perimeter to estimate the amount of fencing needed for square plots to secure their fields and livestock.
- Art and Craft: In art and craft projects, such as creating square frames or decorations, the perimeter helps in cutting materials to the right length.
Example Calculations
Here are some example problems to illustrate the application of perimeter calculations:
A square garden has a side length of 8 meters. To find the perimeter, use the formula:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{side} \]
Substitute the side length:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 8 = 32 \text{ meters} \]
The perimeter of the garden is 32 meters.
A farmer wants to fence a square field with each side measuring 15 meters. Calculate the perimeter:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 15 = 60 \text{ meters} \]
The farmer needs 60 meters of fencing.
An interior designer is planning a square room with a side length of 12 feet. Determine the length of baseboards required to cover the perimeter of the room:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 4 \times 12 = 48 \text{ feet} \]
The room requires 48 feet of baseboards.
By understanding and using the formula for the perimeter of a square, various real-life problems and planning tasks can be efficiently solved.

Visual Representation and Diagrams
Understanding the perimeter of a square becomes easier with visual representations and diagrams. Here, we will provide clear diagrams and step-by-step explanations to illustrate the concept.
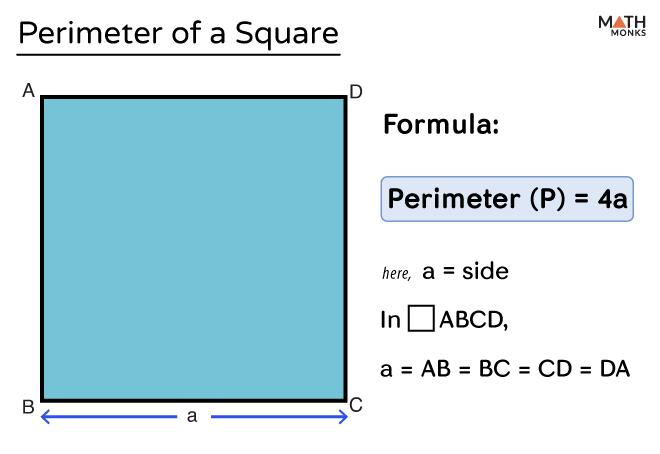
Diagram of a Square
Below is a diagram of a square with its sides labeled:
In the diagram above, each side of the square is labeled as \( a \).
Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter of a square is the total length around the square. Since all four sides of a square are equal, the perimeter (P) is calculated as:
\( P = 4a \)
Step-by-Step Calculation
- Identify the length of one side of the square. Let's denote it as \( a \).
- Multiply the length of the side by 4 to get the perimeter:
- If \( a = 5 \) units, then \( P = 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units.
Interactive Diagram
To further illustrate, let's look at an interactive diagram where you can adjust the length of the sides:
Using tools like Geogebra, you can change the value of \( a \) and observe how the perimeter changes in real-time.
Examples
Let's go through a couple of examples to reinforce the concept:
- Example 1: If the side length \( a = 7 \) cm, the perimeter \( P = 4 \times 7 = 28 \) cm.
- Example 2: If the side length \( a = 10 \) m, the perimeter \( P = 4 \times 10 = 40 \) m.
Conclusion
Visualizing the perimeter of a square through diagrams and interactive tools can significantly enhance understanding. Practice drawing and labeling squares, and use interactive resources to experiment with different side lengths.
Advanced Topics and Further Reading
The perimeter of a square might seem like a straightforward concept, but there are several advanced topics and interesting mathematical extensions worth exploring. Here, we delve into some of these topics to enhance your understanding and provide further reading resources.
-
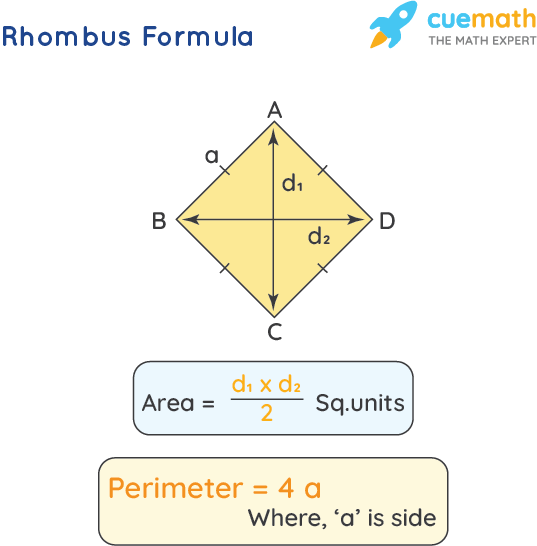
1. Perimeter Using Diagonal
When the diagonal of a square is known, the perimeter can be calculated using the formula:
\[
P = 2\sqrt{2} \times d
\]where \(d\) is the length of the diagonal. This formula is derived from the Pythagorean theorem, considering that the diagonal forms a right triangle with two sides of the square.
For example, if the diagonal is 10 cm, the perimeter would be:
\[
P = 2\sqrt{2} \times 10 = 20\sqrt{2} \approx 28.28 \text{ cm}
\] -
2. Perimeter Using Area
If the area of a square is known, the perimeter can be calculated with the following steps:
- Calculate the side length \(a\) from the area \(A\) using:
\[
a = \sqrt{A}
\] - Then, calculate the perimeter \(P\) using:
\[
P = 4a
\]
For instance, if the area is 36 square meters, the side length is \(6\) meters, and the perimeter is:
\[
P = 4 \times 6 = 24 \text{ meters}
\] - Calculate the side length \(a\) from the area \(A\) using:
-
3. Perimeter and Quadrilateral Inequality
It is interesting to note that among all quadrilaterals with a given perimeter, the square has the maximum area. This property highlights the efficiency of the square in enclosing space compared to other quadrilaterals.
The relationship can be summarized as:
\[
16 \times \text{Area} = \text{Perimeter}^2
\]For any other quadrilateral, this inequality holds:
\[
16 \times \text{Area} < \text{Perimeter}^2
\] -
4. Applications in Optimization Problems
The properties of squares are extensively used in optimization problems, especially in fields like architecture, engineering, and computer science. For instance, when designing a plot of land to maximize usable space while minimizing fencing cost, the square shape often provides an optimal solution.
Further Reading
FAQs about Perimeter of a Square
Below are some frequently asked questions about the perimeter of a square:
- What is the Perimeter of a Square in Math?
The perimeter of a square in math is the total length around its boundary. The formula for the perimeter of a square is expressed as \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \).
- What is the Formula for the Perimeter of a Square?
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a square is \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \). This formula comes from the fact that all four sides of a square are equal in length.
- How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Square?
To calculate the perimeter of a square, you simply multiply the length of one side by 4. For example, if one side of a square is 5 units, the perimeter is \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units.
- What is the Area and Perimeter of a Square?
The area of a square is the space contained within its boundaries, calculated by the formula \( \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \). The perimeter is the total length around the square, calculated by \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \).
- How to Find the Side Length of a Square When the Perimeter is Given?
If the perimeter \( P \) is given, the side length can be found using the formula \( \text{side} = \frac{P}{4} \). For example, if the perimeter is 20 units, each side is \( \frac{20}{4} = 5 \) units.
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Square When the Area is Given?
When the area \( A \) is given, you can find the side length by taking the square root of the area: \( \text{side} = \sqrt{A} \). Then, use the side length to find the perimeter: \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \). For example, if the area is 25 square units, the side length is \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) units, and the perimeter is \( 4 \times 5 = 20 \) units.
- What is the Unit of Perimeter of a Square?
The perimeter of a square is measured in linear units, such as meters (m), centimeters (cm), inches (in), etc., depending on the units used for the side length.
- How to Use a Perimeter of Square Calculator?
A perimeter of square calculator is a tool that quickly calculates the perimeter when you input the side length. Simply enter the side length into the calculator, and it will compute the perimeter using the formula \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \).
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Square When the Diagonal is Given?
If the diagonal \( d \) is given, the side length can be found using the formula \( \text{side} = \frac{d}{\sqrt{2}} \). Then, calculate the perimeter using \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \). For example, if the diagonal is \( 8\sqrt{2} \) units, the side length is \( \frac{8\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}} = 8 \) units, and the perimeter is \( 4 \times 8 = 32 \) units.
Summary and Conclusion
The perimeter of a square is a fundamental concept in geometry that is essential for understanding various mathematical principles and real-life applications. Here is a comprehensive summary of the key points discussed in this guide:
- The perimeter of a square is the total distance around the outside of the square.
- To calculate the perimeter, you need to know the length of one side of the square.
- The formula for the perimeter of a square is:
- Where P represents the perimeter and s represents the length of one side of the square.
- To find the perimeter, simply multiply the length of one side by 4.
For example, if the side length of a square is 5 units, the perimeter is:
Understanding the perimeter of a square is useful in various real-life contexts such as construction, design, and any scenario where determining the boundary length is necessary.
To avoid common mistakes:
- Ensure you are using the correct formula for the perimeter and not confusing it with the area.
- Double-check the length of the side measurement before performing the calculation.
In conclusion, mastering the concept of the perimeter of a square enhances your mathematical skills and prepares you for more advanced geometrical studies. This guide has provided a detailed exploration of the definition, formula, calculation steps, common errors, and practical applications of the perimeter of a square.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi của hình vuông với Thầy J. Video này phù hợp cho những ai muốn nắm vững công thức tính chu vi hình vuông.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Hình Vuông | Toán Học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm diện tích và chu vi của hình vuông. Video này phù hợp cho những ai muốn nắm vững công thức tính diện tích và chu vi hình vuông.
Cách Tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi Hình Vuông