Topic how to find the square root of 12: Discovering how to find the square root of 12 can be a fascinating journey through various mathematical methods. Whether using estimation, long division, or advanced techniques, uncover the steps and insights to accurately determine this value. Learn about rational and irrational numbers, and see how to simplify and approximate roots effectively.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Square Root of 12
- Introduction
- Table of Contents
- Definition and Basic Understanding
- Methods to Find the Square Root of 12
- Simplification of √12
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Solved Examples
- Conclusion
- Definition and Basic Understanding
- Methods to Find the Square Root of 12
- Simplification of √12
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Solved Examples
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE:
How to Find the Square Root of 12
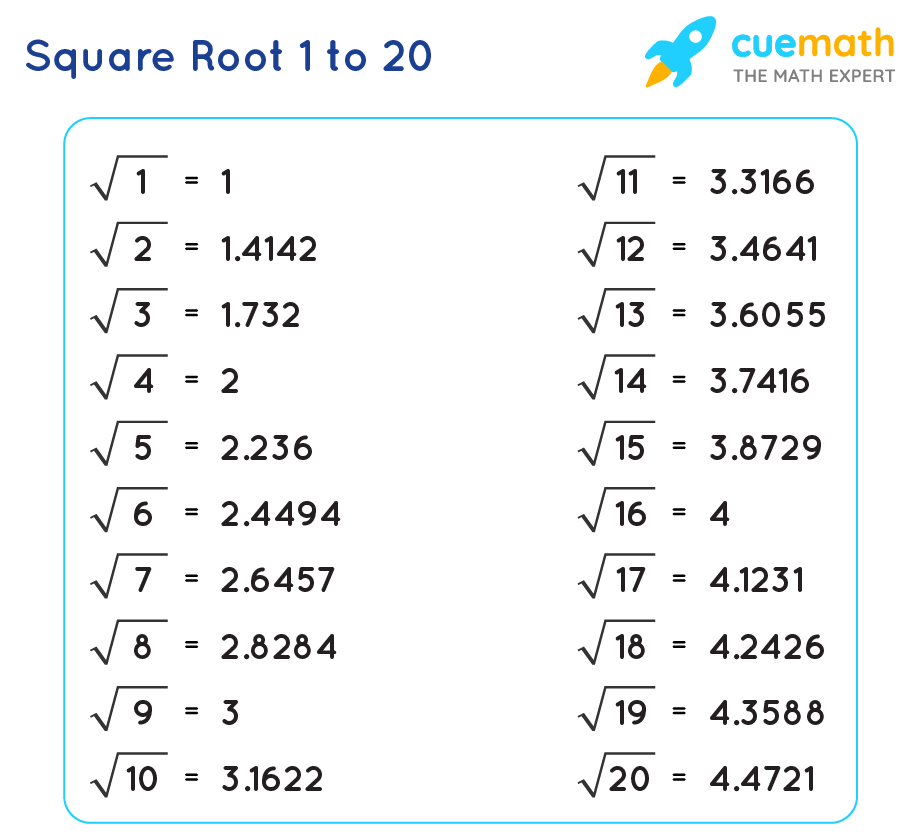
The square root of 12 can be determined through several methods. Here, we will explore the prime factorization method and the long division method. We will also discuss some properties and examples.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization of 12 is:
\[ 12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \]
Taking the square root of both sides:
\[ \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 3} = 2 \sqrt{3} \]
So, the square root of 12 in its simplest radical form is \( 2\sqrt{3} \).
Long Division Method
The long division method for finding the square root of 12 involves the following steps:
- Start by grouping the digits of the number in pairs from right to left. Since 12 has only two digits, we consider it as one group.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 12. This number is 3 because \( 3^2 = 9 \).
- Subtract \( 9 \) from 12 to get 3 and bring down a pair of zeros to get 300.
- Double the quotient obtained (which is 3) and write it as the new divisor (i.e., 6__).
- Find a digit to fill in the blank such that the new divisor times this digit is less than or equal to 300.
- Repeat the process to get more decimal places as needed.
Using this method, you will find that:
\[ \sqrt{12} \approx 3.464 \]
Properties of the Square Root of 12
- The square root of 12 is an irrational number.
- In its decimal form, it is approximately \( 3.464 \).
- In its simplest radical form, it is \( 2\sqrt{3} \).
Examples
Example 1
If the area of a circle is \( 12\pi \) square inches, find the radius.
Solution:
\[
\pi r^2 = 12\pi \\
r^2 = 12 \\
r = \sqrt{12} \approx 3.464 \text{ inches}
\]
Example 2
Help Ryan simplify the square root of 12 to its lowest radical form.
Solution:
\[
\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3} = 2\sqrt{3}
\]
READ MORE:
Introduction
Finding the square root of 12 involves understanding both rational and irrational numbers, and utilizing various mathematical methods. The square root of 12 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 3.464. This introduction covers different methods to find the square root, including estimation, the long division method, and the Newton-Raphson method, providing a comprehensive understanding of the process.
- Estimation Method: Recognizes that the square root of 12 lies between the squares of 3 and 4 (9 and 16), providing a rough estimate.
- Long Division Method: A systematic approach similar to traditional division, allowing for digit-by-digit approximation.
- Newton-Raphson Method: An iterative numerical technique to refine an initial guess to a more accurate approximation.
Each method offers a unique approach to finding the square root, catering to different needs and levels of precision.
Table of Contents
Definition and Basic Understanding
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the number 12, its square root is approximately 3.464, an irrational number that cannot be precisely expressed as a fraction.
Methods to Find the Square Root of 12
Estimation Method
Estimate the value by recognizing it lies between two known squares. Since 12 is between the squares of 3 and 4 (9 and 16, respectively), its square root must be between 3 and 4.
Long Division Method
This method provides a systematic approach to find the square root digit by digit, similar to traditional long division.
Newton-Raphson Method
An iterative numerical technique that refines an initial guess to find better approximations of the square root.
Calculator Method
Using a calculator’s square root function is the most straightforward way to find the precise approximation of the square root.
Numerical Series or Sequences
Some advanced mathematical series or sequences converge to square roots based on their properties, offering another method of approximation.

Simplification of √12
To simplify √12, express 12 as a product of its prime factors: 12 = 2 × 2 × 3, then simplify to 2√3.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the simplified form of √12?
The simplified form of √12 is 2√3.
What is equivalent to the square root of 12?
Equivalent to the square root of 12 is the expression 2√3.
What cubed root equals 12?
No perfect cube root equals 12, as cube roots typically result from multiplying a number by itself three times.
Can you take the square root of 12?
Yes, you can take the square root of 12, resulting in an irrational number approximately equal to 3.464.
Is 12 a natural number?
Yes, 12 is a natural number, as it is a whole, positive number.
Solved Examples
Various solved examples illustrate the methods to find the square root of 12 using prime factorization, long division, and more.
Conclusion
Understanding how to find the square root of 12 enhances mathematical proficiency and aids in applications across various fields.

Definition and Basic Understanding
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical notation, the square root of a number \(x\) is written as \(\sqrt{x}\). The square root of 12, denoted as \(\sqrt{12}\), is an irrational number, which means it cannot be exactly expressed as a simple fraction.
To understand the square root of 12 more deeply, let's break it down:
- The symbol \(\sqrt{}\) is known as the radical symbol, and the number under the radical symbol is called the radicand.
- The square root of 12 can be simplified by expressing 12 as a product of its prime factors: \(12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3\). Using this factorization, we can simplify \(\sqrt{12}\) as follows:
\[\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 3} = \sqrt{4 \times 3} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{3} = 2\sqrt{3}\]
This shows that the simplest radical form of \(\sqrt{12}\) is \(2\sqrt{3}\).
In decimal form, \(\sqrt{12}\) is approximately equal to 3.464. This approximation is derived using methods such as long division or a calculator.
Steps to Approximate the Square Root of 12
- Estimation: Recognize that 12 lies between the perfect squares of 9 (which is \(3^2\)) and 16 (which is \(4^2\)), so \(\sqrt{12}\) is between 3 and 4.
- Prime Factorization: Break down 12 into its prime factors \(12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3\), then simplify to \(2\sqrt{3}\).
- Using a Calculator: Utilize a calculator's square root function to find a more precise value, resulting in approximately 3.464.
Properties of the Square Root of 12
- Irrational Number: \(\sqrt{12}\) is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be exactly represented as a fraction.
- Decimal Form: The decimal approximation of \(\sqrt{12}\) is 3.464, but this is an approximation and not exact.
- Radical Form: The simplest form of \(\sqrt{12}\) in terms of radicals is \(2\sqrt{3}\).
Understanding how to find and work with the square root of 12 is a fundamental mathematical skill that can be applied in various fields, from basic arithmetic to more advanced applications in science and engineering.
Methods to Find the Square Root of 12
Estimation Method
The estimation method involves recognizing that the square root of 12 lies between the square roots of 9 and 16, which are 3 and 4 respectively. By narrowing down the range, we estimate the square root of 12 to be approximately 3.5.
Long Division Method
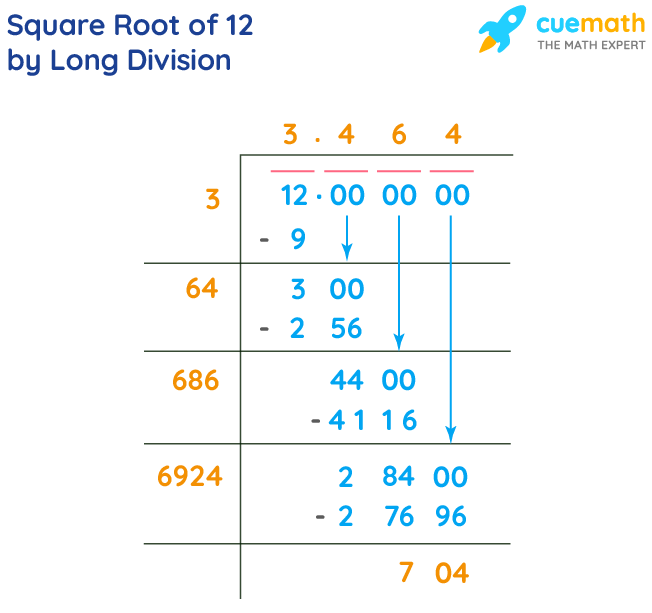
The long division method provides a step-by-step approach to finding the square root of a number. Here are the steps to find the square root of 12:
- Start by pairing the digits of 12 from right to left. For 12, we have only one pair: (12).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair. In this case, 32 = 9, which is less than 12.
- Subtract 9 from 12 to get 3, and bring down a pair of zeros, making it 300.
- Double the divisor (3) to get 6. Determine how many times 6 fits into 30 without exceeding it. The answer is 4 (6x4=24).
- Continue the process with the new pairs of zeros. The quotient obtained after several iterations will be the square root of 12, approximately 3.464.
Newton-Raphson Method
The Newton-Raphson method is an iterative numerical technique used to find successively better approximations to the roots (or zeroes) of a real-valued function. To find the square root of 12:
- Start with an initial guess, say x0 = 3.5.
- Use the formula: xn+1 = (xn + 12/xn) / 2.
- Iterate the process until the difference between successive approximations is less than the desired precision.
- The final approximation will be around 3.464.
Calculator Method
The simplest method to find the square root of 12 is by using a calculator. Most calculators have a square root function, which directly gives the result as approximately 3.464.
Numerical Series or Sequences
Advanced mathematical series, such as the Taylor series, can be used to approximate the square root of 12. These series involve expanding functions into an infinite sum of terms calculated from the values of its derivatives at a single point.
Simplification of √12
Simplifying the square root of 12 involves expressing it in its simplest radical form. Here are the steps to achieve this:
- Identify the factors of 12:
The factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
- Find the largest perfect square factor:
Among the factors, 4 is the largest perfect square.
- Rewrite 12 as a product of this factor:
12 can be expressed as 4 × 3.
- Apply the square root to both factors:
Using the property √(a × b) = √a × √b, we get:
√12 = √(4 × 3) = √4 × √3
- Simplify the square roots:
The square root of 4 is 2. Therefore:
√4 × √3 = 2√3
Thus, the simplified form of √12 is 2√3.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the simplified form of √12?
The simplified form of \( \sqrt{12} \) is \( 2\sqrt{3} \). This is achieved by expressing 12 as the product of its prime factors: 12 = 2 × 2 × 3, then simplifying to \( 2\sqrt{3} \).
What is the equivalent of the square root of 12?
The equivalent of the square root of 12 is the expression \( 2\sqrt{3} \), or approximately 3.464 in decimal form.
What cubed root equals 12?
No perfect cube root equals 12. The cube root of 12, denoted as \( \sqrt[3]{12} \), is an irrational number approximately equal to 2.289.
Can you take the square root of 12?
Yes, you can take the square root of 12, resulting in an irrational number approximately equal to 3.464.
Is 12 a natural number?
Yes, 12 is a natural number as it is a whole, positive number.
What is the square root of 12 rounded?
The square root of 12 rounded to different decimal places are:
- To the nearest tenth: 3.5
- To the nearest hundredth: 3.46
- To the nearest thousandth: 3.464
What two numbers fall between the square root of 12?
The square root of 12 lies between the numbers 3 and 4, as 12 lies between the squares of these two numbers (9 and 16, respectively).
Can there be two square roots of a number?
Yes, all positive real numbers have two square roots: one positive and one negative. The positive square root is often referred to as the principal square root. For example, the square roots of 9 are 3 and -3.

Solved Examples
Below are some solved examples to help understand the process of finding the square root of 12 and applying it in various mathematical contexts.
Example 1: Basic Calculation
Problem: Find the value of \( \sqrt{12} \).
Solution: The square root of 12 can be simplified by expressing 12 as a product of its prime factors: \( 12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \). Thus, \( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{4 \times 3} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{3} = 2\sqrt{3} \). Using the approximate value of \( \sqrt{3} \approx 1.732 \), we get \( 2 \times 1.732 = 3.464 \). So, \( \sqrt{12} \approx 3.464 \).
Example 2: Simplifying Expressions
Problem: Simplify \( 3\sqrt{12} + 2\sqrt{3} \).
Solution: First, simplify \( \sqrt{12} \) as \( 2\sqrt{3} \). Then the expression becomes \( 3(2\sqrt{3}) + 2\sqrt{3} = 6\sqrt{3} + 2\sqrt{3} \). Combine the like terms to get \( (6 + 2)\sqrt{3} = 8\sqrt{3} \).
Example 3: Geometric Application
Problem: Find the radius of a circle with an area of \( 12\pi \) cm2.
Solution: The formula for the area of a circle is \( \pi r^2 \). Given \( \pi r^2 = 12\pi \), we can cancel \( \pi \) from both sides to get \( r^2 = 12 \). Taking the square root of both sides, \( r = \sqrt{12} \). Using the simplified form, \( r = 2\sqrt{3} \approx 3.464 \) cm. Therefore, the radius is approximately 3.464 cm.
Example 4: Expression Evaluation
Problem: Evaluate \( 3\sqrt{12} + 6\sqrt{3} \).
Solution: Substitute \( \sqrt{12} = 2\sqrt{3} \) into the expression: \( 3(2\sqrt{3}) + 6\sqrt{3} = 6\sqrt{3} + 6\sqrt{3} = 12\sqrt{3} \). The final answer is \( 12\sqrt{3} \).
Example 5: Simplification
Problem: Simplify \( \frac{\sqrt{12}}{\sqrt{3}} \).
Solution: Using the property \( \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} = \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} \), we get \( \frac{\sqrt{12}}{\sqrt{3}} = \sqrt{\frac{12}{3}} = \sqrt{4} = 2 \).
Conclusion
Finding the square root of 12 involves various methods, each offering unique insights and levels of precision. Whether through estimation, the long division method, the Newton-Raphson method, using a calculator, or leveraging numerical series, understanding these techniques enhances mathematical proficiency. By simplifying √12 to 2√3, we appreciate the relationship between prime factors and their roots, reinforcing foundational concepts in mathematics.
Mastering these methods not only aids in solving specific problems but also develops critical thinking and analytical skills applicable across various fields. The ability to approximate and simplify square roots is a valuable tool in both academic and real-world scenarios, facilitating a deeper comprehension of mathematical principles and their applications.
In summary, exploring the square root of 12 enriches our mathematical toolkit, enabling us to approach complex problems with confidence and precision. Whether you're a student, educator, or enthusiast, the journey through these methods offers valuable learning experiences and practical knowledge.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 12: Sqrt(12)
READ MORE:
Căn Bậc Hai của 12 = ? Hãy đơn giản hóa từng bước một