Topic square root examples: Explore the world of square roots with our comprehensive guide. Discover simple and advanced examples of calculating square roots, and learn how they are applied in various real-life situations and mathematical problems. Whether you're a student or a curious learner, mastering square roots will enhance your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities.
Table of Content
- Square Root Examples
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Basic Examples of Square Roots
- Calculating Square Roots by Hand
- Using Calculator for Square Roots
- Square Root of Fractions and Decimals
- Real-Life Examples of Square Roots
- Applications of Square Roots in Geometry
- Square Roots in Algebraic Equations
- Advanced Topics in Square Roots
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá căn bậc hai với Mr. J trong video này! Hiểu rõ hơn về căn bậc hai qua các ví dụ dễ hiểu và chi tiết.
Square Root Examples
Understanding square roots is essential in mathematics. Here are detailed explanations and examples to help you grasp the concept better.
Definition
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root is denoted by the symbol √.
Properties of Square Roots
- A perfect square number has an integer square root.
- Both positive and negative numbers can be squared to give the same result (e.g., \(5^2 = 25\) and \((-5)^2 = 25\)).
- The square root of a negative number is undefined in the set of real numbers.
Examples of Square Roots
- The square root of 16 is 4 because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- The square root of 25 is 5 because \(5 \times 5 = 25\), but also \(-5 \times -5 = 25\).
- The square root of 49 is 7 because \(7 \times 7 = 49\).
Square Root Formula
The formula to find the square root of a number \(x\) is given by:
\(\sqrt{x} = y\)
where \(y^2 = x\).
Methods to Calculate Square Roots
-
Repeated Subtraction Method
Subtract consecutive odd numbers from the given number until you reach zero. The number of subtractions performed is the square root.
Example: Calculate the square root of 25:
25 - 1 = 24 24 - 3 = 21 21 - 5 = 16 16 - 7 = 9 9 - 9 = 0 The number of subtractions is 5, so the square root of 25 is 5.
-
Prime Factorization Method
Factorize the number into prime factors, pair them, and multiply one number from each pair.
Example: Calculate the square root of 144:
144 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 Pairs: (2 × 2), (2 × 2), (3 × 3) Square root: 2 × 2 × 3 = 12 -
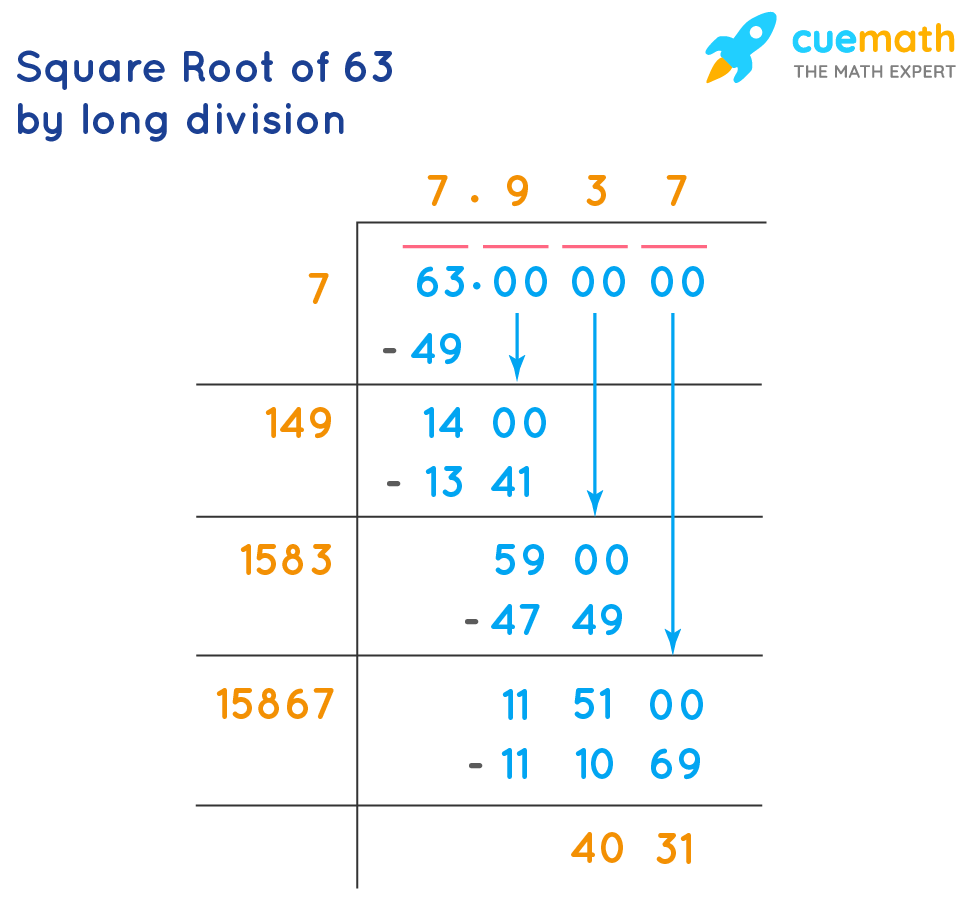
Long Division Method
Use long division to find the square root by repeatedly dividing and averaging.
Examples of Solving Equations with Square Roots
Square roots are used to solve various algebraic equations:
-
Example: Solve \(x^2 = 25\)
Solution: \(x = \pm \sqrt{25} = \pm 5\)
-
Example: Solve \(x^2 - 9 = 0\)
Solution: \(x^2 = 9\)
\(x = \pm \sqrt{9} = \pm 3\)
Square Roots of Non-Perfect Squares
Non-perfect squares have square roots that are not integers:
- The square root of 2 is approximately 1.414.
- The square root of 3 is approximately 1.732.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental mathematical operations that find widespread use in various fields, from basic arithmetic to advanced calculus and engineering. Understanding square roots is crucial for solving equations involving squares and for understanding the concept of inverse operations.
Here are the key points covered in an introduction to square roots:
- Definition: A square root of a number x is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives x. It is denoted by √x.
- Basic Examples: Learning how to calculate square roots of perfect squares like 4, 9, 16, etc.
- Properties: Properties such as the square root of a product and the square root of a quotient.
- Real-Life Applications: Practical uses of square roots in fields such as geometry, physics, and computer science.
- Calculation Methods: Techniques for calculating square roots manually or using calculators and computers.
Mastering square roots lays the foundation for understanding more complex mathematical concepts and their applications in everyday life.
Basic Examples of Square Roots
Understanding basic examples of square roots helps in grasping the concept and applying it effectively:
- Perfect Squares: Square roots of perfect squares like √4, √9, √16, etc.
- Decimal Numbers: Square roots of decimal numbers such as √0.25, √1.44, √2.25, etc.
- Fractions: Calculating square roots of fractions like √(1/4), √(9/16), √(16/25), etc.
- Approximations: Approximating square roots of non-perfect squares like √2, √3, √5, etc.
- Negative Numbers: Understanding the concept of imaginary numbers when dealing with square roots of negative numbers.
By mastering these basic examples, you will build a solid foundation for more complex mathematical operations involving square roots.
Calculating Square Roots by Hand
Calculating square roots manually involves several methods depending on the complexity of the number:
- Estimation Method: Approximating the square root by finding the closest perfect squares.
- Long Division Method: Using long division to iteratively find the square root of a number.
- Prime Factorization Method: Decomposing the number into its prime factors to simplify the square root calculation.
- Newton's Method: Iterative approximation method that converges to the square root with successive calculations.
Each method provides a different approach to calculating square roots manually, offering flexibility based on the mathematical background and preference of the individual.
Using Calculator for Square Roots
Calculating square roots using a calculator is straightforward and efficient:
- Basic Calculators: Most basic calculators have a square root function denoted by √ or "sqrt".
- Scientific Calculators: Scientific calculators offer more precise square root calculations and can handle larger numbers and decimals.
- Steps: Enter the number you want to find the square root of, then press the square root button to get the result.
- Decimal Places: Adjust the settings or round the result to the desired number of decimal places as needed.
Using a calculator simplifies the process of finding square roots, making it accessible for quick calculations in various mathematical and real-life contexts.
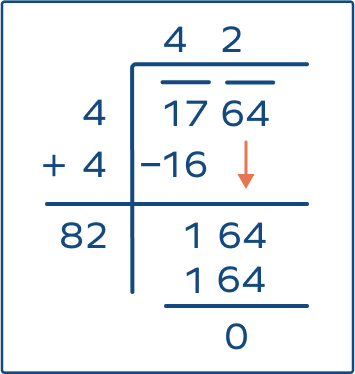
Square Root of Fractions and Decimals
Calculating square roots of fractions and decimals involves specific considerations:
- Fractions: To find the square root of a fraction, calculate the square root of the numerator and the square root of the denominator separately.
- Example: √(4/9) = (√4) / (√9) = 2/3.
- Decimals: Square roots of decimals can be found using calculators or by converting them into fractions first.
- Example: √0.25 = √(25/100) = 0.5.
- Approximations: For non-perfect squares, express the result as a decimal or fraction to the desired accuracy.
Understanding how to handle fractions and decimals in square root calculations expands your ability to solve mathematical problems involving various types of numbers.
Real-Life Examples of Square Roots
Square roots are applied in various real-life scenarios, showcasing their practical significance:
- Construction: Calculating square roots helps in determining dimensions and areas of structures.
- Finance: In financial modeling, square roots are used in calculations related to risk assessment and portfolio management.
- Engineering: Engineers use square roots to analyze vibrations, electrical circuits, and signal processing.
- Physics: In physics, square roots are essential for calculating velocities, energies, and forces in equations involving quadratic relationships.
- Technology: Computer graphics and image processing utilize square roots for pixel intensity calculations and spatial transformations.
Understanding how square roots are applied in these contexts enhances problem-solving skills and underscores their importance in everyday applications.
Applications of Square Roots in Geometry
Square roots play a crucial role in geometry, particularly in various geometric calculations and shapes:
- Pythagorean Theorem: Finding the lengths of sides in right triangles involves square roots, where a² + b² = c².
- Area and Perimeter: Calculating the area and perimeter of squares, rectangles, and circles often requires square roots.
- Distance Formula: Determining the distance between two points (x₁, y₁) and (x₂, y₂) in a coordinate plane involves square roots: √((x₂ - x₁)² + (y₂ - y₁)²).
- Volume: Finding the volume of three-dimensional shapes like cubes and spheres involves cube roots, which are related to square roots.
- Geometric Mean: Calculating the geometric mean of two numbers is directly related to their square roots.
Mastering the application of square roots in geometry enhances understanding of geometric concepts and facilitates accurate calculations in various geometric scenarios.
Square Roots in Algebraic Equations
Square roots are integral in solving algebraic equations, providing solutions to various types of equations:
- Quadratic Equations: Solving equations of the form ax² + bx + c = 0 involves taking square roots to find the values of x.
- Exponential Equations: Equations where variables are in exponents often require square roots to isolate the variable.
- Systems of Equations: Square roots can be used in systems of equations to find intersections or common solutions.
- Transformations: Algebraic transformations often involve square roots, such as in shifting and scaling operations.
- Complex Numbers: Square roots are used extensively in complex number operations, particularly in solving equations involving imaginary numbers.
Understanding how to apply square roots in algebraic equations enhances problem-solving abilities and provides insights into the relationships between variables and their solutions.
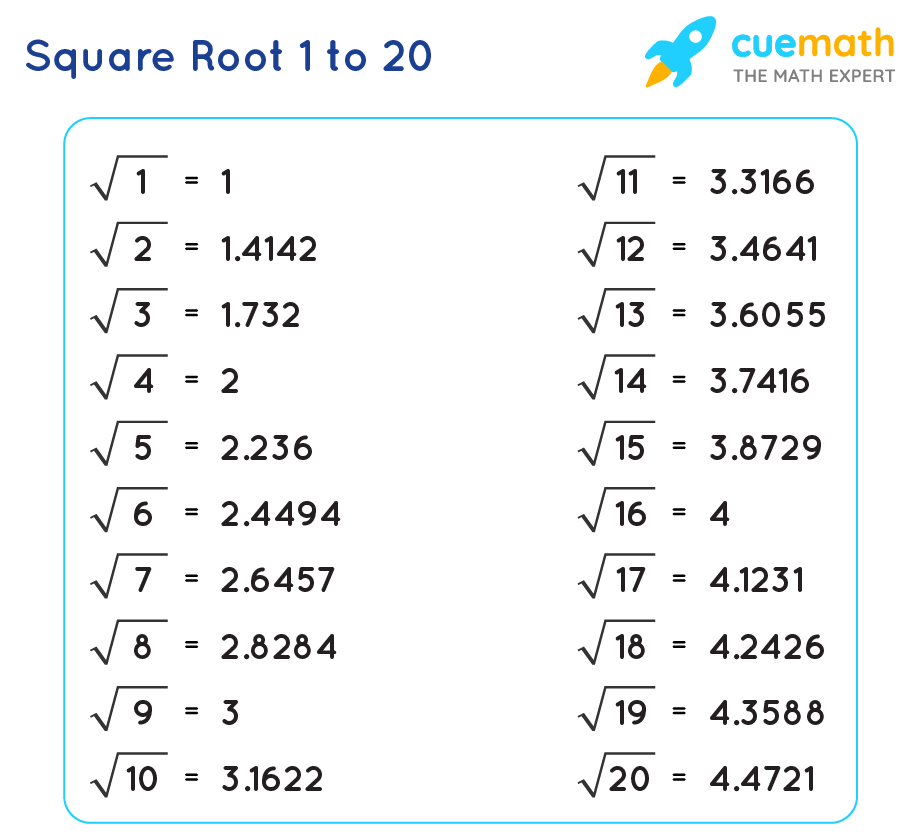
Advanced Topics in Square Roots
In this section, we will explore some advanced topics related to square roots, including properties, complex numbers, and applications in higher mathematics. Understanding these concepts requires a solid grasp of basic square root principles.
Properties of Square Roots
- Non-Negative Property: For any non-negative real number \( a \), the square root \( \sqrt{a} \) is also non-negative.
- Product Property: For any non-negative real numbers \( a \) and \( b \), \( \sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b} \).
- Quotient Property: For any non-negative real numbers \( a \) and \( b \) (with \( b \neq 0 \)), \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \).
- Power Property: For any non-negative real number \( a \) and positive integer \( n \), \( \sqrt{a^n} = a^{\frac{n}{2}} \).
Square Roots of Complex Numbers
To find the square root of a complex number \( z = a + bi \) (where \( a \) and \( b \) are real numbers), we use the following method:
- Convert \( z \) to polar form: \( z = r(\cos \theta + i \sin \theta) \), where \( r = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \) and \( \theta = \tan^{-1}(\frac{b}{a}) \).
- Apply the formula for the square root in polar form: \[ \sqrt{z} = \sqrt{r} \left( \cos \frac{\theta}{2} + i \sin \frac{\theta}{2} \right) \]
- Convert the result back to rectangular form if necessary.
Applications in Higher Mathematics
Square roots play a crucial role in various fields of higher mathematics, including:
- Quadratic Equations: The solutions to a quadratic equation \( ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \) involve square roots in the quadratic formula: \[ x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a} \]
- Eigenvalues and Eigenvectors: In linear algebra, the square root of matrices and their eigenvalues are often used in solving systems of linear equations and in principal component analysis.
- Probability and Statistics: The standard deviation, a measure of the spread of a set of values, is the square root of the variance.
- Complex Analysis: The study of functions of a complex variable often involves the square roots of complex numbers and their properties.
Special Functions Involving Square Roots
Several special functions in mathematics involve square roots, including:
- Bessel Functions: These functions, which are solutions to Bessel's differential equation, often include terms with square roots.
- Legendre Polynomials: These polynomials, which are solutions to Legendre's differential equation, can also involve square roots.
Table of Square Root Identities
| Identity | Description |
|---|---|
| \(\sqrt{a^2} = |a|\) | The square root of a squared number is the absolute value of the number. |
| \(\sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\) | The product property of square roots. |
| \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\) | The quotient property of square roots. |
| \(\sqrt{a^2 + b^2}\) | Often used in the Pythagorean theorem for finding the hypotenuse of a right triangle. |
Khám phá căn bậc hai với Mr. J trong video này! Hiểu rõ hơn về căn bậc hai qua các ví dụ dễ hiểu và chi tiết.
Căn bậc hai là gì? | Toán học với Mr. J
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu về căn bậc hai và căn bậc ba với Mr. J! Video này cung cấp các ví dụ minh họa và giải thích chi tiết về hai khái niệm quan trọng trong toán học.
Căn bậc hai và Căn bậc ba | Toán học với Mr. J