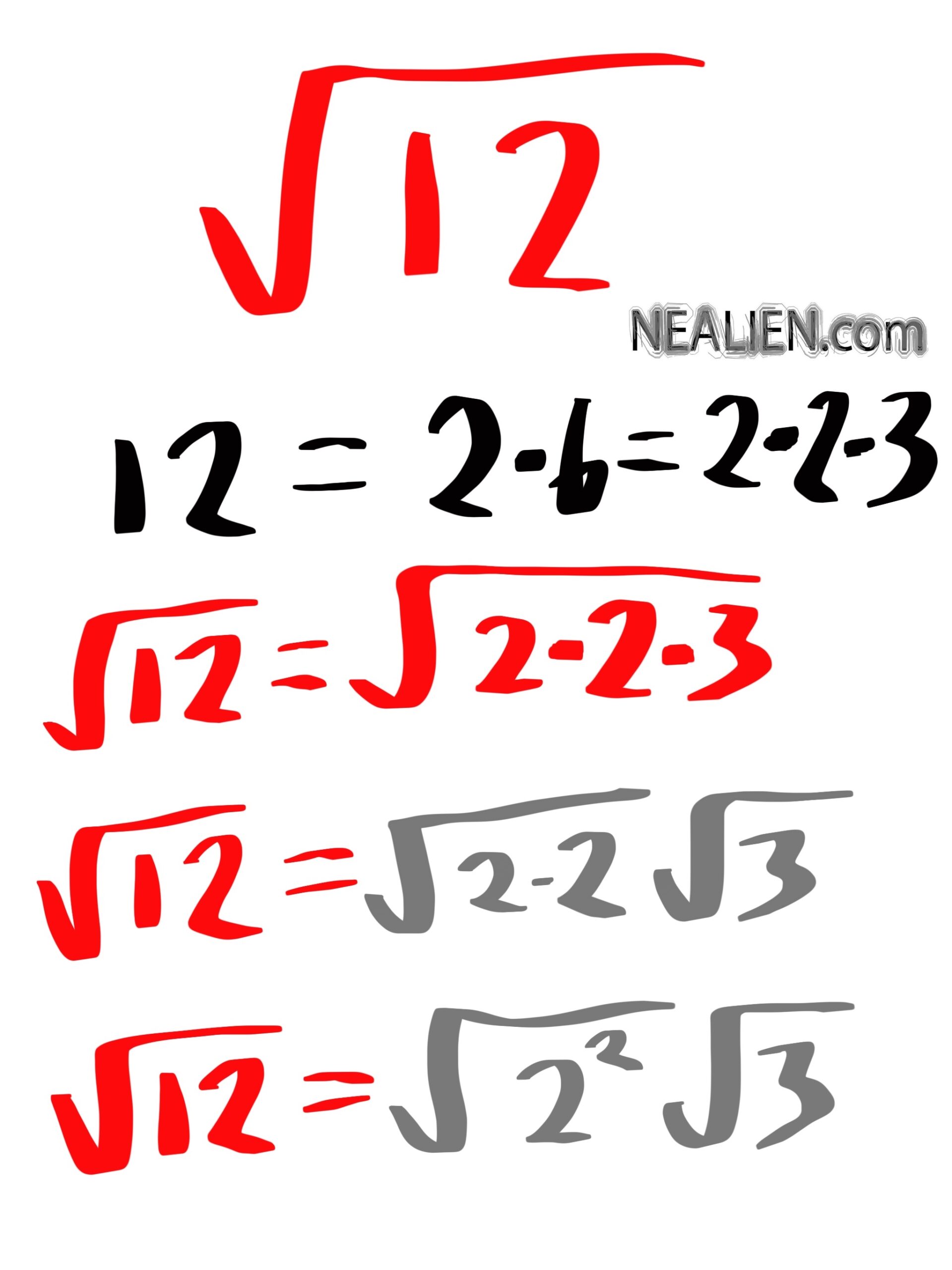Topic is the square root of 12 rational: The square root of 12 is not a rational number. This is because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction of two integers. Instead, it is an irrational number, which means its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. Understanding why the square root of 12 is irrational can deepen your comprehension of the properties of numbers and their classifications.
Table of Content
- Is the Square Root of 12 Rational?
- Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
- Why the Square Root of 12 is Irrational
- Methods to Find the Square Root of 12
- Simplified Radical Form of the Square Root of 12
- Square Root of 12 in Decimal Form
- FAQs on the Square Root of 12
- Real-Life Applications of the Square Root of 12
- YOUTUBE:
Is the Square Root of 12 Rational?
The square root of 12, denoted as \( \sqrt{12} \), is an interesting topic in mathematics. Let’s explore whether it is a rational or irrational number.
Definition of Rational and Irrational Numbers
- Rational Numbers: These can be expressed as the ratio of two integers (i.e., in the form \( \frac{p}{q} \) where \( q \neq 0 \)). Examples include 1/2, 3, and -4.
- Irrational Numbers: These cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. They have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions. Examples include \( \pi \) and \( \sqrt{2} \).
Analyzing the Square Root of 12
To determine if \( \sqrt{12} \) is rational or irrational, consider the following:
- Perfect Squares: A number is a perfect square if its square root is an integer. For instance, 9 is a perfect square because \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \).
- Calculation: The square root of 12 is approximately \( \sqrt{12} \approx 3.4641 \). Since 12 is not a perfect square, its square root cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- Simplification: The square root of 12 can be simplified as \( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{4 \times 3} = 2\sqrt{3} \). Even in this simplified form, \( 2\sqrt{3} \) is still irrational because \( \sqrt{3} \) is irrational.
Conclusion
Based on the above analysis, we can conclude that the square root of 12 is an irrational number. It cannot be written as a ratio of two integers, and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
| Number | Square Root | Rational/Irrational |
| 12 | \( \sqrt{12} \approx 3.4641 \) | Irrational |
Additional Information
- You can use a calculator to verify the value of \( \sqrt{12} \approx 3.4641 \).
- This value cannot be precisely written as a fraction, confirming its irrationality.
READ MORE:
Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
Rational and irrational numbers are two fundamental concepts in mathematics, particularly in the study of real numbers. Understanding these types of numbers is essential for grasping more complex mathematical theories and applications.
Rational Numbers:
- A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers, where p and q are integers and q is not zero.
- Examples of rational numbers include 1/2, 3, -7, and 0.75. The number 3 can be written as 3/1, and 0.75 can be expressed as 3/4.
- Rational numbers can be either terminating decimals or repeating decimals. For example, 0.5 (which is 1/2) is a terminating decimal, and 0.333... (which is 1/3) is a repeating decimal.
Irrational Numbers:
- An irrational number cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Irrational numbers have non-terminating and non-repeating decimal expansions.
- Examples of irrational numbers include √2, π (pi), and e. These numbers cannot be written as exact fractions of two integers.
- The square root of any non-perfect square is an irrational number. For example, √12 is irrational because it cannot be simplified to a fraction of two integers.
Let's break down the key properties:
| Rational Numbers | Irrational Numbers |
| Can be written as p/q | Cannot be written as p/q |
| Terminating or repeating decimals | Non-terminating, non-repeating decimals |
| Examples: 1/2, 4, 0.75 | Examples: √2, π, e |
Understanding these distinctions helps in various mathematical operations and in the study of more advanced topics. For instance, knowing that the square root of 12 is irrational allows us to handle it differently in equations and proofs.
Why the Square Root of 12 is Irrational
To understand why the square root of 12 is irrational, we need to delve into the nature of rational and irrational numbers. Rational numbers can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, whereas irrational numbers cannot be written as a simple fraction.
The square root of 12, denoted as \( \sqrt{12} \), can be simplified. Let's break down the steps:
- Factorize the number under the square root:
- 12 = 2 × 2 × 3
- Rewrite the square root using these factors:
- \( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3} = \sqrt{4 \times 3} \)
- Simplify the square root:
- \( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{3} = 2\sqrt{3} \)
Here, \( 2\sqrt{3} \) is in its simplest form. To determine if this number is rational, we look at \( \sqrt{3} \). Since 3 is not a perfect square, \( \sqrt{3} \) is an irrational number. Therefore, any multiple of \( \sqrt{3} \), including \( 2\sqrt{3} \), is also irrational.
To confirm, let’s assume \( \sqrt{12} \) is rational. Then, it can be expressed as \( \frac{a}{b} \) where a and b are integers with no common factors (in simplest form). Squaring both sides gives:
This implies:
This leads to \( a^2 = 12b^2 \), meaning \( a^2 \) is a multiple of 12. However, for \( a^2 \) to be divisible by 12, \( a \) itself must be divisible by 2 and 3, indicating that both a and b share common factors, contradicting our initial assumption. Thus, \( \sqrt{12} \) is irrational.
Therefore, the square root of 12 is irrational because it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers, due to the irrationality of \( \sqrt{3} \).
Methods to Find the Square Root of 12
Finding the square root of 12 involves different methods, each with its own approach. Here, we explore the prime factorization method, long division method, and approximation using calculators or computers.
Prime Factorization Method
- Express 12 as a product of its prime factors:
\( 12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \)
- Pair the prime factors:
\( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 3} \)
- Take the square root of each pair:
\( \sqrt{12} = 2\sqrt{3} \)
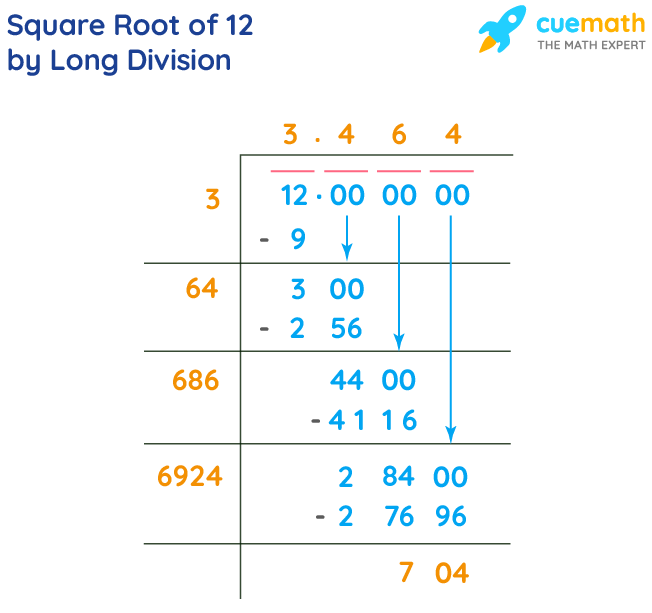
Long Division Method
- Set up the number in pairs from right to left:
12
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair:
\( 3^2 = 9 \)
- Subtract and bring down the next pair:
12 - 9 = 3
- Double the quotient and find the next digit:
\( 6x \leq 30 \rightarrow x = 5 \)
- Repeat the process for more precision.
Approximation Using Calculators and Computers
Using a calculator: Enter 12 and press the square root (√) button. The result is approximately \( 3.4641 \).
Using a computer: In Excel, Numbers, or Google Sheets, use the function
=SQRT(12)to get approximately \( 3.4641 \).
These methods provide a comprehensive way to understand and calculate the square root of 12, highlighting its irrational nature and various approximation techniques.
Simplified Radical Form of the Square Root of 12
To simplify the square root of 12, we need to express it in its simplest radical form. This involves finding factors of 12 that are perfect squares. Here's a step-by-step process to simplify √12:
First, identify the factors of 12:
- 12 = 2 × 2 × 3
Next, group the factors into pairs of perfect squares:
- 12 = (2 × 2) × 3
Take the square root of the perfect square factor and move it outside the radical:
- √12 = √(22 × 3) = 2√3
Therefore, the simplified radical form of the square root of 12 is 2√3. This form is useful for exact calculations and further mathematical operations.
Square Root of 12 in Decimal Form
The square root of 12, represented as \(\sqrt{12}\), is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. When calculated, the square root of 12 is approximately equal to 3.4641016151377544. This value continues indefinitely without repeating, which is characteristic of irrational numbers.
To express \(\sqrt{12}\) in decimal form to various degrees of precision:
- To the nearest tenth: \(\sqrt{12} \approx 3.5\)
- To the nearest hundredth: \(\sqrt{12} \approx 3.46\)
- To the nearest thousandth: \(\sqrt{12} \approx 3.464\)
For practical purposes, these approximations are often sufficient. However, the more decimal places used, the more accurate the representation of the square root of 12 will be.
It's also worth noting that the decimal form of \(\sqrt{12}\) can be found using calculators or software tools like Excel or Google Sheets, which have built-in functions for calculating square roots.
Here is how you can calculate it using Excel:
- Open Excel and select a cell.
- Type
=SQRT(12)and press Enter. - The cell will display the result: 3.4641016151377544.
This method ensures you get a precise decimal value for \(\sqrt{12}\) quickly and easily.
FAQs on the Square Root of 12
Here are some frequently asked questions regarding the square root of 12, addressing common queries and providing detailed explanations.
- What is the simplified form of the square root of 12?
The simplified form of the square root of 12 is \(2\sqrt{3}\). This is obtained by factoring out the largest perfect square from 12, which is 4, giving \( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{4 \cdot 3} = 2\sqrt{3} \).
- Is the square root of 12 a rational number?
No, the square root of 12 is not a rational number. Rational numbers can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, but \( \sqrt{12} \) is an irrational number because it cannot be precisely expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-repeating and non-terminating.
- How can the square root of 12 be calculated?
The square root of 12 can be calculated using various methods:
- Using a calculator: Simply input 12 and press the square root button to get approximately 3.464.
- Long division method: This traditional method involves a systematic process of estimating and refining the value.
- Newton-Raphson method: This iterative numerical technique refines an initial guess to get a more accurate approximation.
- What is the square root of 12 in decimal form?
In decimal form, the square root of 12 is approximately 3.464. This value is derived from calculator approximations and various numerical methods.
- Can the square root of 12 be written as a fraction?
As an irrational number, the exact square root of 12 cannot be written as a simple fraction. However, it can be approximated as a fraction for practical purposes, such as \( \frac{346}{100} \), which simplifies to 3.46 when rounded to two decimal places.
Real-Life Applications of the Square Root of 12
The square root of 12, approximately 3.464, has several real-life applications across various fields. Here are some notable examples:
- Engineering and Architecture: The square root of 12 is used in calculations involving areas and distances. For instance, if an area in a blueprint is given as 12 square units, the side length of a square with this area is the square root of 12, which is crucial for accurate construction and design.
- Physics: In physics, square roots are often encountered in formulas involving wave mechanics and other phenomena. The square root of 12 might appear when calculating parameters like the root mean square (RMS) speed in kinetic theory of gases, or in resolving vector components.
- Statistics: The square root of 12 is used in statistics when dealing with variances and standard deviations. For example, in calculating the standard deviation of a dataset where the variance sums up to 12, the standard deviation would be the square root of 12.
- Mathematics and Education: Understanding and simplifying √12 is a part of learning about irrational numbers, radicals, and their properties. It's an essential concept in algebra and helps in developing problem-solving skills.
- Finance: In finance, the square root of 12 might be used in models involving time value of money or in certain types of risk assessments where squared terms are prevalent.
These examples illustrate that while the square root of 12 might seem abstract, it plays a crucial role in practical and theoretical applications across various disciplines.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 12: Căn(12)