Topic flocabulary area and perimeter: Explore the exciting world of geometry with Flocabulary's Area and Perimeter content. Learn how music and interactive lessons make understanding these fundamental concepts both fun and memorable. Dive into creative resources that turn math challenges into an enjoyable learning experience, perfect for students and educators alike!
Table of Content
- Flocabulary: Area and Perimeter
- Introduction to Area and Perimeter
- Flocabulary Overview: Engaging Learning through Music
- Understanding Area
- Understanding Perimeter
- Formulas for Calculating Area
- Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
- Visual Learning: Diagrams and Videos
- Interactive Learning Activities
- Common Mistakes and Tips for Success
- Practice Problems and Solutions
- Real-Life Applications of Area and Perimeter
- Assessment and Evaluation Tools
- Additional Resources and References
- Conclusion: Mastering Area and Perimeter with Flocabulary
- YOUTUBE: Video hấp dẫn về cách tìm diện tích và chu vi qua nhạc rap giáo dục. Thích hợp cho chương trình toán học và giúp học sinh nắm vững các khái niệm toán học cơ bản.
Flocabulary: Area and Perimeter
Flocabulary offers engaging and educational resources to help students understand mathematical concepts such as area and perimeter. These resources are designed to make learning fun and effective through the use of rap videos, interactive activities, and lesson plans.
Key Features
- Video Lessons: Flocabulary provides educational rap videos that explain the concepts of area and perimeter in an entertaining way, making it easier for students to grasp these mathematical ideas.
- Interactive Activities: The platform includes various activities that reinforce the learning from the videos. These activities are designed to be engaging and educational, ensuring students apply what they have learned.
- Word Problems: Flocabulary integrates word problems to combine math and literacy skills, allowing students to create and solve problems based on the concepts they have learned.
- Real-Life Applications: Lessons connect math skills to real-life situations, helping students understand the practical applications of area and perimeter in everyday life.
- Math Facts Challenge: Students can participate in challenges to master basic math facts related to area and perimeter, enhancing their fluency and confidence in the subject.
- Math Vocabulary: The platform emphasizes the importance of math vocabulary, providing activities and games to help students learn and use new terms effectively.
Lesson Implementation
Flocabulary suggests several ways to integrate their resources into the classroom:
- Introduction to New Content: Use videos at the beginning of a lesson to introduce new concepts and spark student interest.
- Review and Reinforcement: Incorporate videos and activities throughout the lesson to reinforce understanding and provide additional practice.
- End-of-Year Review: Use the videos and activities to review key concepts at the end of the school year or before exams.
Mini Games
Flocabulary offers mini games that make learning math fun. These games focus on essential skills such as multiplication and division, helping students practice and improve their proficiency in these areas.
| Game Name | Description |
| Math Facts Challenge | Students work on mastering basic math facts through engaging challenges. |
| Vocabulary Game | A game that helps students learn and use math vocabulary effectively. |
Conclusion
Flocabulary's resources for teaching area and perimeter are comprehensive and engaging, making math instruction enjoyable and effective for students. By using videos, interactive activities, and practical applications, students can better understand and retain these important mathematical concepts.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Area and Perimeter
Welcome to the world of geometry, where understanding area and perimeter is essential for solving various mathematical problems. These fundamental concepts help you calculate the size of different shapes and figures, which is crucial in both everyday life and advanced math.
Area measures the surface within a shape. It tells you how much space is covered by the shape. The formula for area varies depending on the shape:
- Rectangle: \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \)
- Triangle: \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Circle: \( A = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \)
Perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. It's like walking around the boundary of a shape. Here are some formulas for perimeter:
- Rectangle: \( P = 2 \times (\text{length} + \text{width}) \)
- Triangle: \( P = \text{side}_1 + \text{side}_2 + \text{side}_3 \)
- Circle: \( P = 2 \times \pi \times \text{radius} \) (Circumference)
To help visualize these concepts, consider the following examples:
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
| Square | \( A = \text{side}^2 \) | \( P = 4 \times \text{side} \) |
| Parallelogram | \( A = \text{base} \times \text{height} \) | \( P = 2 \times (\text{base} + \text{side}) \) |
By mastering area and perimeter, you'll be able to solve a wide range of practical problems, from finding the amount of paint needed for a wall to calculating the length of fencing required for a garden. Let's dive deeper into these concepts and explore how Flocabulary makes learning them engaging and fun!
Flocabulary Overview: Engaging Learning through Music
Flocabulary revolutionizes the way students learn math by combining educational content with the power of music and rhythm. This innovative approach turns traditional learning into an interactive and enjoyable experience, making complex topics like area and perimeter easier to understand and retain. Here’s how Flocabulary makes learning engaging:
1. Educational Rap Videos:
- Flocabulary creates educational rap songs that explain key concepts in a fun and memorable way.
- These videos use catchy lyrics and engaging visuals to simplify mathematical principles.
- Students can easily recall information through the rhythm and repetition of the music.
2. Interactive Lyrics and Activities:
- Flocabulary provides interactive lyrics, allowing students to follow along and engage with the content.
- Activities and quizzes are integrated into the lessons to reinforce learning and assess understanding.
3. Visual and Kinesthetic Learning:
- Visual aids such as diagrams and animations in the videos help students grasp abstract concepts.
- Kinesthetic learners benefit from activities that involve movement and interaction, making learning dynamic.
4. Comprehensive Lesson Plans:
- Flocabulary offers complete lesson plans that align with educational standards and goals.
- These plans include objectives, key vocabulary, and guided practice to support teachers in delivering effective instruction.
5. Real-World Connections:
- Flocabulary connects mathematical concepts to real-life situations, helping students see the relevance of what they learn.
- Examples include calculating the area for gardening projects or the perimeter for building fences, making math practical and relatable.
Flocabulary's engaging approach not only makes learning about area and perimeter fun but also ensures that students can apply these concepts in real-world scenarios. This fusion of music and education is designed to enhance retention and make learning an enjoyable journey for every student.
Understanding Area
Area is a fundamental concept in geometry that measures the space within the boundaries of a two-dimensional shape. Learning how to calculate area is crucial for solving various real-world problems, from designing a garden to planning floor space. Here’s a detailed guide to understanding and calculating area:
1. Definition and Concept:
- The area of a shape represents the amount of space it covers.
- It is measured in square units, such as square meters (\(\text{m}^2\)), square feet (\(\text{ft}^2\)), or square inches (\(\text{in}^2\)).
2. Basic Area Formulas:
| Shape | Formula | Explanation |
| Square | \( A = \text{side}^2 \) | Multiply the length of one side by itself. |
| Rectangle | \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \) | Multiply the length by the width. |
| Triangle | \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \) | Multiply the base by the height and divide by two. |
| Circle | \( A = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \) | Multiply pi (approximately 3.14159) by the radius squared. |
| Parallelogram | \( A = \text{base} \times \text{height} \) | Multiply the base by the height (perpendicular distance). |
| Trapezoid | \( A = \frac{1}{2} \times (\text{base}_1 + \text{base}_2) \times \text{height} \) | Add the lengths of the two bases, multiply by the height, then divide by two. |
3. Steps to Calculate Area:
- Identify the Shape: Determine the type of shape you are working with (e.g., square, rectangle, circle).
- Measure Dimensions: Measure the necessary dimensions (such as length, width, radius, or height) in appropriate units.
- Apply the Formula: Use the corresponding area formula for the shape to calculate the area.
- Check Units: Ensure that the units are squared, such as square meters or square inches.
4. Example Problems:
- Example 1: To find the area of a rectangle with a length of 8 meters and a width of 5 meters, use the formula \( A = \text{length} \times \text{width} \):
Solution: \( A = 8 \, \text{m} \times 5 \, \text{m} = 40 \, \text{m}^2 \) - Example 2: To find the area of a circle with a radius of 4 centimeters, use the formula \( A = \pi \times \text{radius}^2 \):
Solution: \( A = \pi \times 4 \, \text{cm}^2 = 16 \pi \, \text{cm}^2 \approx 50.27 \, \text{cm}^2 \)
By mastering these formulas and steps, you can calculate the area of various shapes and apply this knowledge to practical situations. Flocabulary's engaging approach helps reinforce these concepts through interactive lessons and music, making learning about area both fun and effective.
Understanding Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is the total distance around the outside of that shape. It is calculated by adding up the lengths of all the sides. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter is essential for solving various real-world problems and is a fundamental concept in geometry.
Basic Concept of Perimeter
Perimeter is a measure of the boundary of a two-dimensional shape. It is the sum of all the side lengths of the shape. For example, to find the perimeter of a rectangle, you add the lengths of all four sides. If the lengths of the sides of a rectangle are given as length (L) and width (W), the perimeter (P) can be calculated using the formula:
Calculating Perimeter of Common Shapes
- Rectangle:
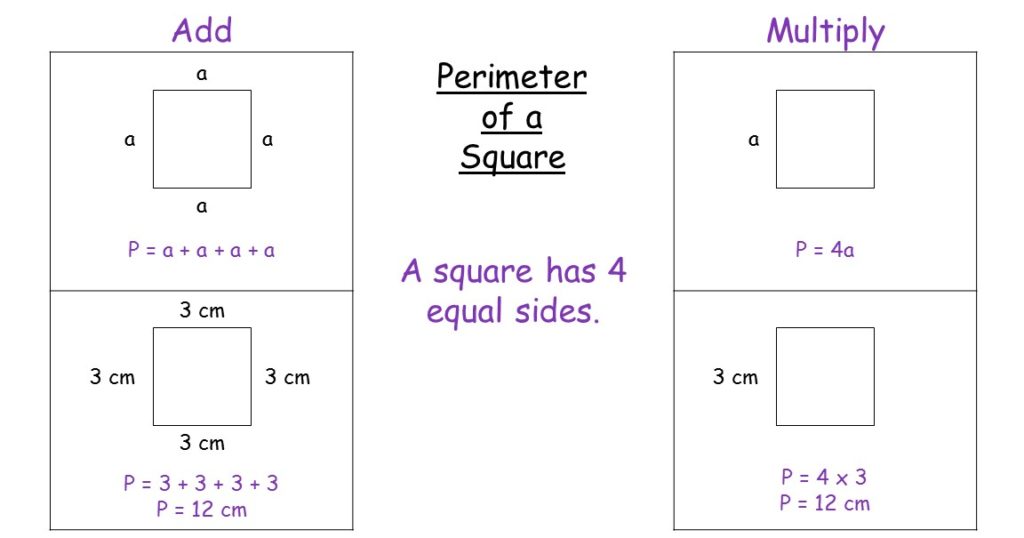
\( P = 2L + 2W \) - Square: A square has four equal sides. If the length of one side is \( a \), then the perimeter is:
\( P = 4a \) - Triangle: The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. If the sides are \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), then the perimeter is:
\( P = a + b + c \) - Circle: For a circle, the perimeter is called the circumference. It is calculated using the formula:
\( C = 2\pi r \) , where \( r \) is the radius of the circle.
Example Problems
- Rectangle: Find the perimeter of a rectangle with a length of 8 units and a width of 5 units.
\( P = 2 \times 8 + 2 \times 5 = 16 + 10 = 26 \) units - Square: Find the perimeter of a square with a side length of 7 units.
\( P = 4 \times 7 = 28 \) units - Triangle: Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides measuring 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units.
\( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) units
Interactive Learning
Flocabulary offers engaging videos and interactive activities to help students understand and practice perimeter calculations. These resources use music and rhythm to make learning fun and memorable, which can be particularly effective for young learners.
Visual Aids
Utilizing diagrams and visual representations can significantly enhance the understanding of perimeter. Drawing shapes and labeling their sides can help students visualize the addition of side lengths. Interactive tools and digital platforms, such as those offered by Flocabulary, provide dynamic ways to explore and reinforce these concepts.
Common Mistakes and Tips
- Forgetting to add all sides: Ensure that every side length is included in the total perimeter calculation.
- Confusing area with perimeter: Remember that area measures the space inside a shape, while perimeter measures the distance around the shape.
- Using consistent units: Always use the same units for all side lengths when calculating the perimeter.
Practice Problems
Regular practice with varied problems can help solidify the understanding of perimeter. Flocabulary provides a range of practice problems with solutions to help students test and improve their skills.
By mastering the concept of perimeter, students can solve real-life problems involving boundaries and measurements, enhancing their overall mathematical proficiency.

Formulas for Calculating Area
Calculating the area of different shapes is a fundamental skill in mathematics. Below are the formulas and explanations for calculating the area of various common shapes.
Area of a Rectangle
The area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length (L) by its width (W). The formula is:
Area of a Square
A square is a special type of rectangle where all four sides are of equal length. If the length of a side is \( a \), the formula for the area is:
Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle is calculated using the base (b) and the height (h). The formula is:
Area of a Parallelogram
Similar to a rectangle, the area of a parallelogram is found by multiplying the base (b) by the height (h). The formula is:
Area of a Trapezoid
The area of a trapezoid, which has two parallel sides of different lengths (a and b), is calculated by the following formula:
Area of a Circle
The area of a circle is calculated using its radius (r). The formula is:
Example Problems
- Rectangle: Find the area of a rectangle with a length of 10 units and a width of 4 units.
\( \text{Area} = 10 \times 4 = 40 \) \text{ square units} - Square: Find the area of a square with a side length of 5 units.
\( \text{Area} = 5^2 = 25 \) \text{ square units} - Triangle: Find the area of a triangle with a base of 8 units and a height of 5 units.
\( \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 8 \times 5 = 20 \) \text{ square units} - Circle: Find the area of a circle with a radius of 3 units.
\( \text{Area} = \pi \times 3^2 = 9\pi \) \text{ square units}
Interactive Learning
Flocabulary offers interactive videos and activities that make learning these formulas fun and engaging. These resources are designed to help students understand and remember how to calculate the area of different shapes effectively.
Visual Aids
Using visual aids such as diagrams and digital tools can greatly enhance comprehension. Drawing the shapes and labeling their dimensions helps students visualize and better understand the calculation process. Flocabulary’s interactive platforms provide excellent visual learning tools for students.
Common Mistakes and Tips
- Mixing up dimensions: Ensure you correctly identify and use the base, height, and side lengths as required by each formula.
- Confusing area with perimeter: Remember, area measures the space inside a shape, while perimeter measures the distance around the shape.
- Consistent units: Always use the same units for all measurements when calculating area.
Understanding and mastering these formulas will enable students to solve a variety of mathematical problems and apply these skills in real-world scenarios.
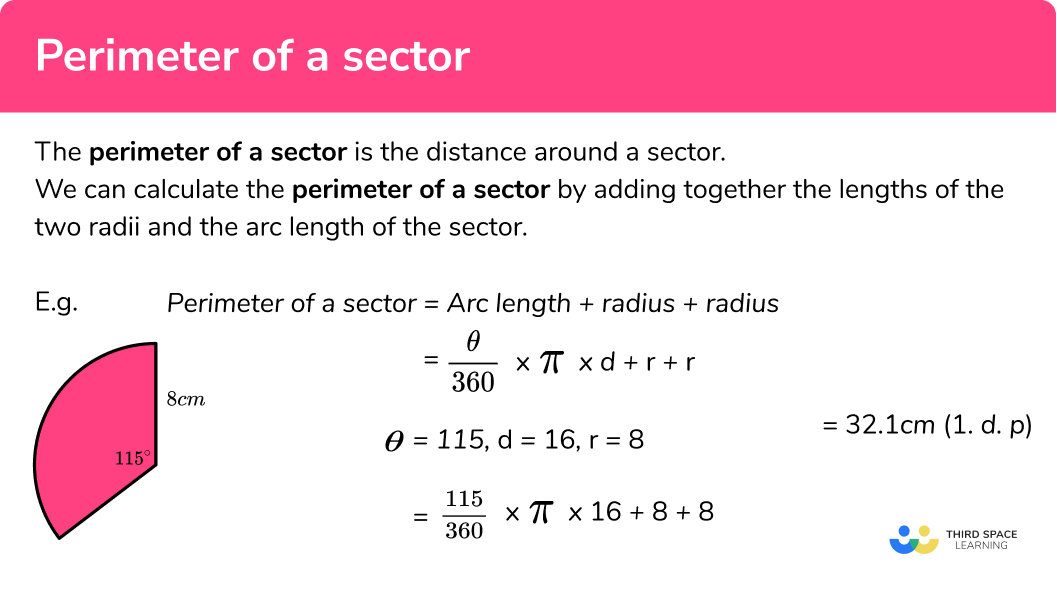
Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
Perimeter is the total distance around the outside of a two-dimensional shape. To calculate the perimeter, you simply add up the lengths of all the sides. Here are the formulas for calculating the perimeter of various shapes:
- Rectangle:
The perimeter of a rectangle is calculated by adding together the lengths of all four sides. Since opposite sides of a rectangle are equal, the formula can be simplified to:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2 \times (\text{Length} + \text{Width})
\] - Square:
All sides of a square are equal, so the perimeter is four times the length of one side:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 4 \times \text{Side}
\] - Triangle:
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = \text{Side}_1 + \text{Side}_2 + \text{Side}_3
\] - Circle (Circumference):
The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is calculated using the radius (r) or diameter (d) of the circle. The formulas are:
\[
\text{Circumference} = 2 \pi r
\] or \[
\text{Circumference} = \pi d
\] - Regular Polygon:
For a regular polygon (a polygon with all sides and angles equal), the perimeter is the length of one side multiplied by the number of sides (n):
\[
\text{Perimeter} = \text{Side} \times n
\]
By using these formulas, you can easily determine the perimeter of various geometric shapes, which is a fundamental skill in geometry.
Visual Learning: Diagrams and Videos
Understanding area and perimeter can be greatly enhanced through visual learning techniques such as diagrams and videos. Flocabulary provides a range of engaging resources to help students grasp these concepts.
Here are some key visual learning tools and strategies:
- Diagrams:
- Grid Diagrams:
Use grid diagrams to visually represent the area of different shapes. By counting the unit squares within the grid, students can better understand how area is calculated.

- Shape Outlines:
Outlining shapes and labeling their sides helps students visualize and calculate perimeter. Diagrams showing the step-by-step process of adding side lengths reinforce learning.

- Grid Diagrams:
- Videos:
- Educational Rap Videos:
Flocabulary’s hip-hop videos incorporate music and rhythm to teach mathematical concepts. These videos are designed to be memorable and entertaining, making it easier for students to retain information about area and perimeter.
- Interactive Tutorials:
Interactive video tutorials guide students through the process of calculating area and perimeter with real-life examples and engaging animations. These videos often include quizzes and prompts to keep students actively involved.
- Educational Rap Videos:
By integrating these visual learning tools into the curriculum, educators can make the concepts of area and perimeter more accessible and engaging for students. Visual aids help in breaking down complex ideas into understandable segments, ensuring better comprehension and retention.
Interactive Learning Activities
Interactive learning activities are a fantastic way to engage students and help them understand the concepts of area and perimeter in a fun and meaningful manner. Here are some activities that can be incorporated into lessons:
-
Hands-On Manipulatives: Use square tiles or blocks to create shapes and explore their area and perimeter. For example, give students a set of tiles and ask them to form different rectangles. Discuss how the number of tiles (area) remains the same but the perimeter can change based on the shape.
-
Interactive Whiteboard Activities: Utilize digital tools and apps on interactive whiteboards to draw shapes and measure their area and perimeter. Students can use these tools to experiment with different configurations and instantly see the results.
-
Group Projects: Have students work in groups to design a floor plan for a small building or garden. They will need to calculate the area and perimeter of each room or section. This promotes teamwork and practical application of mathematical concepts.
-
Games and Challenges: Implement educational games that focus on calculating area and perimeter. For instance, set up a treasure hunt where students must solve area and perimeter problems to find the next clue.
-
Storytelling and Role-Playing: Create scenarios where students must use their knowledge of area and perimeter to solve problems. For example, pretend to be architects designing a park or astronauts planning a space station layout.
-
Technology Integration: Use online platforms and educational apps that offer interactive exercises on area and perimeter. These platforms often include immediate feedback and adaptive learning paths to help students master the concepts.
-
Real-Life Applications: Organize activities where students measure actual objects in the classroom or schoolyard. They can calculate the perimeter of the playground or the area of the classroom walls, making the math concepts tangible and relevant.
-
Flocabulary Videos and Songs: Incorporate engaging videos and songs from Flocabulary that teach area and perimeter through music and visual aids. These resources make learning memorable and fun.
By incorporating these interactive activities into your lessons, you can create a dynamic learning environment that not only helps students understand area and perimeter but also fosters a love for mathematics.

Common Mistakes and Tips for Success
Understanding the common mistakes in calculating area and perimeter can help students avoid errors and build a solid foundation in geometry. Here are some frequent mistakes and tips to ensure success:
-
Mistake: Confusing Area and Perimeter
Students often mix up the formulas for area and perimeter. Remember, the area measures the surface inside a shape, while the perimeter is the distance around the shape.
Tip: Use visual aids and real-life examples to differentiate between area and perimeter. For example, compare a fenced garden (perimeter) to the lawn inside the fence (area).
-
Mistake: Incorrectly Adding Side Lengths
When calculating the perimeter, students might forget to add all the side lengths or double-count them.
Tip: Teach students to mark each side as they add it to avoid counting errors. Using a systematic approach, such as moving clockwise around the shape, can also help.
-
Mistake: Using Wrong Units
Students sometimes use different units for measurements, leading to incorrect calculations.
Tip: Emphasize the importance of using consistent units. Practice converting units when necessary and always label answers with the correct units.
-
Mistake: Incorrect Application of Formulas
Using the wrong formula for complex shapes can result in incorrect area or perimeter calculations.
Tip: Encourage students to break down complex shapes into simpler ones (e.g., rectangles and triangles) and use the appropriate formulas for each part.
-
Mistake: Overlooking Shape Properties
Forgetting properties of shapes, such as all sides of a square being equal, can lead to errors.
Tip: Reinforce the properties of different shapes and use them to simplify calculations. For example, knowing that all sides of a rectangle are equal can streamline finding the perimeter.
-
Mistake: Incorrectly Counting Units on a Grid
When using a grid to find the area, students might miscount the squares.
Tip: Teach students to count systematically, using rows and columns to ensure every unit is accounted for. Practice with grid paper can enhance accuracy.
-
General Tips for Success:
- Practice regularly with a variety of shapes to build confidence and proficiency.
- Use interactive tools and apps to visualize and manipulate shapes, reinforcing the concepts of area and perimeter.
- Encourage collaborative learning through group projects and discussions to address common mistakes and share strategies.
By being aware of these common mistakes and applying the tips provided, students can improve their understanding and accuracy in calculating area and perimeter.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Practicing area and perimeter problems helps reinforce understanding and application of these concepts. Below are a variety of practice problems along with their solutions to guide you through different scenarios and shapes.
-
Problem 1: Rectangle
Find the perimeter and area of a rectangle with a length of 8 units and a width of 5 units.
- Perimeter: \(P = 2(l + w)\)
- \(P = 2(8 + 5) = 2 \times 13 = 26\) units
- Area: \(A = l \times w\)
- \(A = 8 \times 5 = 40\) square units
-
Problem 2: Square
Calculate the perimeter and area of a square with each side measuring 4 units.
- Perimeter: \(P = 4a\)
- \(P = 4 \times 4 = 16\) units
- Area: \(A = a^2\)
- \(A = 4^2 = 16\) square units
-
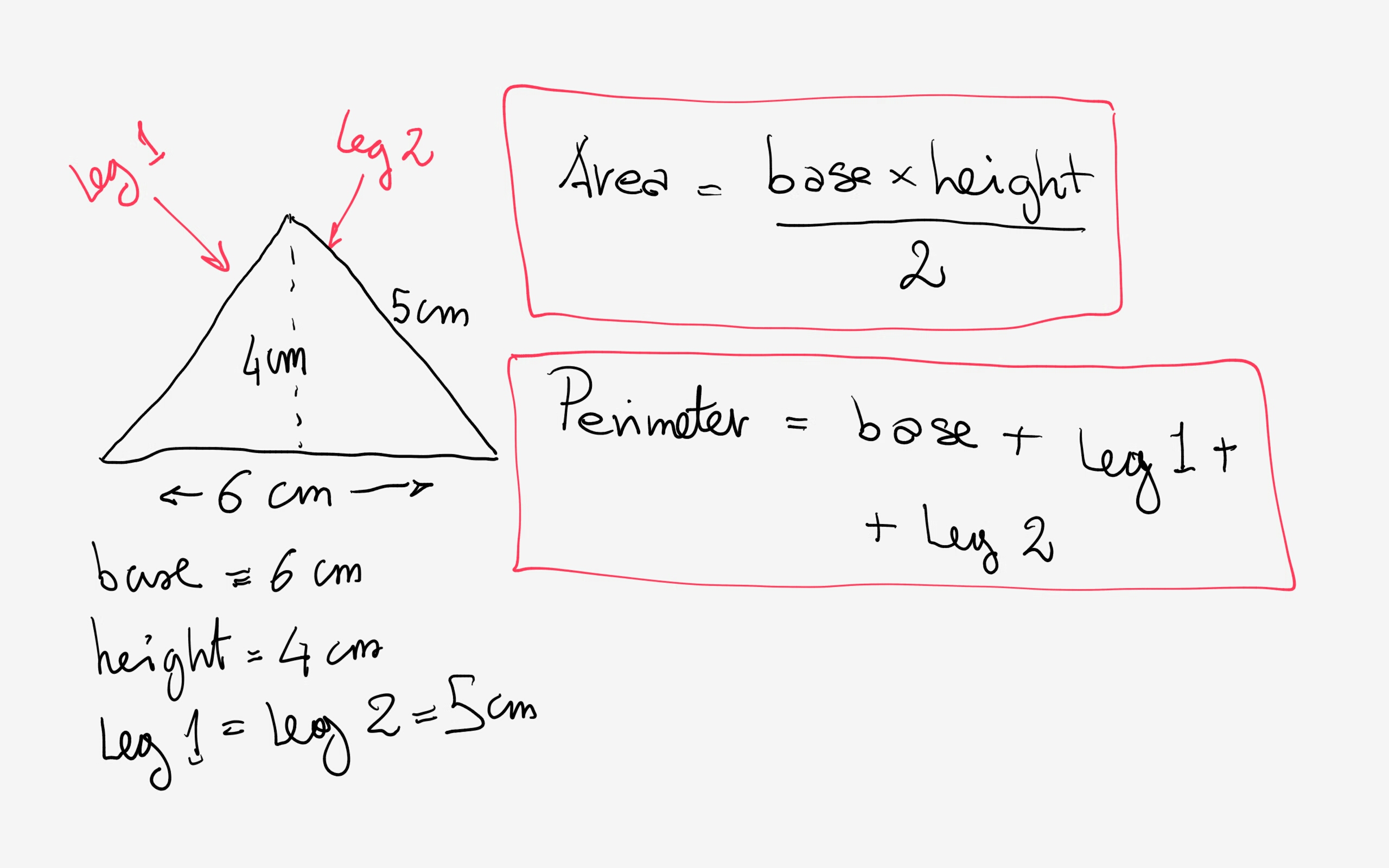
Problem 3: Triangle
Determine the perimeter and area of a triangle with sides 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units, and a height of 4 units corresponding to the base of 3 units.
- Perimeter: \(P = a + b + c\)
- \(P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12\) units
- Area: \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height}\)
- \(A = \frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 4 = 6\) square units
-
Problem 4: Circle
Find the circumference and area of a circle with a radius of 7 units.
- Circumference: \(C = 2\pi r\)
- \(C = 2 \times \pi \times 7 = 14\pi\) units
- Area: \(A = \pi r^2\)
- \(A = \pi \times 7^2 = 49\pi\) square units
These practice problems cover basic shapes and their properties, providing a solid foundation for understanding and calculating area and perimeter in various contexts. Keep practicing with different dimensions and shapes to master these essential math skills!
Real-Life Applications of Area and Perimeter
The concepts of area and perimeter are not just academic exercises; they have numerous practical applications in our daily lives. Understanding these applications can help students see the relevance of these mathematical concepts and how they can be used to solve real-world problems.
1. Architecture and Construction
- Building Layouts: Architects and builders use area calculations to determine the amount of space available in different parts of a building. This helps in planning the layout of rooms and ensuring efficient use of space.
- Material Estimation: Perimeter calculations are used to estimate the amount of materials needed for building projects, such as fencing, framing, and tiling. For instance, knowing the perimeter of a room helps in determining the length of baseboards needed.
2. Interior Design
- Flooring: Interior designers calculate the area of floors to determine the amount of flooring material required, whether it be tiles, carpet, or hardwood.
- Wall Paint: The area of walls is measured to estimate the quantity of paint needed to cover them, ensuring a smooth and cost-effective painting process.
3. Landscaping and Gardening
- Garden Planning: Gardeners use area calculations to design plots for planting. This helps in determining the space needed for different plants and ensuring they have enough room to grow.
- Fencing: Calculating the perimeter of a garden helps in determining the length of fencing required to enclose the space, which is essential for protecting plants from animals.
4. Sports and Recreation
- Sports Fields: The area and perimeter of sports fields, such as soccer fields, basketball courts, and running tracks, are calculated to ensure they meet official size regulations and to plan maintenance activities.
5. Agriculture
- Field Measurement: Farmers calculate the area of their fields to plan crop rotation, irrigation, and the application of fertilizers and pesticides. This helps in optimizing the yield and managing resources efficiently.
6. Art and Design
- Creating Art: Artists use area and perimeter calculations when creating large-scale artworks or murals to ensure their designs fit within the intended spaces.
- Graphic Design: Graphic designers need to understand the area to design layouts for posters, flyers, and other printed materials.
By recognizing these real-life applications, students can appreciate the importance of mastering area and perimeter. These concepts are not only fundamental to mathematics but also essential skills that enhance problem-solving abilities in various fields.
Assessment and Evaluation Tools
Assessing student understanding of area and perimeter can be achieved through a variety of interactive and engaging tools. Flocabulary offers several assessment options that help teachers evaluate student comprehension effectively.
-
Online Quizzes: Flocabulary provides auto-graded formative assessments that allow students to demonstrate their understanding through interactive quizzes. These quizzes are integrated into the lesson sequence and help teachers gauge student progress immediately.
-
Assigning Units: Teachers can set up classes or student groups in their Flocabulary accounts, making it easy to assign specific units to students. This feature supports differentiated instruction by allowing assignments to be tailored to individual or group needs.
-
Reporting Tools: The teacher dashboard includes comprehensive reporting tools that track assignment progress and quiz performance. Teachers can view individual scores and use the Comprehension Analysis grid to identify trends and pinpoint areas for reteaching or independent practice.
-
Performance Tasks: Tasks such as creating word problems or applying math concepts to real-life scenarios help assess student ability to apply their knowledge practically. These tasks not only test computational skills but also enhance problem-solving and critical thinking.
Using these tools, teachers can create a well-rounded assessment strategy that not only evaluates student understanding but also fosters an engaging and supportive learning environment.

Additional Resources and References
To further enhance your understanding and teaching of area and perimeter, here are some valuable resources and references:
- Flocabulary Unit on Area and Perimeter: Explore the comprehensive lesson plans, videos, and interactive activities provided by Flocabulary. This unit includes educational rap songs, quizzes, and printable resources to engage students and reinforce concepts.
- Math Goodies - Area and Perimeter Song Video: This video introduces perimeter and area of polygons through a catchy song, making it easier for students to remember and understand these concepts. The Math Goodies website also offers related calculators, games, and puzzles.
- Edu2Know - Engaging Strategies for Mastering Math Concepts: Learn about different strategies to make math engaging through collaborative activities, printable worksheets, and assessment tools. This resource also highlights the use of outer space-themed videos to teach area and perimeter.
- Khan Academy - Area and Perimeter Lessons: Khan Academy offers a series of lessons and practice exercises on calculating the area and perimeter of various shapes, including rectangles, triangles, and circles. These lessons are designed to build a strong foundation in geometry.
- Quizlet - Flocabulary Flashcards: Use these flashcards to help students memorize key terms and formulas related to area and perimeter. This interactive study tool can be used for both individual and group learning sessions.
By utilizing these resources, educators can provide a well-rounded and engaging learning experience for students, ensuring they master the concepts of area and perimeter effectively.
Conclusion: Mastering Area and Perimeter with Flocabulary
Flocabulary's innovative approach to teaching area and perimeter helps students grasp these fundamental concepts through engaging music and visual aids. By transforming traditional lessons into interactive and entertaining experiences, Flocabulary ensures that learners not only understand but also enjoy math.
Here's a step-by-step guide to mastering area and perimeter with Flocabulary:
- Watch and Learn: Start with Flocabulary's educational videos that introduce area and perimeter concepts through catchy songs and relatable examples. These videos are designed to make the learning process enjoyable and memorable.
- Interactive Activities: Engage with interactive activities and quizzes available on Flocabulary's platform. These activities reinforce the concepts covered in the videos, ensuring students can apply what they've learned.
- Visual Aids: Utilize diagrams and visual aids provided in the lessons. These resources help students visualize the shapes and formulas, making it easier to understand how to calculate area and perimeter.
- Practice Problems: Solve practice problems that vary in difficulty. This step-by-step practice builds confidence and proficiency in calculating area and perimeter.
- Real-Life Applications: Connect math to real-life scenarios. Flocabulary’s lessons often include examples of how area and perimeter are used in everyday life, making the learning experience more relevant and practical.
- Assessment Tools: Use Flocabulary’s assessment tools to evaluate understanding and track progress. These tools help identify areas where students may need additional support or practice.
- Continuous Improvement: Encourage continuous learning and improvement. Revisit challenging topics, watch videos again, and engage in new activities to strengthen understanding.
By integrating music, visuals, and interactive learning, Flocabulary makes mastering area and perimeter an enjoyable journey. Students are not only able to comprehend these essential math concepts but also retain the knowledge for long-term success.
Embrace the rhythm of learning with Flocabulary and watch as your mathematical skills grow stronger and more confident!
Video hấp dẫn về cách tìm diện tích và chu vi qua nhạc rap giáo dục. Thích hợp cho chương trình toán học và giúp học sinh nắm vững các khái niệm toán học cơ bản.
Cách Tìm Diện Tích và Chu Vi | Rap Giáo Dục cho Chương Trình Toán Học
READ MORE:
Video bài hát vui nhộn về diện tích và chu vi dành cho học sinh lớp 3 và 4. Giúp trẻ em học toán qua âm nhạc một cách dễ dàng và thú vị.
Bài Hát Diện Tích và Chu Vi Cho Trẻ Em | Lớp 3 - 4