Topic whats the square root of 116: Discover the fascinating world of square roots with our comprehensive guide on "What's the Square Root of 116?" Learn how to calculate it, understand its properties, and explore real-life applications. This article will simplify complex concepts, making mathematics more approachable and enjoyable for everyone. Join us as we delve into the square root of 116 and more!
Table of Content
- Square Root of 116
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding the Square Root of 116
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 116
- Prime Factorization Method
- Approximation Techniques
- Decimal Representation
- Applications of Square Roots in Real Life
- FAQ about Square Roots
- Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
- Advanced Topics Related to Square Roots
- Interactive Tools and Calculators
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 116 bằng phương pháp dễ hiểu và chi tiết. Thích hợp cho học sinh và người yêu thích toán học.
Square Root of 116
The square root of 116 can be expressed in various ways, both in its exact form and its approximate decimal form.
Exact Form
The exact form of the square root of 116 is given by:
$$\sqrt{116} = 2\sqrt{29}$$
Decimal Form
The decimal form of the square root of 116 is approximately:
$$\sqrt{116} \approx 10.77032961$$
Calculation Methods
Prime Factorization
To find the square root of 116 using prime factorization:
- Factor 116 into its prime factors: \(116 = 2^2 \times 29\)
- Apply the square root to the prime factors: \(\sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29} = 2\sqrt{29}\)
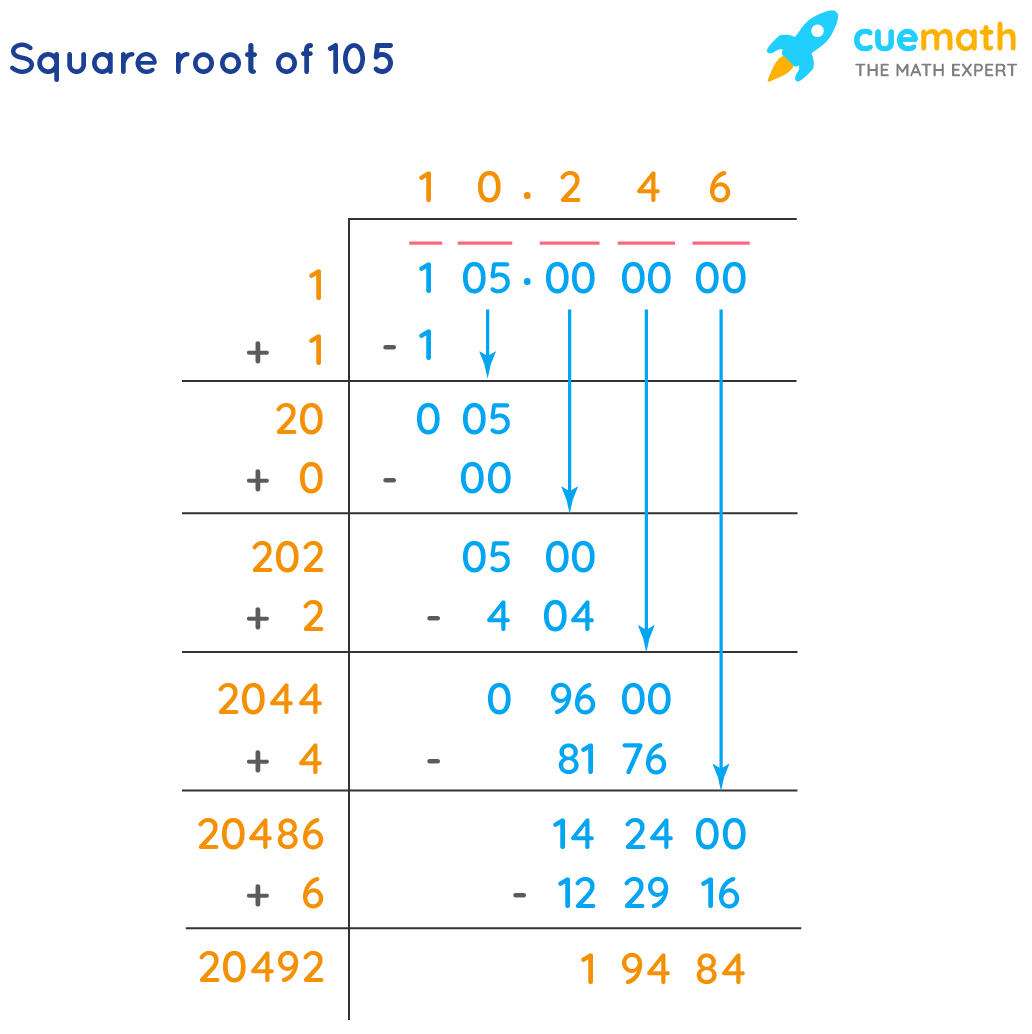
Long Division Method
The long division method is another way to find the square root of 116:
- Start by grouping the digits in pairs from the decimal point.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 116.
- Subtract this number from 116 and bring down pairs of zeros.
- Repeat the process to find the decimal places.
Properties of the Square Root of 116
| Property | Value |
| Exact Form | $$2\sqrt{29}$$ |
| Decimal Form | $$10.77032961$$ |
| Irrational Number | Yes |
Applications
The square root of 116 can be used in various mathematical and real-world applications, such as:
- Calculating distances in geometry using the Pythagorean theorem.
- Solving quadratic equations.
- Physics and engineering calculations where root values are required.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are fundamental concepts in mathematics, representing a number that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. Understanding square roots is essential for various mathematical calculations and real-world applications. Let's explore the concept of square roots in detail.
- Definition: The square root of a number \( x \) is a number \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). It is denoted as \( \sqrt{x} \).
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: a positive root and a negative root. For example, the square roots of 116 are \( \sqrt{116} \approx 10.77032961 \) and \( -\sqrt{116} \approx -10.77032961 \).
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because their square roots are integers. For instance, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) and \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \).
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers that are not perfect squares have irrational square roots. These roots cannot be expressed as exact fractions and have non-repeating decimal expansions. An example is \( \sqrt{116} = 2\sqrt{29} \approx 10.77032961 \).
To calculate square roots, various methods can be used:
- Prime Factorization: Break down the number into its prime factors and simplify. For instance, \( 116 = 2^2 \times 29 \), so \( \sqrt{116} = 2\sqrt{29} \).
- Long Division Method: A manual method that involves dividing the number into pairs of digits and finding the root digit by digit.
- Using Calculators: Modern calculators and computer algorithms can quickly find square roots to many decimal places.
Square roots are used in various fields, including geometry, physics, engineering, and finance, making them an indispensable tool in both academic and practical contexts.
Understanding the Square Root of 116
The square root of 116 is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the number 116. Mathematically, this is represented as \( \sqrt{116} \). Calculating square roots can be approached through various methods, such as prime factorization, long division, and approximation techniques.
In its simplified radical form, the square root of 116 can be expressed as \( 2\sqrt{29} \). This is derived by factoring 116 into its prime components:
- 116 can be factored into \( 2^2 \times 29 \).
- Taking the square root of \( 2^2 \) gives 2, hence \( \sqrt{116} = 2\sqrt{29} \).
Using the long division method, the square root of 116 can be approximated step-by-step:
- Start with 116.000000 and pair the digits from the right. Divide 1 by a number such that (number × number) ≤ 1, giving quotient 1 and remainder 0.
- Double the quotient to get 2. Bring down 16 for division. Find a number such that (20 + that number) × that number ≤ 16. We use 0 and bring down 1600 as the new dividend.
- With the new divisor as 200, find a number to multiply with 200 that gives ≤ 1600, which is 7 (207 × 7 = 1449).
- Repeat the steps until the desired precision is achieved, giving \( \sqrt{116} \approx 10.770 \).
Here are some important points about the square root of 116:
- The square root of 116 is approximately 10.770 to three decimal places.
- \( \sqrt{116} \) is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- It lies between the square roots of 100 (10) and 121 (11), so \( 10 < \sqrt{116} < 11 \).
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 116
Calculating the square root of 116 involves understanding different methods to arrive at the precise value. Below are some common methods used to calculate the square root of 116.
1. Prime Factorization
This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors. However, since 116 is not a perfect square, this method is not ideal for finding an exact square root but can help simplify the process.
- Prime factorize 116: \( 116 = 2^2 \times 29 \)
- Rewrite under the square root: \( \sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29} \)
- Simplify: \( \sqrt{116} = 2\sqrt{29} \)
- Approximate: \( 2\sqrt{29} \approx 2 \times 5.385 \approx 10.77 \)
2. Long Division Method
The long division method is more suitable for finding the square root of numbers that are not perfect squares. Here's how it works:
- Pair the digits of 116 from right to left: 1 | 16
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 1: 1 (since \(1^2 = 1\))
- Subtract and bring down the next pair: 0 and 16 → 016
- Double the divisor and find the next digit: 2 and trial numbers 20x x ≤ 16 → 26
- Continue the process to get more precise digits.
Using this method, we find that the square root of 116 is approximately 10.77.
3. Using a Calculator
A straightforward method is to use a scientific calculator:
- Enter 116
- Press the square root (√) button
- Read the result: \( \sqrt{116} \approx 10.7703 \)
4. Estimation and Refinement
Another method is to estimate and then refine the approximation:
- Estimate between known squares: \(10^2 = 100\) and \(11^2 = 121\), so \(10 < \sqrt{116} < 11\)
- Refine the guess by averaging or using iterative methods to hone in on the exact value.
5. Using Exponential Form
Square roots can also be expressed using exponents:
\( 116^{1/2} \approx 10.7703 \)
Conclusion
By utilizing these methods, you can determine that the square root of 116 is approximately 10.77. Understanding and practicing these techniques can help improve your mathematical skills and comprehension.
Prime Factorization Method
Calculating the square root of a number using the prime factorization method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to use this method to find the square root of 116.
- Factorize the number: Start by finding the prime factors of 116. The prime factors of 116 are 2 and 29, since 116 = 22 x 29.
- Express under the square root: Rewrite the square root of 116 as the product of the square roots of its factors: \[ \sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29} \]
- Simplify the expression: Since the square root of a product is the product of the square roots, you can simplify: \[ \sqrt{2^2 \times 29} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{29} \] The square root of \(2^2\) is 2, so the expression simplifies to: \[ 2 \sqrt{29} \]
- Approximate the value: Calculate the decimal value of \(2 \sqrt{29}\). The approximate value of \(\sqrt{29}\) is 5.385, so: \[ 2 \times 5.385 \approx 10.77 \]
Thus, the square root of 116 in simplest radical form is \(2 \sqrt{29}\) and in decimal form, it is approximately 10.77.

Approximation Techniques
The square root of 116 can be approximated using several techniques. Here, we discuss a couple of effective methods: the average method and using nearby perfect squares.
Using Nearby Perfect Squares
We start by identifying two perfect square numbers between which 116 lies. In this case, 100 (10²) and 121 (11²) are the nearest perfect squares. Thus, we know:
- √100 < √116 < √121
- 10 < √116 < 11
Therefore, we know that the square root of 116 is between 10 and 11.
Average Method
We can refine this approximation further using the average method:
- Divide 116 by one of the square roots within our range. For instance, dividing by 10.5:
- Next, average the result with 10.5:
- Thus, an approximation of √116 is 10.774.
\[ 116 ÷ 10.5 ≈ 11.048 \]
\[ (11.048 + 10.5) ÷ 2 = 21.548 ÷ 2 = 10.774 \]
Iterative Method
We can further improve the approximation by repeating the process:
- Divide 116 by the latest approximation, 10.774:
- Average this result with 10.774:
- Therefore, √116 ≈ 10.769.
\[ 116 ÷ 10.774 ≈ 10.764 \]
\[ (10.764 + 10.774) ÷ 2 ≈ 10.769 \]
Refinement
Repeating these steps several times will yield a more precise approximation. For practical purposes, √116 is approximately 10.77 when rounded to two decimal places.
Visualization with a Graph
For a better understanding, one can plot the function \( y = x^2 \) and see where it intersects with \( x = 116 \) on the graph. This intersection point will visually confirm the approximate value of the square root.
Conclusion
While the above methods provide an approximate value of the square root of 116, using a calculator will give a more precise result. The calculated square root of 116 is approximately 10.7703 when rounded to four decimal places.
Decimal Representation
The square root of 116 is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. The approximate value of the square root of 116 is:
\(\sqrt{116} \approx 10.7703\)
To provide a more detailed decimal representation, here are the first few digits:
\(\sqrt{116} \approx 10.770329614269007\)
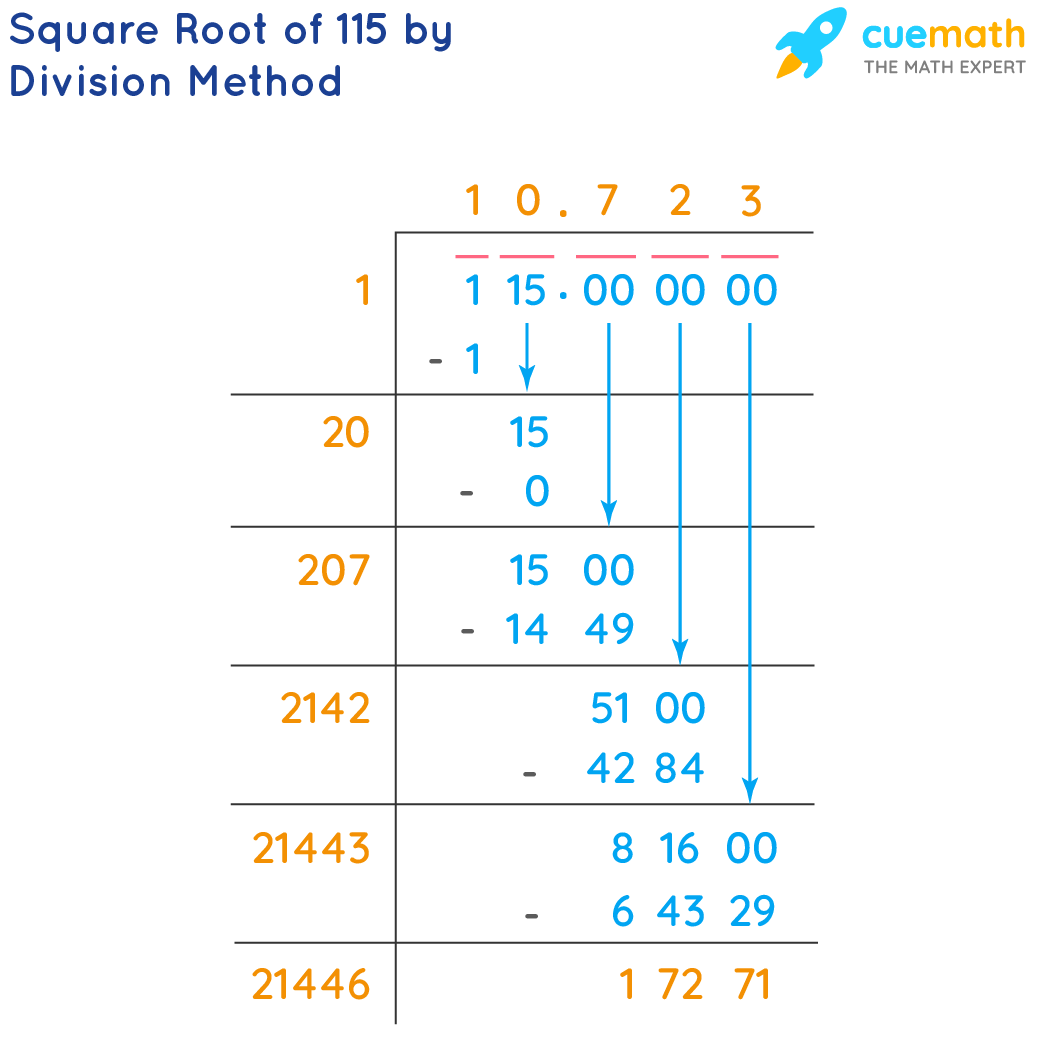
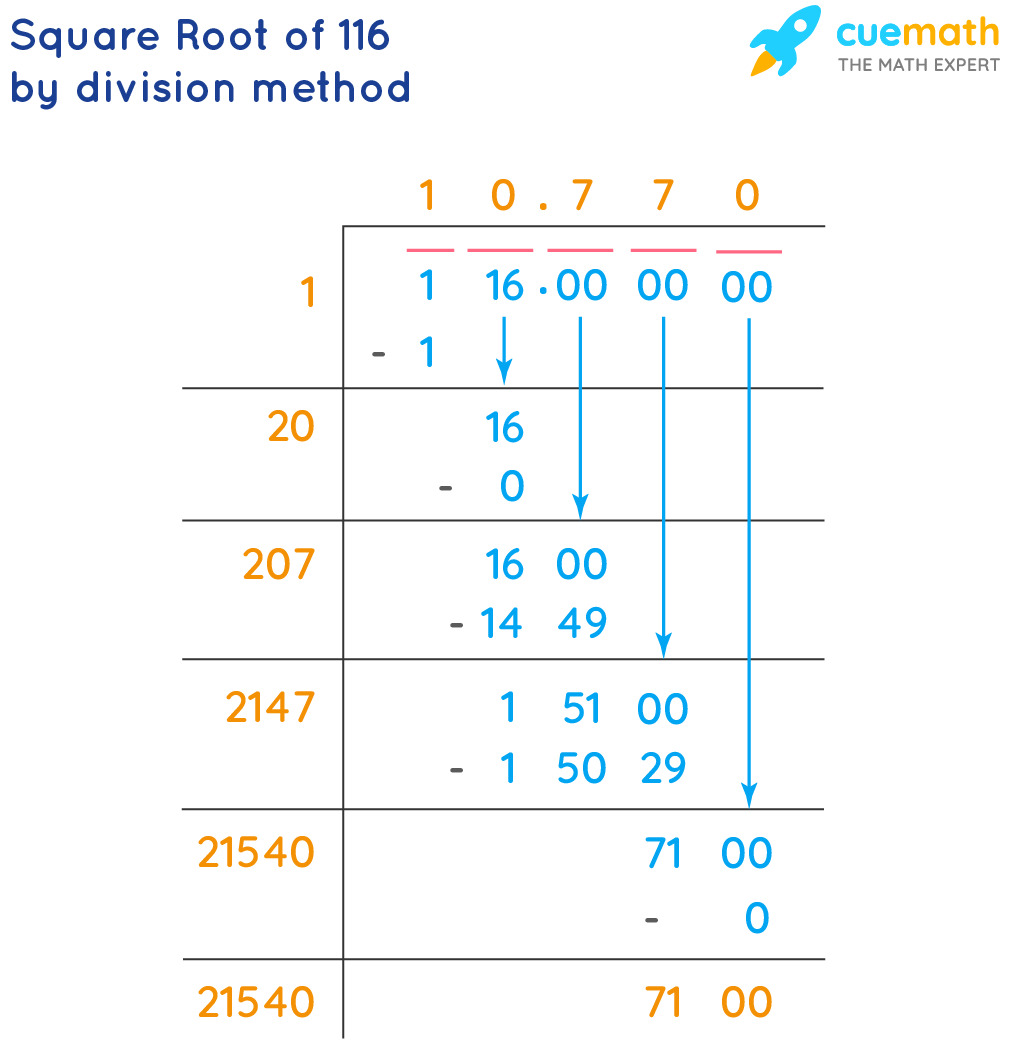
Here is a step-by-step approach to approximate the square root of 116 using the long division method:
- Pair the digits of 116 starting from the decimal point, placing a bar over each pair. In this case, we write 116 as 1 16.000000.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair (1 in this case). This number is 1, since \(1^2 = 1\).
- Subtract \(1^2\) from 1, giving us 0. Bring down the next pair (16), making it 16.
- Double the divisor (1), giving us 2. Determine how many times 2 goes into 16 without exceeding it. The answer is 7 (since \(27 \times 7 = 189\)).
- Place 7 in the quotient, giving us 1.7. Multiply 27 by 7, resulting in 189. Subtract 189 from 1600 (since we brought down 00), resulting in 1411. Bring down the next pair of zeros (00), making it 141100.
- Double the quotient (17), giving us 34. Determine how many times 34 goes into 1411 without exceeding it. The answer is 4 (since \(344 \times 4 = 1376\)).
- Place 4 in the quotient, giving us 1.74. Multiply 344 by 4, resulting in 1376. Subtract 1376 from 14110, resulting in 3410. Bring down the next pair of zeros (00), making it 341000.
- Continue this process to get a more precise value of the square root.
This method can be continued to achieve the desired level of accuracy. Using a calculator or computer, the square root of 116 is more precisely given by:
\(\sqrt{116} \approx 10.770329614269007...\)
This decimal can be extended as far as needed for precision in various applications. Here is a table showing the square root of 116 to various decimal places:
| Decimal Places | Approximation |
|---|---|
| 1 | 10.8 |
| 2 | 10.77 |
| 3 | 10.770 |
| 4 | 10.7703 |
| 5 | 10.77033 |
| 6 | 10.770329 |
| 7 | 10.7703296 |
| 8 | 10.77032961 |
Applications of Square Roots in Real Life
Square roots are a fundamental mathematical concept with numerous practical applications in various fields. Below are some key areas where square roots are used in real life:
- Geometry: Square roots are essential in calculating the lengths of sides in right triangles using the Pythagorean theorem. For example, the distance between two points in a plane can be found using the formula \(D = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}\).
- Physics: Square roots help determine quantities such as velocities, accelerations, and forces. In wave mechanics, the intensity of sound waves or light can be calculated using square roots.
- Engineering: In structural engineering, square roots are used to determine natural frequencies of buildings and bridges to predict how they will respond to vibrations and loads.
- Finance: Square roots are used to calculate volatility in stock prices, which involves taking the square root of the variance to understand the risk associated with an investment.
- Statistics: Standard deviation, a measure of data dispersion, is the square root of the variance. This metric is crucial for data analysis and helps statisticians make informed decisions.
- Computer Science: In graphics and game development, square roots are used to calculate distances between objects, as well as in algorithms for encryption and data security.
- Navigation: Square roots are used to calculate distances between geographical points, aiding in route planning for aviation and maritime navigation.
- Medicine: Dosage calculations often involve square roots, particularly in determining the correct dose of medication based on body surface area.
Overall, square roots are indispensable in various scientific, engineering, financial, and everyday applications, making them a vital part of mathematical education and practical problem-solving.
FAQ about Square Roots
This section provides answers to common questions about square roots, including the square root of 116.
- What is a square root?
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 25 is 5, because 5 x 5 = 25. In mathematical notation, the square root of 25 is written as √25 = 5.
- What is the square root of 116?
The square root of 116 is approximately 10.77. This means that 10.77 x 10.77 ≈ 116.
- Is the square root of 116 a rational or irrational number?
The square root of 116 is an irrational number. This is because it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers, and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating: 10.770329614269...
- How can I calculate the square root of a number?
There are several methods to calculate the square root of a number, including:
- Using a calculator: Most scientific calculators have a square root function.
- Using the long division method: This method involves a step-by-step division process to find the square root.
- Using approximation techniques: Estimating and refining the value through successive approximations.
- What are the applications of square roots in real life?
Square roots are used in various real-life applications, such as:
- Geometry: Calculating the length of the sides of a right triangle using the Pythagorean theorem.
- Engineering: Determining the dimensions of materials and structures.
- Physics: Solving equations involving energy, force, and motion.
- Finance: Calculating the standard deviation in statistics and risk assessment.
- Can square roots be negative?
Every positive number has two square roots: a positive and a negative root. For example, the square roots of 116 are +10.770329614269 and -10.770329614269. The positive square root is called the principal square root.
Common Mistakes and Misconceptions
Understanding the square root of a number can be tricky, and there are several common mistakes and misconceptions that people often encounter. Here are some of the most frequent errors to watch out for:
- Incorrect Simplification: A common mistake is to incorrectly simplify the square root of a sum or difference. For example, assuming that \(\sqrt{a + b} = \sqrt{a} + \sqrt{b}\) is incorrect. The correct approach is to treat the terms inside the square root as a whole.
- Misunderstanding Radical Expressions: Another frequent error is simplifying expressions involving radicals incorrectly. For example, \(\sqrt{a \cdot b}\) correctly simplifies to \(\sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\), but this rule does not apply to sums or differences under the square root.
- Ignoring Negative Solutions: When solving quadratic equations, students often forget that the square root can yield both positive and negative results. For instance, the equation \(x^2 = 116\) has two solutions: \(x = \sqrt{116}\) and \(x = -\sqrt{116}\).
- Prime Factorization Errors: When using prime factorization to simplify square roots, errors often occur in the factorization process. Ensuring that all prime factors are correctly identified and paired is crucial.
- Decimal Approximation Mistakes: When approximating square roots, students might round incorrectly or use insufficient decimal places, leading to inaccurate results. For example, \(\sqrt{116} \approx 10.77\), but more precision might be needed depending on the context.
- Application Errors in Real-Life Problems: Misapplying the square root in real-life scenarios, such as geometry problems involving areas and lengths, can lead to incorrect conclusions. Understanding the context and applying the square root appropriately is essential.
By being aware of these common mistakes and misconceptions, you can approach problems involving square roots with greater accuracy and confidence.
Advanced Topics Related to Square Roots
The study of square roots extends beyond basic calculations and encompasses several advanced topics. Here are some key areas:
1. Irrational Numbers
Square roots often result in irrational numbers. For example, the square root of 116 is approximately 10.770, which is a non-terminating and non-repeating decimal. This means cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
2. Simplifying Radicals
Simplifying square roots involves breaking down the number into its prime factors. For instance,
. This simplified form can be useful in various mathematical contexts.
3. Complex Numbers
Square roots are also essential in the study of complex numbers. For example, the square root of a negative number involves the imaginary unit where . This extends the concept of square roots into a new number system.
4. Solving Quadratic Equations
The quadratic formula involves square roots and is fundamental in solving quadratic equations.
5. Numerical Methods
Various numerical methods exist for approximating square roots, such as the Newton-Raphson method. These techniques are valuable in computer science and numerical analysis where exact solutions are not feasible.
6. Real-World Applications
Square roots have practical applications in fields such as engineering, physics, and finance. For instance, they are used in calculating distances, determining standard deviations in statistics, and modeling natural phenomena.
7. Pythagorean Theorem
The Pythagorean theorem uses square roots to find the length of the hypotenuse in a right triangle:
. This is crucial in geometry and trigonometry.
8. Fourier Transforms
In advanced mathematics, square roots appear in Fourier transforms and signal processing, playing a role in analyzing waveforms and signals.
These advanced topics illustrate the depth and breadth of applications and implications of square roots in various fields of study and practical scenarios.
Interactive Tools and Calculators
There are numerous interactive tools and calculators available online that can help you understand and calculate the square root of 116. These tools not only provide the square root but also offer detailed steps and additional functionalities to enhance your learning experience.
Square Root Calculator
A simple and effective tool to find the square root of any number, including 116. This calculator can also simplify the radical form and provide the decimal approximation.
How to Use the Square Root Calculator
- Enter the number (116 in this case) into the input box.
- Press the "Calculate" button to get the result.
- The calculator will display the principal square root and, if applicable, the simplified radical form.
- For educational purposes, some calculators also show the calculation steps.
Additional Features
Some advanced calculators offer more features:
- Graphing Capabilities: Visualize the square root function on a graph.
- Complex Numbers: Calculate square roots of negative numbers and display complex results.
- Historical Calculations: Save and review previous calculations for comparison.
- Mobile Compatibility: Use the calculators on mobile devices for convenience.
Why Use Interactive Tools?
Using interactive tools and calculators for square roots can significantly enhance your understanding and efficiency. They provide instant results, step-by-step solutions, and visual aids that help in grasping the concept better. These tools are particularly useful for students, educators, and anyone looking to quickly and accurately perform mathematical calculations.
Conclusion
The square root of 116, approximately 10.7703, plays a significant role in various mathematical and real-life applications. Understanding the methods to calculate it, such as prime factorization, long division, and the use of calculators, helps in grasping the concept thoroughly.
Knowing that 116 is not a perfect square and that its square root is an irrational number adds to the comprehension of its properties and behavior in different mathematical contexts. This insight is valuable for advanced studies and practical applications, from geometry to complex calculations.
By exploring advanced topics and utilizing interactive tools and calculators, one can deepen their understanding of square roots and their significance. This comprehensive guide aimed to provide clarity and detail on the square root of 116, ensuring a solid grasp of its computation and implications.
Embracing these mathematical concepts opens doors to further exploration and application in both academic and real-world scenarios. The journey through the square root of 116 is a stepping stone to more complex and fascinating mathematical discoveries.

Hướng dẫn cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 116 bằng phương pháp dễ hiểu và chi tiết. Thích hợp cho học sinh và người yêu thích toán học.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 116: sqrt(116)
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn tìm căn bậc hai của 116 một cách dễ hiểu và chi tiết. Thích hợp cho học sinh và người yêu thích toán học.
Căn Bậc Hai của 116