Topic how to calculate a perimeter of a triangle: Discover the essentials of calculating the perimeter of a triangle. This comprehensive guide provides clear formulas, step-by-step methods, and practical examples to help you easily determine the perimeter of any triangle type. Whether you're dealing with equilateral, isosceles, or right triangles, you'll find all the information you need right here.
Table of Content
- How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Introduction
- Definition of Perimeter
- General Formula for the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Types of Triangles
- Calculating the Perimeter of Special Triangles
- Equilateral Triangle
- Isosceles Triangle
- Right Triangle
- Using the Law of Cosines for Perimeter Calculation
- Using the Law of Sines for Perimeter Calculation
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách tính chu vi của một tam giác bằng các phương pháp đơn giản và dễ hiểu.
How to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around the triangle. It can be calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides. The formula for the perimeter (P) of a triangle with sides a, b, and c is:
Special Types of Triangles
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal. The perimeter is:
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal. The perimeter is:
- Right Triangle: One angle is 90 degrees. Using the Pythagorean Theorem, the perimeter is:
Other Methods
If you know two sides and the included angle (SAS), use the Law of Cosines:
After finding side c, use
If you know one side and the two angles (ASA), use the Law of Sines:
Then find the remaining sides and use
Examples
- Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides 5 cm, 4 cm, and 2 cm:
- Find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle with each side 10 cm:

READ MORE:
Introduction
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental concept in geometry. The perimeter is the total distance around the triangle, which is obtained by adding the lengths of its three sides. The general formula for the perimeter (P) of a triangle with sides a, b, and c is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Triangles can be classified into different types such as equilateral, isosceles, and right triangles, each having specific methods to calculate their perimeter. For instance, in an equilateral triangle where all three sides are equal, the perimeter is simply:
\[ P = 3a \]
For an isosceles triangle, where two sides are equal, the formula becomes:
\[ P = 2l + b \]
Right triangles use the Pythagorean theorem to find the missing side if only two sides are known, and then sum up all three sides. Understanding these formulas and methods ensures accurate calculation of the perimeter for various triangle types.
Definition of Perimeter
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around the outside of the triangle. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides of the triangle. The formula for the perimeter of a triangle is:
$$P = a + b + c$$
Where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
For different types of triangles, specific relationships can simplify the calculation:
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal. The formula simplifies to $$P = 3s$$ where \(s\) is the length of a side.
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are of equal length. The formula is $$P = 2l + b$$ where \(l\) is the length of the equal sides and \(b\) is the base.
- Right Triangle: Using the Pythagorean theorem, the perimeter can be found if at least two side lengths are known.
To find the perimeter of a triangle when some side lengths or angles are known, other methods can be used:
- Side-Angle-Side (SAS) Method: If two sides and the included angle are known, use the law of cosines to find the third side, then add all sides.
- Angle-Side-Angle (ASA) Method: If two angles and one side are known, use the law of sines to find the missing sides, then sum all sides.
General Formula for the Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around the triangle, which can be calculated by summing the lengths of its three sides. This is true for any type of triangle, whether it is scalene, isosceles, or equilateral. The formula to calculate the perimeter is straightforward:
Here, a, b, and c are the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
- Equilateral Triangle: Since all sides are equal, the perimeter is , where s is the length of a side.
- Isosceles Triangle: With two equal sides, the perimeter is , where l is the length of the equal sides and b is the base.
- Right Triangle: If the triangle has a right angle, the perimeter can be found using the Pythagorean theorem to determine the hypotenuse if not given, then adding all sides: .
In summary, knowing the lengths of all three sides allows us to calculate the perimeter easily by adding them together. This simple yet essential formula is a fundamental aspect of geometry.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle involves summing the lengths of its three sides. Here are the steps to follow:
- Identify the sides of the triangle:
In a triangle, label the sides as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \). These sides can be given directly or calculated using coordinates or other methods.
- Measure the lengths of the sides:
Using a ruler or other measuring tool, measure the lengths of each side. If you have the coordinates of the vertices, use the distance formula to calculate the lengths.
- Distance formula: If the vertices of the triangle are \((x_1, y_1)\), \((x_2, y_2)\), and \((x_3, y_3)\), the lengths of the sides can be calculated as:
\[
a = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]\[
b = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2}
\]\[
c = \sqrt{(x_1 - x_3)^2 + (y_1 - y_3)^2}
\]
- Distance formula: If the vertices of the triangle are \((x_1, y_1)\), \((x_2, y_2)\), and \((x_3, y_3)\), the lengths of the sides can be calculated as:
- Sum the lengths of the sides:
Add the lengths of the three sides to find the perimeter.
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\]
For example, if a triangle has sides of lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} = 12 \, \text{cm}
\]

Types of Triangles
Triangles are classified based on the lengths of their sides and the measures of their angles. Here, we will discuss the various types of triangles and their properties.
By Sides
- Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all three sides of equal length. Consequently, all three internal angles are also equal, each measuring 60 degrees.
Perimeter Formula: \( P = 3a \) where \( a \) is the length of one side.
- Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length, and the third side is of a different length. The angles opposite the equal sides are also equal.
Perimeter Formula: \( P = 2a + b \) where \( a \) is the length of the equal sides and \( b \) is the length of the base.
- Scalene Triangle
A scalene triangle has all sides of different lengths. Consequently, all three internal angles are different as well.
Perimeter Formula: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
By Angles
- Acute Triangle
An acute triangle has all three internal angles less than 90 degrees.
- Right Triangle
A right triangle has one internal angle equal to 90 degrees. The side opposite this angle is the hypotenuse, the longest side of the triangle.
Perimeter Formula: \( P = a + b + c \) where \( c \) is the hypotenuse, and \( a \) and \( b \) are the other two sides.
- Obtuse Triangle
An obtuse triangle has one internal angle greater than 90 degrees.
Calculating the Perimeter of Special Triangles
There are several types of special triangles, each with unique properties that simplify the calculation of their perimeters. Here, we will explore how to calculate the perimeter of equilateral, isosceles, and right triangles.
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all three sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter is straightforward:
\[ P = 3s \]
where \( s \) is the length of one side.
Example: If each side of an equilateral triangle is 6 cm, then the perimeter is:
\[ P = 3 \times 6 = 18 \, \text{cm} \]
Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. The formula for the perimeter is:
\[ P = 2l + b \]
where \( l \) is the length of the equal sides and \( b \) is the base.
Example: If the equal sides are 5 cm each and the base is 8 cm, then the perimeter is:
\[ P = 2 \times 5 + 8 = 18 \, \text{cm} \]
Right Triangle
A right triangle has one 90-degree angle. The perimeter can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotenuse if it is not given:
\[ h = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \]
where \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the two legs. The perimeter is then:
\[ P = a + b + h \]
Example: If the legs are 3 cm and 4 cm, then the hypotenuse is:
\[ h = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \, \text{cm} \]
So, the perimeter is:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{cm} \]
By understanding these formulas, you can easily calculate the perimeter of these special triangles in various scenarios.
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a special type of triangle where all three sides are equal in length, and all three interior angles are equal, each measuring 60 degrees. This unique property makes it one of the simplest and most symmetrical types of triangles.
Properties of an Equilateral Triangle
- All three sides are equal: \(a = b = c\)
- All three interior angles are 60 degrees
- It is a regular polygon
Formulas for an Equilateral Triangle
| Property | Formula |
|---|---|
| Perimeter | \(P = 3a\) |
| Area | \(A = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}a^2\) |
| Height | \(h = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a\) |
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Measure the length of one side of the equilateral triangle. Let's denote this length as \(a\).
- Use the perimeter formula for an equilateral triangle: \(P = 3a\).
- Multiply the length of the side by 3 to find the perimeter.
For example, if the side length of an equilateral triangle is 5 cm, the perimeter would be calculated as follows:
- Side length (\(a\)) = 5 cm
- Perimeter (\(P\)) = \(3 \times 5 = 15\) cm
Example Calculation
Suppose you have an equilateral triangle with a side length of 7 units. The perimeter would be:
\(P = 3 \times 7 = 21\) units
Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle is a type of triangle that has two sides of equal length. These two equal sides are known as the legs of the triangle, and the third side is known as the base. The angles opposite the equal sides are also equal.
Formula for the Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
The perimeter \( P \) of an isosceles triangle can be calculated using the following formula:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
where:
- \( a \) is the length of the equal sides (legs).
- \( b \) is the length of the base.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of an Isosceles Triangle
- Identify the lengths of the two equal sides \( a \) and the base \( b \).
- Substitute these values into the formula \( P = 2a + b \).
- Simplify the expression to find the perimeter.
- Assign the appropriate unit to the result, which will be the same as the unit of the given side lengths.
Example Calculation
Consider an isosceles triangle with each of the equal sides measuring 5 units and the base measuring 8 units. To find the perimeter:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
Substitute \( a = 5 \) and \( b = 8 \):
\[ P = 2(5) + 8 = 10 + 8 = 18 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is 18 units.
Special Case: Isosceles Right Triangle
An isosceles right triangle has a right angle (90°) and two equal legs. The hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem.
\[ \text{Hypotenuse} = \sqrt{a^2 + a^2} = a\sqrt{2} \]
Thus, the perimeter \( P \) of an isosceles right triangle with legs of length \( a \) is given by:
\[ P = 2a + a\sqrt{2} = a(2 + \sqrt{2}) \]
Example Calculation for Isosceles Right Triangle
For an isosceles right triangle with each leg measuring 3 units, the perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[ P = 3(2 + \sqrt{2}) = 3(2 + 1.414) \approx 3(3.414) \approx 10.242 \text{ units} \]
Therefore, the perimeter of the isosceles right triangle is approximately 10.242 units.
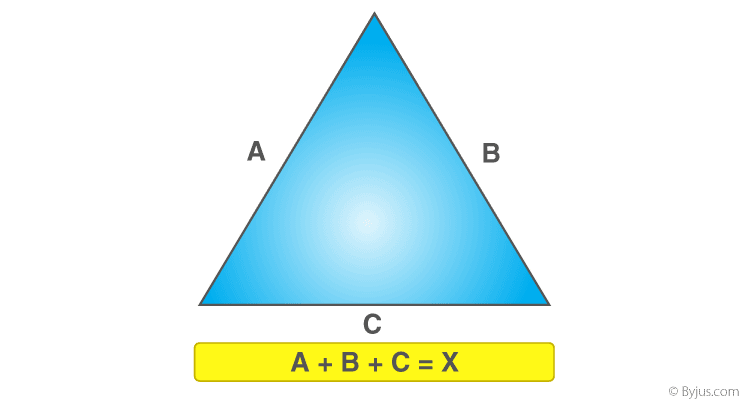
Right Triangle
A right triangle has one angle equal to 90 degrees. To calculate the perimeter of a right triangle, you need to know the lengths of its three sides: the two legs (a and b) and the hypotenuse (c).
-
Identify the lengths of the two legs of the right triangle. These are the sides that form the right angle.
-
If the length of the hypotenuse (the side opposite the right angle) is not given, use the Pythagorean theorem to calculate it:
\[
c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}
\] -
Add the lengths of the three sides to find the perimeter:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = a + b + c
\]
Here is a step-by-step example:
-
Suppose the lengths of the legs are \( a = 3 \) and \( b = 4 \).
-
Calculate the hypotenuse using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[
c = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5
\] -
Add the lengths of the sides to find the perimeter:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12
\]
Thus, the perimeter of a right triangle with legs of lengths 3 and 4 and a hypotenuse of 5 is 12 units.
Using the Law of Cosines for Perimeter Calculation
The Law of Cosines is a useful tool for calculating the perimeter of a triangle when the length of one side is unknown, or when dealing with non-right triangles. Here are the detailed steps to calculate the perimeter using the Law of Cosines:
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
-
Identify the known values: You should know the lengths of two sides of the triangle and the measure of the included angle (the angle between the two known sides).
-
Apply the Law of Cosines: The Law of Cosines formula is:
\[ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(C) \]Where \( c \) is the length of the side opposite angle \( C \), and \( a \) and \( b \) are the lengths of the other two sides.
-
Solve for the unknown side: Rearrange the formula to solve for \( c \):
\[ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cos(C)} \]Calculate the value of \( c \) using the known side lengths and the cosine of the angle.
-
Calculate the perimeter: Once you have all three sides, use the perimeter formula:
\[ P = a + b + c \]Add the lengths of all three sides to find the perimeter of the triangle.
Example Calculation
Let's consider an example where the sides \( a \) and \( b \) are 8 cm and 11 cm, respectively, and the included angle \( C \) is 37°:
-
First, apply the Law of Cosines:
\[ c^2 = 8^2 + 11^2 - 2 \cdot 8 \cdot 11 \cdot \cos(37^\circ) \] -
Calculate the values:
\[ c^2 = 64 + 121 - 176 \cdot \cos(37^\circ) \]Using a calculator, find \( \cos(37^\circ) \approx 0.7986 \):
\[ c^2 = 64 + 121 - 176 \cdot 0.7986 \]
\[ c^2 = 64 + 121 - 140.6896 \]
\[ c^2 = 44.3104 \]
\[ c = \sqrt{44.3104} \approx 6.66 \text{ cm} \] -
Finally, calculate the perimeter:
\[ P = a + b + c = 8 + 11 + 6.66 = 25.66 \text{ cm} \]
Using the Law of Sines for Perimeter Calculation
The Law of Sines is a powerful tool in trigonometry that relates the sides and angles of a triangle. It is particularly useful for finding unknown sides or angles when given some initial information about the triangle. The formula for the Law of Sines is given by:
\[ \frac{a}{\sin A} = \frac{b}{\sin B} = \frac{c}{\sin C} \]
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle, and \( A \), \( B \), and \( C \) are the opposite angles.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter Using the Law of Sines
- Identify the given values: Determine which sides and angles of the triangle are known. You need at least one side and its opposite angle, plus one other angle or side.
- Use the sum of angles in a triangle: If two angles are known, the third angle can be found using \( A + B + C = 180^\circ \).
- Apply the Law of Sines: Use the Law of Sines formula to find the unknown sides. For example, if \( a \), \( A \), and \( B \) are known, find \( b \) using:
\[ b = \frac{a \cdot \sin B}{\sin A} \]
- Repeat for other sides: Use the same process to find the third side if necessary. For example, if \( a \), \( b \), and \( B \) are known, find \( c \) using:
\[ c = \frac{a \cdot \sin C}{\sin A} \]
- Calculate the perimeter: Once all side lengths are known, sum them to find the perimeter:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
Example
Consider a triangle with sides \( a = 8 \), \( b = 6 \), and angle \( A = 45^\circ \). To find the perimeter:
- Calculate the third angle: Suppose \( B = 60^\circ \). Then \( C = 180^\circ - 45^\circ - 60^\circ = 75^\circ \).
- Find side \( c \) using the Law of Sines:
\[ \frac{c}{\sin 75^\circ} = \frac{8}{\sin 45^\circ} \] \[ c = \frac{8 \cdot \sin 75^\circ}{\sin 45^\circ} \approx 10.32 \]
- Calculate the perimeter:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 8 + 6 + 10.32 = 24.32 \]
Using these steps, you can find the perimeter of any triangle given sufficient initial information.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some common questions related to calculating the perimeter of a triangle:
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a triangle?
The perimeter of a triangle is the sum of the lengths of its three sides. If the sides are denoted as \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\), the formula is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
- How do I find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle?
In an equilateral triangle, all three sides are equal. If the length of each side is \(a\), the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 3a \]
- How do I calculate the perimeter of an isosceles triangle?
An isosceles triangle has two equal sides. If the lengths of the two equal sides are \(a\) and the base is \(b\), the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2a + b \]
- How can I find the perimeter of a right triangle?
For a right triangle, if you know the lengths of the two legs \(a\) and \(b\), you can find the hypotenuse \(c\) using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \]
Then, the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
- What if I only know two sides and the included angle (SAS triangle)?
Use the law of cosines to find the third side:
\[ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2 - 2ab \cdot \cos(\gamma)} \]
Then, the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
- How do I calculate the perimeter if I have the coordinates of the vertices?
If the vertices of the triangle are at \((x_1, y_1)\), \((x_2, y_2)\), and \((x_3, y_3)\), use the distance formula to find the lengths of the sides:
\[ a = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
\[ b = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_2)^2 + (y_3 - y_2)^2} \]
\[ c = \sqrt{(x_3 - x_1)^2 + (y_3 - y_1)^2} \]
Then, the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
- Can a triangle have the same area and perimeter?
It is possible for a triangle to have the same numerical value for its area and perimeter, but this is rare and specific to certain dimensions.

Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách tính chu vi của một tam giác bằng các phương pháp đơn giản và dễ hiểu.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi của Một Tam Giác
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn từ Thầy J về cách tính chu vi của một tam giác một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Cách Tìm Chu Vi của Một Tam Giác | Toán với Thầy J