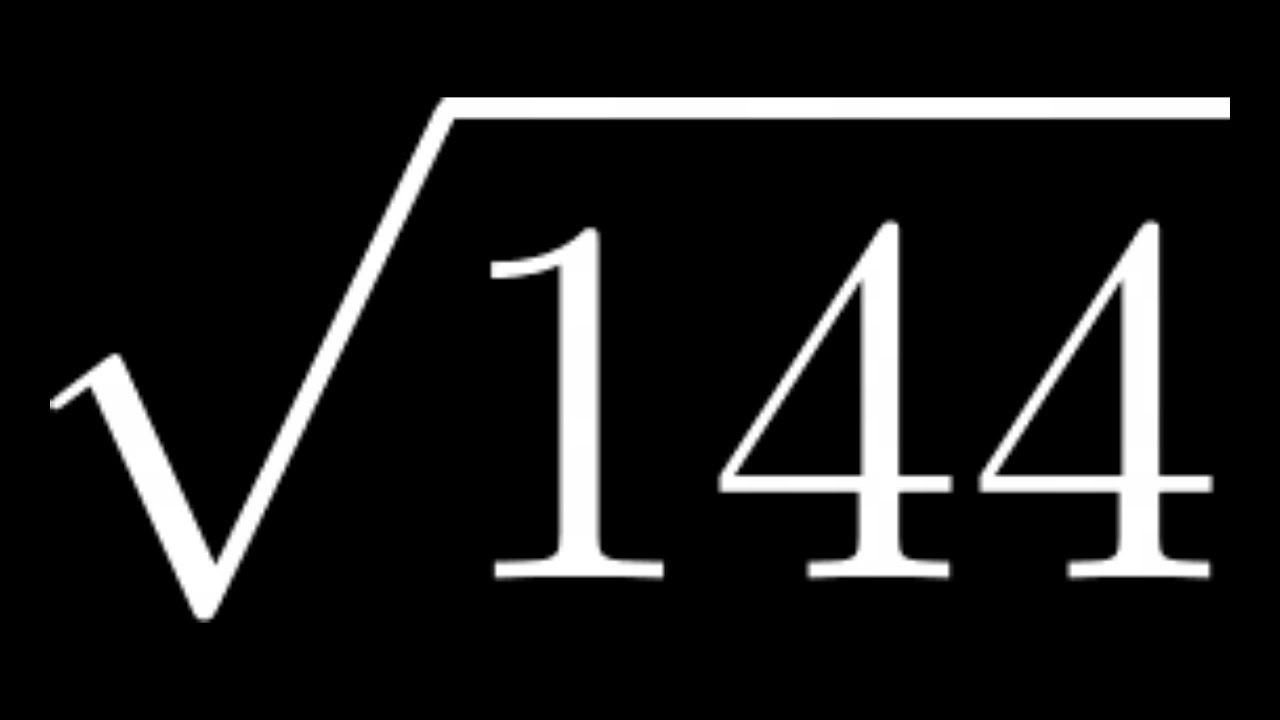Topic 196 square roots: Discover the fascinating world of 196 square roots and unravel the mysteries behind perfect squares. This comprehensive guide explores methods to calculate the square root of 196, its properties, and practical applications in various fields. Join us on this mathematical journey to deepen your understanding and appreciation of square roots.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Roots of 196
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 196
- Prime Factorization Method
- Estimation and Approximation Method
- Using a Calculator
- Rational Number
- Perfect Square
- Even Number
- Importance in Mathematics
- Use in Engineering and Physics
- Role in Computer Science
- YOUTUBE: Làm thế nào để tìm căn bậc hai của 196 bằng phân tích thừa số nguyên tố? Hướng dẫn tìm căn bậc hai của 196 một cách dễ dàng và nhanh chóng.
Understanding the Square Roots of 196
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In this section, we will explore the square roots of 196 and understand the various methods to find them.
What is the Square Root of 196?
The square root of 196 is a number which, when multiplied by itself, results in 196. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
\[\sqrt{196}\]
The principal square root of 196 is:
\[\sqrt{196} = 14\]
This is because:
\[14 \times 14 = 196\]
Positive and Negative Square Roots
Every positive real number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. For 196, the square roots are:
\[\sqrt{196} = 14\] and \[-\sqrt{196} = -14\]
Methods to Find the Square Root of 196
- Prime Factorization Method:
Break down 196 into its prime factors:
\[196 = 2^2 \times 7^2\]
Taking the square root of both sides, we get:
\[\sqrt{196} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 7^2} = 2 \times 7 = 14\]
- Estimation and Approximation:
By estimating and adjusting, we find that:
- Using a Calculator:
Simply enter 196 and press the square root button to get 14.
Properties of the Square Root of 196
- Rational Number: Since 14 can be expressed as a fraction (14/1), the square root of 196 is a rational number.
- Perfect Square: 196 is a perfect square because its square root is an integer.
- Even Number: Both 196 and its square root, 14, are even numbers.
Applications of the Square Root of 196
Understanding square roots is crucial in various fields such as engineering, physics, and computer science. The square root of 196 can be applied in solving quadratic equations, geometry (calculating areas and volumes), and many real-world problems.
Conclusion
The square root of 196 is 14. It is important to know both the positive and negative roots, as well as the methods to find them. Mastery of these concepts enhances problem-solving skills in mathematics and its applications.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental concepts in mathematics that involve finding a number which, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. For example, the square root of 196 is 14, since \(14 \times 14 = 196\). This section will guide you through the basic principles and methods of calculating square roots, emphasizing their importance and applications.
Mathematically, if \(a^2 = b\), then \(a\) is the square root of \(b\). This means that for any positive number \(b\), there are always two square roots: one positive and one negative. For instance, the square roots of 196 are 14 and -14, as both \(14^2\) and \((-14)^2\) equal 196.
Understanding square roots is crucial for various mathematical operations and real-world applications. They are widely used in geometry, algebra, and calculus, helping to simplify expressions and solve equations. The process of finding a square root can be done through several methods, including prime factorization, long division, and using a calculator.
- Prime Factorization: Break down the number into its prime factors and then group them into pairs. For 196, the prime factors are \(2 \times 2 \times 7 \times 7\), which simplifies to \(2 \times 7 = 14\).
- Long Division: This method involves dividing the number into smaller parts to find an approximate value of the square root. It's useful for non-perfect squares.
- Calculator: The simplest method, where you input the number and use the square root function to get the result directly.
In addition to these methods, square roots play a vital role in understanding the properties of numbers, especially in distinguishing between rational and irrational numbers. A rational number can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, while an irrational number cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
By mastering square roots, you can enhance your mathematical skills and tackle more complex problems with confidence. Whether you're calculating areas, solving quadratic equations, or exploring advanced mathematical theories, square roots provide a solid foundation for your mathematical journey.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 196
Calculating the square root of 196 can be approached using several methods. Here are some detailed steps and techniques:
-
Prime Factorization Method:
- Express 196 as a product of its prime factors: \( 196 = 2 \times 2 \times 7 \times 7 \).
- Group the factors into pairs: \( (2 \times 7) \times (2 \times 7) = 14 \times 14 \).
- Take the square root of each pair: \( \sqrt{196} = \sqrt{14^2} = 14 \).
-
Long Division Method:
- Write 196 and pair the digits from the right, forming two pairs: 1 and 96.
- Find a number \( n \) such that \( n \times n \leq 1 \). Since \( 1 \times 1 = 1 \), \( n = 1 \).
- Subtract the obtained value from the first pair and bring down the next pair (96), making the new dividend 96.
- Find a number \( m \) such that \( 2m \times m \leq 96 \). Since \( 24 \times 4 = 96 \), \( m = 4 \).
- Thus, the square root of 196 is 14.
-
Calculator Method:
- Use a calculator with a square root function.
- Input 196 and press the square root button.
- The result will be 14.
-
Estimation Method:
- Since 196 is close to 200, estimate that the square root is close to the square root of 200.
- The square root of 200 is approximately 14.14.
- Therefore, the square root of 196 is close to 14.
These methods provide flexibility in calculating the square root of 196, allowing for a thorough understanding of different mathematical techniques.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a straightforward way to find the square root of a number by breaking it down into its prime factors. Here's a detailed, step-by-step guide to finding the square root of 196 using prime factorization:
- First, decompose 196 into its prime factors.
- Start by dividing 196 by the smallest prime number, which is 2:
- 196 ÷ 2 = 98
- Continue dividing by 2:
- 98 ÷ 2 = 49
- 49 is not divisible by 2, so move to the next prime number, which is 7:
- 49 ÷ 7 = 7
- 7 ÷ 7 = 1
- Now, we have the prime factors of 196 as: 2 × 2 × 7 × 7.
- Group the prime factors into pairs of equal factors:
- (2 × 2) and (7 × 7)
- Take one factor from each pair:
- 2 and 7
- Multiply these factors together to get the square root:
- 2 × 7 = 14
Therefore, the square root of 196 is 14.
Estimation and Approximation Method
Estimating the square root of a number involves finding an approximate value close to the actual square root. For 196, a perfect square, we can apply estimation techniques useful for non-perfect squares as well. Here are step-by-step methods:
Method 1: Finding Perfect Squares
-
Identify the perfect squares closest to 196. The number 196 falls between the perfect squares of 169 (132) and 225 (152).
- 169 < 196 < 225
-
Since 196 is exactly equal to 142, we already know the exact square root. For practice, assume it is unknown and use the following approximation:
Method 2: Averaging Method
-
Choose a reasonable guess, say 14. Since 196 is a perfect square, our initial guess can be quite close.
-
Divide 196 by your guess:
- \( \frac{196}{14} = 14 \)
-
Average the result with the original guess:
- \( \text{New estimate} = \frac{14 + 14}{2} = 14 \)
-
Since the result does not change, we conclude that the square root of 196 is 14.
Method 3: Guess and Check
-
Start with an initial guess. Let's try 13 and 15:
- \( 13^2 = 169 \) (too low)
- \( 15^2 = 225 \) (too high)
-
Since 196 is closer to 225, our next guess can be closer to 15. However, trying 14 directly:
- \( 14^2 = 196 \)
-
We find that 14 is the exact square root.
Conclusion
Estimating the square root of 196 using various methods highlights the precision of these techniques. While 196 is a perfect square, these methods are highly beneficial for approximating non-perfect squares. Practicing with perfect squares reinforces understanding and accuracy in estimation techniques.

Using a Calculator
Calculating the square root of 196 using a calculator is straightforward and can be done with various types of calculators, including basic, scientific, and online calculators. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use each type:
Using a Basic Calculator
- Turn on the calculator.
- Enter the number 196.
- Press the square root (√) button. This button is usually located above one of the number keys and may require you to press a "Shift" or "2nd" key first.
- The display will show the result, which is 14.
Using a Scientific Calculator
- Turn on the calculator.
- Make sure it is in the correct mode for arithmetic calculations.
- Enter the number 196.
- Press the square root (√) button. On most scientific calculators, this is a dedicated button.
- Verify that the display shows 14 as the result.
Using an Online Calculator
Online calculators can be very convenient for quickly finding square roots. Here’s how to use one:
- Open your web browser and go to an online calculator website, such as or .
- Enter 196 in the input field.
- Click the button to calculate the square root, often labeled as "Calculate" or directly showing the square root symbol.
- The result will be displayed on the screen, which is 14.
Using a calculator ensures that you get the correct square root value quickly and accurately. This method is particularly useful for larger numbers or when precision is required.
Rational Number
The square root of 196, which is 14, is a rational number. To understand why, let's delve into the concept of rational numbers and how they apply to the square root of 196.
A rational number is defined as any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers, where p and q are integers and q is not zero. In simpler terms, a number is rational if it can be written as a fraction with both the numerator and the denominator being whole numbers.
The square root of 196 can be expressed as:
\[\sqrt{196} = 14\]
Since 14 is a whole number, it can also be written as a fraction:
\[14 = \frac{14}{1}\]
This clearly fits the definition of a rational number, as 14 and 1 are both integers and the denominator is not zero.
Additionally, 196 is a perfect square, which means its square root is an integer. The property of perfect squares having integer roots further supports that the square root of 196 is rational. To summarize, since 14 is a whole number and can be expressed as a fraction, the square root of 196 is indeed a rational number.
Perfect Square
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. The number 196 is a perfect square because it can be written as \( 14 \times 14 \). In mathematical terms, this is expressed as \( 196 = 14^2 \) or \( \sqrt{196} = 14 \).
Perfect squares have unique properties that make them significant in mathematics. Here are some key characteristics and properties of perfect squares:
- Integer Square Roots: The square root of a perfect square is always an integer. For 196, the square root is 14.
- Geometric Representation: A perfect square can be represented as a square in geometry. For example, a square with each side of length 14 units has an area of 196 square units.
- Even and Odd Perfect Squares: The perfect square of an even number is always even, and the perfect square of an odd number is always odd. Since 14 is even, 196 is also even.
Perfect squares are essential in various fields such as algebra, geometry, and number theory. They help in simplifying mathematical expressions and solving quadratic equations.
Here are some examples of perfect squares:
- \( 1^2 = 1 \)
- \( 2^2 = 4 \)
- \( 3^2 = 9 \)
- \( 4^2 = 16 \)
- \( 5^2 = 25 \)
- \( 14^2 = 196 \)
In summary, 196 is a perfect square, making it a valuable number in mathematical studies and practical applications.
Even Number
The square root of 196 is 14. One of the fundamental properties of 14 is that it is an even number. This property has several implications in mathematics and its applications:
- Definition: An even number is any integer that can be exactly divided by 2. Since 14 ÷ 2 = 7, 14 is an even number.
- Square Root Property: The square root of any even perfect square will always be even. Since 196 is an even perfect square (196 = 14²), its square root is also even.
- Mathematical Operations:
- When an even number is squared, the result is always an even number (e.g., 14² = 196).
- When an even number is multiplied by any integer, the result is always even (e.g., 14 × 3 = 42).
The property of being even is significant in various mathematical contexts:
- Factorization: In the prime factorization of 196, the presence of the prime number 2 confirms that 196 is even. Prime factorization of 196 is 2 × 2 × 7 × 7.
- Divisibility: 196 is divisible by 2, 14, and other factors, simplifying calculations in algebra and number theory.
Understanding that the square root of 196 is an even number aids in recognizing patterns and properties within the realm of numbers, enhancing comprehension of mathematical concepts.
Importance in Mathematics
The square root of 196, which is 14, holds significant importance in various mathematical concepts and applications. Here are some key reasons why understanding square roots, including the square root of 196, is vital in mathematics:
- Basic Arithmetic and Algebra: The concept of square roots is fundamental in arithmetic and algebra. It helps in solving quadratic equations, simplifying expressions, and understanding the properties of numbers.
- Geometry: Square roots are essential in geometry, especially when dealing with the Pythagorean theorem, which relates the lengths of the sides of a right triangle. For instance, if the hypotenuse of a right triangle is 14 units, the square root of 196 helps in determining the possible integer values of the other two sides.
- Measurement and Scaling: In measurement, square roots are used to calculate areas and volumes. For example, if a square has an area of 196 square units, its side length is 14 units.
- Number Theory: Square roots play a critical role in number theory. Understanding perfect squares, like 196, helps in exploring properties of integers, prime factorization, and the distribution of primes.
- Statistics and Probability: Square roots are used in statistics for calculating standard deviation and variance, which are measures of data dispersion. The ability to compute these values accurately is essential for data analysis.
Overall, the concept of square roots, including the square root of 196, is integral to a wide range of mathematical disciplines, making it a crucial topic for students and professionals alike to master.
Use in Engineering and Physics
The square root of 196 is a fundamental concept used in various engineering and physics applications. Understanding this concept helps in simplifying complex calculations and solving real-world problems. Here are some key applications:
-
Structural Engineering:
In structural engineering, square roots are essential for determining the natural frequency of structures such as bridges and buildings. The natural frequency is crucial for assessing how structures will react to dynamic loads like wind, earthquakes, and traffic. Calculating the square root of stiffness over mass helps engineers design safer and more resilient structures.
-
Electrical Engineering:
Electrical engineers use square roots to calculate power, voltage, and current in AC circuits. For instance, the root mean square (RMS) value of alternating current is used to express AC voltage or current in a manner that relates to the equivalent DC value. This is vital for designing and analyzing electrical systems.
-
Wave Mechanics:
In physics, the square root function is used in wave mechanics to determine wave speed. For example, the speed of a wave on a string is determined by the square root of the tension divided by the linear mass density. This relationship helps physicists understand how different factors affect wave propagation.
-
Vibration Analysis:
Square roots are used in vibration analysis to calculate the natural frequencies of mechanical systems. This is essential in designing systems that avoid resonance, which can cause excessive vibrations and potential failure. Engineers calculate the square root of stiffness and mass properties to predict and mitigate these effects.
-
Signal Processing:
In signal processing, square roots are used to compute the energy of a signal. For example, the RMS value of a signal, which involves taking the square root of the average of the squares of the values, is used to quantify the signal's power. This is important for analyzing and optimizing communication systems.
Overall, the square root of 196, which simplifies to 14, is a useful computation in these fields, making it easier to perform various critical analyses and calculations efficiently.
Role in Computer Science
The square root of 196, which is 14, plays a significant role in various aspects of computer science. Understanding and efficiently computing square roots is crucial for algorithms, computer graphics, cryptography, and data structures.
-
Algorithms:
In algorithm design, the ability to compute square roots efficiently can impact the performance of various applications. For instance, the Newton-Raphson method is commonly used for finding square roots due to its fast convergence. This method iteratively improves the approximation of the square root, making it highly efficient for large numbers.
-
Computer Graphics:
In computer graphics, square root calculations are essential for operations like vector normalization, where the magnitude of a vector is determined using the square root of the sum of its components squared. Efficient square root algorithms help in rendering smoother graphics and real-time simulations.
-
Cryptography:
Square roots play a vital role in cryptographic algorithms. For instance, in public-key cryptography, algorithms like RSA use mathematical functions involving square roots for encryption and decryption processes. Efficient computation of square roots ensures the security and speed of these cryptographic protocols.
-
Data Structures:
Square roots are used in various data structures and algorithms for optimizing performance. For example, in spatial data structures like quad-trees, which are used to partition a two-dimensional space, square root calculations help in determining distances and organizing hierarchical structures.
Overall, the ability to compute and understand square roots is fundamental in computer science, influencing the efficiency and effectiveness of algorithms, graphics, cryptography, and data management.
Làm thế nào để tìm căn bậc hai của 196 bằng phân tích thừa số nguyên tố? Hướng dẫn tìm căn bậc hai của 196 một cách dễ dàng và nhanh chóng.
Hướng dẫn tìm căn bậc hai của 196 / Căn bậc hai của 196 / Tìm căn bậc hai của 196
READ MORE:
Căn bậc hai của 196 | Bình phương của 196.
Căn bậc hai của 196 | Bình phương 196