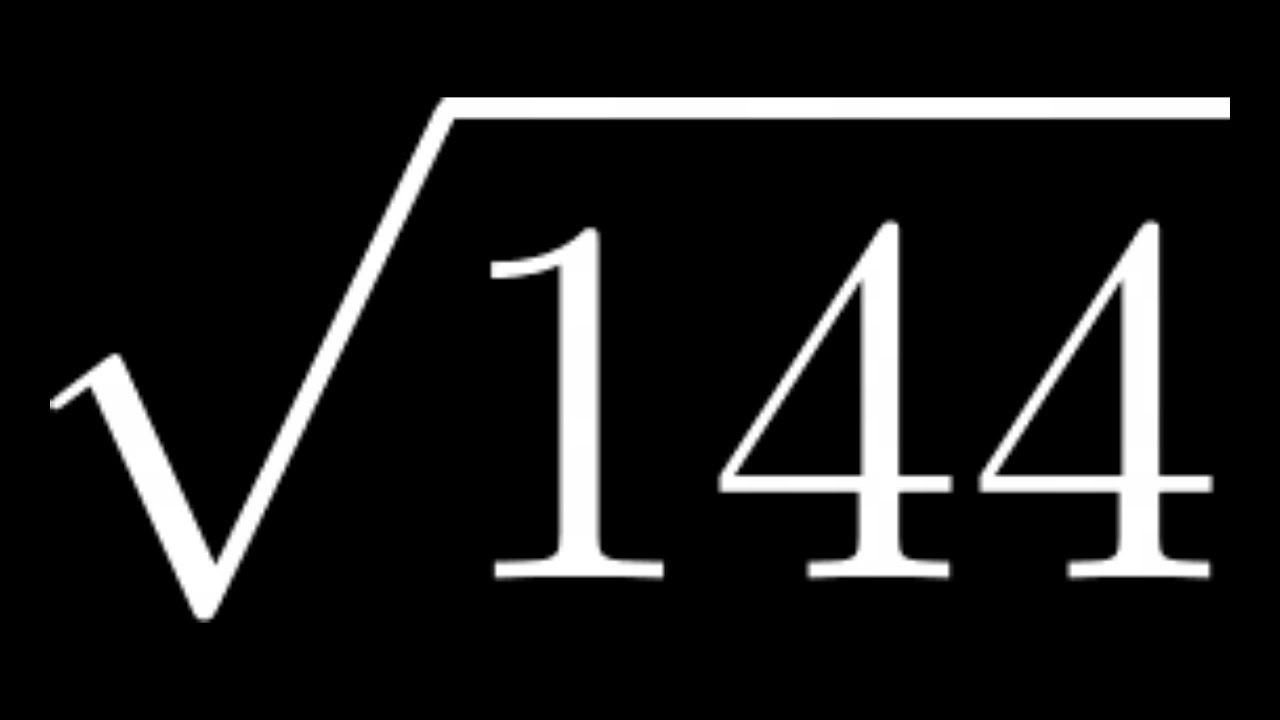Topic what is the square root of 196: The square root of 196 is a fascinating mathematical concept with many applications. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about the square root of 196, including its properties, calculations, and real-life uses. Dive in to explore perfect squares, mathematical explanations, and more!
Table of Content
- Square Root of 196
- Introduction to Square Roots
- What is the Square Root of 196?
- Properties of the Square Root of 196
- Perfect Squares and Their Roots
- How to Calculate the Square Root of 196
- Applications of the Square Root of 196
- Square Root in Geometry
- Square Root in Algebra
- Square Root in Everyday Life
- Alternative Methods to Find Square Roots
- Historical Context and Importance
- Common Misconceptions
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Practice Problems and Solutions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách tìm căn bậc hai của 196 bằng phân tích thành số nguyên tố / Căn bậc hai của 196 / 196 Căn bậc hai.
Square Root of 196
The square root of 196 is a fundamental concept in mathematics, often encountered in various branches such as algebra and geometry.
Mathematical Explanation
To find the square root of 196, we need to determine a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 196. This can be expressed as:
\\(\sqrt{196}\)
Since \(14 \times 14 = 196\), we have:
\\(\sqrt{196} = 14\\)
Properties
- The square root of 196 is 14.
- It is a positive real number.
- 196 is a perfect square, which means its square root is an integer.
Applications
The square root of 196 is used in various practical and theoretical contexts, such as:
- Geometry: Calculating the side length of a square with an area of 196 square units.
- Physics: Solving problems involving quadratic equations and physical dimensions.
- Everyday Calculations: Simplifying radical expressions in algebra.
| Expression | Result |
| \\(\sqrt{196}\\) | 14 |
| \\(196^{0.5}\\) | 14 |
Understanding the square root of 196 can help in recognizing patterns and solving problems in higher-level math and science.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are a fundamental concept in mathematics, often encountered in various fields such as algebra, geometry, and everyday problem-solving. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is denoted by the radical symbol (√).
For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because \(3 \times 3 = 9\). Similarly, the square root of 25 is 5 because \(5 \times 5 = 25\). Square roots can be positive or negative since both \(3^2 = 9\) and \((-3)^2 = 9\). However, in most contexts, the principal (positive) square root is considered.
Understanding square roots is crucial for solving quadratic equations, working with exponents, and simplifying expressions in algebra. They also play a significant role in geometry, where they are used to determine the side lengths of squares and right triangles.
Let's explore the concept of square roots step by step:
- Identify the number for which you need to find the square root.
- Determine if the number is a perfect square (a number that is the square of an integer).
- Use the square root symbol (√) to denote the square root.
- If the number is not a perfect square, use approximation methods or a calculator to find the square root.
Square roots are not limited to integers. They can also be applied to fractions and decimals. For instance, the square root of 0.25 is 0.5 because \(0.5 \times 0.5 = 0.25\).
In the next sections, we will delve deeper into the specific example of finding the square root of 196, along with its mathematical properties and applications.
What is the Square Root of 196?
The square root of 196 is a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing the number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 196. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
\[\sqrt{196} = 14\]
Here, 14 is the principal (positive) square root of 196. This result is derived from the equation:
\[14 \times 14 = 196\]
Thus, 14 is the number that satisfies the condition of being squared to produce 196.
Properties of the Square Root of 196
- Rational Number: The square root of 196 is a rational number because it can be expressed as a simple fraction, \(\frac{14}{1}\).
- Perfect Square: 196 is a perfect square, meaning its square root is an integer (14).
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 196
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down 196 into its prime factors:
\[196 = 2 \times 2 \times 7 \times 7 = (2 \times 7) \times (2 \times 7) = 14 \times 14\]
Therefore, \(\sqrt{196} = 14\).
- Long Division Method: Using long division to find the square root involves pairing the digits from right to left and finding the closest match, which confirms that \(\sqrt{196} = 14\).
- Calculator: Simply inputting 196 and pressing the square root function will yield 14.
Why is the Square Root of 196 Important?
Understanding the square root of 196 helps in various mathematical contexts, including algebra and geometry, and provides a basis for more complex operations and problem-solving techniques. Knowing that 196 is a perfect square allows for simpler computations and a deeper comprehension of numerical relationships.
Properties of the Square Root of 196
The square root of 196 has several interesting properties, making it a notable number in mathematics. Below are some of the key properties:
- Perfect Square: 196 is a perfect square, meaning its square root is an integer. Specifically, \(\sqrt{196} = 14\).
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. Therefore, the square roots of 196 are \(+14\) and \(-14\).
- Even Root: Since 196 is an even number, its square root, 14, is also even.
- Rational Number: The square root of 196 is a rational number because it can be expressed as a fraction \(\frac{14}{1}\).
- Multiplicative Property: The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots. For 196, this can be shown as \(\sqrt{196} = \sqrt{14 \times 14} = 14\).
In addition to these properties, the square root of 196 can be verified using different mathematical methods:
Prime Factorization Method
Prime factorization involves breaking down 196 into its prime factors:
- 196 can be written as \(2 \times 2 \times 7 \times 7\).
- Grouping the prime factors into pairs gives \((2 \times 7) \times (2 \times 7)\).
- The square root of each pair is taken: \(2 \times 7 = 14\).
- Thus, \(\sqrt{196} = 14\).
Long Division Method
The long division method involves the following steps:
- Start by pairing the digits of 196 from right to left (19 and 6).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the leftmost pair (19). This number is 4 (since \(4^2 = 16\)).
- Subtract 16 from 19, bring down the next pair of digits (6), and get 36.
- Double the quotient (4) to get 8, and find a number \(x\) such that \(80x \times x \leq 3600\). Here, \(x = 4\) again.
- Thus, the quotient is 14, confirming that \(\sqrt{196} = 14\).
Understanding these properties and methods highlights the fundamental nature of square roots in mathematics and their practical applications.
Perfect Squares and Their Roots
Perfect squares are numbers that are the product of an integer multiplied by itself. For example, the number 196 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as \(14 \times 14\). Below is a list of perfect squares and their roots for integers from 1 to 20.
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 1 | \(\sqrt{1} = 1\) |
| 4 | \(\sqrt{4} = 2\) |
| 9 | \(\sqrt{9} = 3\) |
| 16 | \(\sqrt{16} = 4\) |
| 25 | \(\sqrt{25} = 5\) |
| 36 | \(\sqrt{36} = 6\) |
| 49 | \(\sqrt{49} = 7\) |
| 64 | \(\sqrt{64} = 8\) |
| 81 | \(\sqrt{81} = 9\) |
| 100 | \(\sqrt{100} = 10\) |
| 121 | \(\sqrt{121} = 11\) |
| 144 | \(\sqrt{144} = 12\) |
| 169 | \(\sqrt{169} = 13\) |
| 196 | \(\sqrt{196} = 14\) |
| 225 | \(\sqrt{225} = 15\) |
| 256 | \(\sqrt{256} = 16\) |
| 289 | \(\sqrt{289} = 17\) |
| 324 | \(\sqrt{324} = 18\) |
| 361 | \(\sqrt{361} = 19\) |
| 400 | \(\sqrt{400} = 20\) |
Perfect squares have unique properties. For example:
- They are always non-negative.
- The square of an even number is even, and the square of an odd number is odd.
- All perfect squares end in 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9.
- They are the sum of consecutive odd numbers. For instance, \(1 + 3 = 4\) (which is \(2^2\)) and \(1 + 3 + 5 + 7 = 16\) (which is \(4^2\)).
Understanding perfect squares and their roots is fundamental in various areas of mathematics, including algebra and geometry. They also have practical applications in fields like engineering, physics, and computer science.
How to Calculate the Square Root of 196
Calculating the square root of 196 can be done using several methods. Below are some of the most common approaches:
1. Prime Factorization Method
- Factorize 196 into its prime factors:
- 196 ÷ 2 = 98
- 98 ÷ 2 = 49
- 49 ÷ 7 = 7
- 7 ÷ 7 = 1
- So, 196 can be written as \(2^2 \times 7^2\).
- To find the square root, take the square root of each prime factor pair:
- \(\sqrt{196} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 7^2} = 2 \times 7 = 14\)
2. Long Division Method
- Pair the digits of 196 from right to left (96 and 1).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 1. This is 1:
- 1 × 1 = 1
- Subtract 1 from 1 to get 0 and bring down the next pair (96) to get 096.
- Double the quotient (1), which gives 2. Now find a digit X such that 2X × X ≤ 96:
- 24 × 4 = 96
- The digit X is 4, so add 4 to the quotient (making it 14) and subtract 96 from 96 to get 0.
- The final quotient is 14, thus \(\sqrt{196} = 14\).
3. Estimation and Approximation Method
- Recognize that 196 is close to 200, whose approximate square roots are known (between 14 and 15).
- Estimate:
- \(14^2 = 196\)
- Thus, \(\sqrt{196} = 14\).
4. Using a Calculator
The most straightforward method is to use a calculator:
- Enter 196 into the calculator.
- Press the square root (√) button.
- The calculator will display 14.
5. Using Exponential Notation
In exponential notation, the square root of a number can be expressed as the number raised to the power of 0.5:
\(\sqrt{196} = 196^{0.5} = 14\)
Applications of the Square Root of 196
The square root of 196, which is 14, finds applications in various fields. Here are some significant areas where this mathematical concept is utilized:
-
Geometry:
In geometry, the square root of 196 is used to calculate the side length of squares and rectangles. For example, if the area of a square is 196 square units, each side of the square will be 14 units long. This is crucial in designing and constructing geometric shapes with precise dimensions.
-
Architecture and Construction:
Architects and builders use the square root of 196 to determine distances and measurements when designing structures. For instance, calculating the diagonal of a square room with sides of 14 feet each helps in determining the placement of elements within the space.
-
Navigation:
In navigation, the square root of 196 helps in calculating distances on maps. For example, to find the direct distance between two points that form a right triangle with legs of 14 units each, navigators use the Pythagorean theorem, which involves square roots.
-
Physics and Engineering:
In physics, the square root of 196 is used in various formulas, such as those involving kinematics and dynamics. Engineers may use this value when calculating stress, strain, and other properties in materials science.
-
Finance:
Financial analysts use the square root of 196 in statistical calculations, such as determining standard deviations and variances. These calculations help in assessing the risk and volatility of financial instruments.
-
Computer Science:
In computer science, square roots are used in algorithms for graphics and data processing. The value 14 might be used to optimize calculations involving distances and transformations in 2D and 3D space.
-
Statistics:
Statisticians use the square root of 196 to calculate standard deviations, which measure the dispersion of a dataset. This is essential for data analysis and making inferences from statistical studies.
-
Daily Life:
In everyday scenarios, the square root of 196 is used in various practical applications, such as determining the size of a square plot of land with an area of 196 square meters, where each side would be 14 meters long.
Square Root in Geometry
The square root of 196, which is 14, finds several applications in geometry, particularly in calculations involving areas and distances.
Here are some key applications:
-
Calculating Areas:
If you have a square with an area of 196 square units, the length of each side of the square is the square root of 196, which is 14 units. This is derived from the formula for the area of a square:
\( \text{Area} = \text{side}^2 \)
Since the area is 196, we have:
\( \text{side} = \sqrt{196} = 14 \)
-
Pythagorean Theorem:
In a right triangle, the square root of 196 can be used to find the length of a side when the hypotenuse or other side lengths are known. For instance, if the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 14 (since \( 14^2 = 196 \)), and one leg is known, the other leg can be found using:
\( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 \)
Where \( c \) is the hypotenuse (14), and \( a \) and \( b \) are the legs of the triangle. Solving for one leg when the hypotenuse and the other leg are known involves taking square roots.
-
Circle Geometry:
The diameter of a circle with an area of 196π square units can be found using the formula for the area of a circle:
\( \text{Area} = \pi r^2 \)
Given that the area is 196π, we can solve for the radius:
\( \pi r^2 = 196\pi \)
\( r^2 = 196 \)
\( r = \sqrt{196} = 14 \)
Therefore, the diameter (which is twice the radius) is 28 units.
-
Scaling and Proportions:
In geometry, scaling figures while maintaining proportions often requires using square roots. For example, if a figure's dimensions need to be increased such that its area becomes 196 times its original area, the side lengths of the figure need to be scaled by the square root of 196, which is 14.
Understanding the square root of 196 and its applications in geometry allows for solving various practical and theoretical problems efficiently.
Square Root in Algebra
In algebra, understanding square roots like \( \sqrt{196} \) is crucial for solving equations and manipulating expressions involving squares. Let's break down how to handle \( \sqrt{196} \) algebraically:
- Recognize that \( \sqrt{196} \) represents the number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 196.
- Start by identifying 196 as a perfect square, specifically \( 196 = 14 \times 14 \).
- Thus, \( \sqrt{196} = 14 \).
- In algebraic terms, \( \sqrt{196} \) simplifies to 14 because \( 14^2 = 196 \).
- When solving algebraic equations involving \( \sqrt{196} \), substitute \( 14 \) into the equation where necessary.
Understanding the algebraic properties of square roots helps in various mathematical contexts, from solving quadratic equations to simplifying expressions in algebraic manipulations.

Square Root in Everyday Life
The concept of square roots, such as \( \sqrt{196} \), manifests in various practical situations in everyday life:
- Measurements: When determining the length of a square or rectangular area with an area of 196 square units, knowing \( \sqrt{196} = 14 \) helps in accurate measurement.
- Engineering: Engineers use square roots extensively in calculations involving areas, volumes, and structural stability.
- Finance: Understanding square roots aids in calculating interest rates, risk assessments, and financial projections.
- Technology: In fields like computer graphics and digital signal processing, square roots are essential for calculating distances, speeds, and frequencies.
- Science: Scientists rely on square roots for analyzing data distributions, error calculations, and experimental measurements.
- Education: Teaching square roots helps students grasp mathematical concepts and problem-solving skills applicable in many disciplines.
By understanding square roots like \( \sqrt{196} \), individuals can apply mathematical principles effectively in various real-world scenarios.
Alternative Methods to Find Square Roots
There are various methods to find the square root of a number like 196:
- Prime Factorization Method: Decompose 196 into prime factors and take half of the exponents of each prime factor.
- Estimation Method: Use approximation techniques to find a close estimate of the square root.
- Newton's Method: Iterative numerical method to approximate square roots.
- Using a Calculator: Modern calculators can compute square roots directly.
- Binomial Expansion: Expand \( (a + b)^2 \) and solve for \( a \) and \( b \).
Each method has its advantages depending on the context and level of accuracy required.
Historical Context and Importance
The concept of square roots, including \( \sqrt{196} \), holds significant historical and mathematical importance:
- Ancient Mathematics: Ancient civilizations such as Babylonians and Egyptians understood basic principles of square roots for practical measurements and constructions.
- Greek Mathematics: Mathematicians like Pythagoras and Euclid explored geometric and arithmetic properties of numbers, including square roots.
- Islamic Mathematics: Scholars during the Islamic Golden Age made advancements in algebra and arithmetic, further developing techniques for calculating square roots.
- Renaissance and Enlightenment: European mathematicians expanded on ancient and Islamic knowledge, refining methods for solving quadratic equations and understanding square roots.
- Modern Mathematics: Today, square roots are fundamental in algebra, geometry, calculus, and many scientific disciplines, playing a crucial role in both theoretical and applied mathematics.
Understanding the historical development of square roots enriches our appreciation of mathematical concepts and their applications throughout human history.
Common Misconceptions
There are several common misconceptions related to square roots, especially concerning \( \sqrt{196} \):
- Confusion with Negative Numbers: Some mistakenly believe that square roots always result in positive numbers, ignoring the concept of both positive and negative roots.
- Complexity in Calculation: People often assume that finding square roots is always complicated, overlooking straightforward methods like prime factorization or using calculators.
- Irrelevance in Everyday Life: Many think square roots have no practical use outside of academic contexts, neglecting their applications in fields such as engineering, finance, and technology.
- Perception of Difficulty: There's a misconception that understanding square roots requires advanced mathematical knowledge, when in reality, basic arithmetic suffices for many applications.
- Historical Misunderstandings: Misconceptions about the historical origins and development of square roots may lead to incorrect assumptions about their significance and usage.
Clearing up these misconceptions promotes a better understanding and appreciation of the role square roots play in mathematics and everyday life.
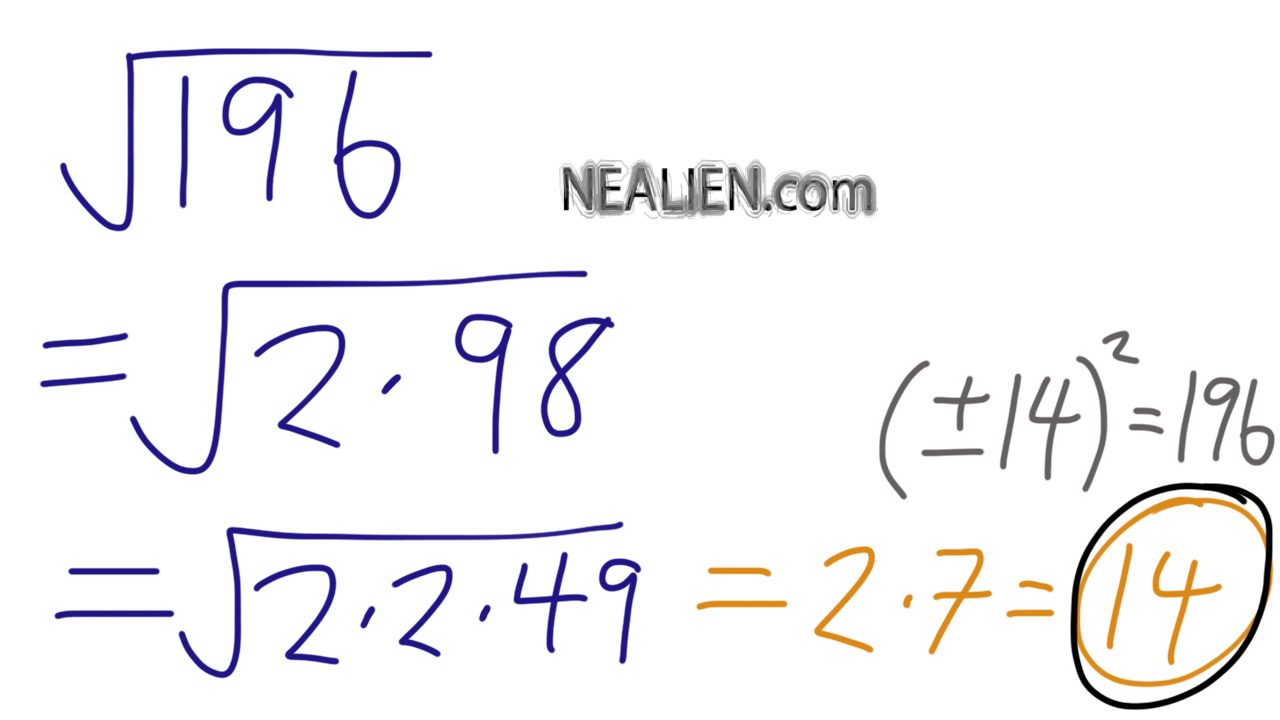
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the square root of 196?
The square root of 196 is 14.
-
How can I calculate the square root of 196 without a calculator?
You can calculate the square root of 196 manually by recognizing it as a perfect square and taking the square root of its factors.
-
Why is 196 a perfect square?
196 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as \( 14^2 \).
-
What are some real-life applications of knowing the square root of 196?
Understanding the square root of 196 is useful in fields like geometry for calculating side lengths of squares and rectangles, in physics for determining distances and velocities, and in finance for calculating interest rates and growth.
-
Can the square root of 196 be a negative number?
No, the square root of 196 is a positive number, specifically 14. In mathematical terms, \( \sqrt{196} = 14 \).
-
What historical significance does the square root of 196 hold?
The square root of 196 is significant historically as it demonstrates ancient and modern mathematical techniques in understanding numbers and their properties.
Practice Problems and Solutions
Test your understanding of the square root of 196 with these practice problems:
-
Problem 1:
Calculate \( \sqrt{196} \).
Solution: \( \sqrt{196} = 14 \).
-
Problem 2:
Find the square root of a number that is 196 times smaller than 1.
Solution: \( \sqrt{0.01 \cdot 196} = 0.14 \).
-
Problem 3:
Determine the area of a square with each side measuring \( \sqrt{196} \) units.
Solution: The area is \( 196 \) square units.
-
Problem 4:
What is the square root of \( 784 \)?
Solution: \( \sqrt{784} = 28 \).
-
Problem 5:
Using estimation, approximate \( \sqrt{196} \).
Solution: Estimated as \( \sqrt{196} \approx 14 \).
Conclusion
Understanding the square root of 196, which is \( \sqrt{196} = 14 \), illuminates the broader significance of mathematical concepts in various aspects of life. From practical applications in measurements and engineering to theoretical implications in algebra and geometry, the concept of square roots plays a pivotal role. It serves as a foundation for problem-solving and critical thinking across disciplines, emphasizing the beauty and utility of mathematics in both historical and contemporary contexts.
Hướng dẫn cách tìm căn bậc hai của 196 bằng phân tích thành số nguyên tố / Căn bậc hai của 196 / 196 Căn bậc hai.
How to Find Square Root of 196 by Prime Factorization / Square Root of 196 / 196 Square Root
READ MORE:
Căn bậc hai của 196 | Căn bậc hai 196.
Square root of 196 | Root 196