Topic square root of 210: The square root of 210 is a fascinating mathematical concept that opens doors to various applications and calculations. Discover the exact value, methods to calculate it, and its significance in different contexts. Join us as we explore the intricacies and practical uses of √210 in this comprehensive guide.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 210
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Definition of the Square Root of 210
- Exact and Decimal Form of √210
- Is 210 a Perfect Square?
- Rational or Irrational Nature of √210
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 210
- Step-by-Step Simplification of √210
- Practical Applications of Square Roots
- Related Calculations
- YOUTUBE:
Square Root of 210
The square root of 210 is a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 210. The value of the square root of 210 can be expressed in various forms:
Exact Form
\(\sqrt{210}\)
Decimal Form
\(\sqrt{210} \approx 14.491376746189\)
Calculation Methods
- Calculator: To find the square root of 210, enter 210 and press the square root button (\(\sqrt{x}\)).
- Excel/Google Sheets: Use the formula
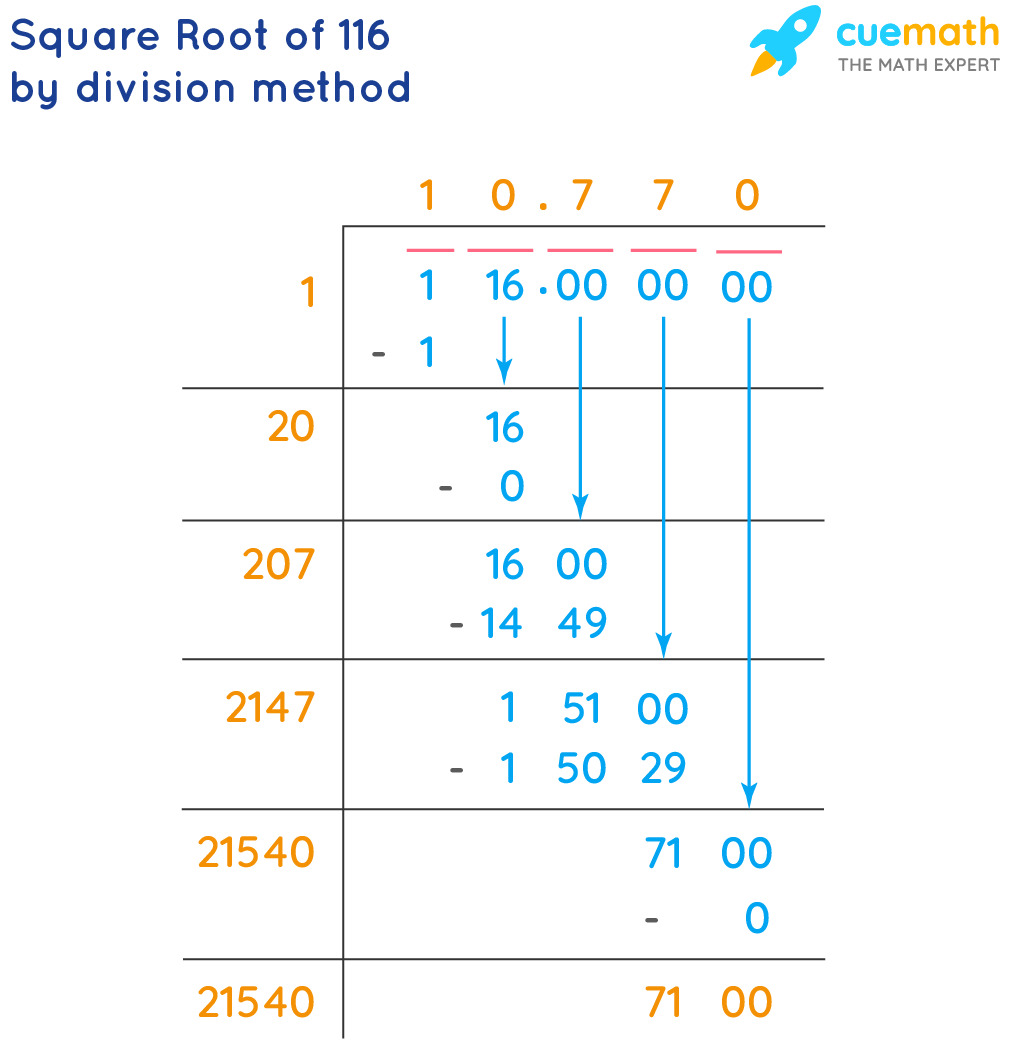
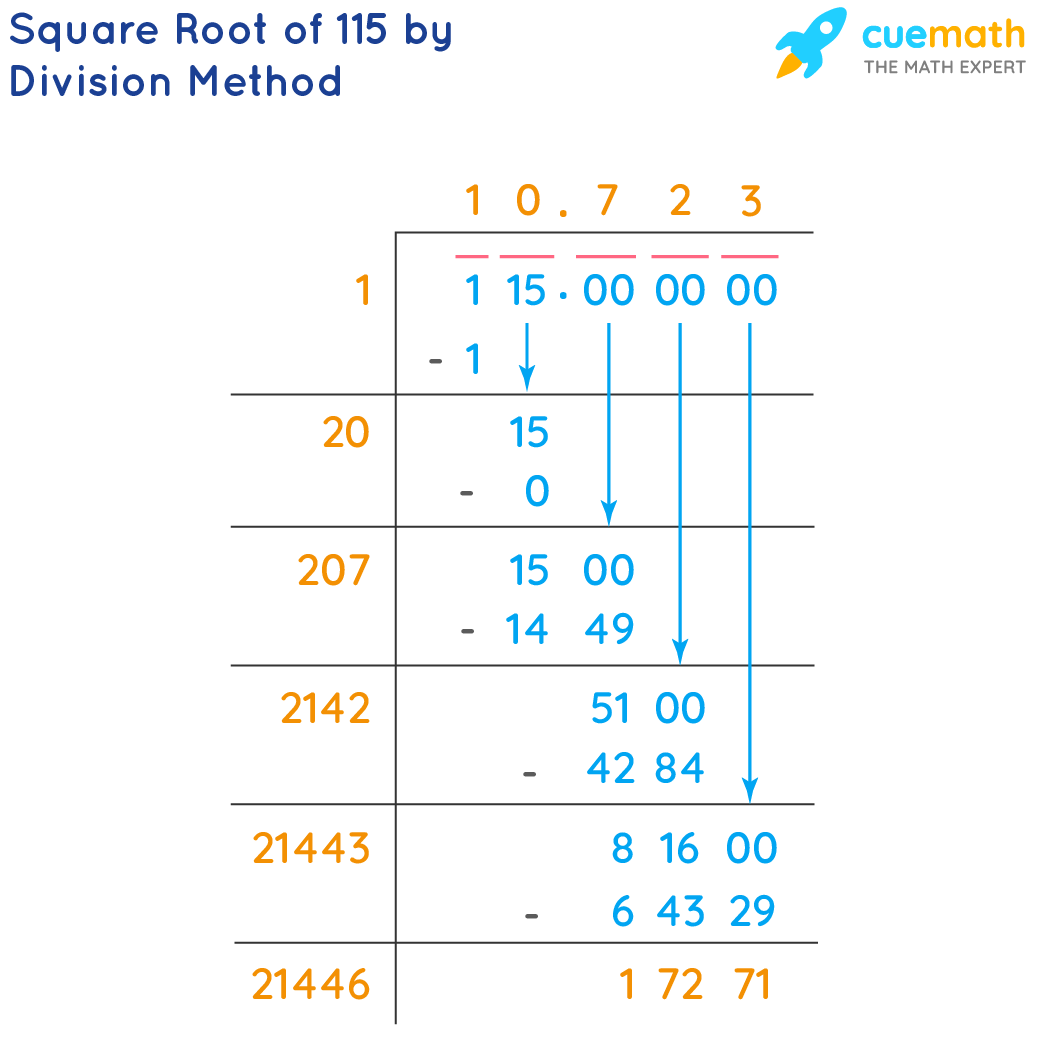
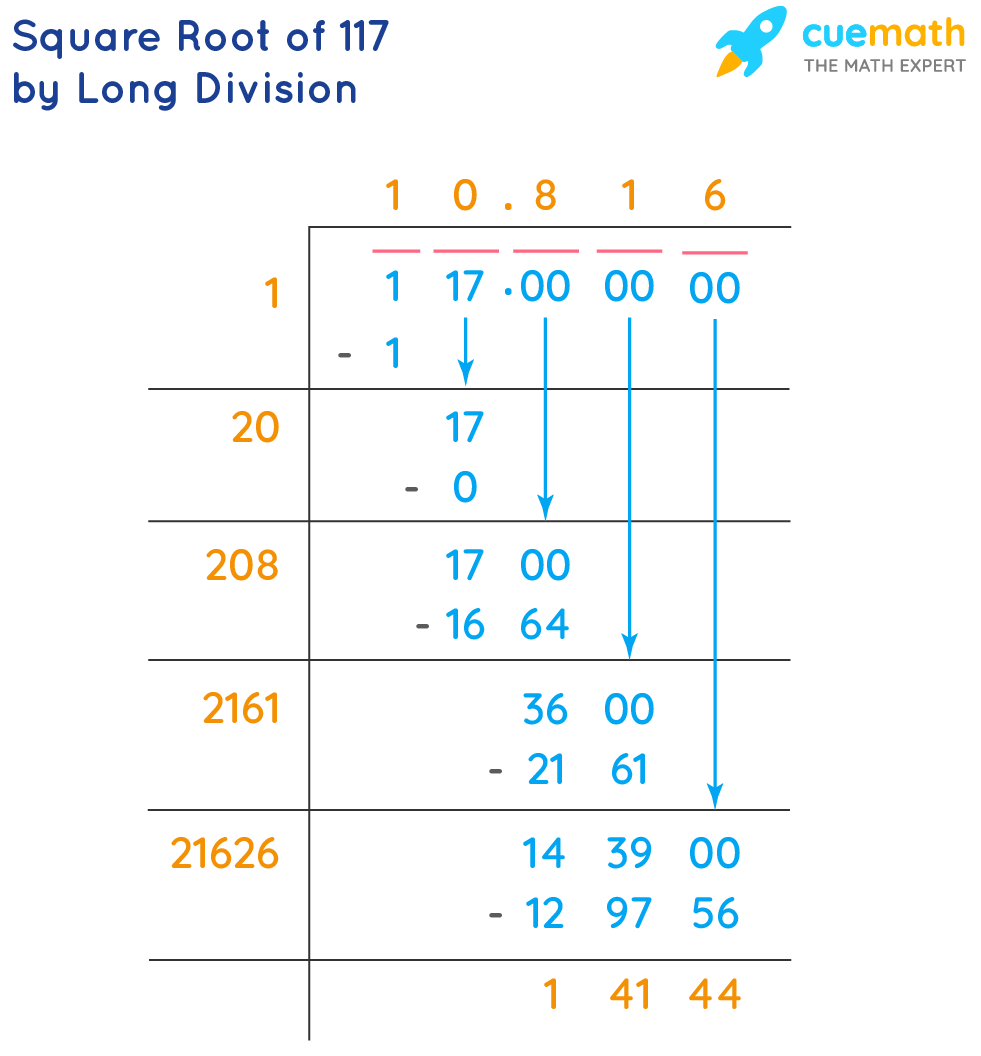
=SQRT(210)to get the result. - Long Division Method: This manual method involves finding the closest perfect squares and using them to approximate the square root.
Properties of the Square Root of 210
- Irrational Number: The square root of 210 cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, making it an irrational number.
- Not a Perfect Square: 210 is not a perfect square, as its square root is not an integer.
Applications
The square root of 210 is useful in various mathematical problems, such as solving quadratic equations and finding the side length of a square with an area of 210 square units.
Example Problems
- Quadratic Equation: Solve \(x^2 - 210 = 0\).
Solution: \(x = \pm\sqrt{210} \approx \pm14.491\)
- Area of a Square: Find the side length of a square with an area of 210 square units.
Solution: Side length \( = \sqrt{210} \approx 14.491\) units.
Table of Roots
| Root | Value |
|---|---|
| Square Root (\( \sqrt{210} \)) | 14.491 |
| Cube Root (\( \sqrt[3]{210} \)) | 5.944 |
| Fourth Root (\( \sqrt[4]{210} \)) | 3.807 |
Conclusion
The square root of 210 is approximately 14.491, an irrational number, and useful in various mathematical applications.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 210 is approximately 14.491 because 14.491 × 14.491 ≈ 210. This value can be represented in several forms, such as the radical form (√210) or exponential form (210^0.5).
Square roots play a fundamental role in various mathematical theories and applications. They are used to simplify expressions, solve quadratic equations, and model physical phenomena. Understanding square roots is essential for advancing in fields like algebra, geometry, and calculus.
There are multiple methods to calculate square roots, including:
- Prime Factorization: This method involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and then pairing them to find the square root. It is most effective for perfect squares.
- Long Division: This technique is useful for finding square roots of non-perfect squares. It involves a step-by-step division process to approximate the root.
- Using a Calculator: Most scientific calculators have a square root function that allows for quick and accurate computation.
- Estimation Method: This involves approximating the square root by finding two consecutive integers between which the square root lies and then refining the estimate.
The square root of 210 is not a perfect square, which means it is an irrational number. An irrational number cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansion. In this case, √210 ≈ 14.4913767462.
Square roots are denoted by the radical symbol (√). For example, √210 can also be written as 210^(1/2). The principal square root is the positive value of the square root, which is commonly used in most mathematical contexts.
Understanding square roots and their properties is crucial for solving various mathematical problems and for applications in science and engineering. Whether using manual methods or digital tools, mastering the calculation of square roots is an essential skill in mathematics.
Definition of the Square Root of 210
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For 210, the square root is represented as √210.
In mathematical terms, this can be expressed as:
\(\sqrt{210} = q \times q = q^2\)
where \(q\) is the square root of 210.
The exact form of the square root of 210 is an irrational number and is approximately equal to 14.491376746189 in decimal form.
To further understand this, consider the prime factorization of 210:
- 210 = 2 × 3 × 5 × 7
This form shows that 210 is not a perfect square, confirming that its square root is an irrational number.
Here is a brief table of other roots of 210:
| Root | Value |
| Square Root (√210) | 14.491 |
| Cube Root (³√210) | 5.944 |
| Fourth Root (⁴√210) | 3.807 |
Understanding these roots is fundamental in various mathematical concepts and applications.
Exact and Decimal Form of √210
The square root of 210, denoted as √210, is a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 210. This value can be expressed in two main forms: exact form and decimal form.
Exact Form
In exact form, the square root of 210 is represented using a radical sign as √210. This form is often used when the square root does not simplify into a neat, rational number.
Decimal Form
When expressed in decimal form, the square root of 210 is approximately 14.491376746189. This decimal representation is derived from calculating the square root using a calculator or a numerical method. Since the decimal is non-terminating and non-repeating, √210 is classified as an irrational number.
Methods to Calculate
-
Prime Factorization:
To simplify √210 using prime factorization, you find the prime factors of 210, which are 2, 3, 5, and 7. Since 210 is not a perfect square, it remains under the radical as √210.
-
Long Division Method:
This method is used to find a more precise decimal form of √210. It involves dividing 210 by successive approximations until the desired accuracy is achieved.
Is 210 a Perfect Square?
A perfect square is a number that is the square of an integer. In other words, a number is a perfect square if you can find an integer that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. To determine if 210 is a perfect square, we need to check if there is an integer n such that n2 = 210.
To find this, we can take the square root of 210:
\(\sqrt{210} \approx 14.491\)
Since 14.491 is not an integer, 210 is not a perfect square. Therefore, there is no integer that, when squared, equals 210. This confirms that 210 is not a perfect square.
Additionally, perfect squares have square roots that are rational numbers. Since \(\sqrt{210}\) is not a rational number, it further verifies that 210 is not a perfect square.

Rational or Irrational Nature of √210
The square root of 210 is a fascinating number that illustrates the difference between rational and irrational numbers. When we talk about rational numbers, we refer to numbers that can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. In contrast, irrational numbers cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and their decimal expansion is non-terminating and non-repeating.
To determine if √210 is rational or irrational, we start by looking at its decimal representation. Calculating the square root of 210 gives us approximately 14.491376746189. This number does not terminate nor does it repeat, indicating that it cannot be precisely expressed as a fraction of two integers.
Therefore, we conclude that:
- The square root of 210 is an irrational number.
- It cannot be written as a simple fraction.
- Its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
This distinction is important in various mathematical applications, particularly in algebra and number theory, where understanding the properties of numbers helps in solving equations and understanding the nature of numbers themselves.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 210
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 210. Here, we will discuss a few of the most common methods, including the prime factorization method, the long division method, and using a calculator for a more precise result.
- Prime Factorization Method
- Find the prime factors of 210: 2, 3, 5, and 7.
- Since 210 cannot be broken down into pairs of identical prime factors, it indicates that 210 is not a perfect square.
- Therefore, the square root of 210 cannot be simplified further using prime factorization.
- Long Division Method
- Start by grouping the digits in pairs from the decimal point. For 210, it is written as 210.000000.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first group. In this case, the largest number is 1, because 12 = 1.
- Subtract the square of this number from the first group and bring down the next pair of digits. Repeat the process.
- Continue the process until you reach the desired precision. The result is approximately 14.4913767462.
- Using a Calculator
- Enter 210 into the calculator.
- Press the square root (√) button.
- The calculator will display the square root of 210, which is approximately 14.4913767462.
These methods provide various ways to calculate the square root of 210, each with its own level of precision and complexity.
Step-by-Step Simplification of √210
To simplify the square root of 210, we need to follow a series of steps:
- Prime Factorization of 210:
- 210 can be factorized as 2 × 3 × 5 × 7.
- Since there are no pairs of prime factors, √210 cannot be simplified further using prime factorization.
- Using the Long Division Method:
- Start with a number, say 15, and find its square (15 × 15 = 225).
- Since 225 is more than 210, try a smaller number, say 14 (14 × 14 = 196).
- Since 196 is less than 210, we can use 14 as our initial estimate.
- Divide 210 by 14 to get a quotient (210 ÷ 14 ≈ 15).
- Average the divisor (14) and the quotient (15) to get a new estimate: (14 + 15) / 2 = 14.5.
- Repeat the process with 14.5, refining the estimate until the desired precision is reached.
- Using a Calculator:
- Enter 210 and press the square root (√) button to get approximately 14.491.
Thus, the square root of 210 in its simplified radical form is √210, and its approximate decimal form is 14.491.
Practical Applications of Square Roots
Square roots have numerous practical applications in various fields. Here are some common uses:
-
Geometry and Construction:
Square roots are often used to determine the length of the sides of a square when the area is known. For example, if a square has an area of \(A\) square units, the length of each side is \(\sqrt{A}\) units. This is useful in construction projects for creating square layouts, such as patios or floors.
Example: If a square patio has an area of 200 square feet, each side would be \(\sqrt{200} \approx 14.1\) feet.
-
Physics and Gravity:
In physics, the time it takes for an object to fall to the ground can be calculated using the square root of the height from which it is dropped. The formula \(\frac{\sqrt{h}}{4}\) is used, where \(h\) is the height in feet.
Example: If an object is dropped from a height of 64 feet, it will take \(\frac{\sqrt{64}}{4} = 2\) seconds to reach the ground.
-
Accident Investigation:
Police use square roots to determine the speed of a vehicle before applying the brakes based on the length of skid marks. The formula used is \(\sqrt{24d}\), where \(d\) is the length of the skid marks in feet.
Example: If skid marks are 190 feet long, the speed of the vehicle was \(\sqrt{24 \times 190} \approx 67.5\) miles per hour.
-
Distance Calculation:
The distance between two points in a 2D or 3D space can be calculated using the Pythagorean theorem, which involves square roots. The distance \(D\) between two points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) in 2D is given by:
\[
D = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}
\]In 3D, the distance formula is extended to:
\[
D = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2 + (z_2 - z_1)^2}
\] -
Mathematical Problem Solving:
Square roots are essential in solving quadratic equations using the quadratic formula:
\[
x = \frac{{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}}{2a}
\]Here, the square root helps find the solutions of the equation \(ax^2 + bx + c = 0\).

Related Calculations
Understanding the square root of 210 opens the door to various related calculations. Here are some significant related calculations:
Square Root of Numbers Around 210
- Square root of 209: √209 ≈ 14.4568
- Square root of 211: √211 ≈ 14.5258
- Square root of 212: √212 ≈ 14.5602
Nth Roots of 210
The Nth root of a number is a value that, when raised to the power of N, gives the original number. Here are some examples:
- Square root (2nd root) of 210: √210 ≈ 14.4914
- Cubic root (3rd root) of 210: ∛210 ≈ 6.0800
- Fourth root of 210: 4√210 ≈ 4.3089
Square of the Square Root of 210
The square of the square root of 210 returns the original number:
\((\sqrt{210})^2 = 210\)
Calculations Involving √210
Here are some practical examples involving the square root of 210:
- Evaluate \(2 \sqrt{210}\):
\[
2 \sqrt{210} = 2 \times 14.4914 \approx 28.9828
\] - Evaluate \(3 + 4 \sqrt{210}\):
\[
3 + 4 \sqrt{210} = 3 + 4 \times 14.4914 \approx 3 + 57.9656 = 60.9656
\]
Solving Equations Involving √210
Consider the equation \(x^2 - 210 = 0\). To solve for \(x\), follow these steps:
- Set the equation equal to zero:
\[
x^2 - 210 = 0 \implies x^2 = 210
\] - Take the square root of both sides:
\[
x = \pm \sqrt{210} \approx \pm 14.4914
\]
Practical Application Example
If the area of a square is 210 square units, the length of each side can be found using the square root:
\[
a^2 = 210 \implies a = \sqrt{210} \approx 14.4914 \text{ units}
\]
These calculations showcase the utility and versatility of the square root of 210 in various mathematical contexts.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 210: Bảng Nội Dung Toàn Diện