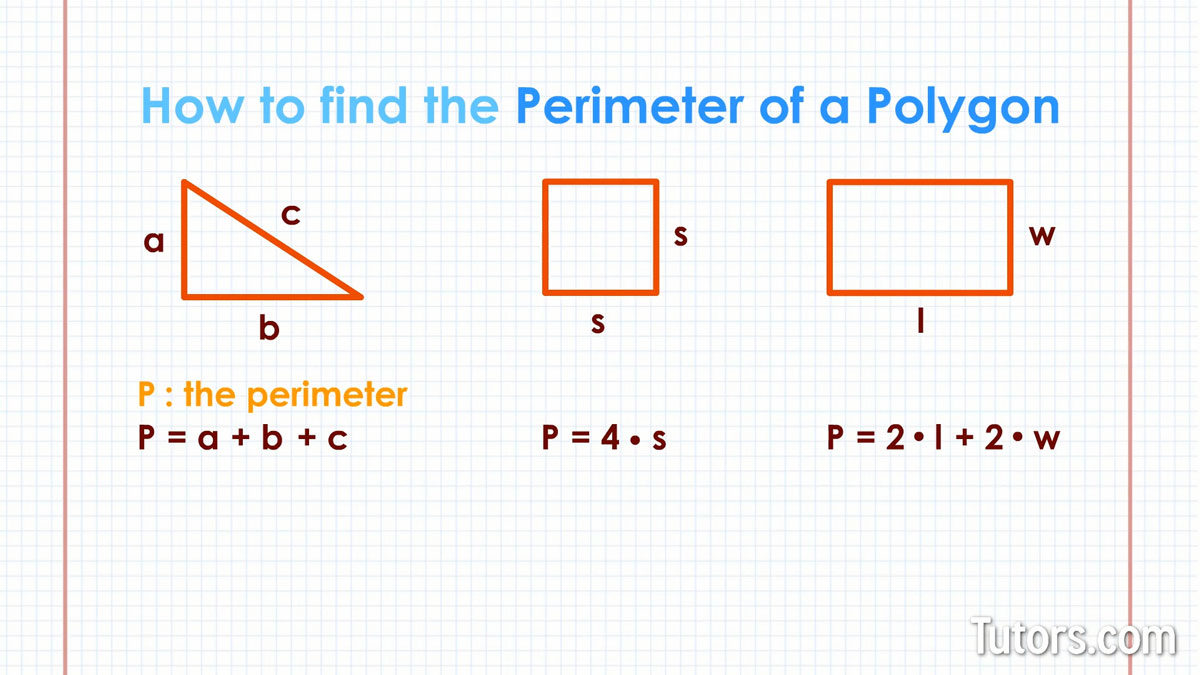
Topic how do you find a perimeter of a polygon: Discover the ins and outs of calculating the perimeter of a polygon with our comprehensive guide. Whether you're a student learning geometry or a professional needing to brush up on the basics, this article covers everything you need to know about finding the perimeter of any polygon, from basic formulas to real-world applications.
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Polygon
- Table of Contents:
- 1. Introduction to Perimeter Calculation
- 2. Understanding Polygon Perimeters
- 3. Basics of Polygon Shapes and Sides
- 4. Techniques to Calculate Perimeter
- 5. Perimeter Calculation for Regular Polygons
- 6. Strategies for Irregular Polygon Perimeter Determination
- 7. Utilizing Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
- 8. Real-world Applications and Examples
- 9. Tips and Tricks for Efficient Perimeter Calculation
- YOUTUBE: Video này hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của mọi đa giác, giúp bạn hiểu rõ và áp dụng trong các bài toán thực tế.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Polygon
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves adding up the lengths of all its sides. Here are the general steps to find the perimeter:
- Determine the type of polygon (e.g., triangle, quadrilateral, pentagon).
- Measure each side of the polygon.
- Add the lengths of all sides together.
For specific types of polygons, there are formulas available:
- For a triangle: Add the lengths of all three sides.
- For a quadrilateral: Add the lengths of all four sides.
- For a regular polygon: Multiply the number of sides by the length of one side.
It's important to remember units when calculating perimeter, whether in inches, centimeters, or any other unit of measurement.

READ MORE:
Table of Contents:
1. Introduction to Perimeter Calculation
2. Understanding Polygon Perimeters
3. Basics of Polygon Shapes and Sides
4. Techniques to Calculate Perimeter
5. Perimeter Calculation for Regular Polygons
6. Strategies for Irregular Polygon Perimeter Determination
7. Utilizing Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
8. Real-world Applications and Examples
9. Tips and Tricks for Efficient Perimeter Calculation
1. Introduction to Perimeter Calculation
Understanding perimeter calculation is fundamental in geometry. It involves determining the total length of the boundary of a polygon. This introductory section delves into the significance of perimeter, its applications in real-world scenarios, and the basic concepts required to comprehend polygon perimeters.
2. Understanding Polygon Perimeters
Polygon perimeters are the total lengths of all the sides of a polygon. This section provides a detailed exploration of various types of polygons, including triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and more. It explains how to identify and measure the sides of different polygons, laying the foundation for calculating their perimeters accurately.
3. Basics of Polygon Shapes and Sides
Understanding the basics of polygon shapes and sides is crucial for calculating perimeter accurately. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional shape with straight sides. Here's a breakdown of essential concepts:
- Polygon Definition: A polygon is formed by connecting straight line segments to create a closed shape. Each segment is called a side, and the point where two sides meet is called a vertex.
- Number of Sides: The number of sides in a polygon determines its type. Common polygons include triangles (3 sides), quadrilaterals (4 sides), pentagons (5 sides), hexagons (6 sides), and so on.
- Types of Polygons: Polygons can be classified based on the number of sides they have. Regular polygons have equal side lengths and angles, while irregular polygons have different side lengths and/or angles.
- Properties: Each polygon has unique properties. For example, in a triangle, the sum of interior angles is always 180 degrees. In a regular polygon, all interior angles are equal.
- Vertices: Vertices are the corners of a polygon where the sides meet. The number of vertices is equal to the number of sides.
Knowing these fundamental aspects of polygons sets the groundwork for accurately finding their perimeters.

4. Techniques to Calculate Perimeter
Calculating the perimeter of a polygon involves adding the lengths of all its sides. Here are several techniques commonly used:
- Sum of Side Lengths: The most straightforward method is to measure each side of the polygon and then add up all the lengths.
- Perimeter Formula: For regular polygons, you can use a formula to find the perimeter. For example, the perimeter of a square with side length \( s \) is \( 4s \), while the perimeter of a regular hexagon with side length \( s \) is \( 6s \).
- Using Coordinates: If the vertices of the polygon are given as coordinates on a coordinate plane, you can use distance formulas to find the lengths of the sides and then add them up.
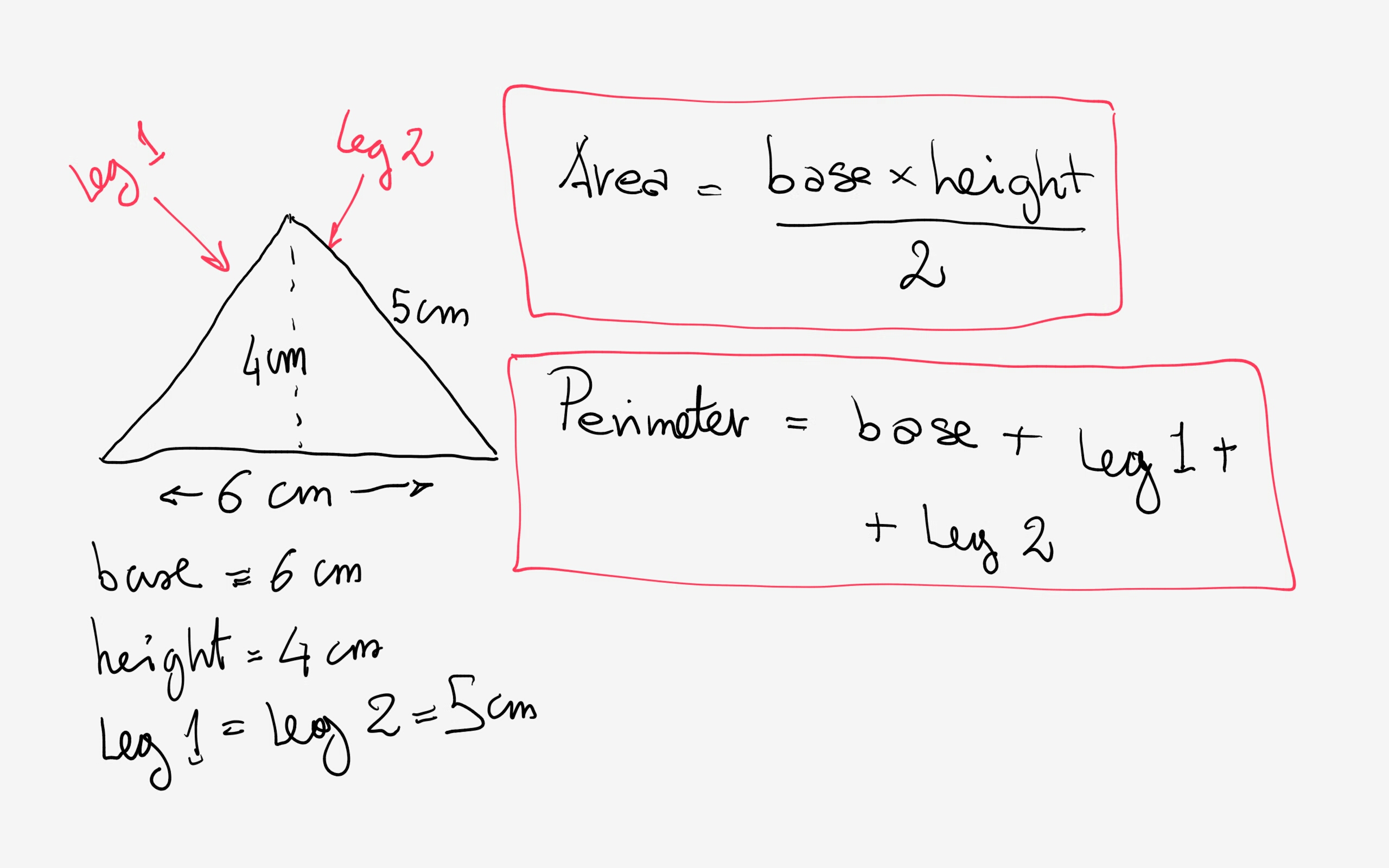
- Heron's Formula: For triangles, Heron's formula can be used to find the perimeter when the lengths of all three sides are known. It is given by \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
- Dividing into Shapes: Sometimes, irregular polygons can be divided into simpler shapes (e.g., triangles, rectangles), and then the perimeters of these shapes can be calculated individually and added together.
Choose the technique that best suits the given polygon and available information to calculate the perimeter accurately.
5. Perimeter Calculation for Regular Polygons
Calculating the perimeter of regular polygons is relatively straightforward due to their uniformity in side lengths and angles. Here's how to find the perimeter:
- Identify Side Length: In a regular polygon, all sides have equal length. Let \( s \) represent the length of one side.
- Count Sides: Determine the number of sides \( n \) in the regular polygon. This will depend on the type of polygon (e.g., triangle, square, pentagon).
- Use Perimeter Formula: The perimeter \( P \) of a regular polygon is given by the formula \( P = ns \), where \( n \) is the number of sides and \( s \) is the length of each side.
- Calculate: Simply multiply the number of sides by the length of each side to find the perimeter of the regular polygon.
For example, the perimeter of a regular hexagon with side length \( s = 5 \) units would be \( P = 6s = 6 \times 5 = 30 \) units.
6. Strategies for Irregular Polygon Perimeter Determination
Calculating the perimeter of irregular polygons can be more challenging than for regular polygons due to variations in side lengths and angles. Here are some strategies to determine the perimeter:
- Measure Sides: If possible, measure each side of the irregular polygon using a ruler or measuring tape. Add up the lengths of all sides to find the perimeter.
- Divide into Regular Polygons: Sometimes, irregular polygons can be divided into simpler regular polygons or shapes with known perimeters. Calculate the perimeters of these individual shapes and then add them together to find the total perimeter of the irregular polygon.
- Use Approximations: In cases where measuring all sides is not feasible, use approximations. For example, if the irregular polygon resembles a shape with known perimeter formulas (e.g., rectangle, triangle), approximate its perimeter using those formulas.
- Software or Apps: Utilize digital tools such as geometry software or mobile applications that allow you to input the coordinates of the polygon's vertices to calculate its perimeter.
- Surveying Techniques: In real-world scenarios, surveying techniques can be employed to accurately measure the perimeter of irregular land plots or structures.
Consider the available resources and characteristics of the irregular polygon to determine the most suitable strategy for finding its perimeter.
7. Utilizing Formulas for Perimeter Calculation
Formulas provide efficient methods for calculating the perimeter of various polygons. Here are some commonly used formulas:
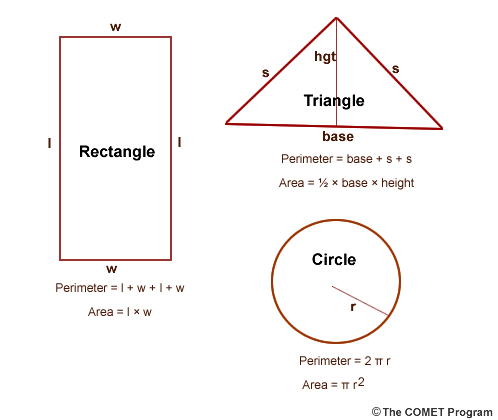
- Rectangle: For a rectangle with length \( l \) and width \( w \), the perimeter \( P \) is given by \( P = 2l + 2w \).
- Square: In a square with side length \( s \), the perimeter \( P \) is calculated as \( P = 4s \).
- Triangle: For a triangle with side lengths \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \), the perimeter \( P \) is found by adding the lengths of all three sides: \( P = a + b + c \).
- Regular Polygon: The perimeter \( P \) of a regular polygon with \( n \) sides and side length \( s \) is given by \( P = ns \).
- Circle: In a circle with radius \( r \), the perimeter (circumference) \( C \) is calculated using the formula \( C = 2\pi r \).
These formulas offer a systematic approach to determine the perimeter of polygons based on their geometric properties. Choose the appropriate formula based on the type of polygon and available information.
8. Real-world Applications and Examples
The concept of finding the perimeter of a polygon has numerous real-world applications across various fields. Here are some examples:
- Construction: Architects and engineers use perimeter calculations extensively in designing buildings, roads, and other structures. Determining the perimeter helps in estimating material requirements and costs.
- Land Surveying: Surveyors use perimeter calculations to measure the boundary of land parcels accurately. This is crucial for property delineation, land development, and legal documentation.
- Fencing: Homeowners and farmers utilize perimeter calculations when installing fences around their properties. Knowing the perimeter helps in determining the amount of fencing material needed.
- Art and Design: Artists and designers incorporate polygonal shapes in their creations. Understanding perimeter calculation allows them to accurately depict and manipulate shapes in their artwork.
- Urban Planning: City planners use perimeter calculations when designing parks, urban spaces, and recreational areas. Calculating perimeters helps in optimizing space usage and creating efficient layouts.
- Geometry in Nature: Perimeter calculations are relevant in studying natural phenomena, such as the shapes of leaves, coastlines, and geological formations. Scientists use these calculations to analyze patterns and structures in nature.
These examples demonstrate the practical significance of perimeter calculations in various real-world scenarios, highlighting the importance of understanding polygonal concepts.
9. Tips and Tricks for Efficient Perimeter Calculation
Efficient perimeter calculation is essential for accurate measurements and practical applications. Here are some tips and tricks to streamline the process:
- Use Standard Formulas: Familiarize yourself with standard formulas for different types of polygons. Knowing these formulas can save time and effort in manual calculations.
- Break Down Complex Shapes: For irregular polygons, break them down into simpler shapes with known formulas. Calculate the perimeters of these individual shapes and then sum them up.
- Utilize Technology: Take advantage of geometry software, calculator apps, or online tools that can quickly compute polygon perimeters based on provided data or coordinates.
- Double-Check Measurements: Ensure accuracy by double-checking measurements of sides and angles. Even small errors can lead to significant discrepancies in perimeter calculation.
- Apply Approximations Wisely: In real-world scenarios where precise measurements are challenging, use approximations judiciously. Round off measurements to reasonable values to simplify calculations.
- Practice Visualization: Visualize the polygon and its components to better understand its structure. This can help in identifying patterns and determining the most efficient approach for perimeter calculation.
By implementing these tips and tricks, you can enhance your efficiency and accuracy in calculating the perimeter of polygons, facilitating various applications in fields such as construction, surveying, and design.
Video này hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của mọi đa giác, giúp bạn hiểu rõ và áp dụng trong các bài toán thực tế.
Chu vi - Tìm Chu vi của Bất kỳ Đa giác Nào
READ MORE:
Xem video này để tìm hiểu cách tính chu vi của một hình đa giác ngoại tiếp và làm thế nào để áp dụng nó trong các bài toán thực tế.
Tìm Chu Vi của Hình Đa Giác Ngoại Tiếp - Math Antics