Topic simplify square root of 144: Understanding how to simplify the square root of 144 can boost your math skills and confidence. This guide provides clear and simple steps to master this fundamental concept, whether you're using basic calculation, prime factorization, or the long division method. Start simplifying today and make math a breeze!
Table of Content
- Understanding and Simplifying the Square Root of 144
- 1. Introduction to Square Roots
- 2. Understanding Perfect Squares
- 3. Simplifying the Square Root of 144
- 4. Basic Calculation Method
- 5. Prime Factorization Method
- 6. Long Division Method
- 7. Visual Representations and Examples
- 8. Applications of Simplified Square Roots
- 9. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- 10. Practice Problems and Solutions
- 11. Interactive Tools and Calculators
- 12. Frequently Asked Questions
- 13. Additional Resources for Learning
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 144 trong video này. Chúng tôi sẽ hướng dẫn bạn từng bước một cách dễ hiểu.
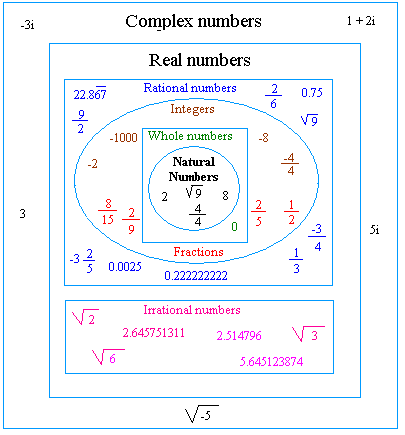
Understanding and Simplifying the Square Root of 144
The square root of 144 is a common mathematical operation often encountered in algebra. Simplifying this square root is straightforward because 144 is a perfect square. Let's explore how to simplify using different methods.
1. Basic Calculation
The square root of 144 is 12 because = 144. This means:
2. Prime Factorization Method
To simplify the square root of 144 using prime factorization:
- Find the prime factors of 144:
- Group the prime factors into pairs:
- Take one number from each pair:
- Multiply these numbers:
3. Long Division Method
The long division method is another way to find the square root of 144:
- Pair the digits starting from the right: 1 | 44
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair:
- Subtract this value and bring down the next pair of digits: 1 | 44 - 1 = 0, bring down 44 to get 044
- Double the quotient and find a digit x such that: (Here x = 2, because 2 * 22 = 44)
- Continue the process until all digits are exhausted.
This method confirms that the square root of 144 is 12.
Conclusion
Whether using basic calculation, prime factorization, or long division, the result is the same:
The simplified square root of 144 is .
Interactive Learning
Practice simplifying square roots with similar methods to gain confidence. Try simplifying or using these techniques.
| Number | Square Root |
| 144 | 12 |
| 225 | 15 |
| 81 | 9 |
Explore more about square roots to deepen your understanding of these fundamental concepts in mathematics.
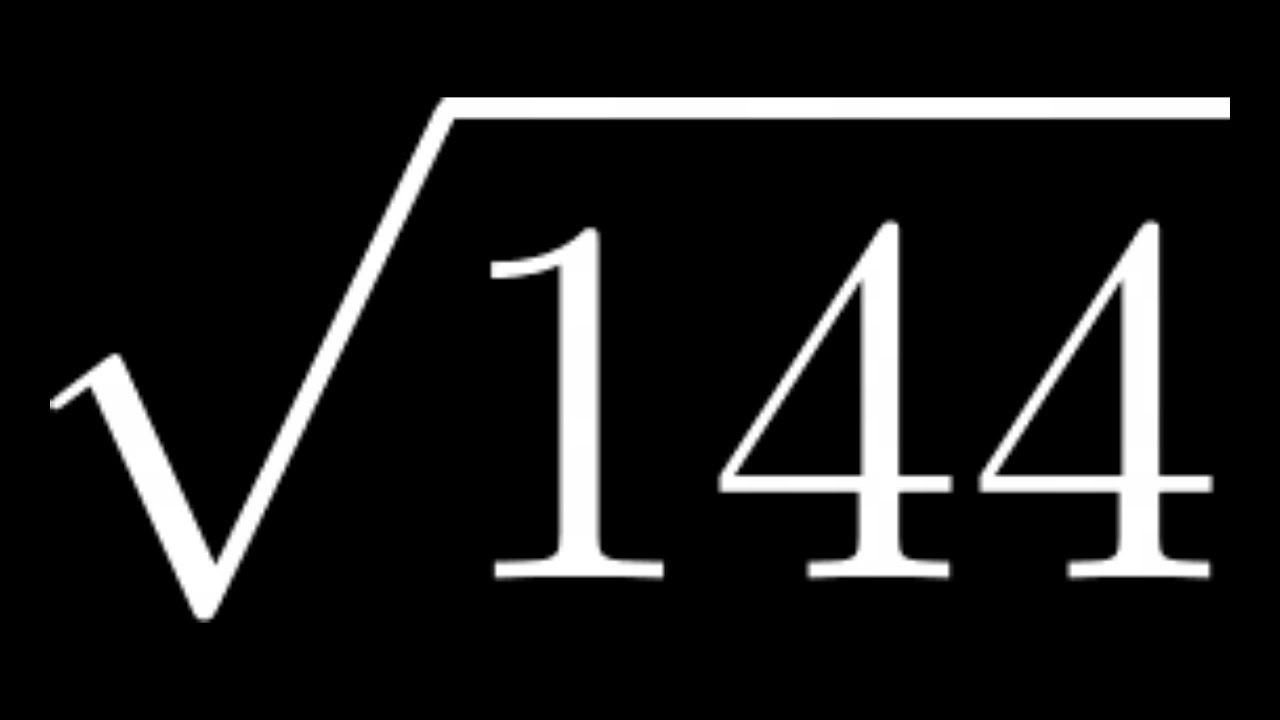
READ MORE:
1. Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental in mathematics and are widely used in various applications. Simplifying square roots allows for easier computation and a clearer understanding of numbers. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. For example, the square root of 144 is 12 because . This concept can be extended to various mathematical operations and real-world scenarios.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to understanding square roots:
- Definition: The square root of a number n is a value x such that . For example, because .
- Notation: The square root is commonly denoted by the radical symbol . For instance, the square root of 144 is written as .
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: a positive root and a negative root. For example, is 12, but -12 is also a square root of 144 since .
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 144 are called perfect squares because their square roots are integers. Common examples include 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, and so on.
- Real-World Applications: Square roots are used in various fields such as geometry (calculating the length of the hypotenuse in a right triangle), physics (determining the root mean square velocity of particles), and finance (calculating volatility in stock prices).
To better understand square roots, consider this table of some common square roots:
| Number | Square Root |
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
| 36 | 6 |
| 49 | 7 |
| 64 | 8 |
| 81 | 9 |
| 100 | 10 |
| 121 | 11 |
| 144 | 12 |
Understanding these basics will provide a solid foundation for mastering more complex concepts involving square roots.
2. Understanding Perfect Squares
Perfect squares are numbers that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. For instance, when we multiply the number 12 by itself, we get 144, making 144 a perfect square because:
Perfect squares are integral to various areas of mathematics and have distinct properties:
- Definition: A perfect square is any integer that is the square of another integer. For example, and .
- Properties: Perfect squares have unique properties that make them easily recognizable:
- Their square roots are whole numbers.
- They always end with 0, 1, 4, 5, 6, or 9 in base 10.
- The sum of the first n odd numbers is always a perfect square. For example, which is .
- Examples: Here are some examples of perfect squares and their corresponding roots:
Number Square Root 1 1 4 2 9 3 16 4 25 5 36 6 49 7 64 8 81 9 100 10 121 11 144 12 169 13 196 14 225 15 256 16 - Recognizing Perfect Squares: Being able to quickly recognize perfect squares can simplify many mathematical problems and calculations. These numbers appear frequently in algebra, geometry, and everyday calculations.
By mastering perfect squares and their properties, you can enhance your mathematical understanding and problem-solving skills.
3. Simplifying the Square Root of 144
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Simplifying the square root of 144 involves finding such a value. Let's go through the steps to simplify \(\sqrt{144}\).
Step-by-Step Simplification
-
First, identify if 144 is a perfect square. A perfect square is an integer that can be expressed as the square of another integer.
- Since \(144 = 12 \times 12\), it is clear that 144 is a perfect square.
-
Therefore, the square root of 144 can be written as:
\[\sqrt{144} = \sqrt{12 \times 12}\]
-
Simplify the expression under the square root:
\[\sqrt{12 \times 12} = 12\]
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 144 is 12.
Understanding the Simplification
Let's break down the process to better understand why \(\sqrt{144} = 12\).
- Perfect Square: A number like 144, which can be written as \(12^2\), is a perfect square.
- Square Root Definition: The square root of a number is one of its two equal factors. For 144, the two equal factors are both 12.
Verification
To verify our result, we can square 12 to see if we get back to 144:
\[12 \times 12 = 144\]
Since this is true, our simplification is correct.
4. Basic Calculation Method
In this section, we will explore the basic calculation method to simplify the square root of 144. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Let's break down the steps:
- Identify the Square Root Symbol:
The square root symbol is \( \sqrt{} \). We are looking to simplify \( \sqrt{144} \).
- Recognize Perfect Squares:
A perfect square is a number that is the square of an integer. Examples include \( 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81, 100, 121, \) and \( 144 \).
- Determine if 144 is a Perfect Square:
We can determine if 144 is a perfect square by finding an integer that, when multiplied by itself, equals 144. This integer is known as the square root.
- Calculate the Square Root:
To find the square root of 144, we look for an integer \( x \) such that \( x \times x = 144 \).
We find that \( 12 \times 12 = 144 \), so \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
- Verify the Result:
Always verify your result by squaring the integer you found. In this case, \( 12^2 = 144 \), confirming that the square root of 144 is indeed 12.
Therefore, the simplified square root of 144 is:
\( \sqrt{144} = 12 \)
| Step | Calculation |
| Recognize 144 as a perfect square | \( 144 = 12 \times 12 \) |
| Calculate the square root | \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \) |
| Verify the result | \( 12^2 = 144 \) |

5. Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a systematic approach to simplify square roots by breaking down the number into its prime factors. Here is a detailed step-by-step method to simplify the square root of 144 using prime factorization:
-
Step 1: Factorize the Number into Prime Factors
First, divide 144 by the smallest prime number (which is 2) and continue dividing the quotient by prime numbers until you reach 1. The factorization process is as follows:
- 144 ÷ 2 = 72
- 72 ÷ 2 = 36
- 36 ÷ 2 = 18
- 18 ÷ 2 = 9
- 9 ÷ 3 = 3
- 3 ÷ 3 = 1
The prime factors of 144 are 2, 2, 2, 2, 3, and 3. In exponent form, this is written as:
\[ 144 = 2^4 \times 3^2 \]
-
Step 2: Group the Prime Factors into Pairs
Arrange the prime factors into pairs of identical numbers:
- (2, 2), (2, 2), (3, 3)
-
Step 3: Multiply One Factor from Each Pair
Select one factor from each pair and multiply them together:
- \[ \sqrt{144} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3)} \]
- \[ \sqrt{144} = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \]
- \[ \sqrt{144} = 12 \]
Thus, the simplified square root of 144 using the prime factorization method is 12. This method ensures that all factors are considered, making it an accurate and reliable way to simplify square roots.
6. Long Division Method
The long division method is a traditional and systematic approach to finding the square root of a number, particularly useful for perfect squares such as 144. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to apply this method to calculate the square root of 144:
-
Set Up the Number
Write 144 and group the digits in pairs from right to left. For 144, place a bar over 44 and another over 1.
1 44 -
Find the Largest Square
Identify the largest square less than or equal to the first group. Here, it is 1 (since 12 = 1). Write 1 as the quotient and subtract 1 from 1.
1 1 - 1 0 -
Bring Down the Next Pair
Bring down the next pair (44) next to the remainder (0), giving 44. Double the quotient (1) and write it as 2, the new divisor's tens digit.
1 1 44 2 -
Find the Units Place Digit
Determine a digit (let’s say x) for the units place such that 2x multiplied by x gives a product ≤ 44. Here, 22 × 2 = 44 fits perfectly.
1 2 1 44 - 44 0
Following these steps, we find that the square root of 144 is 12. The long division method not only helps in finding the square roots of perfect squares but also provides a clear understanding of the process involved in manual calculations.
7. Visual Representations and Examples
Understanding the concept of square roots can be significantly enhanced through visual representations. Here, we will explore different visual methods to represent the square root of 144.
Square Representation
One of the simplest ways to visualize the square root is by using a square. Since 144 is a perfect square, we can draw a square with an area of 144 square units. Each side of this square will be 12 units long because \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
Here is a visual representation:

|
Number Line Representation
A number line can also be useful to show the position of \( \sqrt{144} \) relative to other numbers. On a number line, you can mark the points for perfect squares such as 121 (11^2), 144 (12^2), and 169 (13^2) to show where \( \sqrt{144} \) fits in.
Here is an example:

|
Area Model
An area model can also help in understanding square roots. This involves creating a grid to represent the area of a square. For example, if we make a 12x12 grid, each cell represents 1 unit, and the entire grid represents the area of 144 square units. This helps in visualizing why \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
Here is how you can represent it:

|
Interactive Examples
Interactive tools can further aid in understanding. For instance, online calculators and dynamic geometry software like Desmos can allow students to manipulate and visualize square roots interactively. You can create a virtual square and adjust its dimensions to see how the area changes.
Example interactive tool:
By using these visual representations, students can gain a deeper understanding of the concept of square roots and see how they are derived and represented in different ways.
8. Applications of Simplified Square Roots
Simplified square roots play a crucial role in various fields and real-world scenarios. Understanding and applying these concepts can simplify complex calculations and provide accurate results in different domains. Below are some key applications:
1. Engineering and Construction
In engineering and construction, square roots are essential for calculating lengths, areas, and volumes. For example, to find the diagonal of a square or rectangular structure, you can use the Pythagorean theorem, which involves taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the sides. Simplifying these square roots ensures precise measurements and structural integrity.
2. Finance
In finance, the concept of square roots is used to calculate stock market volatility. The standard deviation, which is the square root of the variance, measures how much a stock's price deviates from its average price over time. This helps investors assess the risk and make informed investment decisions.
3. Science
Scientists use square roots in various calculations, such as determining the velocity of moving objects, the intensity of sound waves, and the absorption of radiation. Simplified square roots make these calculations more manageable and accurate.
4. Statistics
In statistics, square roots are used to calculate the standard deviation, a measure of data dispersion. Simplifying the square root of the variance provides a clearer understanding of how data points deviate from the mean, aiding in data analysis and interpretation.
5. Geometry
Geometry heavily relies on square roots for solving problems involving right triangles, areas, and perimeters of shapes. For instance, the Pythagorean theorem uses square roots to find the lengths of sides in right triangles, simplifying complex geometric calculations.
6. Computer Science
In computer science, square roots are used in algorithms for encryption, image processing, and game physics. Simplifying these calculations can improve computational efficiency and accuracy in software applications.
7. Cryptography
Cryptography employs square roots in creating secure communication systems, such as digital signatures and key exchange algorithms. Simplified square roots help in generating unique keys and ensuring data security.
8. Navigation
Square roots are used in navigation to calculate distances between points and estimate directions. Pilots and navigators use these calculations to plan routes and ensure accurate travel paths.
9. Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineers use square roots to calculate power, voltage, and current in circuits. Simplifying these calculations helps in designing efficient and reliable electrical systems.
10. Cooking
In cooking, square roots can help in scaling recipes accurately. For example, if you need to double a recipe, understanding the square root of the scaling factor can help in adjusting ingredient quantities precisely to maintain flavor balance.
11. Photography
In photography, the aperture size of a camera lens is proportional to the square root of the f-number. Simplifying these calculations helps photographers adjust settings to control the amount of light entering the camera effectively.
12. Computer Graphics
In computer graphics, square roots are used to calculate distances and lengths of vectors in 2D and 3D spaces. Simplifying these calculations ensures smoother and more accurate rendering of graphics.
13. Telecommunications
In telecommunications, square roots are used to model signal strength over distances. Simplifying these models helps in designing efficient communication systems with optimal signal coverage.
By understanding and applying simplified square roots, we can solve complex problems across various fields more efficiently and accurately.

9. Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When simplifying the square root of 144, or any other square root, it's important to be aware of common mistakes and understand how to avoid them. Here are some frequent errors and tips to steer clear of them:
- Incorrect Factorization: Ensure you factorize the number correctly. For instance, 144 should be factorized as \(144 = 12 \times 12\) or \(144 = 2^4 \times 3^2\). Incorrect factorization leads to wrong simplification.
- Ignoring Perfect Squares: Always check if the number is a perfect square. For example, 144 is a perfect square, and its square root is 12. Forgetting this can lead to unnecessary complex calculations.
- Incorrect Use of Square Root Properties: Remember the property \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\). Misapplying this can cause errors. For instance, \(\sqrt{144}\) should be recognized directly as 12, not split into smaller components unless verifying its factors.
- Skipping Steps: Do not skip steps in factorization or simplification. Always write out the intermediate steps to avoid mistakes. For example, show that \( \sqrt{144} = \sqrt{12 \times 12} = 12\).
- Misinterpreting Non-Perfect Squares: Be cautious with numbers that are not perfect squares. Simplify them correctly by factorizing into prime factors. For instance, for \(\sqrt{18}\), recognize that \(18 = 2 \times 9 = 2 \times 3^2\) and simplify to \(3\sqrt{2}\).
By being mindful of these common mistakes and following a structured approach, you can accurately simplify square roots and avoid errors in your calculations.
10. Practice Problems and Solutions
Practicing simplifying square roots can solidify your understanding and help you master the techniques involved. Below are several practice problems along with their step-by-step solutions. Try solving them on your own first, and then check your work against the solutions provided.
Practice Problems
- Simplify \(\sqrt{144}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{72}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{50}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{200}\)
- Simplify \(\sqrt{18}\)
Solutions
-
\(\sqrt{144}\)
- Since \(144\) is a perfect square, we know \(\sqrt{144} = 12\).
-
\(\sqrt{72}\)
- Factor 72 into its prime factors: \(72 = 2^3 \times 3^2\).
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \(72 = (2^2 \times 3^2) \times 2\).
- Simplify inside the square root: \(\sqrt{72} = \sqrt{(2^2 \times 3^2) \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2}\).
-
\(\sqrt{50}\)
- Factor 50 into its prime factors: \(50 = 2 \times 5^2\).
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \(50 = (5^2) \times 2\).
- Simplify inside the square root: \(\sqrt{50} = \sqrt{(5^2) \times 2} = 5\sqrt{2}\).
-
\(\sqrt{200}\)
- Factor 200 into its prime factors: \(200 = 2^3 \times 5^2\).
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \(200 = (2^2 \times 5^2) \times 2\).
- Simplify inside the square root: \(\sqrt{200} = \sqrt{(2^2 \times 5^2) \times 2} = 10\sqrt{2}\).
-
\(\sqrt{18}\)
- Factor 18 into its prime factors: \(18 = 2 \times 3^2\).
- Group the prime factors into pairs: \(18 = (3^2) \times 2\).
- Simplify inside the square root: \(\sqrt{18} = \sqrt{(3^2) \times 2} = 3\sqrt{2}\).
These problems demonstrate the common steps in simplifying square roots: factoring the number into its prime factors, grouping the factors into pairs, and simplifying the square root by removing the pairs. Practice these steps with different numbers to become proficient in simplifying square roots.
11. Interactive Tools and Calculators
Using interactive tools and calculators can simplify the process of finding the square root of numbers, such as 144. These tools provide step-by-step solutions and visual aids, making learning more effective. Here are some recommended tools and their features:
-
Mathway
Mathway offers a comprehensive square root calculator that guides you through the steps of simplifying square roots. You can input any radical expression and receive the simplified form along with decimal approximations.
- Enter the radical expression in the calculator.
- Click the "Calculate" button to see the step-by-step solution.
-
Omni Calculator
Omni Calculator provides an intuitive interface for calculating square roots. It also explains the factors and the simplification process in detail.
- Input the number (e.g., 144) into the calculator.
- The tool shows the simplified square root and the steps involved.
-
Giga Calculator
Giga Calculator offers a straightforward square root calculator and additional resources to understand the concept better. It also includes a table of commonly used square roots.
- Enter the number into the input field.
- Click "Calculate" to get the square root and related explanations.
Using these interactive tools, students and enthusiasts can easily simplify square roots, including the square root of 144, and gain a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical concepts.
12. Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding the simplification of the square root of 144:
-
Is the square root of 144 a rational number?
Yes, the square root of 144 is a rational number. The square roots of 144 are 12 and -12, both of which are rational numbers.
-
What is the prime factorization of 144?
The prime factorization of 144 is \(2^4 \times 3^2\). This can be used to simplify the square root as \( \sqrt{144} = \sqrt{2^4 \times 3^2} = 2^2 \times 3 = 12 \).
-
What different methods can be used to find the square root of 144?
There are several methods to find the square root of 144:
- Long Division Method
- Prime Factorization
- Repeated Subtraction Method
-
What is the square root of -144?
The square root of negative numbers is imaginary. It is represented as \( \sqrt{-144} = 12i \), where \( i \) is the imaginary unit.
-
How do you simplify the square root of 144 using the prime factorization method?
To simplify \( \sqrt{144} \) using prime factorization, follow these steps:
- Prime factorize 144: \(144 = 2^4 \times 3^2\).
- Apply the square root to each factor: \( \sqrt{144} = \sqrt{2^4 \times 3^2} \).
- Use the property of square roots: \( \sqrt{2^4} \times \sqrt{3^2} = 2^2 \times 3 \).
- Simplify the expression: \( 2^2 = 4 \) and \( 4 \times 3 = 12 \).
- Thus, \( \sqrt{144} = 12 \).
-
Can the square root of 144 be expressed in exponential form?
Yes, the square root of 144 can be expressed in exponential form as \( 144^{1/2} \). This is equivalent to 12.

13. Additional Resources for Learning
Here are some additional resources to help you deepen your understanding of simplifying square roots, especially the square root of 144:
-
Online Calculators and Tools:
- - A tool to find the square root of any number.
- - Interactive calculator with explanations and examples.
-
Educational Websites:
- - Detailed video lessons on simplifying square roots.
- - Comprehensive guides on square roots and radicals.
-
Practice Problems:
- - Practice problems with step-by-step solutions.
- - Online tool to solve and simplify square roots with solutions.
-
Textbooks and eBooks:
- - Free downloadable textbook with sections on radicals and square roots.
- - A great reference book with practice problems.
These resources should provide a robust foundation for mastering the concepts and techniques involved in simplifying square roots. Happy learning!
Tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 144 trong video này. Chúng tôi sẽ hướng dẫn bạn từng bước một cách dễ hiểu.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 144: sqrt(144)
READ MORE:
Khám phá căn bậc hai của 144 trong video này. Chúng tôi sẽ hướng dẫn bạn cách đơn giản hóa từng bước một cách dễ hiểu.
Căn Bậc Hai của 144