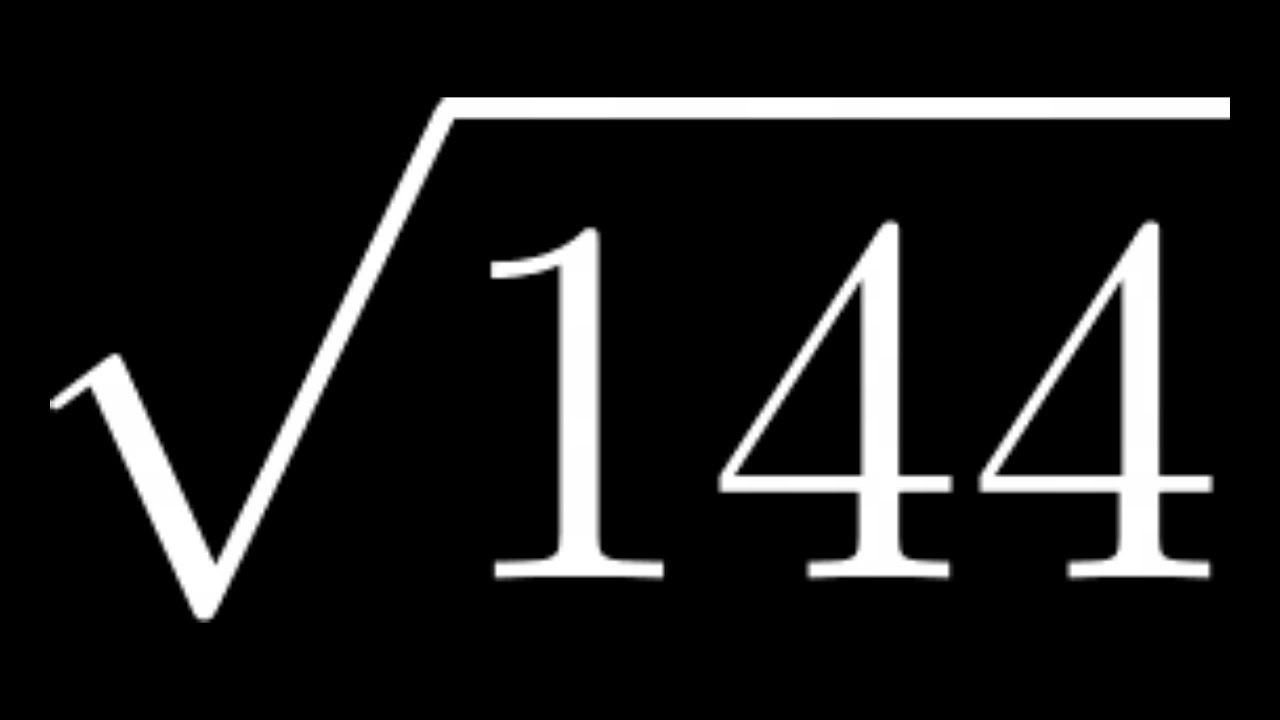Topic 3 square root of 64: Discover the intriguing calculation of 3 square root of 64 in this comprehensive guide. This article simplifies the process, offering a clear and engaging explanation suitable for students, educators, and math enthusiasts. Dive into the world of radicals and multiplication, and learn how to approach similar problems with confidence and ease.
Table of Content
- Understanding 3 Square Root of 64
- Introduction
- Understanding the Expression
- Step-by-Step Simplification
- Mathematical Explanation
- Practical Applications
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Additional Resources
- YOUTUBE: Video này hướng dẫn cách tính căn bậc 3 của 64 mà không cần dùng máy tính.
Understanding 3 Square Root of 64
The expression \(3 \sqrt{64}\) involves calculating the square root of 64 and then multiplying the result by 3.
Calculating the Square Root of 64
The square root of 64 is calculated as follows:
- 64 is a perfect square since it can be expressed as \(8 \times 8\).
- Thus, \(\sqrt{64} = 8\).
Multiplying by 3
Now, we multiply the square root of 64 by 3:
\(3 \times \sqrt{64} = 3 \times 8 = 24\).
Using the Expression in Equations
The expression \(3 \sqrt{64}\) can be used in various mathematical contexts, including solving equations and simplifying expressions. For example:
\[
3 \sqrt{\frac{64}{27}} = 3 \times \frac{8}{3 \sqrt{3}} = \frac{8 \sqrt{3}}{3}
\]
Tables for Reference
Nth Roots of 64
| Index (N) | Nth Root of 64 | Expression | Root |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | Square Root of 64 | \( \sqrt[2]{64} \) | 8.000 |
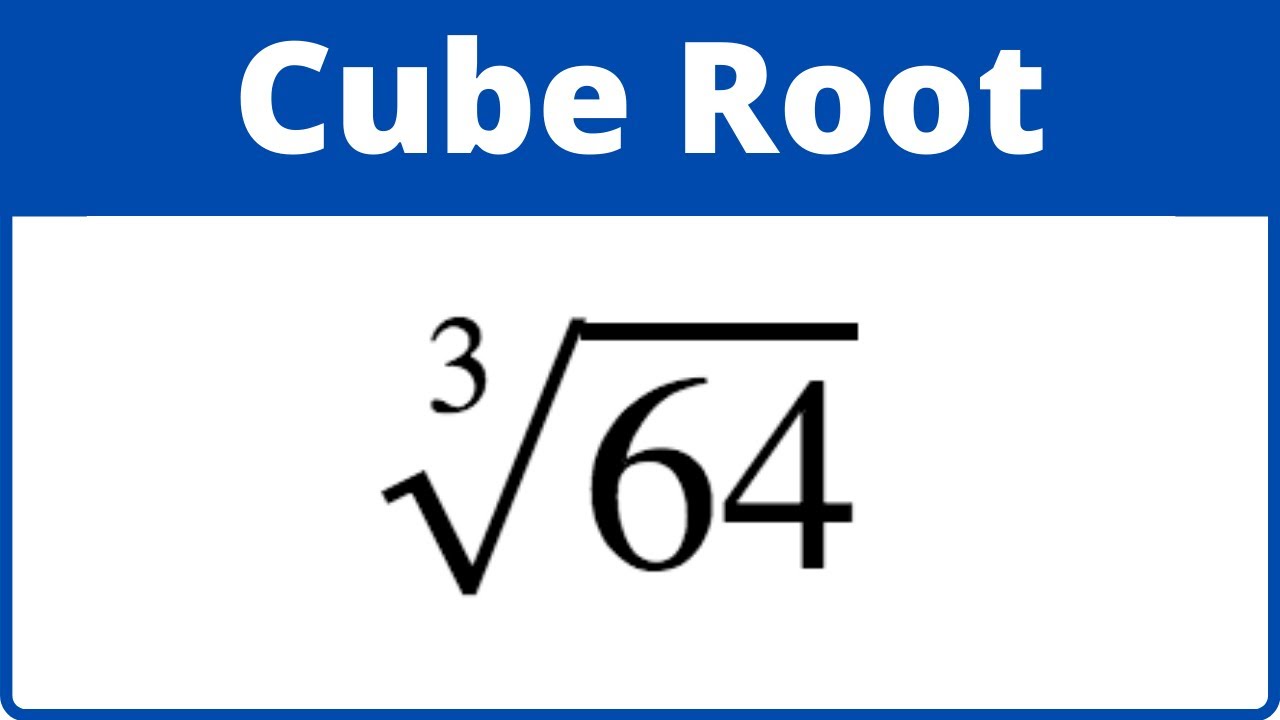
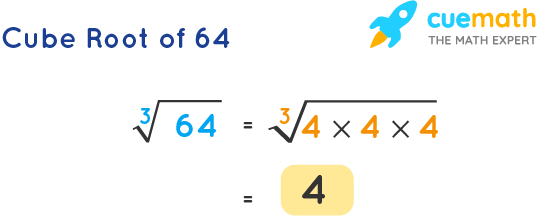
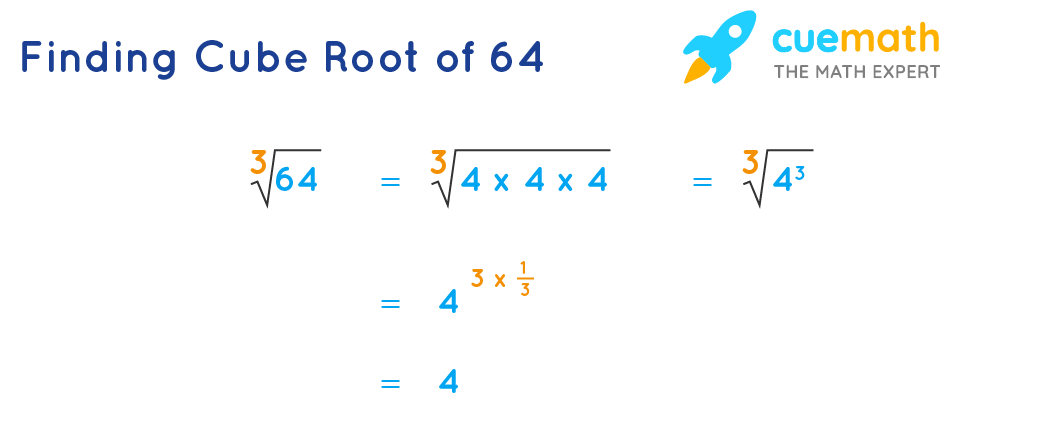
| 3 | Cube Root of 64 | \( \sqrt[3]{64} \) | 4.000 |
| 4 | Fourth Root of 64 | \( \sqrt[4]{64} \) | 2.828 |
Square Roots of Numbers Around 64
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 59 | 7.681 |
| 60 | 7.746 |
| 61 | 7.810 |
| 62 | 7.874 |
| 63 | 7.937 |
| 64 | 8.000 |
| 65 | 8.062 |
READ MORE:
Introduction
The expression "3 square root of 64" combines a constant multiplier and a square root operation. To understand this, we first simplify the square root of 64. The square root of 64 is 8 because \(8 \times 8 = 64\). When we multiply this result by 3, we get \(3 \times 8 = 24\). Thus, the value of 3 square root of 64 is 24. This calculation demonstrates a straightforward application of the properties of square roots and multiplication.
Understanding the Expression
The expression "3 square root of 64" involves two mathematical operations: multiplication and square root. To break it down:
- Calculate the square root of 64: The square root of 64 is 8 because \(8 \times 8 = 64\).
- Multiply the result by 3: After finding the square root, multiply it by 3. So, \(3 \times 8 = 24\).
Thus, the value of "3 square root of 64" is \(24\). This expression highlights the use of basic arithmetic operations and properties of square roots in simplifying mathematical expressions.
Step-by-Step Simplification
To simplify the expression \(3 \sqrt{64}\), follow these steps:
Identify the square root of 64. The prime factorization of 64 is \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\), which gives us \( (2^3)^2 \). Therefore, the square root of 64 is 8.
Rewrite the expression using the simplified square root: \(3 \sqrt{64} = 3 \times 8\).
Multiply the numbers: \(3 \times 8 = 24\).
Thus, \(3 \sqrt{64}\) simplifies to 24.
Mathematical Explanation
The expression "3 square root of 64" refers to finding the square root of 64 and then multiplying the result by 3.
To start, calculate the square root of 64:
- Identify that the square root of 64 is 8, because 8 multiplied by itself (8 * 8) equals 64.
Now, multiply the result by 3:
- Multiply 8 by 3:
| 3 × 8 = 24 |
Therefore, the value of "3 square root of 64" is 24.
This calculation can be summarized as:
3 × √64 = 3 × 8 = 24
Thus, "3 square root of 64" simplifies to 24.
Practical Applications
The cube root of 64, which is 4, finds its use in various practical applications across different fields. Here are some of the notable examples:
- Engineering and Architecture: Engineers and architects use cube roots in calculations involving volume and dimensions. For instance, determining the dimensions of a cubic storage space that can hold a certain volume.
- Physics: Cube roots are used in physics to calculate quantities like the moment of inertia in rotational dynamics, where the distribution of mass in three dimensions is considered.
- Chemistry: In chemistry, the cube root is used when dealing with molecular structures and chemical reactions that involve volume relationships in three-dimensional space.
- Computer Graphics: In computer graphics, cube roots help in algorithms for rendering 3D models, especially in scaling and transformations that require volumetric calculations.
- Economics and Finance: In economics, cube roots can be used in models that predict growth rates over three-dimensional factors, such as population growth in urban planning or market growth predictions.
- Everyday Life: Practical daily uses of cube roots include calculating the size of containers, determining the appropriate amounts of ingredients in recipes requiring volumetric precision, and more.
Let's look at a practical example:
| Application | Description |
|---|---|
| Storage Space Calculation | To determine the side length of a cubic storage box that can hold 64 cubic units, we use the cube root of 64, which is 4. Hence, the box would have dimensions 4x4x4 units. |
| Physics - Moment of Inertia | In rotational dynamics, the cube root helps in finding the distribution of mass. For instance, if the volume of a mass distribution is 64 cubic units, the characteristic length scale would be 4 units. |
By understanding and applying the cube root of 64, one can solve various practical problems efficiently. Whether in complex engineering calculations or simple day-to-day tasks, this mathematical concept proves invaluable.
Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding the cube root of 64 through various examples and practice problems will help solidify the concept. Here are some examples and problems to practice:
Examples
- Basic Calculation: Find the cube root of 64.
Solution: The cube root of 64 is the number that when multiplied by itself three times gives 64. Thus, \( \sqrt[3]{64} = 4 \) because \( 4 \times 4 \times 4 = 64 \).
- Volume of a Cube: A cube has a volume of 64 cubic units. What is the length of each side?
Solution: The length of each side of the cube is the cube root of the volume. Therefore, each side is \( \sqrt[3]{64} = 4 \) units long.
- Scaling Factor: If an object is scaled up so that its volume becomes 64 times larger, by what factor are the linear dimensions increased?
Solution: The linear dimensions are increased by the cube root of 64. Thus, the scaling factor is \( \sqrt[3]{64} = 4 \).
Practice Problems
- Find the cube root of 27.
Hint: \( \sqrt[3]{27} \)
- A storage box has a volume of 125 cubic units. What is the length of each side?
Hint: Use \( \sqrt[3]{125} \)
- If a sphere's volume is 64 times larger than another sphere, by what factor is its radius increased?
Hint: Consider the relationship between the volume and the radius in three dimensions.
- Simplify the expression \( \sqrt[3]{8^3} \).
Hint: Use the property of cube roots to simplify.
- The volume of a cube is given by \( V = s^3 \), where \( s \) is the side length. If \( V = 64 \), find \( s \).
Hint: Solve for \( s \) using the cube root.
By practicing these problems, you can gain a deeper understanding of the concept and its applications.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
When working with the cube root of 64, there are several common mistakes that learners often make. By being aware of these, you can improve your accuracy and understanding.
- Confusing Cube Root with Square Root:
A frequent mistake is confusing the cube root \( \sqrt[3]{x} \) with the square root \( \sqrt{x} \). For example, the square root of 64 is 8, while the cube root of 64 is 4. Always ensure you are using the correct root for the problem at hand.
- Incorrectly Simplifying the Expression:
When simplifying expressions, make sure to apply the correct properties of cube roots. For instance, \( \sqrt[3]{a^3} = a \), not \( a^2 \). An error here can lead to incorrect results.
- Misunderstanding the Notation:
Ensure that you understand the notation for cube roots. The symbol \( \sqrt[3]{x} \) specifically denotes the cube root, not the square root or any other root.
- Errors in Calculating the Cube Root:
When manually calculating the cube root, remember that you need a number that, when multiplied by itself three times, equals the original number. For 64, this number is 4, because \( 4 \times 4 \times 4 = 64 \).
- Neglecting Units in Practical Problems:
In practical applications, always include units in your calculations. For example, if you are calculating the side length of a cube with a volume of 64 cubic units, the side length should be 4 units, not just 4.
Let's consider a detailed example to avoid mistakes:
- Problem: Simplify \( \sqrt[3]{64} \).
Incorrect Approach: Treating it as a square root and writing \( \sqrt{64} = 8 \).
Correct Approach: Recognizing it as a cube root: \( \sqrt[3]{64} = 4 \), because \( 4 \times 4 \times 4 = 64 \).
- Problem: Find the cube root of \( 8^3 \).
Incorrect Approach: Misinterpreting the expression as \( (8^3)^{1/3} = 8^2 = 64 \).
Correct Approach: Using the property of cube roots: \( \sqrt[3]{8^3} = 8 \).
By paying attention to these common mistakes and understanding the correct approaches, you can enhance your problem-solving skills and avoid errors in calculations involving cube roots.
Additional Resources
For further exploration and practice on the concept of cube roots, especially the cube root of 64, here are some additional resources that can be immensely helpful:
- Online Calculators:
Several online calculators can help you quickly find the cube root of any number. These tools are great for checking your work and understanding the step-by-step process.
- Educational Videos:
Video tutorials provide visual and auditory learning, which can be particularly effective for understanding cube roots and their applications. Platforms like YouTube have numerous educational channels dedicated to this topic.
- Interactive Learning Platforms:
Websites offering interactive exercises and problems can greatly enhance your understanding of cube roots. These platforms provide immediate feedback and a variety of problem sets to practice.
- Textbooks and Reference Books:
Textbooks provide a thorough explanation of mathematical concepts. Check your local library or online bookstores for books on algebra and radical expressions.
- Algebra and Trigonometry by Michael Sullivan
- College Algebra by James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, and Saleem Watson
- Online Articles and Tutorials:
Articles and tutorials can provide step-by-step explanations and additional examples to enhance your understanding of cube roots.
By utilizing these resources, you can deepen your comprehension of cube roots and apply this knowledge effectively in various mathematical problems.
Video này hướng dẫn cách tính căn bậc 3 của 64 mà không cần dùng máy tính.
Căn Bậc 3 của 64 mà Không Cần Máy Tính
READ MORE:
Video này hướng dẫn cách sử dụng phân tích thừa số nguyên tố để tìm căn bậc 3 của một số, cụ thể là căn bậc 3 của 64.
Sử Dụng Phân Tích Thừa Số Nguyên Tố Để Tìm Căn Bậc 3 của Một Số, Căn Bậc 3 của 64