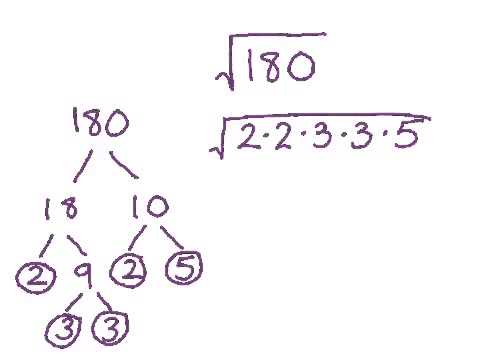Topic 40 square root simplified: Discover how to simplify the square root of 40 through various methods including prime factorization, long division, and more. This comprehensive guide will provide clear steps and examples to help you understand and master the process of simplifying √40.
Table of Content
- Simplifying the Square Root of 40
- Introduction
- Simplifying the Square Root of 40
- Prime Factorization of 40
- Step-by-Step Simplification Process
- Pairing Prime Factors
- Final Simplified Form
- Visual Representation of Simplification
- Applications of Simplified Square Roots
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Practice Problems
- Advanced Techniques
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để biết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 40. Học cách phân tích thừa số nguyên tố và áp dụng các kỹ thuật để giải quyết vấn đề một cách chính xác và nhanh chóng.
Simplifying the Square Root of 40
To simplify the square root of 40, we need to express it in its simplest radical form. This process involves factoring the number under the square root into its prime factors and then simplifying.
Understanding Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because \( 3 \times 3 = 9 \).
Prime Factorization Method
Let's simplify \( \sqrt{40} \) using the prime factorization method:
- Find the prime factors of 40.
- Express 40 as a product of its prime factors.
- Simplify the square root by grouping the prime factors.
First, we find the prime factors of 40:
- 40 is divisible by 2: \( 40 \div 2 = 20 \)
- 20 is divisible by 2: \( 20 \div 2 = 10 \)
- 10 is divisible by 2: \( 10 \div 2 = 5 \)
- 5 is a prime number.
So, the prime factorization of 40 is:
\[
40 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 = 2^3 \times 5
\]
Now, we simplify the square root:
\[
\sqrt{40} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 5}
\]
We can pair the factors of 2 to simplify:
\[
\sqrt{2^3 \times 5} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 2 \times 5} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{2 \times 5} = 2 \sqrt{10}
\]
Therefore, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{40} \) is:
\[
\sqrt{40} = 2 \sqrt{10}
\]

READ MORE:
Introduction
Simplifying the square root of 40 involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and expressing it in its simplest radical form. The square root of 40 is not a perfect square, which means it cannot be simplified to a whole number. However, it can be expressed in a simplified radical form for easier computation and understanding.
The square root of 40 can be written as:
\[ \sqrt{40} \]
To simplify this, we need to factorize 40 into its prime factors. The prime factorization of 40 is:
\[ 40 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 \]
Group the prime factors into pairs:
\[ \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 5)} \]
Simplify the pairs of factors:
\[ \sqrt{(2^2) \times (2 \times 5)} = 2 \sqrt{10} \]
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 40 is:
\[ \sqrt{40} = 2 \sqrt{10} \]
The decimal form of the square root of 40 is approximately:
\[ \sqrt{40} \approx 6.3246 \]
Understanding how to simplify square roots is crucial for solving various mathematical problems, making complex calculations more manageable, and providing a foundation for more advanced mathematical concepts.
Simplifying the Square Root of 40
The square root of 40 can be simplified using the prime factorization method. This method involves breaking down the number 40 into its prime factors and then simplifying the square root. Let's go through the steps:
- Prime Factorization: Start by finding the prime factors of 40. The prime factorization of 40 is:
\( 40 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 \) - Grouping Prime Factors: Next, group the prime factors into pairs:
\( 40 = (2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 5 \) - Applying the Square Root: Apply the square root to each group of prime factors. Remember that the square root of a pair of the same number is that number:
\( \sqrt{40} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 5} \)
\( \sqrt{40} = 2 \sqrt{2 \times 5} \) - Simplify the Expression: Finally, simplify the expression under the radical:
\( \sqrt{40} = 2 \sqrt{10} \)
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 40 is \( 2 \sqrt{10} \).
Prime Factorization of 40
The prime factorization method is a systematic way to simplify the square root of a number by expressing it as a product of its prime factors. Let's go through the steps to simplify the square root of 40 using prime factorization.
- First, identify the prime factors of 40. The prime factorization of 40 is:
\[
40 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5
\] - Group the prime factors into pairs. Since we are dealing with square roots, we look for pairs of the same factors:
\[
40 = (2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 5
\] - Take the square root of each pair of prime factors. Each pair of the same factor can be taken out of the square root as a single factor:
\[
\sqrt{40} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 5} = 2 \times \sqrt{2 \times 5}
\] - Simplify the remaining expression inside the square root:
\[
\sqrt{40} = 2 \times \sqrt{10}
\]
Thus, the simplest form of the square root of 40 is \(2\sqrt{10}\).
This method is efficient and provides an exact form of the square root, making it easier to understand and work with in further mathematical calculations.
Step-by-Step Simplification Process
In this section, we will walk through the process of simplifying the square root of 40 using step-by-step instructions. This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and simplifying the radical expression.
- List the Prime Factors: The first step is to find the prime factors of 40. The prime factorization of 40 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 5.
- Group the Prime Factors: Next, group the prime factors into pairs of the same number. For 40, this looks like 22 × 2 × 5.
- Simplify the Radical: Take the square root of the grouped factors. The square root of 22 is 2. The remaining factors inside the square root are 2 and 5. Therefore, √40 = 2√(2 × 5) = 2√10.
- Final Simplified Form: The simplest radical form of the square root of 40 is 2√10.
By following these steps, you can simplify the square root of 40 efficiently. The simplified form, 2√10, is the exact form, while the decimal approximation of √40 is approximately 6.3246.
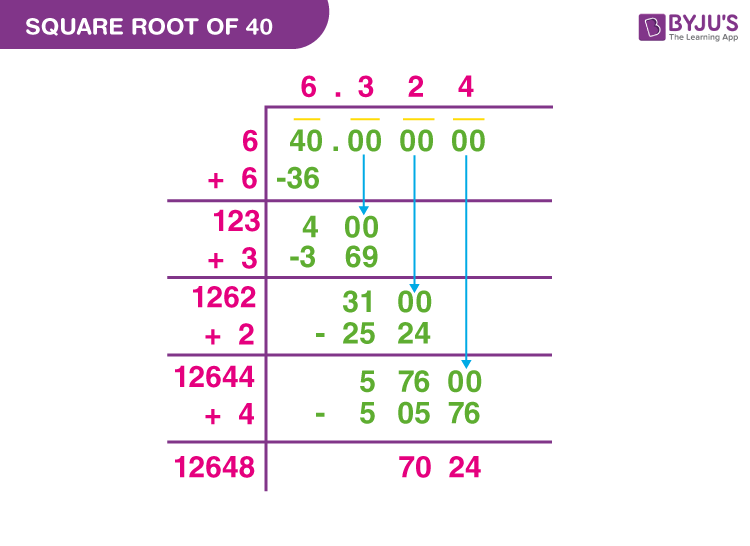
Pairing Prime Factors
To simplify the square root of 40 using the pairing prime factors method, we need to follow a few steps. This method is beneficial because it breaks down the number into its prime factors, making it easier to identify pairs and simplify the square root.
- Prime Factorization: Begin by finding the prime factors of 40. The prime factorization of 40 is:
- 40 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 5
- Group the Pairs: Next, group the prime factors into pairs of the same number:
- √(2 × 2 × 2 × 5) = √((2 × 2) × 2 × 5)
- Simplify the Pairs: Apply the square root to the paired numbers. The square root of a paired number is the number itself:
- √((2 × 2) × 2 × 5) = 2√(2 × 5)
- Combine the Results: Multiply the simplified pairs and any remaining factors under the square root:
- 2√10
Thus, the simplified form of the square root of 40 is 2√10. This method highlights the importance of identifying and pairing prime factors to simplify square roots effectively.
Final Simplified Form
To find the final simplified form of the square root of 40, follow these steps:
- Identify the prime factors of 40:
- Prime factorization of 40: \(40 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5\)
- Group the prime factors into pairs:
- \(40 = (2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 5\)
- Simplify the square root by taking the square root of each pair and leaving the remaining factors inside the radical:
- \(\sqrt{40} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 5} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 2 \times 5}\)
- Since \(\sqrt{2^2} = 2\), we have \(\sqrt{40} = 2\sqrt{2 \times 5} = 2\sqrt{10}\)
Thus, the final simplified form of the square root of 40 is:
\(\sqrt{40} = 2\sqrt{10}\)
This result indicates that the square root of 40, when expressed in its simplest radical form, is \(2\sqrt{10}\).
Visual Representation of Simplification
To visually represent the simplification of the square root of 40, we can break down the process step-by-step using a geometric interpretation. Here's a detailed illustration:
1. Start with the number 40:
- Visualize a square with an area of 40 square units. Since 40 is not a perfect square, the side length will be an irrational number.
2. Prime Factorization:
- First, factorize 40 into its prime factors: \( 40 = 2^3 \times 5 \).
- This can be visualized by creating smaller squares and rectangles that multiply to give the area of 40.
3. Pairing Prime Factors:
- Pair the prime factors to simplify the radical: \( 40 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 = 4 \times 10 \).
- Since \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \), we can simplify \( \sqrt{40} \) as \( 2\sqrt{10} \).
4. Visual Representation:
We can represent this geometrically as follows:
 |
In the diagram:
- The large square represents the number 40.
- The smaller squares within represent the factor 4 (2 x 2).
- The remaining area (a rectangle) represents the factor 10, demonstrating the simplified form \( 2\sqrt{10} \).
5. Graphical Interpretation:
On a number line, you can place markers to show the position of \( \sqrt{40} \) between \( \sqrt{36} \) (which is 6) and \( \sqrt{49} \) (which is 7). The exact position of \( \sqrt{40} \) can be approximated as 6.324, closer to 6.
 |
Using these visual aids helps in understanding the simplification process of square roots, making the abstract concept more concrete and accessible.
Applications of Simplified Square Roots
Simplifying square roots, such as the square root of 40, has numerous practical applications across various fields. Here are some key areas where simplified square roots are used:
- Geometry and Architecture: Simplified square roots help in calculating areas and dimensions of various shapes. For example, determining the diagonal of a rectangle or the height of a triangle often involves square roots, making these calculations more precise and manageable.
- Physics and Engineering: Many formulas in physics, such as those involving acceleration, force, and energy, require the simplification of square roots. This simplification is crucial for accurate predictions and practical calculations in engineering designs and experiments.
- Finance: Square roots are used in various financial calculations, including interest rates, mortgage payments, and risk assessments. Simplifying these calculations can lead to clearer and quicker financial decision-making.
- Computer Science: Algorithms that involve geometric and spatial calculations, such as those used in graphics rendering and machine learning, benefit from the efficiency and optimization provided by simplified square roots.
- Education: Teaching the concept of square roots through simplification helps students understand more complex mathematical concepts. It builds a strong foundation for advanced studies in mathematics.
These applications illustrate the importance of simplifying square roots in making complex problems more manageable and contributing to advancements in technology, science, and mathematics.

Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When simplifying the square root of 40, there are several common mistakes that can lead to errors. Understanding these pitfalls can help you navigate the process more effectively:
- Incorrect Prime Factorization: One common mistake is not correctly identifying the prime factors of 40. Remember, 40 can be factored into 2 * 2 * 2 * 5.
- Incorrect Pairing of Factors: Another mistake is pairing the factors incorrectly during the simplification process. Ensure that you correctly match pairs of identical factors.
- Missing or Adding Factors: Sometimes, factors are accidentally left out or added during the pairing step. Double-check your pairs to ensure all factors are accounted for.
- Forgetting the Square Root: It's easy to forget to take the square root of the perfect squares you paired. Always remember to take the square root of these pairs to simplify correctly.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can simplify the square root of 40 accurately and confidently.
Practice Problems
Practice simplifying the square root of 40 with these problems:
- Simplify \( \sqrt{40} \) using the prime factorization method.
- Verify your result by squaring the simplified form and ensuring it equals 40.
- Apply the simplification technique to find \( \sqrt{160} \).
- Challenge yourself with \( \sqrt{100} \) using the same method.
- Explore other numbers and practice simplifying their square roots.
By working through these practice problems, you'll strengthen your skills in simplifying square roots and gain confidence in handling similar calculations.
Advanced Techniques
Master the simplification of \( \sqrt{40} \) with advanced techniques:
- Estimation Method: Use approximation techniques to estimate \( \sqrt{40} \) to a certain decimal place.
- Continued Fractions: Explore the use of continued fractions to represent \( \sqrt{40} \) in a unique form.
- Approximation by Iteration: Employ iterative methods to approximate \( \sqrt{40} \) with increasing accuracy.
- Application of Newton's Method: Apply Newton's method to refine the approximation of \( \sqrt{40} \).
- Graphical Representation: Visualize \( \sqrt{40} \) on a number line or graph to understand its position and relationship with nearby numbers.
By exploring these advanced techniques, you'll deepen your understanding of square roots and enhance your problem-solving skills.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the simplification of \( \sqrt{40} \) involves understanding its prime factorization and applying systematic techniques:
- Start by identifying the prime factors of 40.
- Pair the factors to simplify the square root.
- Verify your simplified form by squaring it to ensure accuracy.
- Explore advanced techniques like estimation, continued fractions, and iterative methods for deeper understanding.
By practicing these methods, you'll gain confidence in simplifying square roots and applying these skills to solve more complex mathematical problems.

Xem video này để biết cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 40. Học cách phân tích thừa số nguyên tố và áp dụng các kỹ thuật để giải quyết vấn đề một cách chính xác và nhanh chóng.
Hướng dẫn đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 40 | Sqrt(40)
READ MORE:
Xem video này để phân tích chi tiết về căn bậc hai của số 40. Học cách đơn giản hóa và áp dụng các kỹ thuật để giải quyết vấn đề một cách hiệu quả và đáng tin cậy.
Phân tích căn bậc hai của số 40, sqrt(40)