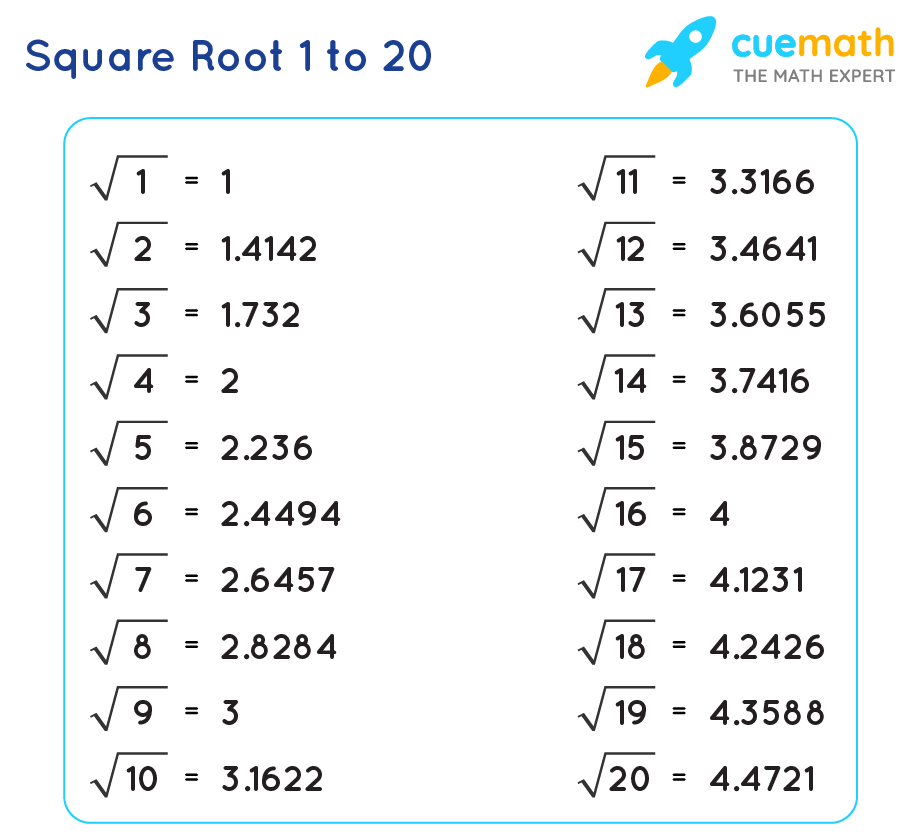
Topic what is the square root of 12 simplified: Understanding the simplified form of the square root of 12 is essential in various mathematical contexts. This article will guide you through the process of simplifying √12, demonstrating how it can be expressed as 2√3. We'll also explore its decimal approximation and discuss its significance in different applications.
Table of Content
- Simplifying the Square Root of 12
- Introduction to Square Roots
- What is the Square Root of 12?
- Methods to Simplify the Square Root of 12
- Prime Factorization Method
- Using Perfect Squares
- Decimal Representation of Square Root of 12
- Applications and Examples
- Common Misconceptions
- FAQs on Square Root of 12
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 12, giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm và ứng dụng thực tế của √12.
Simplifying the Square Root of 12
The square root of 12 can be simplified by expressing it in its simplest radical form. Here's a step-by-step explanation:
Steps to Simplify √12
- Factorize 12 into its prime factors: \(12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3\).
- Group the factors into pairs of equal factors: \(2 \times 2\).
- Take one factor from each pair out of the square root: \(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{4 \times 3} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{3} = 2\sqrt{3}\).
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 12 is:
\[\sqrt{12} = 2\sqrt{3}\]
Decimal Form
In decimal form, the square root of 12 is approximately:
\[\sqrt{12} \approx 3.464\]
Key Points
- The simplified form of \(\sqrt{12}\) is \(2\sqrt{3}\).
- It is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- In decimal form, it is approximately 3.464.
Example Problems
-
Example 1: Simplify \(\sqrt{18}\).
Solution: \(\sqrt{18} = \sqrt{9 \times 2} = \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{2} = 3\sqrt{2}\).
-
Example 2: Simplify \(2\sqrt{12} + 9\sqrt{3}\).
Solution: \(2\sqrt{12} = 2 \times 2\sqrt{3} = 4\sqrt{3}\), thus \(4\sqrt{3} + 9\sqrt{3} = 13\sqrt{3}\).
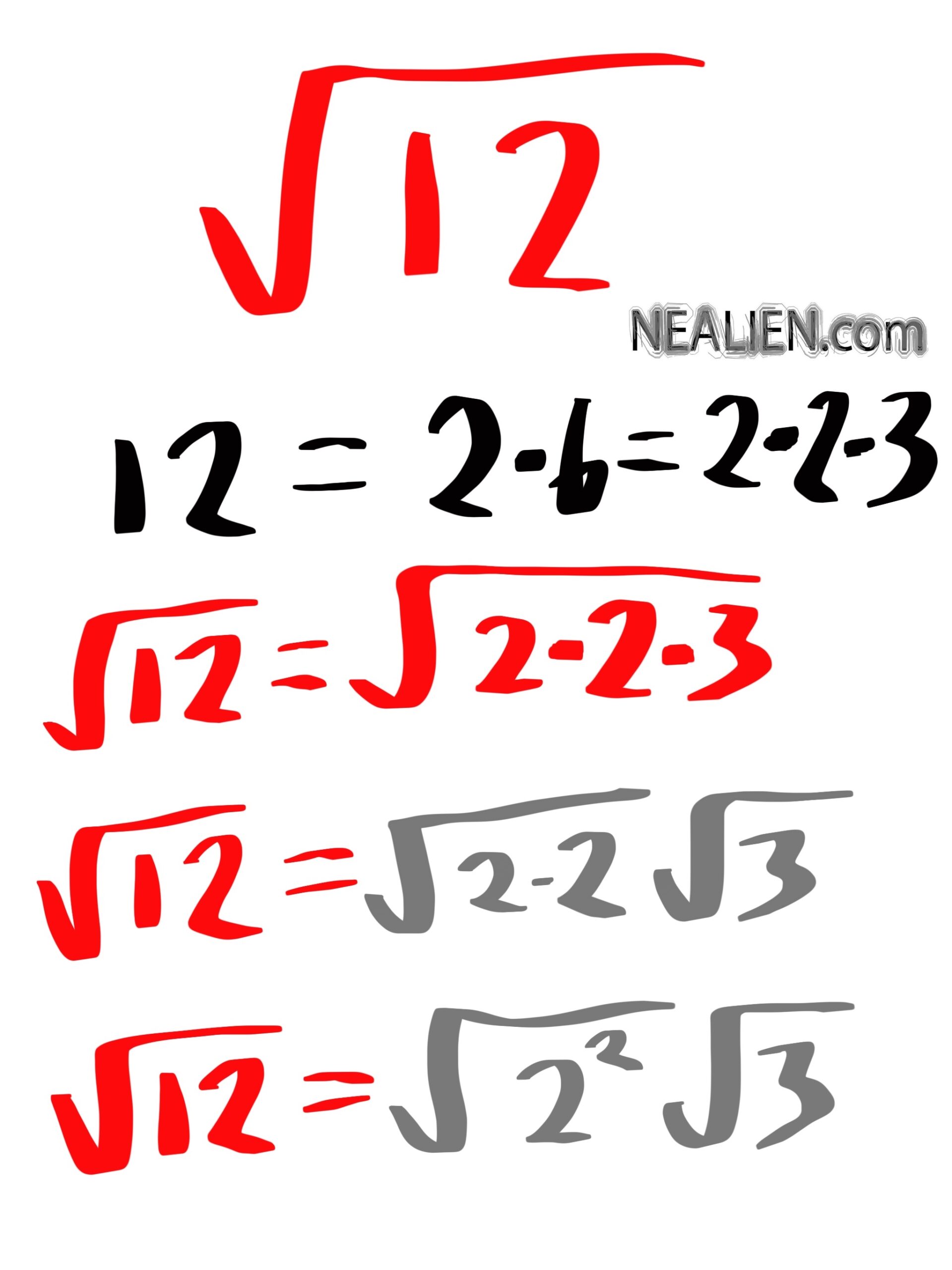
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 12 can be simplified for easier calculations and better understanding. Simplifying square roots involves expressing the number under the radical sign in its simplest form, often by factoring it into prime numbers.
Here is a detailed step-by-step process for simplifying the square root of 12:
- First, factor 12 into its prime factors: 12 = 2 × 2 × 3.
- Next, group the factors into pairs: √12 = √(4 × 3).
- Then, take the square root of the perfect square: √(4 × 3) = √4 × √3.
- Simplify further by calculating the square root of 4: √4 = 2.
- The simplified form is: 2√3.
Therefore, the square root of 12, in its simplest radical form, is 2√3. Understanding and simplifying square roots are essential skills in algebra and higher-level mathematics.
What is the Square Root of 12?
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 12 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating.
Mathematically, the square root of 12 can be written as:
\(\sqrt{12}\)
To find the simplified form of \(\sqrt{12}\), we can use the properties of square roots and factorization.
Simplifying the Square Root of 12
We start by expressing 12 as a product of its prime factors:
12 = 2 × 2 × 3
Since \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\), we can split the square root of 12 into:
\(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{4 \times 3}\)
We know that \(\sqrt{4} = 2\), so we can further simplify:
\(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{4 \times 3} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{3} = 2\sqrt{3}\)
Therefore, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{12}\) is:
\(\sqrt{12} = 2\sqrt{3}\)
Methods to Simplify the Square Root of 12
Simplifying the square root of 12 involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and using properties of square roots. Below are two common methods to simplify the square root of 12:
Prime Factorization Method
To simplify using prime factorization, follow these steps:
- Factorize 12 into its prime factors:
12 = 2 × 2 × 3
- Group the prime factors into pairs:
12 = (2 × 2) × 3
- Apply the property of square roots, which states :
- Simplify further knowing that
Using Perfect Squares
This method simplifies
- Identify the perfect square factors of 12. Here, 4 is a perfect square:
12 = 4 × 3
- Rewrite the square root of 12 as the product of the square roots of its factors:
12 =(4 × 3) =4 ×3 - Simplify knowing that
4 = 2:12 = 23
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 12 is
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is an efficient way to simplify the square root of a number by breaking it down into its prime factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide to simplify the square root of 12 using prime factorization:
- Find the Prime Factors:
First, find the prime factors of 12. We can start by dividing 12 by the smallest prime number:
- 12 ÷ 2 = 6
- 6 ÷ 2 = 3
- 3 is a prime number
So, the prime factorization of 12 is: \( 12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \)
- Group the Prime Factors:
Next, group the prime factors in pairs:
- \( 12 = (2 \times 2) \times 3 \)
- Take the Square Root:
Take the square root of each group of factors:
- \( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 3} \)
- \( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 3} \)
- \( \sqrt{12} = 2 \times \sqrt{3} \)
So, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{12} \) is \( 2\sqrt{3} \).
By using the prime factorization method, we find that the square root of 12 simplifies to \( 2\sqrt{3} \).

Using Perfect Squares
To simplify the square root of 12 using perfect squares, follow these steps:
- First, identify the perfect squares that are factors of 12. The perfect squares less than 12 are 1, 4, and 9.
- Determine which of these perfect squares is the largest factor of 12. In this case, it is 4, since 4 is a factor of 12 and 9 is not.
- Express 12 as a product of this perfect square and another number: \(12 = 4 \times 3\).
- Now, use the property of square roots that states \(\sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b}\). Apply this property to \(\sqrt{12}\):
\(\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{4 \times 3} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{3}\). - Since \(\sqrt{4} = 2\), the expression simplifies to:
\(\sqrt{12} = 2 \times \sqrt{3}\).
Thus, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{12}\) using perfect squares is \(2\sqrt{3}\).
Decimal Representation of Square Root of 12
The square root of 12, denoted as \( \sqrt{12} \), is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating.
When expressed in decimal form, the square root of 12 is approximately 3.464. This value is often rounded to different decimal places depending on the required precision:
- To one decimal place: 3.5
- To two decimal places: 3.46
- To three decimal places: 3.464
- To four decimal places: 3.4641
The process to find this decimal representation typically involves a method such as the long division method or using a calculator. Here's a step-by-step outline of how the long division method works:
- Step 1: Pair the digits of the number from right to left. For 12, it's 12.00 (pairs are 12 and 00).
- Step 2: Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 12. This is 3, since \( 3^2 = 9 \).
- Step 3: Subtract the square from the number: 12 - 9 = 3. Bring down the next pair of zeros to make it 300.
- Step 4: Double the quotient (3) and use it as a new divisor. So, we have 6_ (where _ is the next digit we need to find).
- Step 5: Find a digit (d) such that \( 60d \times d \leq 300 \). This digit is 4, since \( 604 \times 4 = 2416 \).
- Step 6: Repeat the process to add more decimal places as needed.
While we often stop after a few iterations for practical purposes, in theory, you can continue this process indefinitely to get more precise decimal places.
Thus, the square root of 12 in its decimal form is approximately 3.464, a value frequently used in various mathematical applications.
Applications and Examples
The square root of 12, simplified to \(2\sqrt{3}\), has various applications in different fields of science and mathematics. Below are a few examples that illustrate its usage:
-
Geometry:
In geometry, the square root of 12 can be used to determine the length of the diagonal in a rectangle with sides of lengths 2 and \(2\sqrt{3}\). Using the Pythagorean theorem, the diagonal \(d\) can be calculated as:
\[
d = \sqrt{(2)^2 + (2\sqrt{3})^2} = \sqrt{4 + 12} = \sqrt{16} = 4
\] -
Physics:
In physics, the square root of 12 might appear in equations involving periodic motion or wave functions where certain parameters need to be simplified. For example, if the amplitude of a wave is \(2\sqrt{3}\) units, the energy related to the wave can be determined using relevant formulas.
-
Engineering:
In engineering, particularly in structural analysis, the square root of 12 can be useful in calculating forces or moments when dealing with non-standard shapes. For instance, if a triangular component of a structure has a height of \(2\sqrt{3}\) meters and a base of 2 meters, the area \(A\) can be found as:
\[
A = \frac{1}{2} \times base \times height = \frac{1}{2} \times 2 \times 2\sqrt{3} = 2\sqrt{3} \, \text{square meters}
\] -
Mathematics:
In pure mathematics, the square root of 12 is often encountered in algebraic expressions and simplifications. For example, solving quadratic equations or evaluating integrals where the expression \(2\sqrt{3}\) naturally occurs.
These examples show that understanding and simplifying the square root of 12 is not just an academic exercise but has real-world applications that are crucial in various scientific and engineering contexts.
Common Misconceptions
Understanding the square root of 12 can sometimes lead to misconceptions. Here are some common ones, along with clarifications:
-
Misconception 1: The square root of 12 is a rational number.
The square root of 12 is actually an irrational number. This is because its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. The simplified radical form is \(2\sqrt{3}\), and since \(\sqrt{3}\) is irrational, \(2\sqrt{3}\) is also irrational.
-
Misconception 2: \( \sqrt{12} \) can be simplified to a whole number.
The square root of 12 cannot be simplified to a whole number. The closest whole numbers are 3 and 4, but \(\sqrt{12}\) is approximately 3.464, which lies between these values.
-
Misconception 3: \( \sqrt{-12} \) has the same properties as \( \sqrt{12} \).
\( \sqrt{-12} \) is not a real number, as the square root of a negative number results in an imaginary number. In contrast, \( \sqrt{12} \) is a real number.
-
Misconception 4: \( \sqrt{12} \) is the same as \( \frac{\sqrt{12}}{2} \).
This is incorrect. \( \sqrt{12} \) simplifies to \( 2\sqrt{3} \), whereas \( \frac{\sqrt{12}}{2} \) simplifies to \( \sqrt{3} \). They are not the same value.
-
Misconception 5: The simplified radical form of \( \sqrt{12} \) is 4.
While 4 is a perfect square, it is not related to the square root of 12 in terms of simplification. The correct simplified radical form of \( \sqrt{12} \) is \( 2\sqrt{3} \).
FAQs on Square Root of 12
Here are some frequently asked questions about the square root of 12:
-
What is the square root of 12?
The square root of 12 is represented as \( \sqrt{12} \). In its simplest radical form, it is \( 2\sqrt{3} \).
-
Is the square root of 12 a rational or irrational number?
The square root of 12 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
-
How do you simplify \( \sqrt{12} \)?
To simplify \( \sqrt{12} \), you can use prime factorization. The factors of 12 are 2, 2, and 3. Grouping the prime factors, you get \( \sqrt{4 \times 3} \), which simplifies to \( 2\sqrt{3} \).
-
What is the decimal representation of the square root of 12?
The decimal representation of \( \sqrt{12} \) is approximately 3.4641.
-
Can the square root of 12 be written as a fraction?
Since \( \sqrt{12} \) is an irrational number, it cannot be exactly written as a fraction. However, it can be approximated as a fraction, for example, 3.4641 or 3.5/1.
-
How is the square root of 12 used in real life?
The square root of 12 can be used in various applications such as in geometry for calculating areas and distances, in physics for solving equations involving square roots, and in engineering for determining measurements.
Conclusion
Simplifying the square root of 12 is a fundamental skill that enhances our understanding of square roots and their properties. By breaking down the number 12 into its prime factors, we can easily simplify the expression to make it more manageable and insightful.
To recap the steps we have covered:
- Identify the prime factors of 12: \( 12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3 \).
- Group the prime factors in pairs: \( 12 = (2 \times 2) \times 3 \).
- Take the square root of each group: \( \sqrt{12} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 3} = \sqrt{4 \times 3} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{3} \).
- Simplify the square root of the perfect square: \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \), thus \( \sqrt{12} = 2\sqrt{3} \).
The simplified form of the square root of 12 is \( 2\sqrt{3} \). This result can be useful in various mathematical applications, including solving equations, geometry, and even in real-world scenarios where such calculations are needed.
Understanding how to simplify square roots by using prime factorization and recognizing perfect squares allows us to handle more complex mathematical problems with ease and confidence. It is a valuable skill that can be applied to many areas of mathematics and beyond.
We hope this guide has provided a clear and detailed explanation of how to simplify the square root of 12. By following these steps, anyone can master the process and apply it to other numbers as well.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 12, giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm và ứng dụng thực tế của √12.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 12: √12
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tính và đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 12, giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về phương pháp và ứng dụng của nó.
Căn Bậc Hai của 12