Topic x squared calculator: The x squared calculator is an essential tool for anyone dealing with mathematics. This article explores its functions, usage, and benefits, making complex calculations effortless. Whether you're a student or a professional, this guide will help you understand and utilize the x squared calculator effectively.
Table of Content
- Understanding the x Squared Calculator
- Introduction to X Squared Calculator
- Basic Calculations
- Using X Squared Calculator for Different Numbers
- Understanding Squaring Negative Numbers
- Completing the Square Method
- Applications in Algebra
- Using Graphing Calculators for Visualization
- Quadratic Equations and X Squared Calculator
- Practical Examples
- Special Cases in Quadratic Equations
- Interactive Calculators and Online Tools
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách tính tổng của x, tổng của x bình phương và trung bình bằng máy tính khoa học. Video này dành cho những ai muốn học cách sử dụng máy tính khoa học để tính toán các chỉ số thống kê.
Understanding the x Squared Calculator
A squared calculator is a tool that computes the square of a given number. The square of a number, denoted as \( n^2 \), is the result of multiplying the number by itself. This operation is essential in various mathematical computations and applications.
How to Use an x Squared Calculator
- Enter the number you wish to square into the calculator.
- The calculator will automatically compute the square of the entered number.
- For example, if you enter 3, the calculator will output \( 3^2 = 9 \).
Examples of Squared Numbers
| Number | Squared Value |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 3 | 9 |
| 4 | 16 |
| 5 | 25 |
| 6 | 36 |
| 7 | 49 |
| 8 | 64 |
| 9 | 81 |
| 10 | 100 |
Special Considerations
- Squaring Negative Numbers: When squaring negative numbers, ensure to use parentheses. For instance, \((-5)^2\) equals 25, while \(-5^2\) equals -25 due to the order of operations.
- Scientific Notation: The calculator can handle numbers in scientific notation, providing flexibility for a wide range of inputs.
Applications of Squared Numbers
Squared numbers are used in various fields such as geometry, physics, and statistics. They help in calculating area, analyzing quadratic functions, and more.
Additional Resources
For more detailed calculations and examples, you can visit:

READ MORE:
Introduction to X Squared Calculator
An X Squared Calculator is a useful tool for quickly computing the square of any given number. This means multiplying the number by itself to obtain the result. The calculator simplifies this mathematical operation, making it accessible for educational purposes, quick calculations, and solving more complex mathematical problems.
For instance, to find the square of 4, you simply input the number into the calculator, and it performs the operation \( 4^2 = 4 \times 4 = 16 \). The X Squared Calculator is beneficial in various fields such as algebra, physics, engineering, and any other domain requiring frequent square calculations.
Moreover, this calculator is not limited to whole numbers; it can handle decimal numbers and large integers efficiently, providing accurate results promptly. Below are some key features and functionalities of an X Squared Calculator:
- Easy to use interface: Input the number and get the result instantly.
- Handles both positive and negative numbers.
- Supports large numbers and decimal values for comprehensive calculations.
- Educational aid: Helps students understand the concept of squaring numbers.
- Useful in solving algebraic equations involving squared terms.
Using the X Squared Calculator can save time and reduce errors in manual calculations. It is a valuable tool for students, educators, and professionals who require quick and accurate square computations.
Basic Calculations
Using an X squared calculator simplifies the process of computing squared values of numbers. Here are the basic operations you can perform:
- Calculate Square of a Number: Enter a number into the calculator and press the "x²" or similar button to compute its square.
- Calculate Squares of Multiple Numbers: You can sequentially enter numbers and compute their squares one after another.
- Handling Decimal Numbers: X squared calculators often allow input of decimal numbers, enabling calculation of squared values for non-integer inputs.
- Handling Negative Numbers: Some calculators can compute the square of negative numbers, providing both positive and negative squared results.
- Scientific Notation: Advanced X squared calculators may support scientific notation for entering very large or small numbers.
Using X Squared Calculator for Different Numbers
An X squared calculator offers versatility in calculating squares for various types of numbers. Here's how you can use it:
- Whole Numbers: Input whole numbers like 1, 2, 3, etc., and calculate their squares.
- Decimal Numbers: Enter decimal numbers such as 1.5, 2.75, etc., to compute their squared values accurately.
- Negative Numbers: Calculate squares of negative numbers by inputting values like -1, -2, -3, etc.
- Fractions: Some calculators support fractions, allowing you to enter values like 1/2, 3/4, etc., and calculate their squares.
- Large Numbers: Use the calculator to find squares of large numbers such as 1000, 10000, etc., quickly and accurately.
Understanding Squaring Negative Numbers
When using an X squared calculator, understanding how it handles negative numbers is important. Here’s a detailed explanation:
- Positive Result: Squaring a negative number yields a positive result. For example, (-3)² = 9.
- Calculation Process: The calculator computes the square of the absolute value of the negative number and then assigns a positive sign to the result.
- Example: Inputting -5 into the calculator will result in the calculation (-5)² = 25, where the negative sign is removed in the squared result.
- Consistency: This behavior is consistent across most X squared calculators, ensuring predictable results when squaring negative numbers.

Completing the Square Method
The completing the square method is a technique used to solve quadratic equations by transforming them into a perfect square trinomial. Here’s a step-by-step approach:
- Step 1: Rewrite the Equation: Start with a quadratic equation in the form \( ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \).
- Step 2: Adjust the Constant Term: Move the constant term \( c \) to the right side of the equation.
- Step 3: Complete the Square: Take half of the coefficient of \( x \) ( \( \frac{b}{2} \) ) and square it. Add and subtract this square inside the equation.
- Step 4: Factorize: Write the left side as a squared binomial and simplify the equation.
- Step 5: Solve for \( x \): Take the square root of both sides to solve for \( x \).
Applications in Algebra
X squared calculators find numerous applications in algebra, enhancing problem-solving capabilities in various scenarios:
- Quadratic Equations: Easily solve quadratic equations and verify solutions.
- Factoring: Aid in factoring quadratic expressions into linear factors.
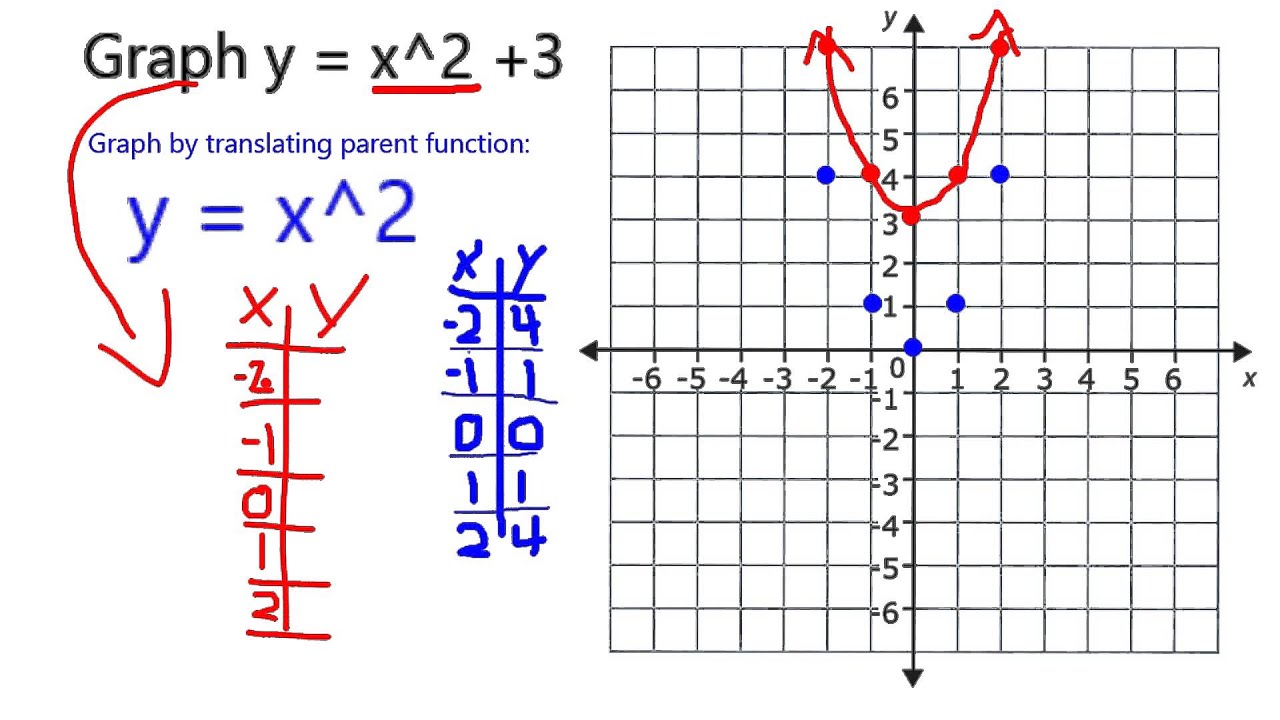
- Graphing: Plot quadratic functions to visualize their shape and characteristics.
- Roots and Solutions: Determine roots and solutions of quadratic equations efficiently.
- Application Problems: Solve real-world algebraic problems involving quadratic relationships.
Using Graphing Calculators for Visualization
Graphing calculators are powerful tools that aid in visualizing mathematical functions, particularly quadratic equations, in the following ways:
- Plotting Functions: Graph quadratic functions \( f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c \) to see their parabolic shape.
- Adjustable Parameters: Modify coefficients \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) to observe changes in the parabola's position, width, and direction.
- Identifying Roots: Locate the roots (x-intercepts) of the quadratic equation graphically.
- Maximum or Minimum Points: Determine the vertex of the parabola, representing its maximum or minimum point.
- Real-World Applications: Apply graphing calculators to model and analyze real-world scenarios that involve quadratic relationships.
Quadratic Equations and X Squared Calculator
An X squared calculator is invaluable for solving quadratic equations efficiently. Here’s how it simplifies the process:
- Input: Enter the coefficients \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) of the quadratic equation \( ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \) into the calculator.
- Calculation: The calculator computes the roots of the quadratic equation using the quadratic formula or other methods.
- Accuracy: Provides accurate solutions, including real and complex roots, depending on the nature of the coefficients.
- Verification: Verify the solutions by substituting them back into the original equation to ensure correctness.
- Visualization: Some calculators graphically display the quadratic equation, helping visualize the roots, vertex, and overall shape of the parabola.

Practical Examples
Here are practical examples demonstrating the use of an X squared calculator in various scenarios:
- Example 1: Finding Squares: Calculate \( 5^2 \), \( 7^2 \), and \( 10^2 \) using the X squared calculator.
- Example 2: Solving Quadratic Equations: Solve \( x^2 - 4x + 3 = 0 \) to find the roots using the calculator.
- Example 3: Visualizing Quadratic Functions: Graph \( y = x^2 + 2x - 3 \) to observe its shape and find its vertex and roots.
- Example 4: Calculating Negative Squares: Determine \( (-6)^2 \) and \( (-8)^2 \) to understand how the calculator handles negative numbers.
- Example 5: Real-World Applications: Use the calculator to solve practical problems involving quadratic relationships, such as calculating areas of squares and rectangles.
Special Cases in Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations can present special cases that require specific attention when using an X squared calculator:
- Case 1: Perfect Squares: Identify equations where the discriminant ( \( b^2 - 4ac \) ) equals zero, resulting in perfect square solutions.
- Case 2: Imaginary Solutions: Encounter equations with a negative discriminant, indicating complex roots that involve imaginary numbers.
- Case 3: Double Roots: Solve equations where the discriminant equals zero, resulting in repeated or double roots.
- Case 4: Zero Coefficient: Handle equations with a zero coefficient for \( x \), simplifying to a linear equation or a constant.
- Case 5: Quadratic Formula Verification: Use the X squared calculator to verify solutions obtained from the quadratic formula for accuracy.
Interactive Calculators and Online Tools
Interactive X squared calculators and online tools provide convenient ways to perform calculations and explore quadratic equations:
- User-Friendly Interface: Access calculators with intuitive interfaces that allow easy input of coefficients and immediate display of results.
- Real-Time Calculation: Obtain instant solutions for quadratic equations, including real and complex roots.
- Graphical Representation: Some tools offer graphing capabilities to visualize quadratic functions and their characteristics.
- Step-by-Step Solutions: Guides users through solving quadratic equations using methods like factoring, completing the square, or the quadratic formula.
- Accessibility: Available across various platforms including web browsers, making them accessible anytime and anywhere.
Hướng dẫn cách tính tổng của x, tổng của x bình phương và trung bình bằng máy tính khoa học. Video này dành cho những ai muốn học cách sử dụng máy tính khoa học để tính toán các chỉ số thống kê.
Cách tính tổng của x, tổng của x bình phương và trung bình bằng máy tính khoa học || Hướng dẫn thống kê
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính số bình phương trên máy tính khoa học. Video này sẽ giúp bạn nắm vững cách sử dụng máy tính để tính toán số bình phương một cách dễ dàng.
Hướng dẫn máy tính 6: Số bình phương trên máy tính khoa học
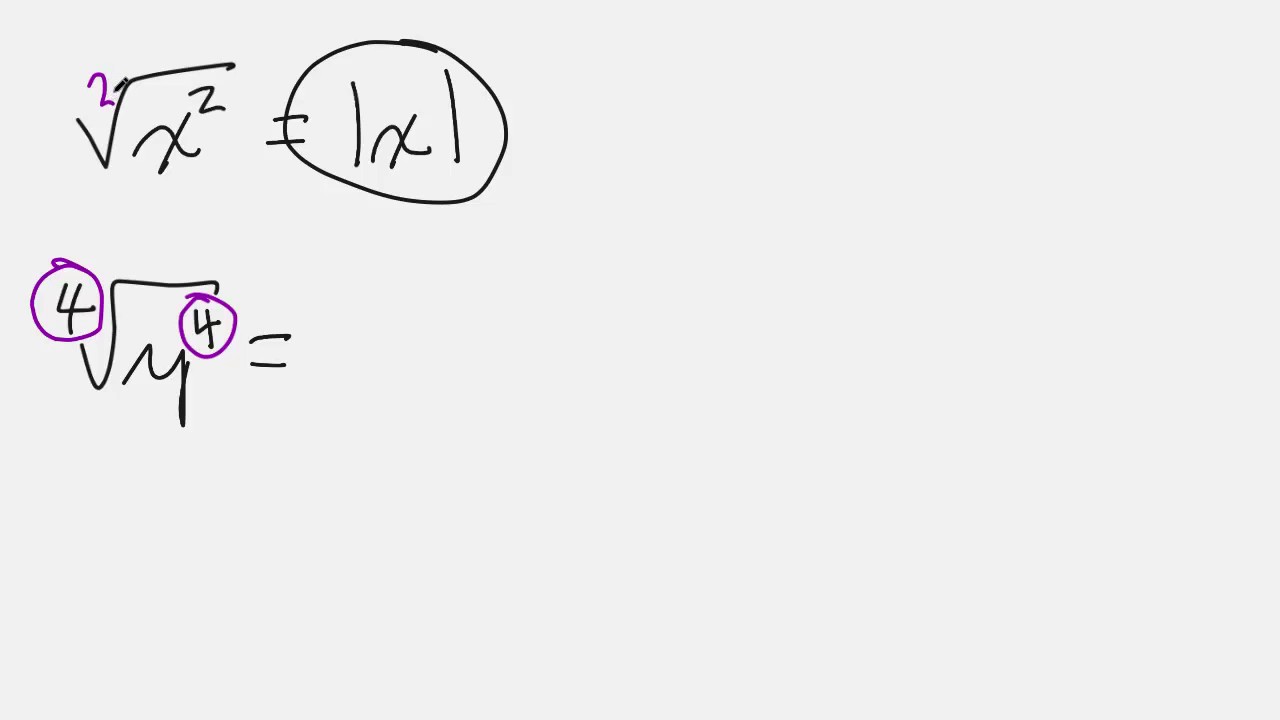



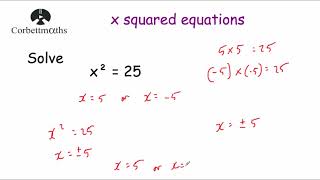
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Chi-SquareStatistic_Final_4199464-7eebcd71a4bf4d9ca1a88d278845e674.jpg)




