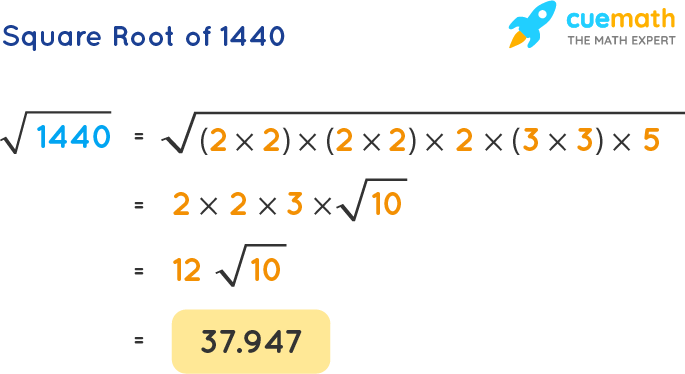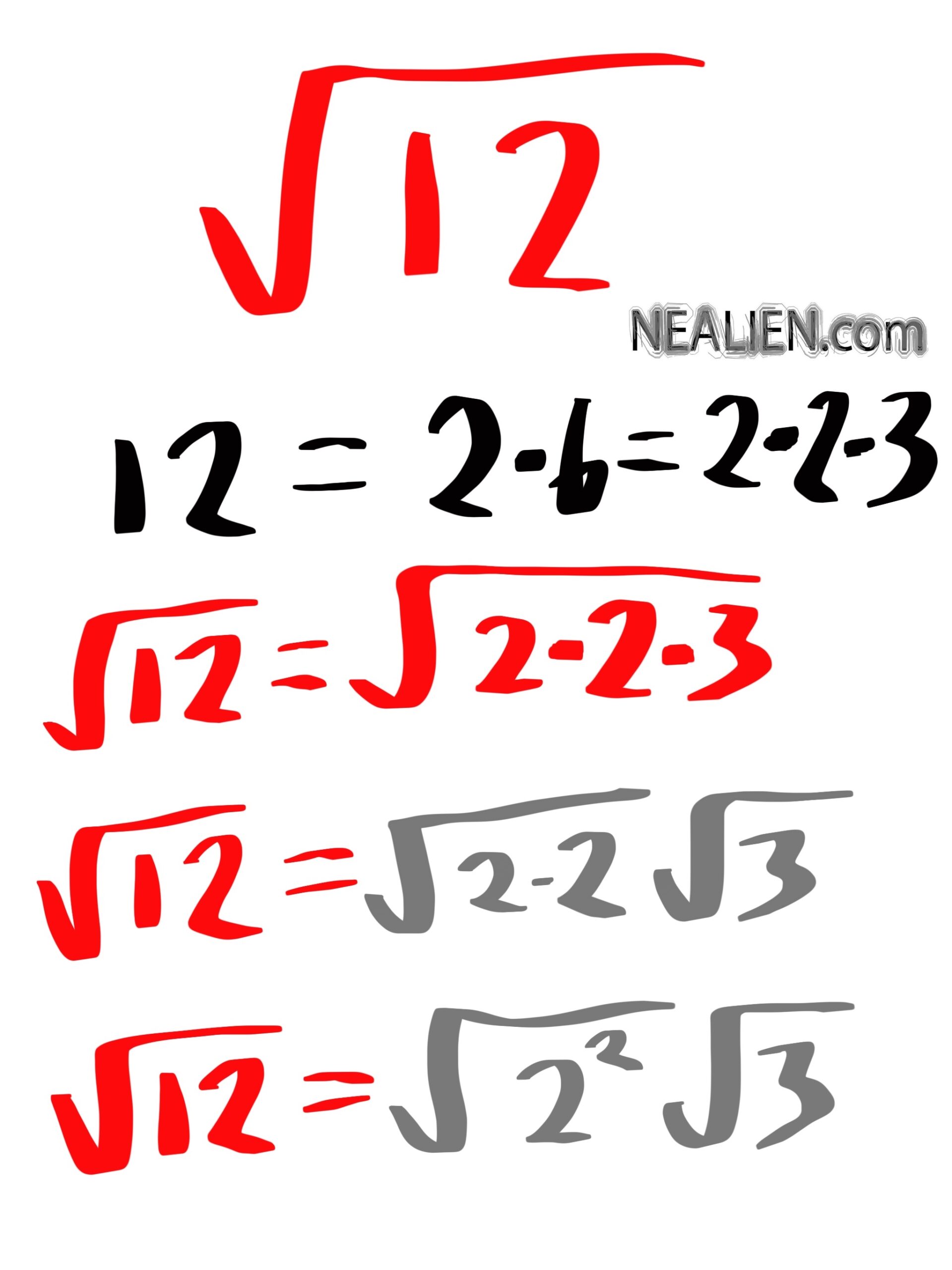Topic square root of 144: The square root of 144 is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications. Whether you're solving equations or exploring geometry, understanding why \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \) is essential. Dive into this article to uncover the significance, calculation methods, and real-world uses of the square root of 144.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of 144
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding the Square Root of 144
- Mathematical Definition and Properties
- Calculating the Square Root of 144
- Verification of the Result
- Positive and Negative Roots
- Square Root of 144 in Different Forms
- Applications of Square Root of 144
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ về cách tính căn bậc hai của 144 và ứng dụng của nó trong toán học và đời sống.
Understanding the Square Root of 144
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the number 144, the square root is:
$$\sqrt{144} = 12$$
Why is the Square Root of 144 Equal to 12?
The square root of 144 equals 12 because:
- When 12 is multiplied by itself, the result is 144.
- Mathematically, this can be expressed as \( 12 \times 12 = 144 \).
Calculation Steps
- Identify the number: \(144\).
- Determine the number whose square equals \(144\).
- The solution is \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
Verification
To verify the result, you can multiply the square root by itself:
Since the product is equal to 144, our calculation is correct.
Properties of the Square Root of 144
- Perfect Square: 144 is a perfect square, meaning its square root is a whole number.
- Positive and Negative Roots: While the principal square root is positive (12), there is also a negative square root: -12. Thus, both \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \) and \( \sqrt{144} = -12 \).
- Applications: The square root of 144 is commonly used in various mathematical and real-life applications, such as geometry and algebra.
Representation in Different Forms
The square root of 144 can also be represented in exponential form as:
\( 144^{0.5} = 12 \)
Or in radical form:
Conclusion
Understanding the square root of 144 and its properties helps in grasping fundamental concepts in mathematics. Knowing that \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \) enables easier calculation and application in various problems.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The concept of square roots is a fundamental aspect of mathematics that is essential for understanding various numerical and algebraic operations. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number.
For example, if \( x \) is the square root of \( n \), then:
$$ x^2 = n $$
In simpler terms, the square root of a number reverses the process of squaring. For instance, since \( 12 \times 12 = 144 \), the square root of 144 is 12.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how to understand square roots:
- Identify the number whose square root you need to find. This number is called the radicand. In our case, the radicand is \( 144 \).
- Find a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals the radicand. For \( 144 \), this value is \( 12 \), since \( 12 \times 12 = 144 \).
- Express the square root using the radical symbol (\( \sqrt{} \)). For 144, this is written as \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
Square roots have unique properties and applications:
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 144, 121, and 100 are called perfect squares because they have whole number square roots.
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: a positive root and a negative root. For example, both \( 12 \) and \( -12 \) are square roots of \( 144 \) because \( 12^2 = 144 \) and \( (-12)^2 = 144 \).
- Applications: Square roots are used in various fields, including geometry (calculating distances, areas, and angles), physics (understanding motion and energy), and statistics (measuring variability).
Understanding the basics of square roots helps in solving quadratic equations, working with algebraic expressions, and applying mathematical principles in real-world scenarios. The square root of 144, which is 12, is a classic example that illustrates these concepts clearly.
Understanding the Square Root of 144
The square root of 144 is a fascinating mathematical concept that highlights the relationship between numbers and their roots. To understand why the square root of 144 is 12, let's delve into the details step by step.
Firstly, let's recall the definition of a square root. The square root of a number \( n \) is a value \( x \) such that:
$$ x^2 = n $$
For the number 144, we are looking for a value that satisfies:
$$ x^2 = 144 $$
The solution to this equation is \( x = 12 \) because:
$$ 12 \times 12 = 144 $$
Here’s how we determine the square root of 144:
- Identify the Perfect Square: Check if 144 is a perfect square. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. Since \( 12 \times 12 = 144 \), we identify 144 as a perfect square.
- Find the Square Root: Determine which number, when squared, gives 144. We know that \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \) because \( 12^2 = 144 \).
- Verify the Result: To ensure the correctness, you can reverse the process by squaring the result. \( 12^2 \) indeed equals 144, confirming that \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
There are a few key points to note about the square root of 144:
- Positive and Negative Roots: While the principal square root of 144 is 12, there is also a negative root. This means that both \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \) and \( \sqrt{144} = -12 \), because \( (-12) \times (-12) = 144 \).
- Simplification: Square roots simplify calculations and help in solving quadratic equations. The fact that 144 is a perfect square makes it straightforward to find its square root.
- Applications: The square root of 144 appears in various mathematical contexts, including geometry (such as finding the side length of a square with area 144) and algebra.
Understanding why \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \) is not only useful for solving mathematical problems but also provides insight into how numbers relate to one another through their roots. This knowledge is foundational for further exploration in mathematics.
Mathematical Definition and Properties
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. This concept is essential in various branches of mathematics, from basic arithmetic to complex algebraic expressions. For the number 144, its square root is expressed as:
$$ \sqrt{144} = 12 $$
Let’s explore the mathematical definition and properties of the square root of 144:
1. Mathematical Definition
The square root of 144 can be defined as a number \( x \) that satisfies the equation:
$$ x^2 = 144 $$
To solve for \( x \), we look for the number which, when squared, equals 144. The solution is:
$$ x = 12 \quad \text{or} \quad x = -12 $$
This indicates that both 12 and -12 are roots of 144 because:
$$ 12 \times 12 = 144 \quad \text{and} \quad (-12) \times (-12) = 144 $$
2. Properties of the Square Root of 144
The square root of 144 exhibits several important properties:
- Perfect Square: Since 144 is a product of an integer (12) squared, it is known as a perfect square. Perfect squares have whole numbers as their square roots.
- Non-Negative Principal Root: The principal square root is always non-negative. For 144, the principal root is 12, denoted as \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
- Symmetry: The square of both a positive and negative number yields a positive result. Hence, both \( 12 \) and \( -12 \) are considered square roots of 144.
- Exponential Representation: The square root can be represented using exponents. For 144, this is expressed as:
$$ \sqrt{144} = 144^{0.5} = 12 $$
- Applications: The concept of square roots is widely used in various mathematical computations, including solving quadratic equations, computing distances in geometry, and analyzing data in statistics.
3. Calculation Methods
To find the square root of 144, several methods can be employed:
- Prime Factorization: Break down 144 into its prime factors and group them in pairs:
- 144 = \( 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \)
- Group the factors: \( (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \)
- Take one factor from each pair: \( 2 \times 2 \times 3 = 12 \)
- Using a Calculator: Modern calculators can quickly compute the square root of any number, providing \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \) instantly.
- Estimation and Refinement: Estimate a close value and refine it using methods like averaging or the Newton-Raphson method.
Understanding the mathematical definition and properties of the square root of 144 enhances comprehension of fundamental concepts in mathematics. This knowledge is crucial for both theoretical studies and practical applications.
Calculating the Square Root of 144
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. To find the square root of 144, we can follow these steps:
- Understanding Perfect Squares:
First, recognize that 144 is a perfect square, meaning it can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself.
- Prime Factorization Method:
Find the prime factors of 144:
- 144 ÷ 2 = 72
- 72 ÷ 2 = 36
- 36 ÷ 2 = 18
- 18 ÷ 2 = 9
- 9 ÷ 3 = 3
- 3 ÷ 3 = 1
The prime factorization of 144 is \( 2^4 \times 3^2 \).
- Taking the Square Root:
To find the square root, take the square root of each factor and multiply them together:
\( \sqrt{144} = \sqrt{2^4 \times 3^2} = \sqrt{2^4} \times \sqrt{3^2} \)
\( \sqrt{2^4} = 2^2 = 4 \)
\( \sqrt{3^2} = 3 \)
So, \( \sqrt{144} = 4 \times 3 = 12 \).
- Verification:
To verify, multiply 12 by itself:
\( 12 \times 12 = 144 \)
Thus, the square root of 144 is indeed 12.

Verification of the Result
To verify the result of the square root of 144, we will use both the multiplication method and the properties of square roots.
Step-by-Step Verification
-
Using Multiplication:
- We know that the square root of 144 is 12.
- To verify, we multiply 12 by itself: \( 12 \times 12 = 144 \).
- Since the product is 144, this confirms that \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
-
Using the Property of Square Roots:
The property of square roots states that if \( x = \sqrt{y} \), then \( x^2 = y \).
- Here, \( x = 12 \) and \( y = 144 \).
- Substitute into the equation: \( 12^2 = 144 \).
- Since this is a true statement, it verifies our result.
Verification with Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is another method to verify the square root:
- Prime factorize 144: \( 144 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 3 \).
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \( (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3) \).
- Take one number from each pair: \( 2 \times 2 \times 3 = 12 \).
- Therefore, \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \), confirming our result.
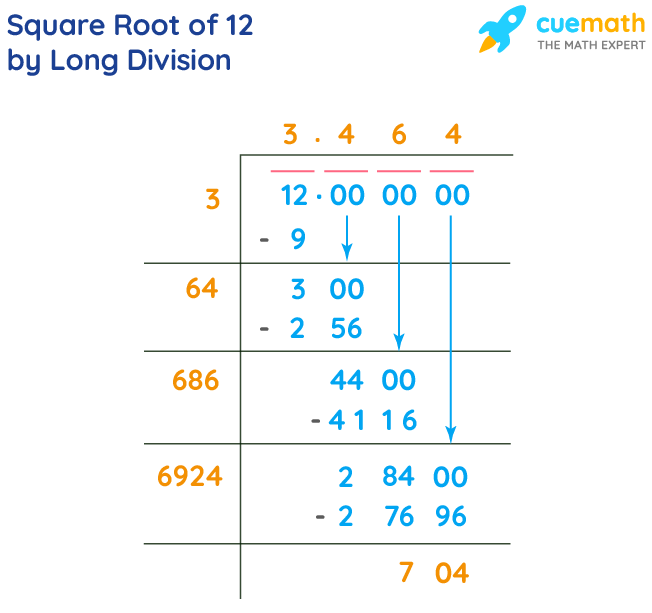
Verification with Long Division Method
- Pair the digits of 144 starting from the right: 1 and 44.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 1. That number is 1.
- Subtract \( 1^2 = 1 \) from 1, getting a remainder of 0. Bring down the next pair of digits (44), making it 44.
- Double the divisor (1) to get 2. Determine a number (X) such that \( 2X \times X \leq 44 \). The number is 2 (since \( 22 \times 2 = 44 \)).
- Perform the division: \( 44 - 44 = 0 \). The quotient obtained is 12, confirming that \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
These methods collectively verify that the square root of 144 is indeed 12.
Positive and Negative Roots
Every positive number has two square roots: a positive root and a negative root. This is because both a positive number and its negative counterpart, when squared, yield the same positive result.
For the number 144, the square roots are:
- Positive square root: \( \sqrt{144} = +12 \)
- Negative square root: \( \sqrt{144} = -12 \)
Mathematically, this is expressed as:
\[ \sqrt{144} = \pm 12 \]
This means that both \(12\) and \(-12\) are solutions to the equation:
\[ x^2 = 144 \]
To understand why, consider the following steps:
- Square both positive and negative roots:
- \( (12)^2 = 12 \times 12 = 144 \)
- \( (-12)^2 = (-12) \times (-12) = 144 \)
- Both results confirm that squaring either \(12\) or \(-12\) gives 144, demonstrating the two valid roots of 144.
In summary, the principal square root refers to the positive root, which is typically the default when using the square root symbol \( \sqrt{} \) without a negative sign. However, both positive and negative roots are considered valid mathematical solutions.
Square Root of 144 in Different Forms
The square root of 144 can be expressed in various forms, each useful in different mathematical contexts. Here we explore several forms and their applications.
- Radical Form: The most common way to express the square root of 144 is in radical form:
\(\sqrt{144}\)
- Simplified Radical Form: Since 144 is a perfect square, it simplifies neatly:
\(\sqrt{144} = 12\)
- Exponential Form: Using exponents, the square root can be written as:
\(144^{\frac{1}{2}} = 12\)
- Decimal Form: As a decimal, the square root of 144 is:
12.0
To understand how these forms are derived, let's break down the calculation:
- First, we perform the prime factorization of 144:
\(144 = 2^4 \times 3^2\)
- Taking the square root involves taking the square root of each factor:
\(\sqrt{144} = \sqrt{2^4 \times 3^2} = 2^2 \times 3 = 4 \times 3 = 12\)
The different forms can be summarized in a table for clarity:
| Form | Representation |
|---|---|
| Radical Form | \(\sqrt{144}\) |
| Simplified Radical Form | \(\sqrt{144} = 12\) |
| Exponential Form | \(144^{\frac{1}{2}} = 12\) |
| Decimal Form | 12.0 |
By understanding these different forms, we gain a deeper insight into the properties and applications of square roots in mathematics.
Applications of Square Root of 144
The square root of 144, which is 12, has various practical applications across different fields. Here are some notable examples:
-
Geometry and Area Calculation
In geometry, the square root is used to determine the side length of a square when the area is known. For example, if a square has an area of 144 square units, the length of each side is 12 units, as \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
-
Construction and Architecture
Square roots are crucial in construction and architecture for determining dimensions. For instance, if a design requires a square section with an area of 144 square feet, each side of the section would be 12 feet long.
-
Physics and Engineering
In physics, square roots are used in formulas involving gravity. For instance, the time \( t \) it takes for an object to fall from a height \( h \) is given by \( t = \frac{\sqrt{h}}{4} \). If an object is dropped from a height of 144 feet, it will take \( t = \frac{\sqrt{144}}{4} = 3 \) seconds to reach the ground.
-
Accident Investigations
Police use square roots to calculate the speed of a vehicle based on skid marks. If the length of the skid marks is \( d \) feet, the speed \( s \) in miles per hour is found using \( s = \sqrt{24d} \). For skid marks measuring 144 feet, the speed would be \( s = \sqrt{24 \times 144} = 12 \times \sqrt{24} \approx 58.8 \) mph.
-
Astronomy and Space Science
In astronomy, square roots help calculate distances between celestial objects. The distance \( D \) between two points in a plane is given by \( D = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \). If this distance equals 144, the straight-line distance between these points is 12 units.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the square root of 144?
The square root of 144 is 12.
-
How do you simplify the square root of 144?
The square root of 144 is simplified by using the prime factorization method, which results in \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
-
Is 144 a perfect square?
Yes, 144 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as \( 12^2 \).
-
What are the two square roots of 144?
The two square roots of 144 are \( +12 \) and \( -12 \), as both \( 12^2 \) and \( (-12)^2 \) equal 144.
-
What is the perfect square after 144?
The perfect square after 144 is 169, which is \( 13^2 \).
-
144 is the square root of which number?
144 is the square root of 20736, as \( 144^2 = 20736 \).
Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ về cách tính căn bậc hai của 144 và ứng dụng của nó trong toán học và đời sống.
Square Root of 144: Hướng dẫn đầy đủ
READ MORE:
Video này hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính căn bậc hai của 144 bằng phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố và ứng dụng của nó trong toán học.
Cách Tìm Căn Bậc Hai của 144 bằng phương pháp Phân Tích Thừa Số Nguyên Tố / Căn Bậc Hai của 144 / 144 Căn Bậc Hai