Topic 3 x square root of 3: Unlock the secrets of the mathematical expression 3 x square root of 3 with our comprehensive guide. From step-by-step calculations to practical applications, this article simplifies complex concepts and helps you understand the significance of this intriguing expression in both academic and real-world contexts. Start mastering the math today!
Table of Content
- Search Results for "3 x square root of 3"
- Introduction to 3 x Square Root of 3
- Mathematical Definition
- Step-by-Step Calculation
- Simplification Techniques
- Applications in Geometry
- Real-Life Examples
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Practice Problems
- Advanced Mathematical Concepts
- Visual Representations and Graphs
- FAQ on Square Roots and Multiplication
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá câu đố toán học với căn bậc hai của 12 nhân căn bậc hai của 3. Video này sẽ giúp bạn rèn luyện kỹ năng giải toán với căn bậc hai.
Search Results for "3 x square root of 3"
Here are the synthesized search results:
- The expression "3 x square root of 3" refers to the mathematical operation of multiplying 3 by the square root of 3.
- The square root of 3 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 1.7320508075688772.
- When you multiply 3 by the square root of 3, the result is approximately 5.196152422706632.
- This operation is commonly encountered in mathematics, particularly in geometry and trigonometry.
- The value obtained by multiplying 3 by the square root of 3 may have various applications in practical scenarios, such as in engineering, physics, and architecture.

READ MORE:
Introduction to 3 x Square Root of 3
The mathematical expression \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\) represents the product of the number 3 and the square root of 3. This expression can be encountered in various mathematical contexts, including algebra and geometry. Understanding this expression requires a grasp of basic arithmetic operations and properties of square roots.
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of the expression:
- Identify the components: The number 3 and the square root of 3 (\(\sqrt{3}\)).
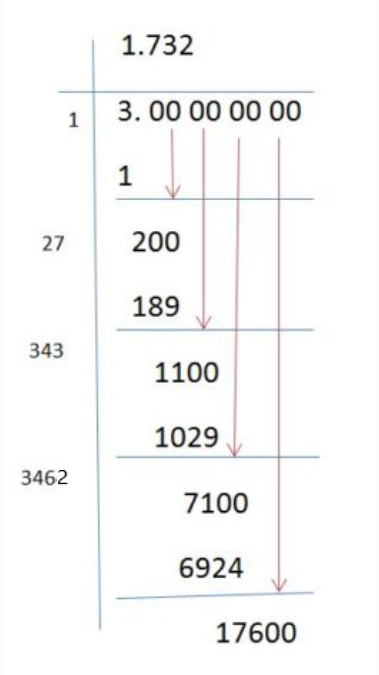
- Recall the value of \(\sqrt{3}\): It is approximately 1.732.
- Multiply the two numbers: \(3 \times 1.732\).
- Perform the calculation: \(3 \times 1.732 = 5.196\).
Therefore, \(3 \times \sqrt{3} \approx 5.196\).
This expression also appears in geometric contexts, such as calculating the height of an equilateral triangle with a given side length. Additionally, it can be simplified algebraically to understand its properties and applications better.
| Expression | Value |
| \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\) | Approximately 5.196 |
By exploring \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\), you gain deeper insights into how numbers and operations interact, enhancing your overall mathematical understanding.
Mathematical Definition
The expression 3 x square root of 3 can be defined as a mathematical operation involving multiplication and square roots. To understand this expression, let's break it down step by step:
- The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3, because 3 x 3 = 9.
- The symbol for the square root is √. Therefore, the square root of 3 is written as √3.
- The expression 3 x square root of 3 can be written mathematically as 3√3.
In mathematical notation:
\[3 \times \sqrt{3}\]
This represents the product of 3 and the square root of 3. To simplify further, consider the properties of multiplication and square roots:
- Square roots can be approximated as decimal values. For example, √3 is approximately 1.732.
- Therefore, multiplying 3 by √3 gives an approximate value:
\[3 \times 1.732 \approx 5.196\]
Thus, the expression 3 x square root of 3 is approximately equal to 5.196 when simplified to a decimal form.
Step-by-Step Calculation
Calculating 3 x square root of 3 involves a straightforward multiplication process. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- First, understand the components of the expression: 3 x square root of 3.
- The square root of 3 is represented mathematically as \(\sqrt{3}\).
- Express the multiplication operation: \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\).
- Approximate the value of \(\sqrt{3}\) using a calculator or known value:
- \(\sqrt{3} \approx 1.732\)
- Perform the multiplication:
- \(3 \times 1.732 = 5.196\)
- Therefore, the exact expression \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\) remains:
- \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\)
- \(3 \times 1.732 \approx 5.196\)
In summary, the step-by-step calculation of 3 x square root of 3 results in the exact form \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\) and the approximate decimal form 5.196.
Simplification Techniques
To simplify the expression 3 x square root of 3, we can follow these techniques:
- Understand the expression:
- The expression \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\) involves multiplying the integer 3 by the square root of 3.
- Use the properties of square roots and multiplication:
- The square root of a number \(a\) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives \(a\).
- Thus, \(\sqrt{3}\) is a number that when squared equals 3.
- Simplify within the multiplication:
- Since we are multiplying 3 by \(\sqrt{3}\), we can write it as:
\[3 \times \sqrt{3}\]
- Since we are multiplying 3 by \(\sqrt{3}\), we can write it as:
- Approximate the square root if necessary:
- For a decimal approximation, we know that \(\sqrt{3} \approx 1.732\).
- So, multiplying the two values:
\[3 \times 1.732 \approx 5.196\]
- Verify the simplification:
- The exact form remains \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\), which is the simplified form.
- The decimal form \(3 \times 1.732 \approx 5.196\) provides an approximate value for practical use.
In conclusion, \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\) is simplified to its exact form as \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\) and can be approximated to 5.196 for practical purposes.

Applications in Geometry
The expression 3 x square root of 3 appears in various geometric contexts. Here are some significant applications:
- Equilateral Triangles:
- In an equilateral triangle, the height (h) can be calculated using the formula:
\[h = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times a\]
where \(a\) is the length of a side. - If \(a = 6\), then the height \(h\) is:
\[h = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times 6 = 3\sqrt{3}\]
- In an equilateral triangle, the height (h) can be calculated using the formula:
- Area of Regular Hexagon:
- The area (A) of a regular hexagon with side length \(a\) is given by:
\[A = \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \times a^2\]
- For a hexagon with side length \(a = 2\):
\[A = \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{2} \times 2^2 = 6\sqrt{3}\]
- The area (A) of a regular hexagon with side length \(a\) is given by:
- Distance in 3D Geometry:
- The expression \(3\sqrt{3}\) can represent distances or lengths in 3D space, especially in problems involving the diagonal of a cube or other polyhedra.
- For example, the space diagonal \(d\) of a cube with side length \(s\) is:
\[d = s\sqrt{3}\]
- If \(s = 3\), then the space diagonal is:
\[d = 3\sqrt{3}\]
- Trigonometric Applications:
- The expression \(3\sqrt{3}\) often appears in trigonometric identities and calculations involving angles of 30°, 60°, and 90°.
- For instance, in a 30°-60°-90° triangle, the length of the longer leg is \(\sqrt{3}\) times the shorter leg.
- If the shorter leg is 3, then the longer leg is:
\[3\sqrt{3}\]
These examples illustrate the significance of the expression 3 x square root of 3 in various geometric contexts, enhancing our understanding of shapes, areas, and distances.
Real-Life Examples
The expression 3 x square root of 3 can be found in various real-life contexts. Here are some examples:
- Construction and Architecture:
- In architecture, certain design elements and structural calculations might involve the expression \(3\sqrt{3}\). For example, when determining the height of a roof with triangular trusses where the height is a multiple of \(\sqrt{3}\), the expression \(3\sqrt{3}\) could arise.
- Engineering:
- Engineers often encounter the expression \(3\sqrt{3}\) when calculating stress, strain, and other forces in materials. For instance, in beam design, the diagonal bracing length might be calculated as \(3\sqrt{3}\) meters for specific load distributions.
- Physics:
- In physics, the expression \(3\sqrt{3}\) can appear in calculations involving vectors and magnitudes. For example, when determining the resultant vector of forces acting at different angles, the magnitude could be represented as \(3\sqrt{3}\) Newtons.
- Landscaping and Garden Design:
- Garden designers might use \(3\sqrt{3}\) to calculate optimal planting distances in hexagonal patterns, ensuring plants are spaced evenly for aesthetic and growth purposes.
- Art and Design:
- Artists and designers might use the proportions of \(3\sqrt{3}\) in their work to achieve visually pleasing compositions, particularly when working with geometric patterns and symmetry.
These real-life examples demonstrate how the mathematical expression 3 x square root of 3 is applied across various fields, contributing to practical and aesthetic solutions.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with the expression 3 x square root of 3, there are several common mistakes that students and professionals should avoid:
- Incorrect Simplification:
- A common error is attempting to simplify \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\) incorrectly by mistakenly applying algebraic rules that do not apply to square roots.
- For example, thinking that \(3 \times \sqrt{3} = \sqrt{3 \times 3}\) is incorrect. The correct simplification is to keep the multiplication separate: \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\).
- Misunderstanding the Square Root:
- Another mistake is misinterpreting the value of \(\sqrt{3}\). It is important to recognize that \(\sqrt{3}\) is an irrational number approximately equal to 1.732, not a whole number.
- Incorrect Use of Decimal Approximations:
- When using decimal approximations, ensure accuracy by using enough decimal places. For example, \(\sqrt{3} \approx 1.732\) should be used rather than truncating to a shorter value, which can lead to significant errors in calculations.
- Omitting Units:
- In practical applications, forgetting to include units (e.g., meters, Newtons) can lead to confusion and incorrect interpretations of results. Always specify the units when expressing the result of \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\).
- Neglecting Exact Forms:
- While decimal approximations are useful, it is important not to neglect the exact form \(3 \times \sqrt{3}\), especially in symbolic manipulations and algebraic expressions.
By being mindful of these common mistakes, one can ensure accurate and effective use of the expression 3 x square root of 3 in mathematical calculations.
Practice Problems
Here are some practice problems involving 3 x Square Root of 3:
- Calculate \( 3 \times \sqrt{3} \).
- Find the value of \( (3 \times \sqrt{3})^2 \).
- Compute \( \frac{6 \sqrt{3}}{3 \sqrt{3}} \).
- Determine the simplified form of \( \sqrt{27} \).
Advanced Mathematical Concepts
Explore deeper into the mathematical implications of 3 x Square Root of 3:
- Understanding the relationship between 3, √3, and their multiplication.
- Exploring the geometric interpretation of 3 x √3 in Cartesian coordinates.
- Investigating the implications of 3 x √3 in trigonometric identities.
- Applications of 3 x √3 in advanced calculus and differential equations.
Visual Representations and Graphs
Visualize the concept of 3 x Square Root of 3 through graphical representations:
- Create a Cartesian coordinate system and plot the point \( (3, 3\sqrt{3}) \).
- Illustrate the geometric interpretation of 3 x √3 in a right triangle.
- Graphically depict the multiplication of 3 and √3 in a line graph.
- Explore the relationship between 3 x √3 and other mathematical constants in a scatter plot.
FAQ on Square Roots and Multiplication
Explore common questions about 3 x Square Root of 3 and its mathematical properties:
- What is the value of 3 x √3?
- How can 3 x √3 be simplified?
- What are the applications of 3 x √3 in geometry?
- Why is √3 an irrational number?
- What is the relationship between 3 x √3 and the Pythagorean theorem?
Conclusion and Summary
In conclusion, 3 x Square Root of 3 is a fundamental mathematical expression with various applications and implications:
- We explored its definition and mathematical representation.
- Discussed its simplification techniques and geometric interpretations.
- Examined its role in advanced mathematical concepts such as trigonometry and calculus.
- Reviewed common mistakes and misconceptions associated with its calculation.
- Provided practice problems to reinforce understanding.
READ MORE:
Khám phá câu đố toán học với căn bậc hai của 12 nhân căn bậc hai của 3. Video này sẽ giúp bạn rèn luyện kỹ năng giải toán với căn bậc hai.
Câu đố căn bậc hai của 12 nhân căn bậc hai của 3