Topic what's the square root of 12: Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the square root of 12. In this article, we will explore various aspects of the square root of 12, including its mathematical representation, decimal and radical forms, simplification methods, and real-life applications. Join us as we delve into the fascinating properties of this irrational number.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 12
- Introduction
- Mathematical Representation
- Decimal and Radical Forms
- Simplification of Square Root of 12
- Prime Factorization Method
- Babylonian Method
- Properties of Square Roots
- Rational and Irrational Numbers
- Applications in Real Life
- FAQs on Square Root of 12
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 12, giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về sqrt(12) trong toán học.
Square Root of 12
The square root of 12 is represented in various forms including radical form, exponent form, and decimal form. Below is a detailed explanation of each form along with examples and methods to find the square root of 12.
Radical Form
The square root of 12 in radical form is:
Exponent Form
In exponent form, the square root of 12 is expressed as:
\[\sqrt{12} = 12^{1/2}\]
Decimal Form
The square root of 12 in decimal form is approximately:
\[\sqrt{12} \approx 3.464\]
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 12
-
Prime Factorization Method
We can express 12 as the product of its prime factors:
\[12 = 2 \times 2 \times 3\]
\[\sqrt{12} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 3} = 2\sqrt{3}\]
-
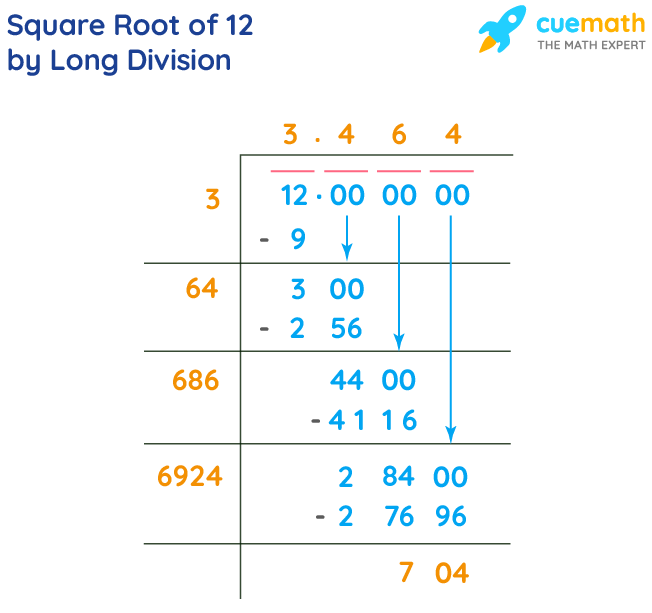
Long Division Method
The long division method involves several steps to find the square root to a certain number of decimal places. After a few iterations, we approximate the square root of 12 as 3.464.
Examples
-
Example 1: Simplify the square root of 12 to its lowest radical form.
Solution: \[\sqrt{12} = 2\sqrt{3}\]
-
Example 2: If the area of a circle is 12π square inches, find the radius of the circle.
Solution: \(\text{Area} = \pi r^2 = 12\pi\)
\(\therefore r = \sqrt{12} = 3.464 \text{ inches}\)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Why is the square root of 12 an irrational number?
The prime factorization of 12 includes the factor 3, which is not in pairs. Therefore, \(\sqrt{12}\) is an irrational number. - What is the square root of 12 rounded to the nearest tenth?
The square root of 12 rounded to the nearest tenth is 3.5. - Can the square root of 12 be represented as a fraction?
Since the square root of 12 is irrational, it cannot be precisely represented as a fraction, but it can be approximated as \(\frac{346}{100}\) or \(\frac{323}{50}\).

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 12 is an important mathematical concept that appears in various fields, from geometry to engineering. Represented as , it is an irrational number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Instead, it can be simplified to in radical form. This guide will explore its decimal approximation, simplification techniques, and applications.
- Decimal Form: The square root of 12 is approximately 3.464, a non-repeating and non-terminating decimal.
- Radical Form: Simplifying gives us .
- Significance: Understanding the square root of 12 is crucial for solving quadratic equations, optimizing designs in engineering, and analyzing geometric shapes.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the mathematical representation, simplification methods, and practical applications of the square root of 12, providing a thorough understanding of this intriguing number.
Mathematical Representation
The square root of 12 can be represented in various forms, each useful for different mathematical purposes. Below, we explore these representations in detail:
- Radical Form: The most basic representation is the radical form: . This notation indicates that we are looking for a number which, when squared, equals 12.
- Simplified Radical Form: The square root of 12 can be simplified by breaking it down into its prime factors. We start with:
- Since , we can write:
- Decimal Form: The square root of 12 in decimal form is approximately 3.464. This can be derived using a calculator or iterative methods like the Babylonian method:
- Start with an initial guess, .
- Apply the formula .
- Repeat until the value stabilizes around .
These different representations of the square root of 12 offer flexibility in various mathematical computations and applications, making it easier to understand and utilize this number in diverse contexts.
Decimal and Radical Forms
The square root of 12 can be expressed in both decimal and radical forms, each providing unique insights into the number's properties. Understanding these forms is crucial for different mathematical applications.
- Radical Form:
The radical form of the square root of 12 is written as . This form is exact and is often used in algebra and geometry.
To simplify the radical form, we factorize 12 into its prime factors:
- Since , we can simplify:
- Decimal Form:
The decimal form of the square root of 12 is an approximation, providing a numerical value that is easy to use in calculations. Using a calculator or numerical methods, we find:
This value can be rounded to 3.464 for most practical purposes, maintaining a high level of accuracy.
Both forms have their uses: the radical form is exact and often preferred in theoretical work, while the decimal form is useful for numerical calculations and real-world applications. Understanding both representations allows for greater flexibility and precision in mathematical problem-solving.
Simplification of Square Root of 12
Simplifying the square root of 12 involves breaking it down into its prime factors and expressing it in a more manageable form. Here is a step-by-step process for simplification:
- Prime Factorization:
Begin by factorizing 12 into its prime factors:
- Therefore,
- Separate the Perfect Square:
Identify the perfect square in the factorization:
- is a perfect square.
- Rewrite the Square Root:
Express the square root of 12 in terms of the perfect square:
- Apply the Square Root to Each Factor:
Separate the square root into the product of the square roots:
- Simplified Form:
The simplified form of the square root of 12 is:
By following these steps, the square root of 12 is simplified to , making it easier to work with in various mathematical contexts.
Prime Factorization Method
The Prime Factorization Method is a straightforward approach to simplify the square root of a number by expressing it in terms of its prime factors. Here’s a detailed, step-by-step guide to using this method for the square root of 12:
- Find the Prime Factors:
Begin by factorizing 12 into its prime components:
- 12 can be divided by 2, a prime number: .
- Next, factorize 6: .
- So, the prime factorization of 12 is: .
- Rewrite Using Prime Factors:
Express the square root of 12 in terms of its prime factors:
- .
- Simplify the Square Root:
Separate the square root into the product of square roots and simplify:
- .
- Final Simplified Form:
The simplified form of the square root of 12 using the prime factorization method is:
- .
Using the Prime Factorization Method, we have effectively simplified the square root of 12 to , which is easier to work with in mathematical calculations.
Babylonian Method
The Babylonian method, also known as Heron's method, is an ancient algorithm for finding the square root of a number. This iterative method is known for its simplicity and speed of convergence. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to use the Babylonian method to find the square root of 12:
- Choose an initial guess. A good starting point for √12 might be 3, since 32 = 9, which is close to 12.
- Apply the formula:
where n is the number you want to find the square root of (12), and x is your current guess. - Compute the next guess. For our initial guess of 3:
Simplifies to:
- Repeat the process with the new guess:
Simplifies to:
- Continue iterating until the desired level of accuracy is achieved. After a few more iterations, the value will converge to approximately 3.4641, which is the square root of 12.
The Babylonian method provides a quick and efficient way to calculate square roots and can be extended to any non-negative number. The precision of the result depends on the number of iterations performed.
Properties of Square Roots
The properties of square roots are fundamental in understanding their behavior and applications in mathematics. Here are several key properties:
- Product Rule: The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots of the factors.
\[\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\]
- Quotient Rule: The square root of a quotient is equal to the quotient of the square roots of the numerator and the denominator.
\[\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \quad \text{for } b \neq 0\]
- Square of a Square Root: Taking the square root of a squared number returns the absolute value of the original number.
\[\sqrt{a^2} = |a|\]
- Non-negative Roots: Square roots are only real and non-negative for non-negative numbers.
\[\sqrt{a} \text{ is real only if } a \geq 0\]
- Zero's Square Root: The square root of zero is zero.
\[\sqrt{0} = 0\]
- Square Root of One: The square root of one is one.
\[\sqrt{1} = 1\]
- Adding and Subtracting Square Roots: Square roots can only be directly added or subtracted if the radicands (the numbers inside the square root) are the same.
\[\sqrt{a} + \sqrt{a} = 2\sqrt{a}\]
- Irrational Numbers: The square root of a non-perfect square is an irrational number, which cannot be exactly represented as a fraction or a terminating/repeating decimal.
For example, \(\sqrt{2}\) is irrational.
Additionally, there are some special properties involving square roots:
- Square Root of Negative Numbers: The square root of a negative number introduces the concept of imaginary numbers. The square root of \(-1\) is denoted as \(i\), and \(\sqrt{-a} = i\sqrt{a}\).
For example, \(\sqrt{-16} = 4i\).
- Even and Odd Numbers:
- The square root of an even number is always even.
- The square root of an odd number is always odd.
Understanding these properties helps in simplifying and solving various mathematical problems involving square roots.
Rational and Irrational Numbers
Numbers can be classified into two broad categories: rational and irrational numbers. Understanding the difference between these two types is essential in mathematics, especially when dealing with square roots.
Rational Numbers
Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction a/b, where a and b are integers, and b is not zero. Rational numbers include integers, finite decimals, and repeating decimals. Examples of rational numbers are:
- \(\frac{1}{2}\)
- 0.75 (which is \(\frac{3}{4}\))
- 2 (which is \(\frac{2}{1}\))
- -5 (which is \(\frac{-5}{1}\))
Irrational Numbers
Irrational numbers, on the other hand, cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. These numbers have non-terminating and non-repeating decimal expansions. Common examples include:
- \(\pi \approx 3.14159...\)
- \(\sqrt{2} \approx 1.41421...\)
- \(e \approx 2.71828...\)
Square Root of 12
The square root of 12, denoted as \(\sqrt{12}\), is an example of an irrational number. This is because \(\sqrt{12}\) simplifies to \(2\sqrt{3}\), and \(\sqrt{3}\) is irrational. Hence, \(\sqrt{12}\) cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. When approximated, \(\sqrt{12} \approx 3.4641...\), and the decimal expansion neither terminates nor repeats.
Comparison of Rational and Irrational Numbers
| Rational Numbers | Irrational Numbers |
|---|---|
| Can be expressed as fractions | Cannot be expressed as fractions |
| Finite or repeating decimals | Non-terminating and non-repeating decimals |
| Examples: \( \frac{1}{2}, 3, 0.75 \) | Examples: \( \pi, \sqrt{2}, e \) |
Properties of Rational and Irrational Numbers
- The sum or product of two rational numbers is always rational.
- The sum of a rational number and an irrational number is always irrational.
- The product of a non-zero rational number and an irrational number is always irrational.
- The sum or product of two irrational numbers can be rational or irrational, depending on the numbers.
Understanding these properties helps in identifying and working with different types of numbers in various mathematical contexts.

Applications in Real Life
Square roots have numerous practical applications in various fields. Here are some of the key areas where the square root of 12 and other square roots are used:
- Engineering and Architecture
Square roots are essential in engineering and architecture for calculating distances, areas, and structural integrity. For example, the Pythagorean theorem, which involves square roots, helps in determining the lengths of sides in right triangles, crucial for design and construction projects.
- Finance
In finance, square roots are used to calculate volatility, risk assessments, and the rate of return on investments. For instance, the standard deviation, a measure of risk, is derived by taking the square root of the variance of investment returns.
- Science and Physics
Square roots are used in various scientific calculations, including those involving wave velocities, radiation intensity, and other physical phenomena. These calculations help scientists understand and predict natural behaviors and develop new technologies.
- Statistics
In statistics, square roots are used to compute standard deviation, a measure of data spread. This helps in understanding data distributions and making informed decisions based on statistical analysis.
- Computer Graphics
In computer graphics, square roots are employed to calculate distances between points and the magnitudes of vectors. This is essential in rendering images and animations accurately in both 2D and 3D environments.
- Navigation
Square roots are used in navigation to compute the shortest distances between two points on a map, crucial for route planning in aviation, maritime, and land transportation.
- Cryptography
In cryptography, square roots play a role in encryption algorithms, key exchanges, and secure communications. They help in creating secure cryptographic systems to protect data transmission.
FAQs on Square Root of 12
-
What is the simplified form of √12?
The simplified form of √12 is 2√3. This is obtained by factoring 12 into 4 and 3, where 4 is a perfect square. Hence, √12 = √(4×3) = 2√3.
-
What is the square root of 12 in decimal form?
The square root of 12 in decimal form is approximately 3.464. This is a rounded value which provides a decimal approximation of the exact square root.
-
Is the square root of 12 rational or irrational?
The square root of 12 is an irrational number. It cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating.
-
How do you find the square root of 12 using the prime factorization method?
To find the square root of 12 using prime factorization, we factorize 12 into its prime factors: 12 = 2 × 2 × 3. Thus, √12 = √(2² × 3) = 2√3.
-
Can you use a calculator to find the square root of 12?
Yes, you can use a calculator to find the square root of 12. Simply enter 12 and use the square root function to get the approximate value, which is 3.464.
-
What is the significance of the square root of 12 in geometry?
In geometry, the square root of 12 can represent the length of the hypotenuse of a right triangle with legs of length 3 and 4. This is derived from the Pythagorean theorem.
-
Is the negative square root of 12 the same as the square root of -12?
No, the negative square root of 12 (which is -√12) is not the same as the square root of -12. The latter involves imaginary numbers and is represented as √(-12) = 2i√3.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 12, giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về sqrt(12) trong toán học.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 12: Sqrt(12)
READ MORE:
Khám phá khái niệm căn bậc hai cùng thầy J, một video hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu về toán học.
Căn Bậc Hai Là Gì? | Toán Học Với Thầy J