Topic square root of 3 value: Discover the mathematical marvel of the square root of 3 in this insightful article. From its precise definition as an irrational number to practical applications in various fields, delve into its significance in mathematics, physics, and engineering. Explore how this fundamental constant impacts our understanding of numerical relationships and problem-solving.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 3 Value
- Introduction to Square Root of 3
- Mathematical Definition and Properties
- Approximate Value of Square Root of 3
- Applications in Mathematics
- Physical and Engineering Applications
- Historical Significance
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để học cách tìm căn bậc hai của số 3 một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Square Root of 3 Value
The square root of 3 (denoted as \( \sqrt{3} \)) is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Its approximate value in decimal form is:
It is one of the important mathematical constants, often used in various branches of mathematics, physics, and engineering.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 3
The square root of 3, denoted as \( \sqrt{3} \), is a fundamental mathematical constant with significant implications across various disciplines. It belongs to the category of irrational numbers, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Its approximate numerical value is \( \sqrt{3} \approx 1.7320508075688772 \). Understanding its properties and applications is essential in mathematics, physics, engineering, and other scientific fields.
Mathematical Definition and Properties
The square root of 3, symbolized as \( \sqrt{3} \), is an irrational number which cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Its precise value, approximately \( 1.7320508075688772 \), makes it an essential constant in mathematics, particularly in geometry and algebra. Properties include its non-repeating decimal nature and its role in Pythagorean triples, contributing significantly to mathematical proofs and problem-solving in various mathematical contexts.
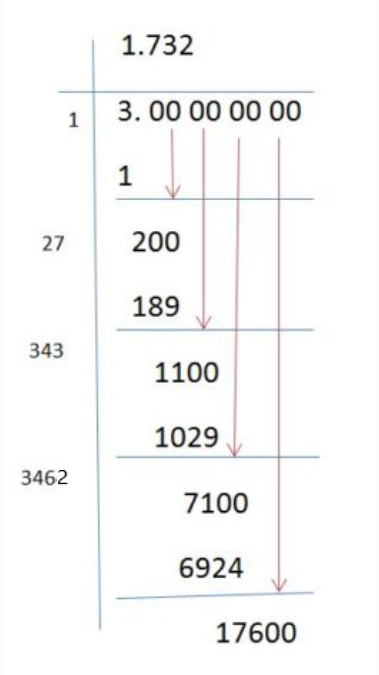
Approximate Value of Square Root of 3
The approximate value of the square root of 3, denoted as \( \sqrt{3} \), is approximately \( 1.7320508075688772 \). This value is crucial in various mathematical calculations, ranging from geometry to numerical analysis. It helps in determining relationships between sides of a triangle, solving quadratic equations, and understanding the magnitude of certain mathematical constants. Its decimal representation continues infinitely without repeating, highlighting its irrational nature.
Applications in Mathematics
The square root of 3, \( \sqrt{3} \), finds extensive applications in various branches of mathematics:
- Geometry: Used in the calculation of diagonal lengths and relationships in geometric shapes.
- Trigonometry: Essential for solving trigonometric equations and understanding angular relationships.
- Number Theory: Plays a role in proving the irrationality of certain numbers and in number-theoretic investigations.
- Algebra: Appears in the solutions of quadratic equations and polynomial roots.
- Calculus: Utilized in calculus functions and the evaluation of limits.
Its precise value aids mathematicians in formulating proofs, solving problems, and exploring mathematical structures.

Physical and Engineering Applications
The square root of 3, \( \sqrt{3} \), plays a crucial role in various physical and engineering applications:
- Electrical Engineering: Used in calculations involving power systems, particularly in three-phase systems.
- Signal Processing: Essential for analyzing signals and understanding their frequency components.
- Structural Engineering: Helps determine the diagonal lengths and dimensions in building designs.
- Fluid Dynamics: Used in equations describing fluid flow and turbulence.
- Computer Graphics: Utilized in algorithms for rendering and calculating geometric shapes.
Its precise numerical value ensures accurate calculations and modeling in these fields, contributing to advancements in technology and innovation.
Historical Significance
The square root of 3, \( \sqrt{3} \), holds historical significance dating back to ancient times:
- Ancient Mathematics: Known to ancient civilizations like the Babylonians and Egyptians for its role in geometric calculations.
- Greek Mathematics: Studied extensively by Greek mathematicians, including Pythagoras and Euclid, in the context of irrational numbers.
- Renaissance and Enlightenment: Continued exploration and understanding of irrational numbers contributed to the development of modern mathematics.
- Modern Era: Its precise value and properties are fundamental in contemporary mathematics, physics, and engineering.
Throughout history, \( \sqrt{3} \) has been integral to the evolution of mathematical thought and its applications in various scientific disciplines.
Conclusion
The square root of 3 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 1.7320508075688772935274463415059. It has significant mathematical properties and applications across various fields.
Mathematically, the square root of 3 is involved in geometric and algebraic contexts, such as in the Pythagorean theorem and trigonometric identities.
Its approximate value makes it useful in numerical calculations and practical applications in engineering and physics, particularly in areas requiring precise measurements and calculations involving triangles and circles.
Throughout history, the square root of 3 has intrigued mathematicians and scientists alike, contributing to the development of mathematical theories and practical applications.
In conclusion, understanding the square root of 3 enriches our knowledge of mathematics and its applications in both theoretical and practical domains.
Xem video này để học cách tìm căn bậc hai của số 3 một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Video: Làm thế nào để tìm căn bậc hai của 3
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm căn bậc hai của số 3 bằng phương pháp chia dài. Tìm hiểu cách tính căn bậc hai của 3 một cách dễ dàng và chính xác.
Cách Tìm Căn Bậc Hai của 3 bằng Phương Pháp Chia Dài / Căn Bậc Hai của 3 / Phương Pháp Chia Dài