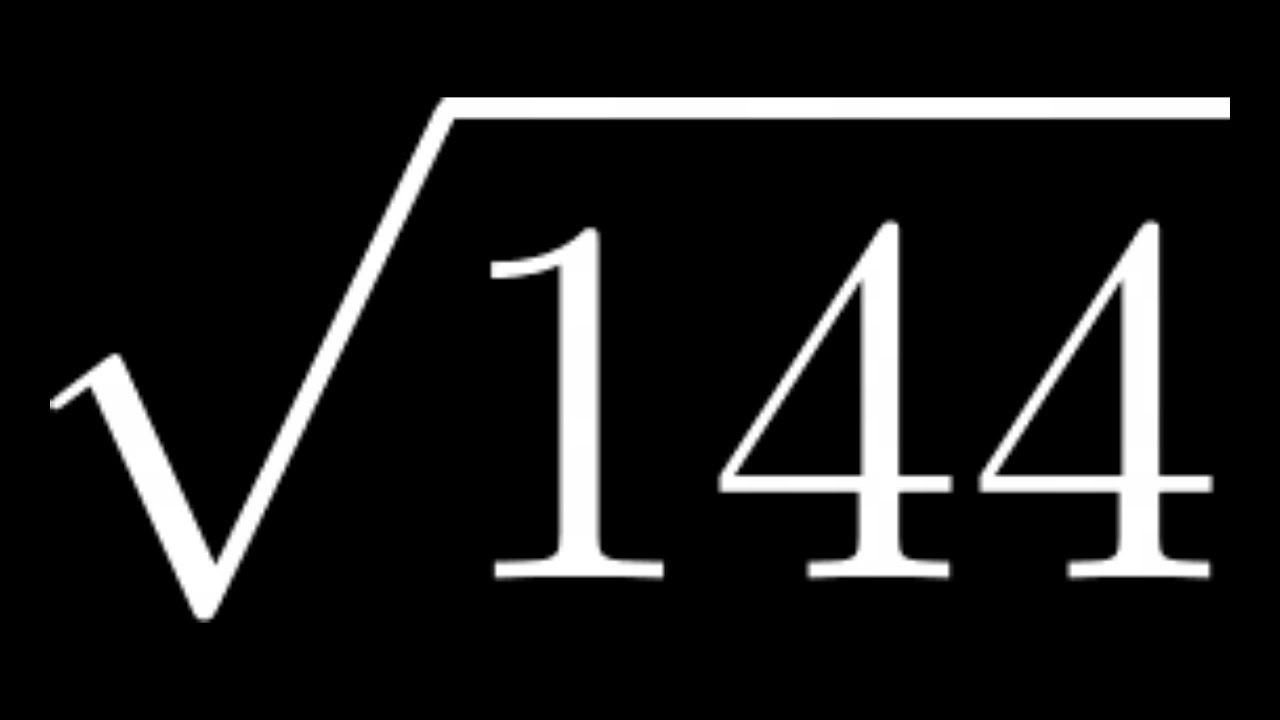Topic negative square root of 144: The negative square root of 144 is a fascinating mathematical concept with practical applications. In this guide, we will explore the meaning, calculation methods, and significance of negative square roots, particularly focusing on the example of 144. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, this article will enhance your understanding and appreciation of this topic.
Table of Content
- Negative Square Root of 144
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding the Concept of Negative Square Roots
- Mathematical Definition of Square Roots
- Calculating the Square Root of 144
- Steps to Find the Negative Square Root
- Representation of Negative Square Roots
- Examples and Applications
- Common Misconceptions
- Importance in Mathematics and Science
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video để học cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 144: sqrt(144). Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu dành cho học sinh và người yêu thích toán học.
Negative Square Root of 144
The square root of a number refers to a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. In the case of 144, the principal (or positive) square root is 12, because:
\[
12^2 = 144
\]
However, square roots can also be negative. This is because multiplying two negative numbers also yields a positive number. Therefore, the negative square root of 144 is -12, because:
\[
(-12)^2 = 144
\]
Properties of Square Roots
- Every positive real number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
- The principal square root is usually the positive root.
- The negative square root is denoted by a negative sign in front of the root.
Mathematical Representation
For any positive number \( a \), its square roots are represented as \( \sqrt{a} \) and \( -\sqrt{a} \). Thus, the square roots of 144 are:
\[
\sqrt{144} = 12 \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{144} = -12
\]
Understanding Negative Square Roots
To find the negative square root of 144, consider the following steps:
- Identify the positive square root of 144, which is 12.
- Apply a negative sign to this value, resulting in -12.
Applications
Negative square roots are important in various fields such as engineering, physics, and mathematics, particularly when dealing with complex numbers and quadratic equations.
| Positive Square Root | Negative Square Root |
| \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \) | \( -\sqrt{144} = -12 \) |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental mathematical operations that are essential for understanding various concepts in algebra, geometry, and beyond. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 144 is 12 because:
\[
12 \times 12 = 144
\]
Square roots can be both positive and negative because both \(12\) and \(-12\) satisfy the equation:
\[
(-12) \times (-12) = 144
\]
Here are some key points about square roots:
- Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative.
- The principal (or positive) square root is usually denoted by the radical symbol \(\sqrt{}\).
- The negative square root is denoted by a negative sign in front of the radical symbol.
In mathematical notation, the square roots of a positive number \(a\) are represented as:
\[
\sqrt{a} \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{a}
\]
For example, the square roots of 144 are:
\[
\sqrt{144} = 12 \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{144} = -12
\]
Square roots have several important properties:
- Non-negative Property: The principal square root is always non-negative.
- Product Property: The square root of a product is the product of the square roots.
- Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is the quotient of the square roots.
These properties are useful in simplifying expressions and solving equations involving square roots.
Understanding the Concept of Negative Square Roots
The concept of negative square roots often confuses many learners, but it is a straightforward and intriguing aspect of mathematics. A square root of a number is a value that, when squared, gives the original number. While the principal (positive) square root of 144 is 12, there is also a negative square root. This is because both positive and negative values can produce a positive result when squared. Specifically:
\[
12^2 = 144 \quad \text{and} \quad (-12)^2 = 144
\]
The negative square root of 144 is represented as \(-\sqrt{144}\), which simplifies to -12. Here’s a step-by-step explanation:
- Identify the Positive Square Root: First, find the positive square root of the number. For 144, it is 12.
- Apply the Negative Sign: Place a negative sign in front of the positive square root to find the negative square root. Thus, the negative square root of 144 is -12.
It's important to note that the square root function generally refers to the principal square root (the positive one). However, in contexts that require all solutions, both positive and negative square roots are considered.
For any positive number \( a \), the square roots are:
\[
\sqrt{a} = \text{positive root} \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{a} = \text{negative root}
\]
Therefore, for 144, we have:
\[
\sqrt{144} = 12 \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{144} = -12
\]
Understanding negative square roots is crucial in solving quadratic equations and other mathematical problems where both roots are required. Here are some properties of negative square roots:
- They are always negative.
- They provide additional solutions to equations.
- They are useful in understanding the complete set of solutions in algebraic problems.
By recognizing and applying both positive and negative square roots, you can gain a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts and solve a broader range of problems.
Mathematical Definition of Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental in mathematics, defined as values that, when multiplied by themselves, yield the original number. Mathematically, if \( x \) is a square root of \( a \), then:
\[
x^2 = a
\]
For a positive number \( a \), there are two square roots: one positive and one negative. This can be represented as:
\[
\sqrt{a} = x \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{a} = -x
\]
where \( \sqrt{a} \) denotes the principal (positive) square root, and \(-\sqrt{a}\) denotes the negative square root. For example, the square roots of 144 are:
\[
\sqrt{144} = 12 \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{144} = -12
\]
In this context, the principal square root of 144 is 12, as it satisfies the equation:
\[
12^2 = 144
\]
Similarly, the negative square root is -12, because:
\[
(-12)^2 = 144
\]
Here are key points to understand the mathematical definition of square roots:
- Principal Square Root: The non-negative square root of a number, denoted by the radical symbol \(\sqrt{}\).
- Negative Square Root: The negative counterpart of the principal square root, denoted by \(-\sqrt{}\).
- Properties of Square Roots: Square roots are used to solve equations and understand relationships in algebra and geometry.
When solving equations, it's crucial to consider both the positive and negative square roots to find all possible solutions. For example, in the quadratic equation:
\[
x^2 = 144
\]
The solutions are:
\[
x = 12 \quad \text{and} \quad x = -12
\]
In summary, the mathematical definition of square roots encompasses both the principal and negative roots, providing a complete understanding of the values that satisfy the equation \( x^2 = a \).
Calculating the Square Root of 144
Calculating the square root of a number involves finding a value that, when multiplied by itself, results in the original number. For 144, this process can be broken down into a few simple steps:
- Identify the Perfect Square: Recognize that 144 is a perfect square, meaning it is the product of an integer multiplied by itself. In this case, 144 is \(12 \times 12\).
- Express as a Square: Write 144 as \(12^2\), indicating that 12 is the positive square root of 144. Mathematically, this is represented as:
- Include the Negative Square Root: Since both positive and negative values can produce the same result when squared, the negative square root is -12. This is shown as:
\[
\sqrt{144} = 12
\]
\[
-\sqrt{144} = -12
\]
Thus, the square roots of 144 are 12 and -12, because:
\[
12^2 = 144 \quad \text{and} \quad (-12)^2 = 144
\]
To summarize, the calculation of the square root of 144 yields two results:
- Principal Square Root: \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \)
- Negative Square Root: \( -\sqrt{144} = -12 \)
Understanding these steps helps in grasping the concept of square roots and applying them to solve various mathematical problems. The key points are identifying the perfect square, expressing it in its squared form, and recognizing both the positive and negative roots.
For any given number \( a \), the square roots can be generalized as:
\[
\sqrt{a} \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{a}
\]
Thus, for 144, we have:
\[
\sqrt{144} = 12 \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{144} = -12
\]
This detailed calculation process ensures a thorough understanding of finding both square roots of any perfect square number.

Steps to Find the Negative Square Root
Finding the negative square root of a number involves a straightforward process. Here are the detailed steps to find the negative square root of 144:
- Identify the Positive Square Root: First, determine the positive square root of the number. For 144, the positive square root is 12, since:
- Understand the Concept: Recognize that a negative number squared also results in a positive number. Hence, the negative square root is just the negative counterpart of the positive square root. Mathematically, this means:
- Express the Negative Square Root: Write the negative square root by placing a negative sign in front of the positive square root. Thus, the negative square root of 144 is:
- Verification: Confirm that squaring the negative root returns the original number. For verification:
\[
12^2 = 144
\]
\[
(-12)^2 = 144
\]
\[
-\sqrt{144} = -12
\]
\[
(-12) \times (-12) = 144
\]
To summarize, the negative square root of 144 can be found by following these steps:
- Determine the positive square root, which is 12.
- Apply the negative sign to this positive square root to find -12.
- Verify the result by squaring -12 to ensure it equals 144.
Therefore, the negative square root of 144 is:
\[
-\sqrt{144} = -12
\]
By understanding these steps, you can find the negative square root of any perfect square, ensuring a comprehensive grasp of the concept.
Representation of Negative Square Roots
Negative square roots are a vital concept in mathematics, and their representation follows specific conventions. Understanding these conventions helps in correctly interpreting and solving mathematical problems. Here's a detailed explanation of how negative square roots are represented:
- Radical Symbol with Negative Sign: The negative square root of a number is represented by placing a negative sign in front of the radical (square root) symbol. For instance, the negative square root of 144 is written as:
- Evaluating the Negative Square Root: To find the negative square root, first find the principal (positive) square root, then apply the negative sign. For 144, the principal square root is 12, so the negative square root is:
- Graphical Representation: On a number line, the negative square root is placed to the left of zero, opposite the positive square root. For 144, the positions are:
- In Equations: When solving quadratic equations, both positive and negative square roots are considered. For example, solving \( x^2 = 144 \) yields:
- Complex Numbers: For negative radicands (numbers under the square root), the negative square roots involve imaginary numbers. However, for positive radicands like 144, the negative square root remains real.
\[
-\sqrt{144}
\]
\[
-\sqrt{144} = -12
\]
\[
-12 \quad \text{(negative square root)} \quad \text{and} \quad 12 \quad \text{(positive square root)}
\]
\[
x = \pm \sqrt{144} \implies x = 12 \quad \text{or} \quad x = -12
\]
Here are additional points to consider:
- Consistency: Always place the negative sign outside the radical symbol to avoid confusion.
- Application: Negative square roots are useful in solving a variety of mathematical problems, including quadratic equations and certain real-world applications.
For instance, consider the quadratic equation \( x^2 = 144 \). The solutions are:
\[
x = 12 \quad \text{and} \quad x = -12
\]
In this equation, 12 is the positive square root, and -12 is the negative square root. By correctly representing and calculating both roots, we ensure a complete solution to the problem.
In summary, representing negative square roots involves placing a negative sign in front of the radical symbol and understanding its implications in various mathematical contexts. This consistent representation aids in accurate problem-solving and deeper comprehension of mathematical principles.
Examples and Applications
The concept of negative square roots, while not commonly used in basic arithmetic, has significant applications in advanced mathematics and various scientific fields. Here are some examples and applications:
Examples
- Example 1: The negative square root of 144 is calculated as follows:
The positive square root of 144 is 12, so the negative square root of 144 is -12. This can be expressed as:
\[\sqrt{144} = 12 \quad \text{and} \quad -\sqrt{144} = -12\]
- Example 2: If an equation involves a term like \(x^2 = 144\), the solutions include both the positive and negative square roots:
\[x = \pm 12\]
Applications
- Complex Numbers:
Negative square roots are crucial in the field of complex numbers. For instance, solving equations like \(x^2 = -144\) requires the use of imaginary numbers:
\[x = \pm \sqrt{-144} = \pm 12i\]
Here, \(i\) is the imaginary unit, where \(i^2 = -1\).
- Quadratic Equations:
In solving quadratic equations, negative square roots often appear under the square root symbol in the quadratic formula:
\[x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}\]
If \(b^2 - 4ac\) is negative, the solutions will include imaginary numbers.
- Physics and Engineering:
In physics and engineering, the concept of negative square roots can be found in wave equations and alternating current (AC) circuit analysis. For example, the use of complex impedance in AC circuits often involves imaginary numbers.
- Signal Processing:
Negative square roots and complex numbers are used in signal processing for the analysis of signals and systems, especially in the context of Fourier transforms.
Common Misconceptions
There are several common misconceptions regarding the negative square root of numbers such as 144. These misunderstandings can lead to errors in mathematical calculations and a flawed grasp of fundamental concepts. Below are some of these misconceptions:
- Misconception 1: Square Roots are Always Positive
Many students incorrectly believe that square roots are always positive. While the principal square root of a positive number is positive, every positive number actually has both a positive and a negative square root.
For example, \(\sqrt{144} = 12\) and \(-\sqrt{144} = -12\). Thus, the complete solution to \(x^2 = 144\) is \(x = \pm 12\).
- Misconception 2: Negative Numbers Have No Real Square Roots
Some believe that negative numbers cannot have square roots. While it is true that they do not have real square roots, they do have complex ones. The square root of -144, for instance, is represented in terms of imaginary numbers: \(\sqrt{-144} = 12i\).
Imaginary numbers are essential in advanced mathematics and engineering, where they are used to solve various equations and represent electrical circuits.
- Misconception 3: The Square Root of Zero is Undefined
There is a misconception that zero has no square root. In fact, zero is the only number whose square root is itself: \(\sqrt{0} = 0\).
- Misconception 4: Complex Numbers are Purely Theoretical
Many think complex numbers are just theoretical constructs with no practical application. In reality, they are widely used in fields like electrical engineering, quantum physics, and applied mathematics. For instance, the impedance in an AC circuit is often represented using complex numbers.
Understanding these common misconceptions is crucial for developing a solid foundation in mathematics and avoiding errors in problem-solving.
Importance in Mathematics and Science
The concept of the negative square root of 144, which is -12, holds significant importance in both mathematics and science. Understanding square roots, including their negative counterparts, is essential for various applications and theoretical foundations.
1. Mathematical Theorems and Equations:
- Pythagorean Theorem: The square root function is integral to the Pythagorean theorem. For example, in right triangle problems, knowing both positive and negative square roots can provide a complete understanding of distance and length calculations.
- Quadratic Equations: Solving quadratic equations often involves square roots. The negative square root represents one of the possible solutions, expanding the set of real solutions.
2. Complex Numbers:
- The study of complex numbers stems from the need to address the square roots of negative numbers. For instance, the square root of -1 is represented as \(i\), the imaginary unit. This extends to roots of other negative numbers, such as \(\sqrt{-144} = 12i\).
- Complex number theory is foundational in fields such as electrical engineering, quantum physics, and applied mathematics, enabling the solution of equations that have no real solutions.
3. Scientific Applications:
- Physics: In physics, particularly in wave mechanics and signal processing, the use of complex numbers (which includes negative square roots) allows for the description of oscillatory motions and waveforms.
- Engineering: Electrical engineering heavily relies on complex numbers to analyze and design circuits. For example, impedance in AC circuits is calculated using complex numbers, involving both positive and negative square roots.
4. Advanced Calculus and Analysis:
- Advanced calculus uses the concept of square roots and their properties in various theorems and integrals. Negative square roots often appear in solving integrals that involve symmetric properties of functions.
- In mathematical analysis, understanding both positive and negative roots contributes to a comprehensive understanding of function behavior and limits.
The negative square root of 144, while seemingly simple, exemplifies the depth and breadth of square root applications across different domains, highlighting its critical role in advancing mathematical understanding and scientific discovery.
Conclusion
The exploration of the negative square root of 144, which is represented as \( \pm 12i \), reveals significant insights into both real and complex number systems. The principal negative square root of 144 is \(-12\), highlighting the existence of two square roots for positive numbers: a positive root and its negative counterpart. When considering negative radicands, the roots become complex numbers, introducing the imaginary unit \(i\), where \(i = \sqrt{-1}\).
The study of square roots, especially negative square roots, is fundamental in advanced mathematics. It serves as a bridge to complex numbers, a critical component in fields such as engineering, physics, and computer science. Complex numbers allow for the solution of equations that have no real solutions, thereby expanding the scope and applicability of mathematical problem-solving techniques.
Understanding the concept of the negative square root of 144 not only solidifies one's grasp of algebraic principles but also paves the way for more complex mathematical theories and applications. It underscores the importance of imaginary numbers in various scientific and technological advancements, providing a foundation for future learning and innovation.
In summary, the negative square root of 144, expressed as \( \pm 12i \), is more than a mathematical curiosity. It exemplifies the seamless integration of real and imaginary numbers, offering profound implications for both theoretical and applied mathematics. Embracing these concepts enables us to tackle more complex challenges and harness the full potential of mathematical reasoning.
Xem video để học cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 144: sqrt(144). Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu dành cho học sinh và người yêu thích toán học.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai Của 144: sqrt(144)
READ MORE:
Xem video để học cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số âm 144: sqrt(-144). Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu dành cho học sinh và người yêu thích toán học.
Đơn Giản Hóa sqrt(-144)