Topic how find the perimeter of a triangle: Discover the easiest methods to find the perimeter of a triangle with our comprehensive guide. Whether you're a student, teacher, or math enthusiast, this article will provide you with clear steps, practical examples, and useful tips to master the concept of triangle perimeters effortlessly. Start learning today!
Table of Content
- How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Introduction to Triangle Perimeters
- Basic Formula for Perimeter Calculation
- Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Applications in Various Fields
- Visual Representations and Diagrams
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Advanced Topics and Special Cases
- FAQs on Triangle Perimeter Calculation
- Conclusion and Summary
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi của một tam giác bằng các phương pháp đơn giản và dễ hiểu, phù hợp cho học sinh và người học toán ở mọi cấp độ.
How to Find the Perimeter of a Triangle
Finding the perimeter of a triangle involves summing the lengths of its three sides. The formula to calculate the perimeter \( P \) of a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Steps to Find the Perimeter
- Identify the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Add the lengths of the three sides using the formula.
- The result is the perimeter of the triangle.
Example
Consider a triangle with side lengths \( a = 5 \) units, \( b = 7 \) units, and \( c = 9 \) units.
Using the formula:
\[ P = 5 + 7 + 9 = 21 \text{ units} \]
Thus, the perimeter of the triangle is 21 units.
Applications
- Geometry: Fundamental concept in calculating distances around triangular shapes.
- Construction: Used in determining the amount of materials needed for triangular layouts.
- Art and Design: Essential for creating accurate and proportional triangular designs.
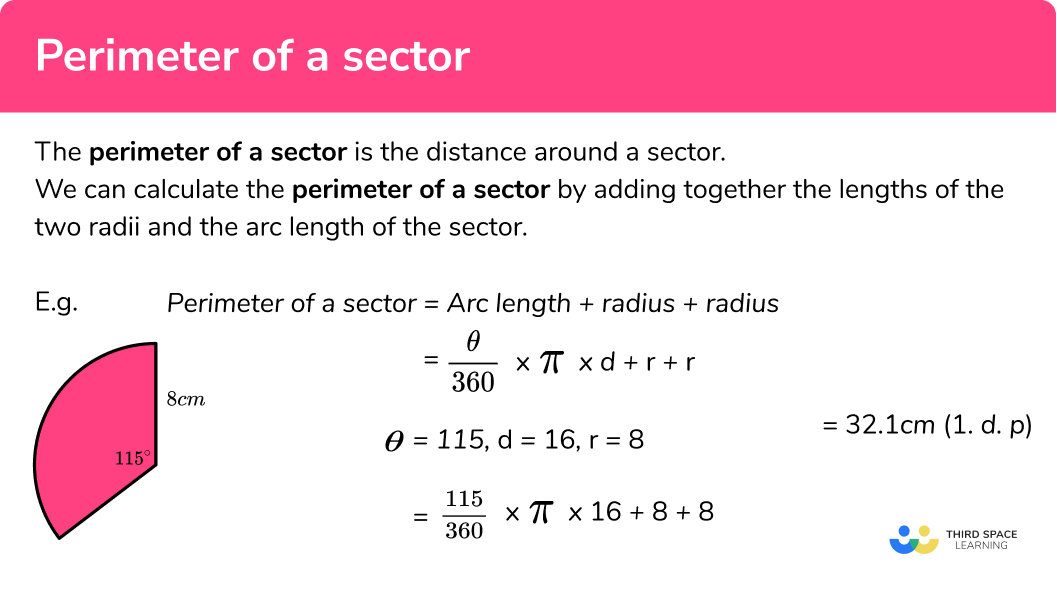
Visual Representation
The following diagram illustrates a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \):
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of a triangle with sides \( a = 6 \) units, \( b = 8 \) units, and \( c = 10 \) units.
- A triangle has sides measuring 4.5 units, 3.2 units, and 5.1 units. Calculate its perimeter.
- If one side of a triangle is 12 units and the other two sides are both 7 units, what is the perimeter?

READ MORE:
Introduction to Triangle Perimeters
Understanding the perimeter of a triangle is fundamental in geometry. The perimeter is the total distance around the triangle, calculated by summing the lengths of its three sides. This measurement is essential in various applications, from basic geometry problems to real-world scenarios in construction and design. Here, we will explore the concept in detail.
The formula to find the perimeter \( P \) of a triangle with sides \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) is:
\[ P = a + b + c \]
Let's break down the process of finding the perimeter into simple steps:
- Identify the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
- Add the lengths together using the formula.
- The result is the perimeter of the triangle.
This straightforward approach ensures you can quickly and accurately determine the perimeter for any triangle.
Consider a triangle with sides of lengths 3 units, 4 units, and 5 units. Using the formula:
\[ P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \text{ units} \]
Thus, the perimeter of this triangle is 12 units. Whether you're dealing with right, isosceles, or equilateral triangles, this method remains consistent, making it a reliable tool in your mathematical toolkit.
- Right Triangle: A triangle with one 90-degree angle.
- Isosceles Triangle: A triangle with two equal sides.
- Equilateral Triangle: A triangle with all three sides equal.
Understanding these concepts will help you tackle more complex problems and enhance your overall geometry skills.
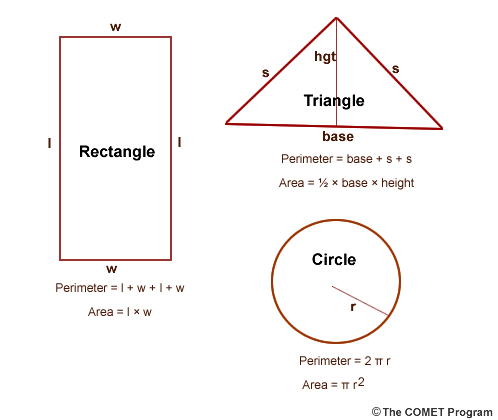
Basic Formula for Perimeter Calculation
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of its three sides. To find the perimeter, you simply add the lengths of all the sides together. The basic formula is:
where:
a is the length of the first sideb is the length of the second sidec is the length of the third side
Let's break down the process step by step:
- Identify the lengths of all three sides: Measure or obtain the lengths of each side of the triangle. Label these lengths as
a ,b , andc . - Substitute the lengths into the formula: Plug the values of
a ,b , andc into the formulaP = a + b + c . - Calculate the sum: Add the values together to find the perimeter.
For example, if you have a triangle with sides of lengths 5 cm, 7 cm, and 10 cm:
- Identify the lengths:
a = 5 ,b = 7 ,c = 10 . - Substitute into the formula:
P = 5 + 7 + 10 . - Calculate the sum:
P = 22 cm.
Therefore, the perimeter of the triangle is 22 cm.
Steps to Calculate the Perimeter of a Triangle
Calculating the perimeter of a triangle is a straightforward process that involves adding the lengths of the triangle's three sides. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Identify the sides of the triangle:
In any triangle, there are three sides. These sides are typically labeled as \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
- Measure the lengths of the sides:
Use a ruler or any other measuring tool to determine the lengths of each side. Ensure you have accurate measurements for \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \).
- Apply the perimeter formula:
The formula to calculate the perimeter (\( P \)) of a triangle is given by:
\( P = a + b + c \)
- Calculate the perimeter:
Substitute the measured lengths of the sides into the formula and perform the addition:
For example, if \( a = 5 \) cm, \( b = 7 \) cm, and \( c = 10 \) cm, then:
\( P = 5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm} + 10 \, \text{cm} \)
\( P = 22 \, \text{cm} \)
- Verify your result:
Double-check your measurements and calculations to ensure accuracy. Ensuring correct measurements and calculations is crucial for the correct perimeter value.
Examples and Practice Problems
Here are some examples and practice problems to help you understand how to calculate the perimeter of different types of triangles:
Example 1: Equilateral Triangle
Find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle with a side length of 7 inches.
Solution:
- Identify the side length of the triangle: \( a = 7 \) inches.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of an equilateral triangle: \( P = 3a \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 3 \times 7 = 21 \) inches.
The perimeter of the equilateral triangle is 21 inches.
Example 2: Isosceles Triangle
Find the perimeter of an isosceles triangle with equal side lengths of 5 feet and the third side length of 7 feet.
Solution:
- Identify the side lengths of the triangle: \( a = 5 \) feet (equal sides), \( b = 7 \) feet (base).
- Use the formula for the perimeter of an isosceles triangle: \( P = 2a + b \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 2 \times 5 + 7 = 10 + 7 = 17 \) feet.
The perimeter of the isosceles triangle is 17 feet.
Example 3: Scalene Triangle
Find the perimeter of a scalene triangle with sides of 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm.
Solution:
- Identify the side lengths of the triangle: \( a = 3 \) cm, \( b = 4 \) cm, \( c = 5 \) cm.
- Use the formula for the perimeter of a triangle: \( P = a + b + c \).
- Calculate the perimeter: \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) cm.
The perimeter of the scalene triangle is 12 cm.
Practice Problems
- Find the perimeter of an equilateral triangle with each side measuring 8 meters.
- Calculate the perimeter of an isosceles triangle with equal sides of 6 inches and a base of 10 inches.
- Determine the perimeter of a triangle with sides 7 cm, 9 cm, and 12 cm.
- A right triangle has a base of 5 meters and a height of 12 meters. Calculate the perimeter of the triangle.
Use the provided formulas and steps from the examples to solve these problems. Check your answers to ensure accuracy and improve your understanding of perimeter calculations.

Applications in Various Fields
The perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental concept in geometry that has numerous practical applications across various fields. Understanding and calculating the perimeter is essential for solving real-world problems in many disciplines. Here are some of the key applications:
- Architecture and Construction: In architecture, the perimeter is crucial for designing and constructing buildings and other structures. It helps in calculating the amount of materials needed, such as the length of fencing required for a triangular plot of land.
- Engineering: Engineers use perimeter calculations in numerous ways, including designing components, analyzing structural integrity, and optimizing material usage. For instance, knowing the perimeter of a triangular component can help determine the amount of material needed for its edges.
- Surveying and Navigation: Surveyors frequently use triangles to measure land areas and distances. The perimeter helps in creating accurate maps and determining property boundaries. In navigation, triangulation methods rely on knowing the perimeter of triangles to pinpoint locations.
- Physics: In physics, especially in mechanics and optics, understanding the properties of triangles and their perimeters can be essential. For example, in studying wave fronts and interference patterns, triangular geometries often play a significant role.
- Computer Graphics: In computer graphics and game design, triangles are the building blocks for modeling complex surfaces and objects. The perimeter helps in rendering these shapes accurately and efficiently.
- Agriculture: Farmers and agricultural planners use the concept of perimeter when designing and optimizing the layout of fields and plots. Knowing the perimeter allows them to efficiently allocate space for planting and irrigation systems.
Overall, the perimeter of a triangle is a versatile and widely applicable concept that aids in various scientific, engineering, and practical endeavors.
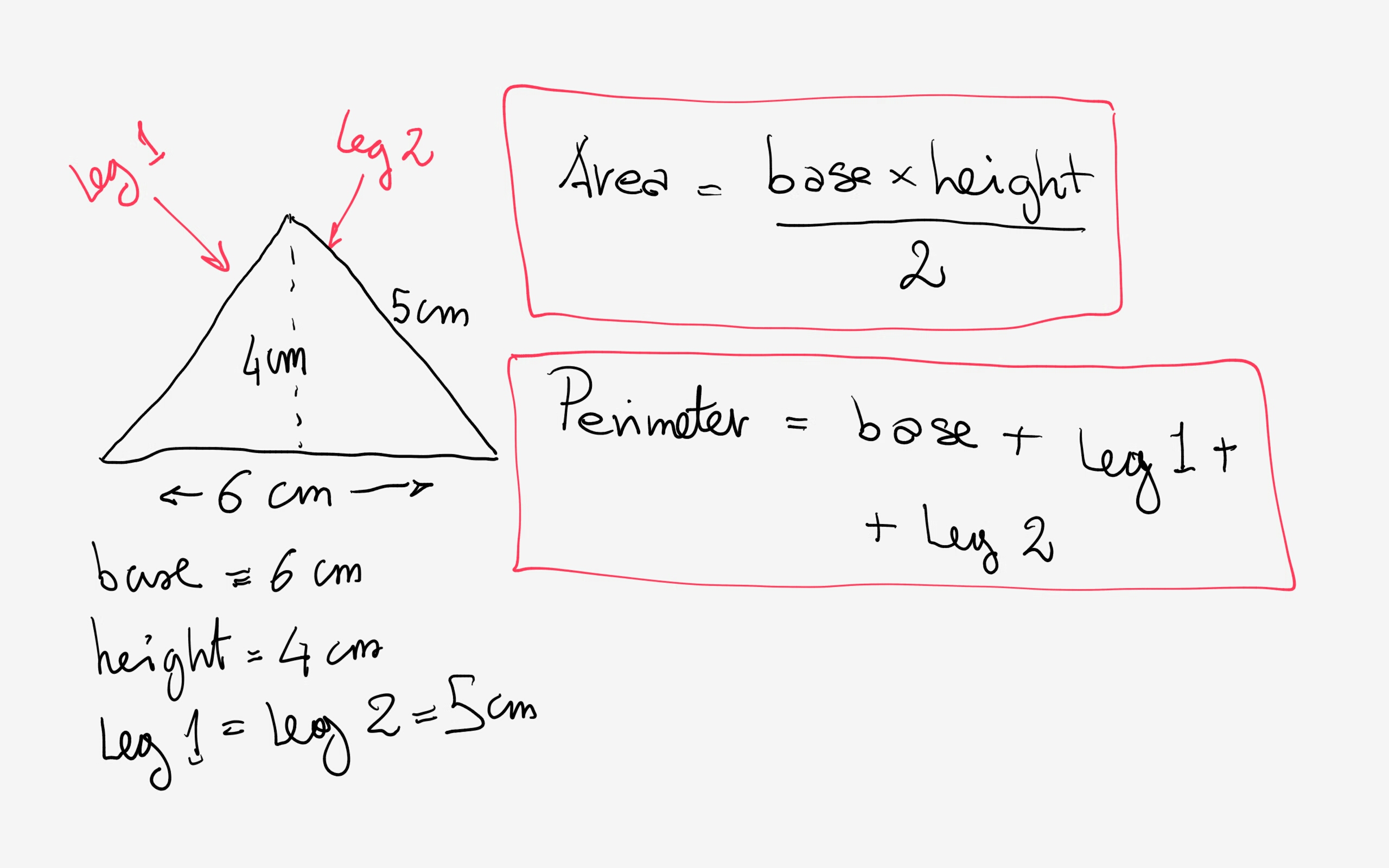
Visual Representations and Diagrams
Visual aids are essential for understanding the concept of a triangle's perimeter. Below are various diagrams and explanations to help you visualize and calculate the perimeter of different types of triangles.
1. Scalene Triangle
A scalene triangle has all sides of different lengths. To find its perimeter, add up the lengths of all three sides.
- Side \( a \)
- Side \( b \)
- Side \( c \)
Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
 |
2. Isosceles Triangle
An isosceles triangle has two sides of equal length. To find its perimeter, add the lengths of the two equal sides and the base.
- Side \( a \) (equal sides)
- Base \( b \)
Formula: \( P = 2a + b \)
 |
3. Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle has all sides of equal length. To find its perimeter, multiply the length of one side by three.
- Side \( a \)
Formula: \( P = 3a \)
 |
4. Right Triangle
A right triangle has one angle of 90 degrees. You can use the Pythagorean theorem to find the length of the hypotenuse if the other two sides are known.
- Side \( a \)
- Side \( b \)
- Hypotenuse \( c \)
Formula: \( P = a + b + c \)
Where \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \)
 |
5. Example Problems
-
Scalene Triangle:
Given sides \( a = 5 \) cm, \( b = 7 \) cm, and \( c = 10 \) cm, calculate the perimeter.
Solution:
\( P = 5 + 7 + 10 = 22 \) cm
-
Isosceles Triangle:
Given equal sides \( a = 8 \) cm and base \( b = 6 \) cm, calculate the perimeter.
Solution:
\( P = 2 \times 8 + 6 = 22 \) cm
-
Equilateral Triangle:
Given side \( a = 4 \) cm, calculate the perimeter.
Solution:
\( P = 3 \times 4 = 12 \) cm
-
Right Triangle:
Given sides \( a = 3 \) cm and \( b = 4 \) cm, calculate the perimeter.
Solution:
First, find the hypotenuse \( c \): \( c = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{9 + 16} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \) cm
Then, \( P = 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 \) cm
Using these visual aids and step-by-step calculations will enhance your understanding of how to find the perimeter of various types of triangles.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
When calculating the perimeter of a triangle, it's important to be aware of common mistakes that can lead to incorrect results. Here are some of the most frequent errors and how to avoid them:
-
Forgetting the Perimeter Formula:
Ensure you remember the formula \( P = a + b + c \), where \( P \) is the perimeter and \( a, b, \) and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides.
-
Mixing Up Perimeter and Area:
Perimeter is the total distance around the triangle, while area measures the space inside it. Use the correct formula for each calculation.
-
Incorrect Unit Conversion:
Always convert all side lengths to the same unit before adding them. For example, convert all measurements to centimeters or meters first.
-
Assuming Incorrect Side Lengths:
Double-check the side lengths, especially in word problems or diagrams, to ensure they are accurate before calculating.
-
Misinterpreting Triangle Types:
Recognize whether the triangle is equilateral, isosceles, or scalene, as this affects the calculation. For instance, in an equilateral triangle, you can simplify the calculation by multiplying one side length by 3.
By keeping these tips in mind, you can avoid common pitfalls and accurately calculate the perimeter of any triangle.
Advanced Topics and Special Cases
Understanding the perimeter of a triangle can be extended to more complex scenarios and special cases. Here are some advanced topics and special cases related to the perimeter of a triangle:
1. Perimeter of Triangles with Special Properties
- Equilateral Triangle: All three sides are equal. The perimeter is calculated as:
\[ P = 3a \]
where \(a\) is the length of each side. - Isosceles Triangle: Two sides are equal. The perimeter is:
\[ P = 2a + b \]
where \(a\) is the length of the equal sides, and \(b\) is the base. - Right Triangle: One angle is \(90^\circ\). The perimeter can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem if two sides are known:
\[ P = a + b + \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \]
where \(a\) and \(b\) are the legs of the triangle.
2. Heron's Formula
For any triangle with sides \(a\), \(b\), and \(c\), the semi-perimeter \(s\) is given by:
\[ s = \frac{a + b + c}{2} \]
Heron's formula for the area \(A\) of the triangle is:
\[ A = \sqrt{s(s - a)(s - b)(s - c)} \]
Knowing the area can help in various advanced geometric problems.
3. Perimeter of Triangles in Coordinate Geometry
When the vertices of a triangle are given by coordinates \((x_1, y_1)\), \((x_2, y_2)\), and \((x_3, y_3)\), the side lengths can be calculated using the distance formula:
\[ d = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2} \]
Then, the perimeter is the sum of these distances.
4. Perimeter in Non-Euclidean Geometry
In spherical or hyperbolic geometry, the concept of perimeter differs from Euclidean geometry. Calculations often require the use of trigonometric identities and more complex formulas.
5. Perimeter of Triangles with Algebraic Expressions
Sometimes, side lengths are given as algebraic expressions. Solving for the perimeter involves simplifying these expressions:
- Example: If the sides are given as \(2x + 3\), \(x + 5\), and \(3x - 4\), then:
\[ P = (2x + 3) + (x + 5) + (3x - 4) = 6x + 4 \]
These advanced topics provide deeper insights into the applications and complexities involved in calculating the perimeter of triangles in various contexts.

FAQs on Triangle Perimeter Calculation
-
What is the perimeter of a triangle?
The perimeter of a triangle is the total length of all its sides. It is calculated by adding the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
-
What is the formula for the perimeter of a triangle?
The formula to calculate the perimeter of a triangle is:
$$ P = a + b + c $$
where \( P \) is the perimeter, and \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the sides of the triangle.
-
How do you calculate the perimeter of an equilateral triangle?
In an equilateral triangle, all three sides are of equal length. Therefore, the formula simplifies to:
$$ P = 3a $$
where \( a \) is the length of one side.
-
What about the perimeter of an isosceles triangle?
In an isosceles triangle, two sides are of equal length. The formula for the perimeter is:
$$ P = 2a + b $$
where \( a \) is the length of the equal sides and \( b \) is the length of the base.
-
How do you find the perimeter of a scalene triangle?
A scalene triangle has all sides of different lengths. The perimeter is calculated using the general formula:
$$ P = a + b + c $$
where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the three sides.
-
Can the perimeter be calculated if one side is missing?
Yes, if two sides and the included angle are known, the missing side can be found using the Law of Cosines, and then the perimeter can be calculated by summing all three sides.
-
What are common mistakes in calculating the perimeter of a triangle?
Common mistakes include using different units for each side, not correctly identifying the lengths of the sides, and incorrect application of special formulas for specific types of triangles.
Conclusion and Summary
Understanding how to find the perimeter of a triangle is a fundamental skill in geometry. By mastering the basic formula, \( P = a + b + c \), where \( a \), \( b \), and \( c \) are the lengths of the triangle's sides, you can easily determine the perimeter of any triangle.
Throughout this guide, we explored various methods for calculating the perimeter, including:
- Using the basic formula for any triangle.
- Applying the Law of Cosines and Law of Sines for more complex cases.
- Special cases such as equilateral, isosceles, and right triangles.
We also delved into practical applications of triangle perimeter calculations in fields such as architecture, engineering, and art. Furthermore, common mistakes were highlighted to help you avoid errors and ensure accurate results.
To sum up, the key takeaways include:
- The perimeter of a triangle is the total distance around its sides.
- Simple addition of side lengths suffices for straightforward cases, while trigonometric approaches are necessary for others.
- Understanding and practicing these concepts can enhance your problem-solving skills in geometry and beyond.
We hope this comprehensive guide has helped you grasp the concept of triangle perimeters. Continue practicing with various problems and explore more advanced topics to deepen your understanding. Remember, learning geometry can be both fun and rewarding!
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách tìm chu vi của một tam giác bằng các phương pháp đơn giản và dễ hiểu, phù hợp cho học sinh và người học toán ở mọi cấp độ.
Làm Thế Nào Để Tìm Chu Vi Của Một Tam Giác | Toán Học với Thầy J
READ MORE:
Xem video hướng dẫn về cách tìm chu vi của một tam giác và hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này.
Làm thế nào để Tìm Chu vi của Một Tam Giác