Topic formula for the perimeter of a triangle: The formula for the perimeter of a triangle is straightforward: sum the lengths of all three sides. Whether you have an equilateral, isosceles, or scalene triangle, calculating the perimeter is easy with the right approach. This article covers different methods, special cases, and practical examples to help you understand and apply this essential geometric concept.
Table of Content
- Formula for the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Introduction to the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Basic Formula for the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Perimeter Formulas for Special Types of Triangles
- Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Real-world Applications
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- YOUTUBE:
Formula for the Perimeter of a Triangle
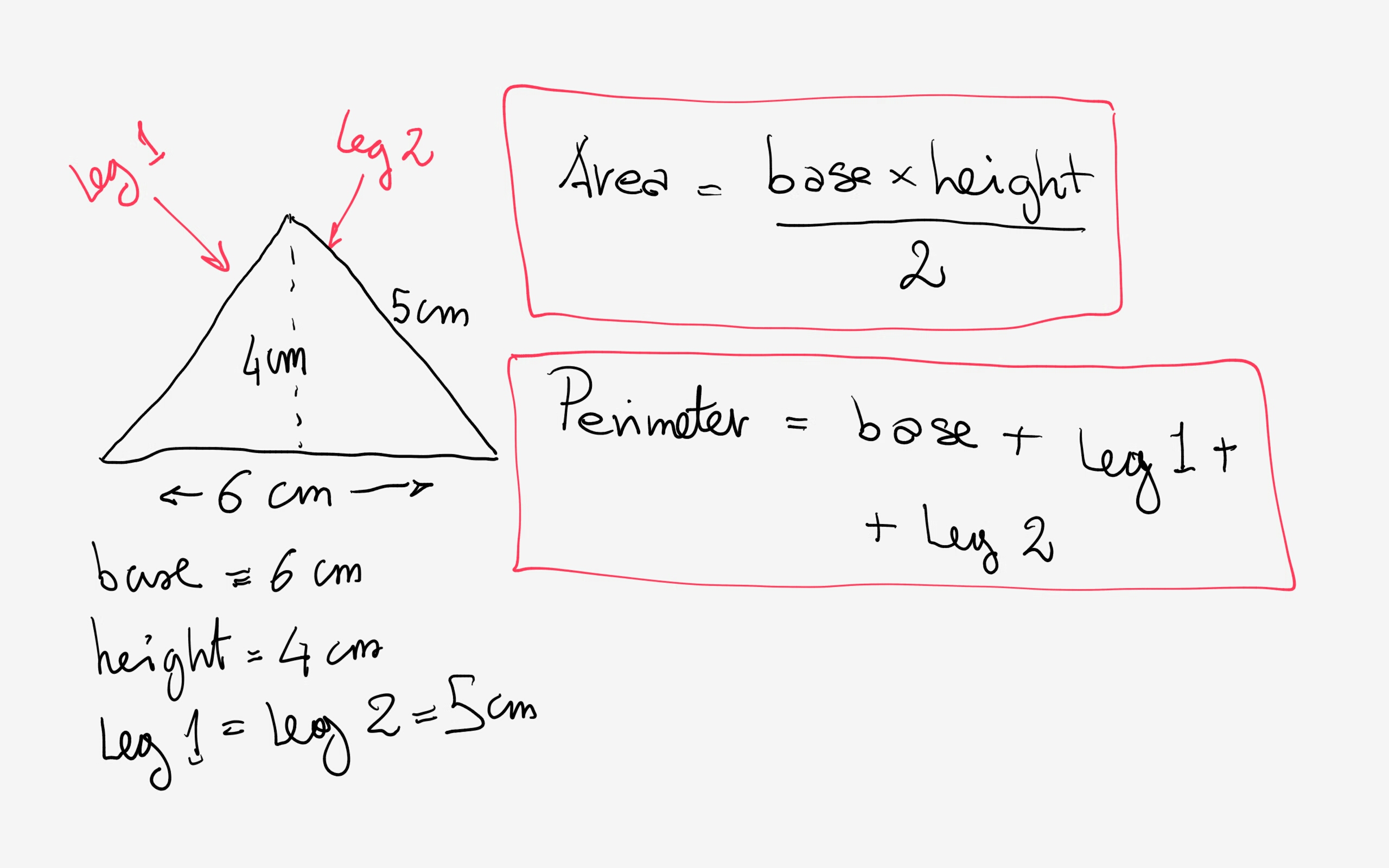
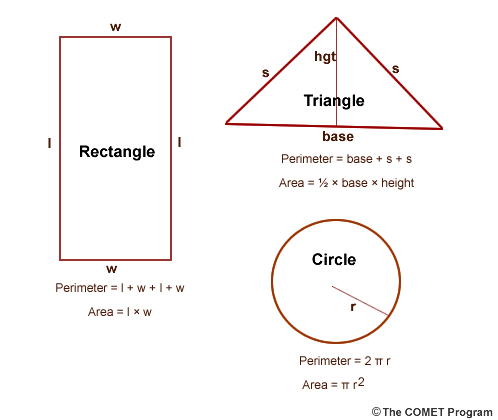
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around the triangle, which is the sum of the lengths of its sides. This can be calculated using different formulas depending on the type of triangle and the information given.
General Formula
For any triangle with sides a, b, and c, the perimeter P is given by:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Special Cases
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal.
If each side is a, then:
\[ P = 3a \]
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal.
If the equal sides are a and the base is b, then:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
- Scalene Triangle: All three sides are of different lengths.
The perimeter is simply the sum of all three sides:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
- Right Triangle: One angle is \(90^\circ\). The sides are the base (b), height (p), and hypotenuse (h).
Using the Pythagorean theorem to find the hypotenuse:
\[ h = \sqrt{b^2 + p^2} \]
Then the perimeter is:
\[ P = b + p + h \]
Examples
- Example 1: A triangle with sides 5 cm, 4 cm, and 3 cm.
Using the general formula:
\[ P = 5 + 4 + 3 = 12 \, \text{cm} \]
- Example 2: An equilateral triangle with each side measuring 6 inches.
Using the equilateral triangle formula:
\[ P = 3 \times 6 = 18 \, \text{inches} \]
- Example 3: A right triangle with base 3 cm, height 4 cm, and hypotenuse calculated using the Pythagorean theorem.
First, find the hypotenuse:
\[ h = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \, \text{cm} \]
Then, the perimeter:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{cm} \]
Practice Problems
- Calculate the perimeter of an isosceles triangle with equal sides of 10 cm and base of 12 cm.
- Find the perimeter of a scalene triangle with sides measuring 7 m, 9 m, and 12 m.
- A right triangle has a base of 8 inches and a height of 6 inches. Find the perimeter.
Conclusion
The formula for the perimeter of a triangle is straightforward but varies slightly depending on the type of triangle. Whether it’s equilateral, isosceles, scalene, or right, understanding these formulas is crucial for solving various geometric problems.

READ MORE:
Introduction to the Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental geometric concept that refers to the total length around the triangle. It is calculated by adding together the lengths of all three sides. Understanding how to find the perimeter is crucial for solving various mathematical problems involving different types of triangles, such as equilateral, isosceles, and scalene triangles.
To find the perimeter of a triangle, use the formula:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
where \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
Here is a step-by-step guide to calculating the perimeter:
- Measure the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Ensure all measurements are in the same unit.
- Add the lengths of the three sides to get the perimeter.
Different types of triangles have specific perimeter formulas:
- Equilateral Triangle: All sides are equal. The formula is \( P = 3a \).
- Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal. The formula is \( P = 2a + b \), where \(a\) is the length of the equal sides, and \(b\) is the base.
- Scalene Triangle: All sides are different. The general formula \( P = a + b + c \) applies.
For example, if a triangle has sides of lengths 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, its perimeter is calculated as follows:
\[ P = 3 \, \text{cm} + 4 \, \text{cm} + 5 \, \text{cm} = 12 \, \text{cm} \]
Understanding the perimeter of a triangle is not only important in geometry but also in real-world applications such as construction, design, and various fields of engineering.
Basic Formula for the Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around the outside of the triangle. It can be calculated by summing the lengths of its three sides. The formula for the perimeter of a triangle is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter
- Identify the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Add the lengths of the three sides using the formula: \[ \text{Perimeter} = a + b + c \]
- The resulting sum is the perimeter of the triangle, expressed in the same units as the side lengths.
Examples
- Example 1: For a triangle with sides 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 5 + 6 + 7 = 18 \, \text{cm} \]
- Example 2: For an equilateral triangle with each side measuring 8 cm, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 3 \times 8 = 24 \, \text{cm} \]
- Example 3: For an isosceles triangle with two sides of 10 cm and a base of 12 cm, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 10 + 10 + 12 = 32 \, \text{cm} \]
- Example 4: For a right triangle with legs of 3 cm and 4 cm, and a hypotenuse of 5 cm, the perimeter is: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \, \text{cm} \]
Perimeter Formulas for Special Types of Triangles
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its sides. Special types of triangles, such as equilateral, isosceles, and right triangles, have unique properties that simplify the calculation of their perimeters. Below are the specific formulas for calculating the perimeter of these special triangles.
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all three sides of equal length. The perimeter \( P \) of an equilateral triangle with side length \( a \) is calculated as:
\[ P = 3a \]
- If each side of an equilateral triangle is 7 inches, the perimeter is \( 3 \times 7 = 21 \) inches.
Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. The perimeter \( P \) of an isosceles triangle with equal sides of length \( a \) and the base of length \( b \) is given by:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
- If the equal sides are 5 feet each and the base is 7 feet, the perimeter is \( 2 \times 5 + 7 = 17 \) feet.
Right Triangle
A right triangle has one angle of 90 degrees. To find the perimeter, you need the lengths of the two legs (\( a \) and \( b \)) and the hypotenuse (\( c \)). The hypotenuse can be found using the Pythagorean theorem:
\[ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \]
Then, the perimeter \( P \) is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
- If the legs of a right triangle are 6 cm and 8 cm, the hypotenuse is \( \sqrt{6^2 + 8^2} = \sqrt{36 + 64} = 10 \) cm. Therefore, the perimeter is \( 6 + 8 + 10 = 24 \) cm.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle involves a straightforward process of summing up the lengths of all its sides. Here are the detailed steps to follow:
-
Identify the lengths of the sides:
Measure or obtain the lengths of all three sides of the triangle. Let's denote these sides as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
-
Apply the perimeter formula:
The basic formula for calculating the perimeter \( P \) of a triangle is:
\[
P = a + b + c
\] -
Add the side lengths:
Sum up the values of \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) to find the perimeter.
- For example, if \( a = 5 \, \text{cm} \), \( b = 6 \, \text{cm} \), and \( c = 7 \, \text{cm} \): \[ P = 5 + 6 + 7 = 18 \, \text{cm} \]
-
Special cases:
If dealing with specific types of triangles, use their respective formulas:
- Equilateral Triangle: \( P = 3a \) where \( a \) is the length of the side.
- Isosceles Triangle: \( P = 2a + b \) where \( a \) is the length of the two equal sides and \( b \) is the base.
- Right Triangle: First, use the Pythagorean theorem if the hypotenuse is unknown: \[ c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \] Then, apply the perimeter formula \( P = a + b + c \).
By following these steps, you can accurately calculate the perimeter of any triangle.

Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding the perimeter of a triangle through examples and practice problems helps solidify the concept. Below are a few examples demonstrating how to calculate the perimeter of different types of triangles.
- Example 1: Find the perimeter of a triangle with side lengths of 5 cm, 6 cm, and 3 cm.
- Using the perimeter formula \( P = a + b + c \).
- Substitute the side lengths: \( P = 5 + 6 + 3 \).
- Calculate the sum: \( P = 14 \) cm.
- Example 2: An equilateral triangle has sides of length 10 cm each. Find its perimeter.
- Since all sides are equal, the formula is \( P = 3a \).
- Substitute the side length: \( P = 3 \times 10 \).
- Calculate the sum: \( P = 30 \) cm.
- Example 3: Find the perimeter of an isosceles triangle where two sides are 10 cm each and the third side is 15 cm.
- Using the perimeter formula \( P = a + b + c \).
- Substitute the side lengths: \( P = 10 + 10 + 15 \).
- Calculate the sum: \( P = 35 \) cm.
- Practice Problem 1: A scalene triangle has sides with lengths of 6 cm, 10 cm, and 8 cm. What is its perimeter?
- Using the perimeter formula \( P = a + b + c \).
- Substitute the side lengths: \( P = 6 + 10 + 8 \).
- Calculate the sum: \( P = 24 \) cm.
- Practice Problem 2: An isosceles triangle has two equal sides with lengths of 5 cm and a remaining side with a length of 2 cm. What is its perimeter?
- Using the perimeter formula \( P = a + b + c \).
- Substitute the side lengths: \( P = 5 + 5 + 2 \).
- Calculate the sum: \( P = 12 \) cm.
- Practice Problem 3: An equilateral triangle has sides with lengths of 7 cm. What is its perimeter?
- Using the perimeter formula \( P = 3a \).
- Substitute the side length: \( P = 3 \times 7 \).
- Calculate the sum: \( P = 21 \) cm.
Real-world Applications
The perimeter formula for a triangle is widely used in various real-world applications. Understanding how to calculate the perimeter of a triangle can be crucial in fields such as construction, land surveying, education, art, and engineering. Here are some detailed examples of how the perimeter of a triangle is applied in real-world scenarios:
- Construction and Architecture: Architects and builders use the perimeter to calculate the amount of materials needed for constructing triangular components like roofs and bridges, ensuring accurate cost estimates and efficient resource allocation.
- Land Surveying: Surveyors use perimeter calculations to define property boundaries, plot land areas, and create accurate maps, which is essential for property assessment and legal documentation.
- Education: Teachers use triangle perimeter problems to teach geometry, helping students understand the relationships between sides and perimeters, which enhances their problem-solving skills.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers use knowledge of triangle perimeters to create balanced and symmetrical compositions in their works.
- Navigation and Geography: Navigators and geographers apply perimeter calculations in triangulation methods to determine precise locations.
- Engineering: Engineers use triangle perimeter formulas in the design of various structures, ensuring stability and safety in projects like bridges and buildings.
- Home Improvement: Homeowners and DIY enthusiasts apply these concepts in planning projects, such as installing tiles or decorative moldings in triangular areas.
- Outdoor Activities: Hikers and campers use triangle perimeter calculations to estimate distances and plan routes, ensuring they have adequate supplies for their trips.
- Business and Finance: Business owners might calculate perimeters for practical purposes, such as determining fencing costs for a commercial property.
These examples highlight the versatility and importance of triangle perimeter calculations across various fields. Mastering this formula not only aids in academic pursuits but also provides valuable skills for practical problem-solving in numerous professional and personal contexts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
The perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental concept in geometry. Here are some frequently asked questions to help you understand this topic better.
- What is the perimeter of a triangle?
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its three sides. It is calculated by adding the lengths of all three sides together.
- What is the formula for the perimeter of a triangle?
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a triangle is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
- How do you find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle?
For an equilateral triangle, all three sides are equal. The formula simplifies to:
\[ P = 3a \]
where \( a \) is the length of each side.
- Can a triangle have the same area and perimeter?
Yes, a triangle can have the same numerical value for its area and perimeter in special cases. These are known as equable triangles.
- How do you find the third side and perimeter of a right triangle given two sides?
To find the third side of a right triangle when the lengths of the other two sides are known, use the Pythagorean theorem:
\[ c^2 = a^2 + b^2 \]
where \( c \) is the hypotenuse and \( a \) and \( b \) are the other two sides. Once you have all three sides, you can calculate the perimeter as usual:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Tam Giác | Toán học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Cách Tìm Chu Vi Tam Giác