Topic what is the square root of 255: Curious about the square root of 255? In this article, we'll explore the exact value, calculation methods, and significance of this mathematical concept. Whether you're a student or math enthusiast, understanding the square root of 255 will enhance your knowledge and problem-solving skills.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 255
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Definition of the Square Root of 255
- Mathematical Representation
- Exact and Approximate Values
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root
- Properties of Square Roots
- Applications of Square Roots
- Importance in Various Fields
- Common Misconceptions
- Historical Context
- Tools and Resources for Calculation
- FAQs on Square Roots
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Video giải thích chi tiết về căn bậc hai của số 255, phương pháp tính toán và ứng dụng thực tế trong các lĩnh vực khác nhau.
Square Root of 255
The square root of 255 is a mathematical value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number 255.
Exact Value
The exact value of the square root of 255 is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. The square root of 255 is denoted as:
\\(\sqrt{255}\\)
Approximate Value
Using a calculator, the approximate value of the square root of 255 is:
\\(\sqrt{255} \approx 15.968719422671311\\)
Calculation Methods
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 255, including:
- Newton's method (also known as the Heron's method)
- Long division method
Properties
The square root function has several important properties:
- \\(\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\\)
- \\(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\\)
- \\((\sqrt{a})^2 = a\\)
Applications
The concept of the square root is used in various fields such as engineering, physics, and finance. For example, it is used in calculating areas of squares, solving quadratic equations, and in statistical formulas.
| Number | Square Root |
| 255 | 15.968719422671311 |
Understanding the square root of 255 and its properties can be beneficial for solving complex mathematical problems and real-world applications.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications in various fields such as engineering, physics, and finance. The square root is denoted by the radical symbol (\\(\sqrt{}\\)).
For example, the square root of 255 is expressed as \\(\sqrt{255}\\).
Key properties of square roots include:
- The square root of a positive number is always positive.
- The square root of zero is zero: \\(\sqrt{0} = 0\\).
- The square root of a negative number is not a real number; it is an imaginary number.
There are various methods to calculate square roots, including:
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down the number into its prime factors and pairing them.
- Long Division Method: A manual technique to find the decimal representation of the square root.
- Newton's Method: An iterative numerical approach for finding successively better approximations to the roots of a real-valued function.
- Using a Calculator: The most straightforward method for quick results.
Understanding square roots is essential for solving quadratic equations, analyzing geometric shapes, and in advanced topics like calculus. The square root function itself has many interesting properties and applications that make it a crucial part of mathematical education.
Definition of the Square Root of 255
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the number 255, its square root is denoted as \(\sqrt{255}\).
Mathematically, this can be represented as:
\[
\sqrt{255} = q \quad \text{such that} \quad q \times q = 255
\]
In decimal form, the square root of 255 is approximately 15.9687, which can be represented as:
\[
\sqrt{255} \approx 15.968719422671
\]
This number is not a perfect square, which means its square root is not an integer. Instead, it is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
In radical form, the square root of 255 is simply written as \(\sqrt{255}\). Since 255 does not have a pair of prime factors, it cannot be simplified further.
Here are some key properties of the square root of 255:
- Decimal Form: \(\sqrt{255} \approx 15.9687\)
- Radical Form: \(\sqrt{255}\)
- Irrational Number: The square root of 255 is an irrational number.
To summarize, the square root of 255 is approximately 15.9687 and is represented in its simplest form as \(\sqrt{255}\).
Mathematical Representation
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. For the number 255, the square root can be represented in several mathematical forms.
In its simplest radical form, the square root of 255 is written as:
\[
\sqrt{255}
\]
Since 255 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number. This means that it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating. The approximate value of the square root of 255 is:
\[
\sqrt{255} \approx 15.9687
\]
The square root can also be expressed using exponent notation, where the square root of a number \(a\) is represented as:
\[
\sqrt{a} = a^{\frac{1}{2}}
\]
Thus, the square root of 255 in exponent form is:
\[
\sqrt{255} = 255^{\frac{1}{2}}
\]
For practical purposes, such as rounding, we can approximate the square root of 255 to different decimal places:
- To the nearest tenth: \(\sqrt{255} \approx 16\)
- To the nearest hundredth: \(\sqrt{255} \approx 15.97\)
- To the nearest thousandth: \(\sqrt{255} \approx 15.969\)
Using a calculator or computer, the square root of 255 can be quickly found using functions like SQRT in Excel or similar tools:
\[
\text{SQRT}(255) \approx 15.968719422671
\]
Understanding the mathematical representation of the square root of 255 helps in various calculations and applications where precise values are necessary.
Exact and Approximate Values
The square root of 255 is a value which, when multiplied by itself, equals 255. This can be represented mathematically as:
\[
\sqrt{255} = x \quad \text{such that} \quad x^2 = 255
\]
Since 255 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number. The exact value of the square root of 255 cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. However, we can approximate it to several decimal places.
The approximate value of \(\sqrt{255}\) is:
\[
\sqrt{255} \approx 15.9687194227
\]
This value can be rounded to various decimal places for simplicity:
- To the nearest whole number: \(\sqrt{255} \approx 16\)
- To two decimal places: \(\sqrt{255} \approx 15.97\)
- To three decimal places: \(\sqrt{255} \approx 15.969\)
Using a calculator or computational tools like Excel or Google Sheets, you can compute this value using the square root function:
\[
\text{SQRT}(255) \approx 15.9687194227
\]
The square root can also be represented using exponents:
\[
\sqrt{255} = 255^{1/2}
\]
In summary, the square root of 255 is approximately 15.9687194227, making it an irrational number that cannot be perfectly simplified but can be expressed and approximated to various decimal places as needed.
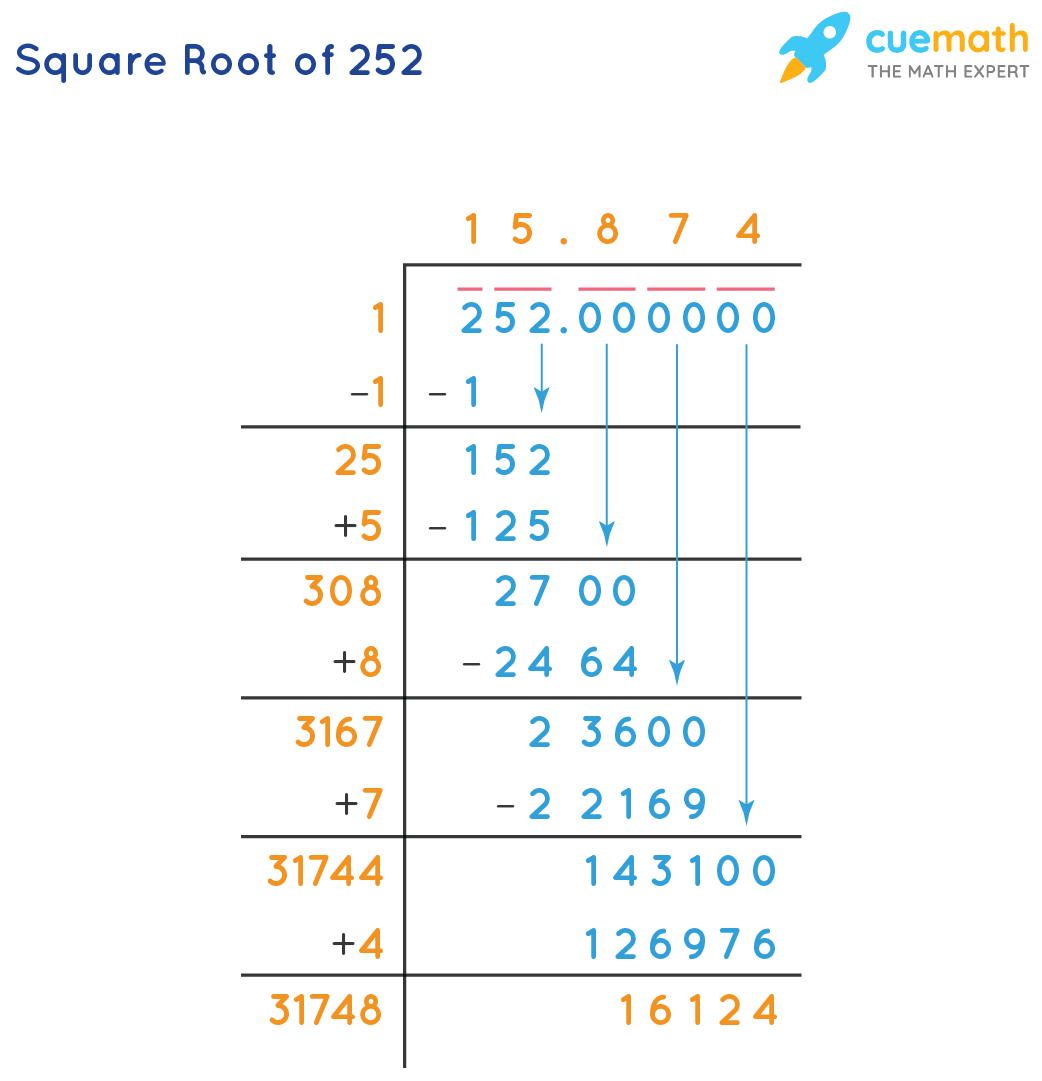
Methods to Calculate the Square Root
There are several methods to calculate the square root of a number, including 255. Below, we will discuss two common methods: the long division method and using a calculator.
1. Long Division Method
The long division method is a manual technique to find the square root of a number. Here's how you can calculate the square root of 255 step-by-step:
- Write 255 as 2 55 00 (pairing the digits from right to left and adding decimal places).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair (2). In this case, it's 1 (since 12 = 1).
- Subtract 1 from 2, bringing down the next pair to get 155.
- Double the number above (1), placing it next to 1 (making it 12), and find a digit X such that 12X * X is less than or equal to 155. X is 1 here (since 121 * 1 = 121).
- Subtract 121 from 155 to get 34, bring down the next pair (00), making it 3400.
- Double 11 (making it 22), find a digit Y such that 22Y * Y is less than or equal to 3400. Y is 5 here (since 225 * 5 = 1125).
- Continue the process until the desired precision is achieved. The final value will be approximately 15.9687.
2. Using a Calculator
Using a calculator is the easiest and fastest method to find the square root of 255:
- Enter 255 and press the square root (√) button. The result is approximately 15.9687.
- For more precision, you can use scientific calculators or software like Excel/Google Sheets by using the formula
=SQRT(255), which will yield a more precise value: 15.968719422671.
3. Prime Factorization Method
Prime factorization is typically used for perfect squares, but it can help understand the roots for any number. Since 255 is not a perfect square, its prime factorization is:
\[ 255 = 3 \times 5 \times 17 \]
This indicates that the square root of 255 cannot be simplified further in radical form.
Conclusion
The square root of 255, using different methods, consistently gives us an approximate value of 15.9687. Each method provides a unique way of understanding and calculating square roots, whether through manual calculations or using technology.
Properties of Square Roots
Square roots have several important properties that are useful in various mathematical contexts. Here are some of the key properties:
- Non-negative Output: The square root of any non-negative number is also a non-negative number. This is represented as \( \sqrt{x} \geq 0 \) for \( x \geq 0 \).
- Product Property: The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots. Mathematically, this is expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}
\] - Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is equal to the quotient of the square roots:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}
\]
(where \( b \neq 0 \)) - Square of a Square Root: Taking the square root of a number and then squaring it returns the original number:
\[
(\sqrt{a})^2 = a
\] - Additive Property: The square root of a sum is not equal to the sum of the square roots. In general,
\[
\sqrt{a + b} \neq \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b}
\] - Even and Odd Perfect Squares: The square root of an even perfect square is even, and the square root of an odd perfect square is odd. For example:
\[
\sqrt{144} = 12 \quad (\text{even})
\]
\[
\sqrt{225} = 15 \quad (\text{odd})
\] - Irrational Numbers: The square root of a non-perfect square is an irrational number. For instance:
\[
\sqrt{2} \approx 1.41421356...
\] - Imaginary Numbers: The square root of a negative number is an imaginary number. This is denoted as:
\[
\sqrt{-a} = i\sqrt{a} \quad (\text{where } i \text{ is the imaginary unit})
\]
Applications of Square Roots
Square roots have a wide range of applications across various fields. Here are some key areas where they play an essential role:
- Engineering and Physics: Square roots are used in engineering and physics to calculate distances, forces, and other quantities. For example, the Pythagorean theorem in geometry, which is fundamental in these fields, involves the square root to determine the length of the hypotenuse in a right-angled triangle.
- Statistics: In statistics, the standard deviation, which measures the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values, is calculated using the square root of the variance.
- Finance: In finance, square roots are used to compute compound interest rates, volatility of financial instruments, and to assess risk. The Black-Scholes model, used for option pricing, involves the square root function.
- Computer Graphics: In computer graphics, algorithms often use square roots to compute distances between points in 2D and 3D space, contributing to rendering, modeling, and animation processes.
- Biology: Square roots are applied in biology, particularly in the study of growth rates and scaling laws, where various biological phenomena are described using power laws involving square roots.
- Architecture and Design: Architects and designers use square roots to create aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound designs, often relying on geometric principles that involve square root calculations.
Overall, the concept of square roots is integral to many scientific, financial, and technical disciplines, making it a fundamental mathematical tool with broad utility.
Importance in Various Fields
The concept of square roots is fundamental in numerous fields, showcasing its broad importance and utility. Here, we explore some of the key areas where square roots, including the square root of 255, play a critical role:
- Mathematics and Geometry:
Square roots are essential in solving quadratic equations and are a core component of the Pythagorean theorem, used to determine distances in geometric shapes.
For example, in a right triangle with legs of lengths \( a \) and \( b \), the length of the hypotenuse \( c \) can be found using \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \).
- Physics:
In physics, square roots are used in various formulas to describe natural phenomena. For instance, in the formula for calculating the RMS (root mean square) velocity of gas particles:
\[ v_{\text{rms}} = \sqrt{\frac{3kT}{m}} \]
where \( k \) is the Boltzmann constant, \( T \) is the temperature, and \( m \) is the mass of a particle.
- Engineering:
Square roots are pivotal in engineering calculations, including determining the natural frequencies of systems, stress and strain in materials, and electrical engineering for calculating power in AC circuits.
- Computer Science:
In computer algorithms, especially those involving graphics and data analysis, square roots are used to calculate distances in various dimensions. For instance, the Euclidean distance between two points in a plane is given by:
\[ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
- Economics and Finance:
Square roots are used in statistical models to analyze financial markets. The standard deviation, a measure of volatility in finance, is derived using square roots:
\[ \sigma = \sqrt{\frac{1}{N}\sum_{i=1}^{N}(x_i - \mu)^2} \]
where \( N \) is the number of observations, \( x_i \) are the individual values, and \( \mu \) is the mean.
- Biology and Medicine:
In biology and medicine, square roots are used in various growth models and to calculate dosages and concentrations. For example, the body surface area (BSA) for determining drug dosages is often calculated using a formula involving the square root:
\[ \text{BSA} = \sqrt{\frac{\text{Height (cm)} \times \text{Weight (kg)}}{3600}} \]
Overall, the square root of 255, like other square roots, is a versatile mathematical tool that finds applications across diverse fields, highlighting its fundamental importance in both theoretical and practical aspects of science and everyday life.

Common Misconceptions
Understanding square roots is essential in mathematics, but several common misconceptions can lead to confusion. Here, we address some of these misconceptions:
- Misconception 1: Only Positive Results
Many believe that the square root of a number is always positive. While the principal square root is positive, every positive number actually has two square roots: a positive and a negative. For example, \(\sqrt{255}\) is approximately \(15.9687194\), but \(-15.9687194\) is also a square root of 255.
- Misconception 2: Square Roots of Negative Numbers
It is often misunderstood that the square root of a negative number does not exist. In reality, the square root of a negative number is a complex number. For example, \(\sqrt{-1} = i\), where \(i\) is the imaginary unit.
- Misconception 3: Simplifying Square Roots Incorrectly
Another common error is simplifying square roots incorrectly. For instance, \(\sqrt{a + b} \neq \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b}\). Correctly, \(\sqrt{a + b}\) needs to be simplified through different methods, such as prime factorization.
- Misconception 4: Assuming Square Roots Distribute Over Multiplication and Division Incorrectly
While it is true that \(\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\) and \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\), this property is often misapplied. For example, \(\sqrt{a + b} \neq \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b}\).
- Misconception 5: All Square Roots Are Rational
Not all square roots are rational numbers. Many square roots are irrational. For example, \(\sqrt{255}\) is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
Addressing these misconceptions is crucial for a correct understanding of square roots and their properties. Always approach square root problems with a clear understanding of these fundamental principles to avoid common pitfalls.
Historical Context
The concept of square roots has a rich history dating back to ancient civilizations. The Babylonians were among the first to develop methods for finding square roots, using an algorithm that closely resembles the modern long division method. This ancient technique demonstrates the early understanding of mathematics and the importance of square roots in solving quadratic equations.
In ancient Greece, mathematicians like Pythagoras and Euclid contributed significantly to the study of square roots. Euclid's "Elements," a foundational text in mathematics, includes propositions related to the properties of square roots and their geometric interpretations. The Greeks' exploration of square roots laid the groundwork for later developments in algebra and number theory.
During the medieval period, Islamic mathematicians preserved and expanded upon Greek mathematical knowledge. Al-Khwarizmi, known as the father of algebra, wrote extensively about methods to solve quadratic equations, which inherently involved the calculation of square roots. His works were later translated into Latin and influenced European mathematics during the Renaissance.
In the 17th century, the advent of the modern decimal system and advancements in algebra made the computation of square roots more accessible. Mathematicians like Isaac Newton developed iterative methods for finding square roots, which improved the accuracy and efficiency of calculations. Newton's method, for example, is still widely used in numerical analysis today.
The square root of 255, an irrational number, cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, reflecting the broader historical development of the concept of irrational numbers. This understanding has profound implications in various fields such as engineering, physics, and computer science, where precise calculations of irrational numbers are crucial.
Overall, the historical context of square roots highlights the evolution of mathematical thought and the enduring significance of this fundamental concept. From ancient algorithms to modern computational techniques, the journey of understanding square roots mirrors the broader progress in the field of mathematics.
Tools and Resources for Calculation
Calculating the square root of a number like 255 can be done using a variety of tools and resources. Here are some of the most commonly used methods and tools:
- Scientific Calculators: Most scientific calculators have a dedicated square root function. Simply enter the number (255) and press the square root (√) button to get the result.
- Online Calculators: Websites like CalculatorSoup and CoolConversion offer online square root calculators. These tools are user-friendly and provide quick results. For example, entering 255 in the square root calculator on CalculatorSoup gives the result 15.968719422671.
- Spreadsheet Software: Programs like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets have built-in functions to calculate square roots. Use the formula
=SQRT(255)or=POWER(255, 1/2)to find the square root of 255. - Mathematical Libraries: For those who prefer programming, many mathematical libraries in languages like Python (NumPy) or MATLAB provide functions to compute square roots. For example, in Python, you can use
numpy.sqrt(255)to get the result.
Below is a table showing the results of calculating different roots of 255:
| Root | Expression | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Square Root | $$ \sqrt{255} $$ | 15.968 |
| Cube Root | $$ \sqrt[3]{255} $$ | 6.341 |
| Fourth Root | $$ \sqrt[4]{255} $$ | 3.996 |
| Fifth Root | $$ \sqrt[5]{255} $$ | 3.029 |
Here is a step-by-step method known as the Babylonian Method to manually calculate the square root:
- Make an initial guess. Let's start with 16.
- Divide 255 by your guess (16), getting 15.9375.
- Averaging the guess and the result: (16 + 15.9375) / 2 = 15.96875.
- Repeat the steps with the new guess until the result stabilizes.
Using these tools and methods, you can accurately determine the square root of 255 and better understand its applications in various fields.
FAQs on Square Roots
Square roots can be a complex topic, so here are some frequently asked questions to help clarify common queries:
- What is the Value of the Square Root of 255?
- Why is the Square Root of 255 an Irrational Number?
- Is the Number 255 a Perfect Square?
- What is the Value of 7 times the Square Root of 255?
- How Do You Simplify the Square Root of 255?
- What is the Square Root of -255?
- How is the Square Root of 255 Calculated?
The square root of 255 is approximately 15.968719422671.
The square root of 255 is considered an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
No, 255 is not a perfect square because it cannot be expressed as the square of an integer. Its prime factorization (31 × 51 × 171) indicates that there are no pairs of prime factors.
The value of 7 times the square root of 255 is approximately 7 × 15.968719422671 = 111.781.
Since 255 does not have any square factors, it cannot be simplified further and is already in its simplest radical form, √255.
The square root of -255 is an imaginary number. It can be expressed as i√255, where i is the imaginary unit (√-1).
The square root of 255 can be calculated using methods such as the long division method for a more accurate result, which yields approximately 15.968719422671.

Conclusion
The square root of 255, approximately 15.9687, is an interesting and useful mathematical concept. Although it is not a perfect square, it holds significant value in various fields such as engineering, physics, and computer science. Understanding the square root of 255 and its properties, such as being an irrational number, helps in grasping more complex mathematical theories and applications.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have explored different aspects of the square root of 255, including its definition, methods to calculate it, and its importance in various disciplines. We also discussed its historical context, common misconceptions, and tools for calculation.
By mastering the concept of square roots, one can enhance their problem-solving skills and apply these principles in real-world scenarios. Whether you are a student, educator, or professional, having a solid understanding of the square root of 255 and its applications will undoubtedly contribute to your mathematical proficiency and overall knowledge.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and a thorough understanding of the square root of 255. For further learning, consider utilizing the tools and resources mentioned in this guide to continue exploring the fascinating world of mathematics.
Video giải thích chi tiết về căn bậc hai của số 255, phương pháp tính toán và ứng dụng thực tế trong các lĩnh vực khác nhau.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 255: Hướng Dẫn Toàn Diện
READ MORE:
Video giải thích chi tiết về căn bậc hai của số 255, phương pháp tính toán và ứng dụng thực tế trong các lĩnh vực khác nhau.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 255