Topic what is the difference between the area and perimeter: Discover the intriguing world of geometry as we explore "What is the Difference Between Area and Perimeter," unraveling the essentials of these fundamental concepts in a simple, engaging manner.
Table of Content
- Understanding Area and Perimeter
- YOUTUBE: Difference between area and perimeter - Key stage 2 maths
- Definition of Area
- Definition of Perimeter
- Key Differences Between Area and Perimeter
- Formulas for Calculating Area and Perimeter
- Units of Measurement for Area and Perimeter
- Practical Applications of Area and Perimeter
- Examples Illustrating Area and Perimeter
- Similarities Between Area and Perimeter
- Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
- Area and Perimeter in Different Shapes
- Interactive Practice Problems on Area and Perimeter
Understanding Area and Perimeter
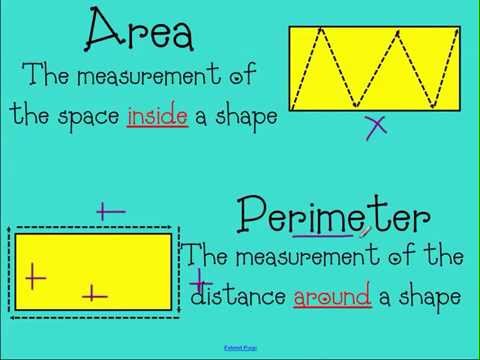
Area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in geometry, often confused due to their related nature, but they describe different properties of shapes. Area represents the amount of space a two-dimensional shape covers, while perimeter is the total length of the shape\"s boundary.
- Area: It is measured in square units, such as square meters or square inches, and is calculated by multiplying the relevant dimensions of a shape. For example, the area of a rectangle is obtained by multiplying its length by its width.
- Perimeter: This is the total length around the edge of a shape, measured in linear units like meters or inches. For a rectangle, the perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all four sides.
Understanding these concepts is essential in various real-world applications, such as land surveying, construction, and interior design, where measurements of space and boundaries are crucial.
| Shape | Area Formula | Perimeter Formula |
| Square | side × side | 4 × side |
| Rectangle | length × width | 2 × (length + width) |
| Circle | π × radius² | 2 × π × radius |
| Triangle | ½ × base × height | Sum of all sides |
For example, a square with each side measuring 11 meters will have an area of 121 square meters and a perimeter of 44 meters. Similarly, a rectangular plot of 12 yards by 10 yards will cover an area of 120 square yards and have a perimeter of 44 yards.
While there is no direct relationship between area and perimeter, understanding both concepts is crucial for accurately calculating and utilizing the dimensions of various shapes in practical scenarios.
READ MORE:
Difference between area and perimeter - Key stage 2 maths
Explore the fascinating difference between two commonly misunderstood concepts in this captivating video! Gain a deeper understanding and broaden your knowledge on this intriguing topic.
Area vs Perimeter - MightyOwl Math - 3rd Grade
Delve into the world of geometry and uncover the captivating debate of area versus perimeter! Discover the significance of both and how they play a vital role in our everyday lives.
Perimeter, Area, and Volume explained - Math with Mr. J
Join us on an educational journey where we unravel the mysteries of perimeter, area, and volume. This must-watch informative video will enhance your understanding of these key mathematical concepts and their practical applications.
Definition of Area
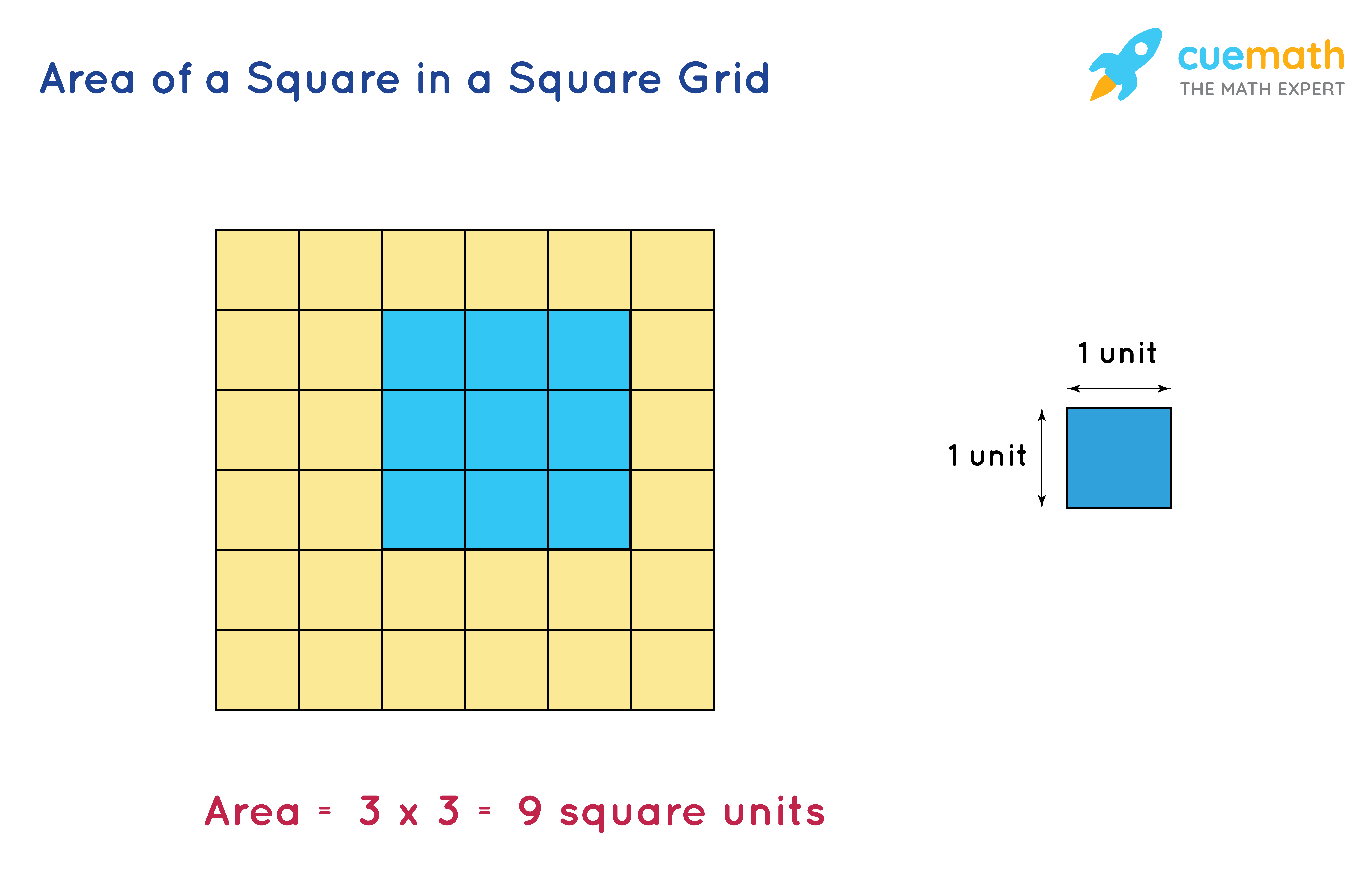
Area is a fundamental concept in geometry, defined as the space or region occupied by a two-dimensional flat object. It is quantified in square units, such as square meters or square inches. The area of a shape can be calculated using various formulas depending on the shape\"s geometry.
- Square: The area of a square is calculated as the length of its side squared (side^2).
- Rectangle: For a rectangle, the area is the product of its length and breadth (length x breadth).
- Triangle: The area of a triangle is half the product of its base and height (1/2 x base x height).
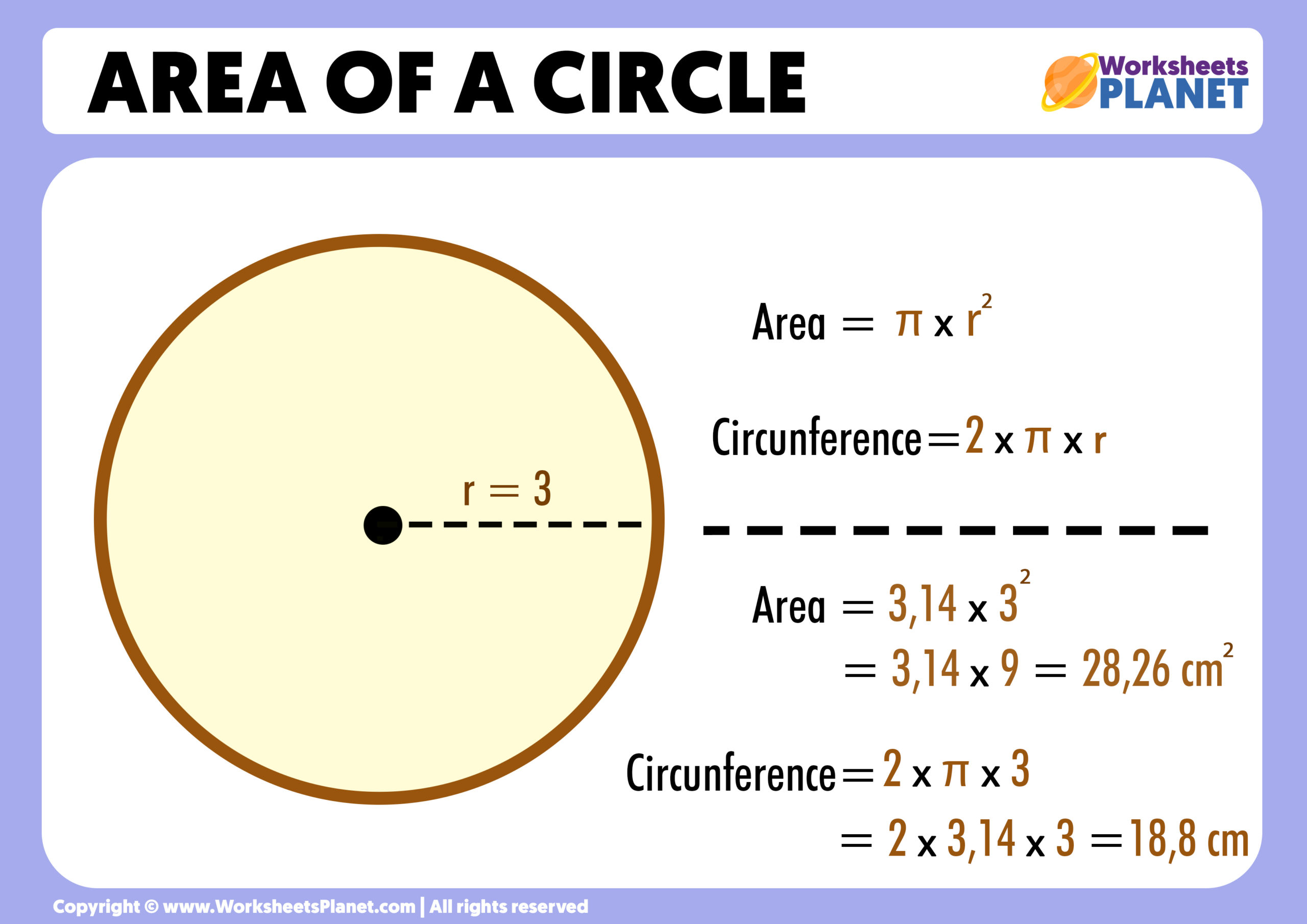
- Circle: A circle\"s area is calculated using the formula π times the radius squared (π x radius^2).
Area is a measure of how much space a shape covers. It helps in various practical applications, like determining the amount of material needed to cover a surface. For example, calculating the area of a room helps in buying the right amount of carpet or paint. Different shapes have unique formulas for calculating their area, and it is essential to apply the correct formula to obtain accurate measurements.
Understanding the concept of area is crucial in fields like architecture, land surveying, and interior design, where accurate measurements of space are vital.
Definition of Perimeter
The perimeter of a shape is defined as the total length of the boundary that encloses a two-dimensional figure. It is a linear measurement and is typically expressed in units such as meters, inches, or feet. The concept of perimeter is essential in various fields, including geometry, construction, and land surveying.
- Simple Shapes: For basic shapes like squares and rectangles, the perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of all sides. For example, the perimeter of a rectangle is twice the sum of its length and breadth (2 x (length + breadth)).
- Circles: The perimeter of a circle, known as the circumference, is calculated using the formula 2πr, where \"r\" is the radius of the circle.
- Polygons: In polygons, the perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all its sides. For irregular polygons, each side length must be measured and summed.
Understanding the perimeter is crucial for practical tasks such as fencing a garden or framing a piece of artwork. The perimeter gives a measure of the boundary length, which is different from the area, a measure of the space enclosed within the boundary.
For instance, wrapping a string around a square and measuring its length gives the perimeter of the square. Similarly, walking around the outside of a garden and measuring the distance covered would provide the garden\"s perimeter.
In summary, while the area focuses on the space inside a shape, the perimeter deals with the distance around it. This distinction is vital for accurately calculating material requirements for various projects.

Key Differences Between Area and Perimeter
Area and perimeter are two fundamental concepts in geometry, each measuring different aspects of shapes. Understanding these differences is crucial for various applications in mathematics and real-world scenarios.
- Conceptual Difference:
- Area refers to the space occupied within a closed two-dimensional shape. It is measured in square units (e.g., square meters, square feet).
- Perimeter, on the other hand, is the total length of the boundary of a shape. It\"s measured in linear units (e.g., meters, feet).
- Dimensional Difference:
- Area calculation involves two dimensions - length and width - of the object.
- Perimeter is concerned with the one-dimensional measurement, which is the length of the shape\"s outline.
- Examples of Usage:
- Area is typically used in contexts like farming (to calculate the land area) or in interior design (for carpeting or flooring).
- Perimeter is used in scenarios such as fencing a property or framing a picture.
- Practical Implication:
- Two shapes can have the same perimeter but different areas. For instance, different rectangles may have the same total boundary length but cover different amounts of space.
- Conversely, shapes can have the same area but different perimeters.
By understanding these differences, one can effectively apply these concepts to solve various problems in geometry, construction, design, and other fields that require spatial measurement and calculation.
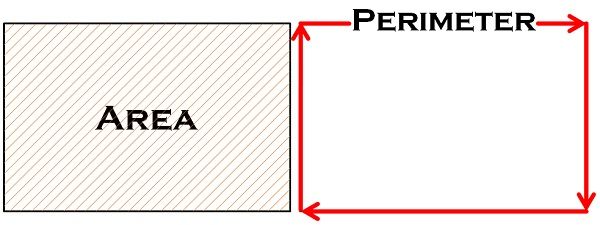
Formulas for Calculating Area and Perimeter
Calculating the area and perimeter of shapes is a fundamental aspect of geometry. Different shapes have specific formulas based on their properties.
These formulas provide a consistent method to determine the extent of a shape\"s surface (area) and the length of its boundary (perimeter). Understanding these formulas is essential in fields such as architecture, engineering, and various scientific disciplines where precise measurements are crucial.

_HOOK_
Units of Measurement for Area and Perimeter
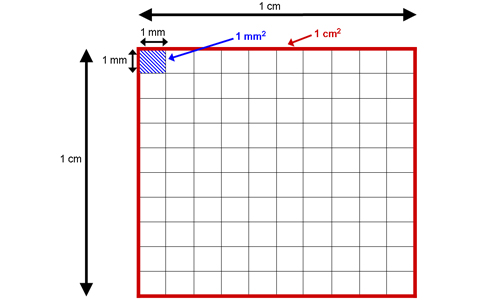
Understanding the units of measurement for area and perimeter is crucial for accurate calculations in geometry. These units are fundamentally different due to the nature of what they measure.
- Area: The area of a shape is measured in square units. This is because area represents the amount of space within a shape. Common units include square meters (m2), square centimeters (cm2), square feet (ft2), etc.
- Perimeter: Perimeter, being the length around a shape, is measured in linear units. These units include meters (m), centimeters (cm), feet (ft), inches (in), etc. The perimeter is essentially a one-dimensional measurement along the boundary of a shape.
It\"s important to use the correct units for each measurement to avoid confusion, especially in practical applications like construction, land surveying, and crafting. Area and perimeter, while related, require distinctly different units due to their different properties.
Practical Applications of Area and Perimeter
The concepts of area and perimeter have numerous practical applications in everyday life and various professional fields. Understanding these geometric measurements is crucial for efficient planning and execution in many scenarios.
- Construction and Architecture: Calculating the area and perimeter is essential in the planning and building of structures. The area helps in determining the amount of space available for use, while the perimeter informs boundary measurements for constructing fences or walls.
- Interior Design: Interior designers use area measurements to plan room layouts, including the placement of furniture, and to determine how much flooring or carpeting is needed.
- Agriculture: Farmers use area calculations to determine the size of their land for planting crops. Perimeter measurements are useful for fencing the property or dividing it into different sections.
- Land Surveying: Area and perimeter calculations are used in land surveying to establish property boundaries and to calculate the size of land parcels for legal and commercial purposes.
- Sports: In sports, understanding the area and perimeter of fields and courts is crucial for game planning and construction. For example, knowing the perimeter of a track or the area of a soccer field.
- Education: These concepts are fundamental in teaching geometry, helping students understand the properties of different shapes and their applications.
These examples highlight the importance of area and perimeter in various aspects of life, demonstrating their utility beyond mere academic concepts.

Examples Illustrating Area and Perimeter
Understanding the concepts of area and perimeter is greatly enhanced through practical examples. Here are some illustrative examples to clarify these concepts:
- Example 1: Square - Consider a square with each side measuring 4 inches. The area of the square is calculated as side2, which in this case is 42 = 16 square inches. The perimeter is calculated as 4 times the side, hence 4 x 4 = 16 inches.
- Example 2: Rectangle - For a rectangle with a length of 12 feet and a breadth of 4 feet, the area is length x breadth, which is 12 x 4 = 48 square feet. The perimeter is 2 times the sum of length and breadth, thus 2 x (12 + 4) = 32 feet.
- Example 3: Triangle - A triangle with a base of 8 inches, a height of 3 inches, and sides of 5 inches each. The area of the triangle is 1/2 x base x height, which is 1/2 x 8 x 3 = 12 square inches. The perimeter is the sum of all sides, so 5 + 8 + 5 = 18 inches.
- Example 4: Circular Garden - A garden with a radius of 50 units. The area of a circle is πr2, thus for this garden, it would be π x 502. The perimeter, or circumference, is 2πr, so 2 x π x 50 units.
These examples demonstrate how the area and perimeter are calculated for different shapes, highlighting the practical application of these concepts in everyday life.

Similarities Between Area and Perimeter
While area and perimeter are distinct concepts in geometry, they share certain similarities that are important in understanding the properties of shapes:
- Related to Geometry: Both area and perimeter are fundamental concepts in the study of geometry, primarily concerning two-dimensional shapes.
- Measurement Tools: They are both used as tools for measuring aspects of shapes - area measures the space within the shape, and perimeter measures the distance around it.
- Applicable to Various Shapes: Both concepts apply to a wide range of geometric shapes, such as squares, rectangles, triangles, and circles.
- Essential in Calculations: Area and perimeter are essential in various calculations, especially in fields like architecture, engineering, and land surveying.
- Formulas Based on Dimensions: The calculation of both area and perimeter is based on the dimensions of the shapes, such as length, width, radius, etc.
Understanding these similarities helps in comprehending the broader scope of these geometric measurements and their applications in various real-world scenarios.
Common Misconceptions and Clarifications
When learning about area and perimeter, certain misconceptions can arise. Here are some common misunderstandings and their clarifications:
- Misconception: Area and Perimeter are Interchangeable
- Clarification: Although they are both measurements related to shapes, area and perimeter serve different purposes. Area measures the space within a shape, while perimeter measures the distance around a shape.
- Misconception: The Same Formulas Apply to All Shapes
- Clarification: Different shapes have unique formulas for calculating area and perimeter. For example, the area of a rectangle is length x breadth, while for a circle, it is π(radius^2).
- Misconception: Larger Perimeter Implies Larger Area
- Clarification: Two shapes can have the same perimeter but different areas. The shape and dimensions affect the area, not just the perimeter.
- Misconception: Units for Area and Perimeter are the Same
- Clarification: Area is measured in square units (e.g., square meters), while perimeter is measured in linear units (e.g., meters).
- Misconception: Calculating Area and Perimeter is Complicated
- Clarification: By understanding and applying the correct formulas, calculating area and perimeter can be straightforward. Practice with different shapes enhances understanding.
Understanding these points helps clear up common confusions and fosters a better grasp of these fundamental geometric concepts.

_HOOK_
Area and Perimeter in Different Shapes
Area and perimeter are calculated differently for various geometric shapes. Each shape has its unique formula for these calculations.
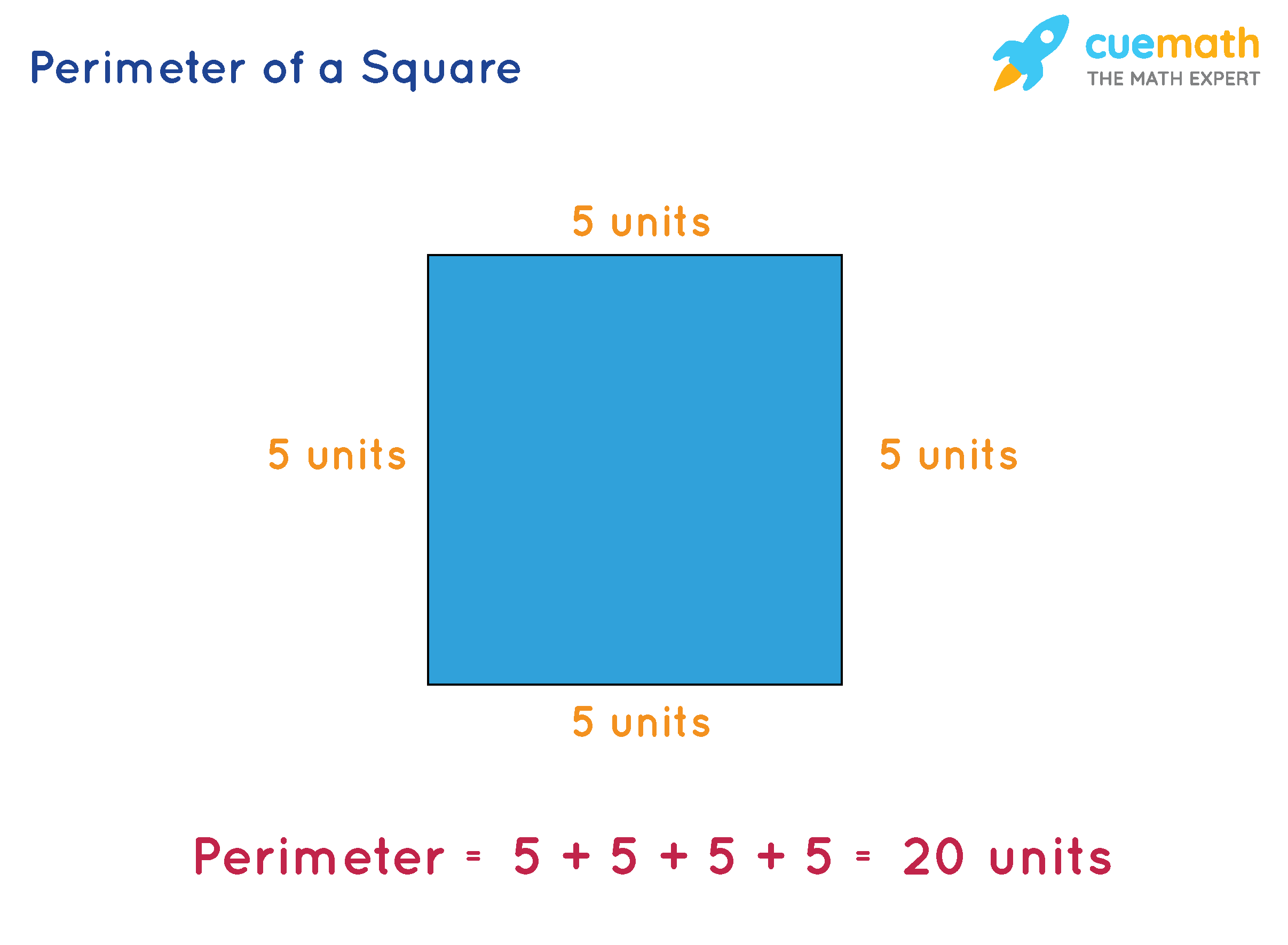
- Square:
- Area: Calculated as the square of one of its sides (side2).
- Perimeter: Four times the length of one side (4 × side).
- Rectangle:
- Area: Product of its length and breadth (length × breadth).
- Perimeter: Twice the sum of its length and breadth (2 × (length + breadth)).
- Triangle:
- Area: Half the product of its base and height (1/2 × base × height).
- Perimeter: Sum of the lengths of all three sides.
- Circle:
- Area: π multiplied by the radius squared (π × radius2).
- Perimeter (Circumference): 2π multiplied by the radius (2π × radius).
These formulas are essential for calculating the extent of space a shape covers (area) and the total length of its boundary (perimeter). Understanding these calculations is fundamental in various applications across mathematics, engineering, and other scientific disciplines.
READ MORE:
Interactive Practice Problems on Area and Perimeter
Engage in fun and interactive practice activities to enhance your understanding of area and perimeter concepts. These activities are suitable for a range of ages and learning levels.
- Perimeter Exploration: Practice finding the perimeter of various shapes by counting units or using given side lengths. Includes a mix of 4 to 7 questions per set to test your skills.
- Area Challenges: Dive into calculating the area of parallelograms, triangles, trapezoids, and composite figures. Each section includes 4 questions and additional quizzes to assess your understanding.
- Area and Perimeter Builder: An interactive online activity ideal for 2nd to 4th graders. Create your own shapes using colorful blocks, explore the relationship between perimeter and area, and solve problems related to building figures with given area and perimeter.
- PhET Interactive Simulations: Engage with simulations that offer a dynamic way to understand the concepts of area and perimeter. These activities are designed to be intuitive and visually appealing.
These interactive exercises will help you learn how to find the area of a shape by counting unit squares, build shapes with specific area and perimeter, and understand the area of irregular shapes by decomposing them into smaller shapes like rectangles, triangles, and squares.
Remember, practicing these problems will not only improve your mathematical skills but also enhance your problem-solving abilities. Have fun while learning!
Discover the intriguing world of geometry by exploring the differences between area and perimeter. Embark on a journey that unveils the essence of these fundamental concepts, enhancing your mathematical understanding and curiosity!