Topic is the square root of 12 rational or irrational: Discover whether the square root of 12 is a rational or irrational number. This intriguing mathematical question delves into the nature of numbers and their classifications, helping to understand the distinction between rational and irrational numbers.
Table of Content
Square Root of 12: Rational or Irrational?
The square root of 12 is an important concept in mathematics, often used to illustrate the distinction between rational and irrational numbers.
Definition
In mathematical terms, the square root of 12 is represented as √12. It is the number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 12.
Is 12 a Perfect Square?
A number is considered a perfect square if its square root is a whole number. Since the square root of 12 is approximately 3.4641, which is not a whole number, 12 is not a perfect square.
Rational or Irrational?
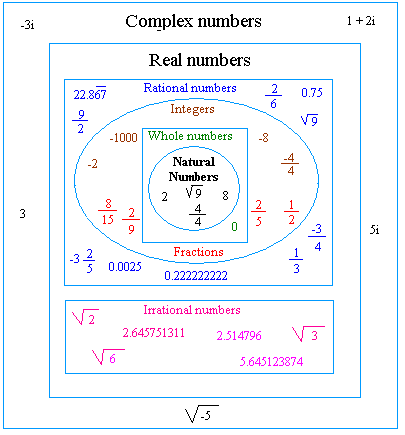
A rational number can be expressed as the fraction of two integers (p/q) where q ≠ 0. An irrational number cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Since 12 is not a perfect square, √12 cannot be simplified to a fraction of integers, making it an irrational number.
Simplifying √12
The square root of 12 can be simplified by breaking it down into prime factors. This gives us:
12 = 22 × 3
Thus, √12 = √(22 × 3) = 2√3
Even though we simplify it, the result (2√3) is still an irrational number.
Calculating √12
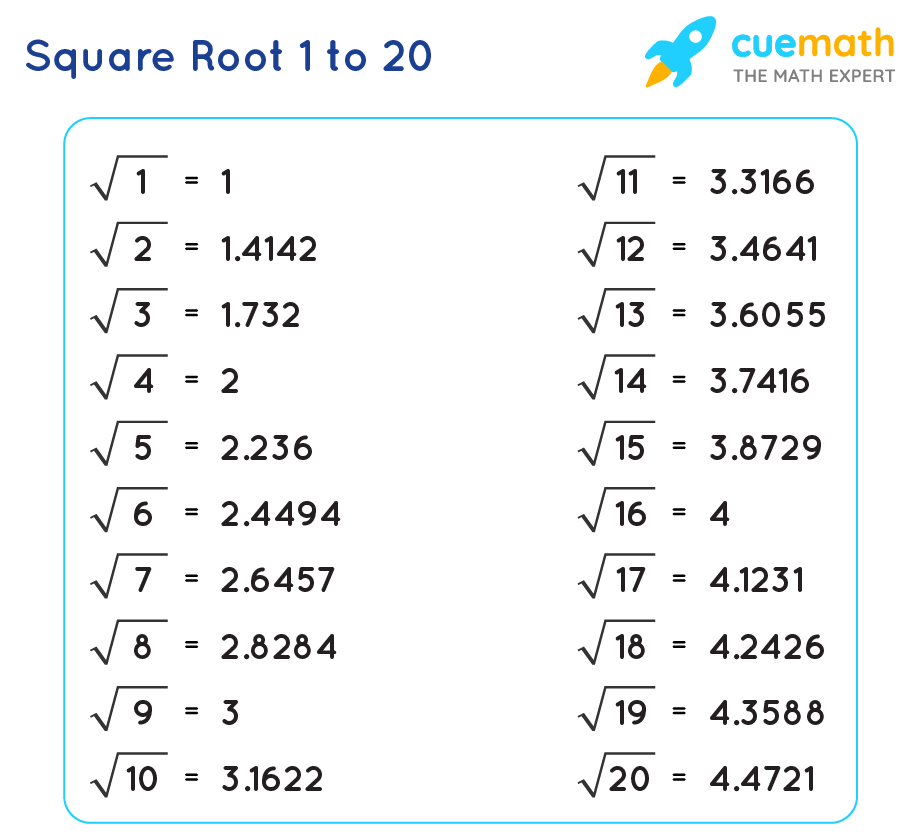
You can calculate √12 using a calculator by typing 12 and pressing the square root (√) button. This gives approximately 3.4641.
In decimal form, √12 ≈ 3.4641, which confirms its irrational nature as it is a non-repeating, non-terminating decimal.
Examples and Applications
- Example: If the area of a circle is 12π square units, the radius can be calculated as r = √12, which is approximately 3.464 units.
- In radical form: 2√3.
- Rounding to the nearest hundredth: 3.46
Conclusion
In conclusion, the square root of 12 is an irrational number. It cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating.
READ MORE:
Introduction
The question of whether the square root of 12 is rational or irrational is a fundamental one in mathematics. A rational number is defined as a number that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. Conversely, an irrational number cannot be expressed as such a fraction and has a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansion. In this context, we will explore why the square root of 12 falls into the category of irrational numbers and discuss various methods to approximate and understand its value.
-
Definition of Irrational Numbers:
Irrational numbers are characterized by their non-repeating and non-terminating decimal forms. Examples include numbers such as \(\pi\) and \(\sqrt{2}\). The square root of 12, denoted as \(\sqrt{12}\), also fits this description.
-
Calculation Methods:
- Estimation: Recognizing that 12 lies between the perfect squares of 9 and 16, we know that \(\sqrt{12}\) is between 3 and 4, closer to 3 since 12 is nearer to 9.
- Long Division Method: A step-by-step division process to approximate the value, yielding a more precise result, approximately 3.464.
- Newton-Raphson Method: An iterative numerical technique that refines an initial guess to converge on a more accurate approximation.
- Calculator Method: Using a calculator's square root function provides a quick and precise approximation.
- Numerical Series or Sequences: Advanced mathematical series or sequences that converge to square roots based on their properties.
-
Mathematical Representation:
The square root of 12 can be expressed in different forms:
- Radical Form: \(\sqrt{12}\)
- Simplified Radical Form: \(2\sqrt{3}\), derived by factoring out the largest perfect square (4) from 12.
- Decimal Form: Approximately 3.464.
-
Applications and Implications:
Understanding the square root of 12 is crucial in various fields, including geometry, where it might represent dimensions or distances. For instance, if the area of a circle is 12π square units, the radius is \(\sqrt{12}\) units.
In conclusion, the square root of 12 is an irrational number, and its understanding can be approached through various mathematical techniques. This exploration enhances mathematical proficiency and facilitates applications in science, engineering, and beyond.
Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
In mathematics, numbers are classified into various types based on their properties. Two important categories are rational and irrational numbers. Understanding these distinctions is fundamental for comprehending more complex mathematical concepts.
Rational Numbers: Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. These numbers include integers, fractions, and finite or repeating decimals. For example:
- Integers: -3, 0, 4
- Fractions: 1/2, 3/4
- Repeating Decimals: 0.333... (which is 1/3), 0.666... (which is 2/3)
Irrational Numbers: Conversely, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a simple fraction of two integers. They are non-repeating and non-terminating decimals. Examples of irrational numbers include the square root of non-perfect squares, such as √12, √7, and π (pi). These numbers do not resolve into a precise fraction and their decimal form continues infinitely without repeating.
Let's delve into why the square root of 12 is considered an irrational number:
- When we find the square root of 12, it approximately equals 3.4641016151377544...
- This decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating, indicating that it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers.
- Therefore, √12 is classified as an irrational number because it doesn't fit the definition of a rational number.
Understanding the distinction between these two types of numbers is crucial for solving mathematical problems and for understanding more advanced concepts in mathematics.
Square Root of 12: Calculation Methods
The square root of 12 is an interesting mathematical concept that can be approached in several ways. Below, we explore various methods to calculate the square root of 12 step by step.
Using Prime Factorization
- First, express 12 as a product of its prime factors:
12 = 2 × 2 × 3
- Then, rewrite the square root of 12 using these factors:
√12 = √(2 × 2 × 3) = √(4 × 3) = 2√3
- So, the simplified radical form of the square root of 12 is:
2√3
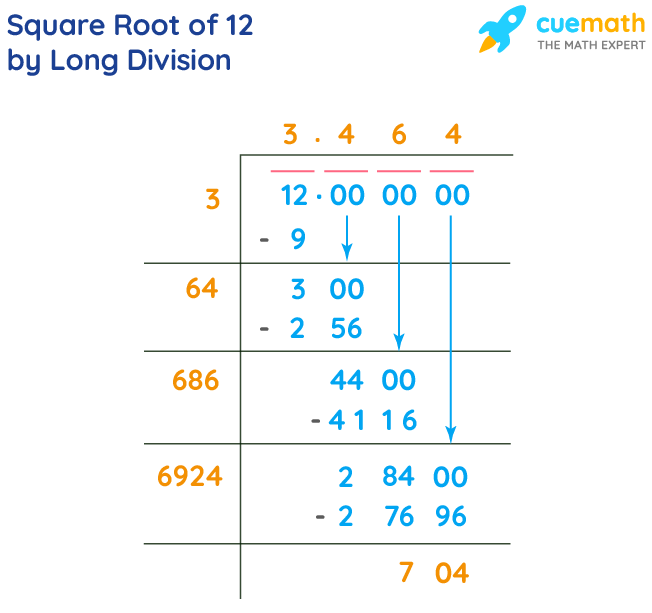
Using the Long Division Method
- Start by grouping the digits in pairs from right to left. For 12, it's 12.00.
12 | 3.46...
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the number. For 12, it's 3, because 3² = 9.
3 × 3 = 9
- Subtract this square from the first group and bring down the next pair of zeros.
12 - 9 = 3
Bring down 00, making it 300.
- Double the number obtained in the quotient (3), which gives 6. Find a digit (x) such that 6x multiplied by x is less than or equal to 300. The digit is 4.
64 × 4 = 256
- Continue the process to get more decimal places if necessary.
The approximate value of √12 is 3.464
Using a Calculator
- Enter the number 12 into the calculator and press the square root (√) button.
- The result will be approximately 3.4641.
Using Exponent Form
The square root of a number can also be expressed using fractional exponents:
√12 = 121/2
By understanding and utilizing these methods, you can calculate the square root of 12 effectively. Each method provides a different perspective and can be used depending on the context and tools available.
Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a method used to express a number as the product of its prime factors. This is particularly useful when simplifying square roots.
Let's apply prime factorization to the number 12:
- First, find the prime factors of 12. The prime factorization of 12 is 2 × 2 × 3, or \(2^2 \times 3\).
Using this factorization, we can simplify the square root of 12:
- Write the square root of 12 in its prime factorized form: \( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 3} \).
- Apply the property of square roots that \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \): \( \sqrt{2^2 \times 3} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{3} \).
- Simplify \( \sqrt{2^2} \) to 2: \( \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{3} = 2 \times \sqrt{3} \).
Therefore, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{12} \) is \( 2\sqrt{3} \). This shows that the square root of 12, when simplified, is an irrational number since \( \sqrt{3} \) is irrational.
Prime factorization is a powerful tool in simplifying square roots, helping to identify the rational and irrational components of the expression.

Simplified Form of the Square Root of 12
To simplify the square root of 12, we need to factorize 12 into its prime factors and simplify the radical expression.
- Step 1: Prime Factorization
- 12 = 2 × 2 × 3
- Step 2: Grouping the Factors
- 12 = (2 × 2) × 3
- Step 3: Simplifying the Radical
- √12 = √((2 × 2) × 3)
- √12 = 2√3
First, we perform the prime factorization of 12. The prime factors of 12 are 2 and 3, as shown below:
Next, we group the prime factors in pairs:
Now, we take the square root of each pair of factors. For the pair (2 × 2), we take one 2 out of the square root, and for the factor 3, we leave it inside the square root:
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 12 is 2√3. This method helps in expressing the square root in its simplest radical form.
Video giải thích √12 là gì: hợp lý, vô lý, số nguyên, hay không phải những cái này.
Q11 | √12 là: -(a) hợp lý (b) vô lý (c) số nguyên (d) không phải những cái này
READ MORE:
Video giải thích sự khác biệt giữa số hợp lý và số vô lý trong bài học Đại Số Trung Cấp, Bài Học 12.
Sự Khác Biệt Giữa Số Hợp Lý và Số Vô Lý, Đại Số Trung Cấp, Bài Học 12