Topic square root of 120 in radical form: Discover how to express the square root of 120 in radical form. Learn the step-by-step process, understand the mathematical principles behind it, and explore its applications. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, this guide will help you grasp the concept of square roots and simplify complex radical expressions.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 120 in Radical Form
- Introduction to Square Root of 120
- What is the Square Root?
- Definition and Notation
- Is 120 a Perfect Square?
- Rational vs. Irrational Numbers
- Simplifying the Square Root of 120
- Prime Factorization Method
- Calculating with a Calculator
- Using Computers for Calculation
- Rounded Values of √120
- Square Root of 120 as a Fraction
- Exponential Representation
- Practical Applications and Examples
- Interactive Tools and Calculators
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 120: sqrt(120). Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ cách thực hiện và áp dụng vào bài toán cụ thể.
Square Root of 120 in Radical Form
The square root of 120 in radical form can be simplified. Here is the detailed process:
Steps to Simplify √120
- Prime Factorization: Find the prime factors of 120.
- 120 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
- Group the prime factors into pairs:
- (2 × 2) and (2 × 3 × 5)
- Take one factor out of each pair:
- 2 comes out of the pair (2 × 2)
- Simplify the remaining expression under the radical:
- √120 = 2√30
Radical Form and Decimal Form
The simplified radical form of the square root of 120 is \( 2\sqrt{30} \).
In decimal form, the square root of 120 is approximately \( 10.954 \).
Properties of √120
- √120 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a ratio of two integers.
- √120 is not a perfect square, which means it doesn't result in a whole number.
Calculations and Examples
Using a calculator, you can find the square root of 120 by typing 120 and then pressing the √ key, which gives approximately 10.9545.
To express √120 as an exponent: \( 120^{1/2} \).

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 120
The square root of 120, denoted as √120, is a value that when multiplied by itself gives the product 120. This number is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
In its simplified radical form, the square root of 120 is expressed as \(2\sqrt{30}\). This form is derived through the process of prime factorization, which involves breaking down 120 into its prime factors and simplifying the square root accordingly.
- Prime Factorization: To simplify √120, we first perform prime factorization on 120. This gives us 120 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5.
- Simplifying the Radical: Taking out the pairs of numbers from under the radical, we get √120 = √(2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5) = 2√30.
- Decimal Form: The decimal form of √120 is approximately 10.954451150103.
This simplification process helps in understanding the properties and applications of square roots in various mathematical problems. The principal square root is always non-negative, and it plays a significant role in different fields of mathematics, including algebra and geometry.
What is the Square Root?
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3, because 3 × 3 = 9. In mathematical notation, the square root is represented by the radical symbol √. For instance, the square root of 120 is written as √120.
Square roots can be categorized into two types:
- Perfect Squares: Numbers that have whole number square roots. For example, 16 is a perfect square because its square root is 4.
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers that do not have whole number square roots, resulting in irrational numbers. For example, 120 is a non-perfect square.
Finding the square root of a non-perfect square, like 120, involves simplification. The simplified radical form of √120 is 2√30.
Steps to Simplify the Square Root of 120:
- Factorize 120 into its prime factors: 120 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5.
- Group the factors into pairs: 120 = (2 × 2) × 2 × 3 × 5.
- Take the square root of each pair: √(2 × 2) = 2.
- Combine the results: √120 = 2√(2 × 3 × 5) = 2√30.
This simplification process helps in understanding and calculating square roots more efficiently.
The square root of 120 in decimal form is approximately 10.954, indicating it is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers.
Understanding square roots is fundamental in various mathematical applications, including solving quadratic equations, calculating areas, and in higher-level mathematics.
Definition and Notation
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the number 120, its square root is the value which, when squared, equals 120. The notation for the square root of 120 is written as \( \sqrt{120} \).
In mathematical terms, if \( a^2 = 120 \), then \( a = \sqrt{120} \).
The square root symbol \( \sqrt{} \) is called a radical sign, and the number inside the radical sign is called the radicand. Therefore, in \( \sqrt{120} \), 120 is the radicand.
Steps to Simplify \( \sqrt{120} \)
- First, perform the prime factorization of 120.
- Group the prime factors into pairs.
- Take one number from each pair and multiply them.
- Simplify inside the radical.
120 can be factored as: \( 120 = 2^3 \times 3 \times 5 \)
From the factorization, we have one pair of 2s: \( 2^2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 5 \)
The pair of 2s gives us a single 2 outside the radical: \( 2 \sqrt{2 \times 3 \times 5} \)
Multiply the numbers inside the radical: \( 2 \sqrt{30} \)
Therefore, the square root of 120 in its simplest radical form is \( 2\sqrt{30} \).
Properties of Square Roots
- The square root of any positive number has both a positive and negative value. However, by convention, the principal square root is taken as the positive value.
- The square root function maps the area of a square to the length of its side.
- The square root of a non-perfect square is always an irrational number. Thus, \( \sqrt{120} \) is irrational.
The approximate decimal value of \( \sqrt{120} \) is 10.954, which is useful for practical calculations.
Is 120 a Perfect Square?
In mathematics, a perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. To determine if 120 is a perfect square, we can check if there exists an integer that, when squared, equals 120.
Let's examine the calculations:
- The square of 10 is 100 (10 × 10 = 100).
- The square of 11 is 121 (11 × 11 = 121).
Since 120 is between 100 and 121, it is clear that there is no integer that squares to 120. Thus, 120 is not a perfect square.
This conclusion means that the square root of 120 is not an integer. Instead, it is an irrational number, which cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. The square root of 120 in its simplest radical form is:
\(\sqrt{120} = 2\sqrt{30}\)
In decimal form, the square root of 120 is approximately 10.954.

Rational vs. Irrational Numbers
In mathematics, numbers are classified into two main categories: rational and irrational numbers. Understanding the difference between these types is essential for various mathematical operations, including working with square roots.
- Rational Numbers: A number is considered rational if it can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. Rational numbers include integers, fractions, and finite or repeating decimals. For example, \( \frac{3}{4} \), 5, and 0.333... (repeating) are all rational numbers.
- Irrational Numbers: An irrational number cannot be written as a simple fraction. These numbers have non-terminating and non-repeating decimal parts. Examples include \( \pi \) (pi), \( e \) (Euler's number), and the square root of non-perfect squares like \( \sqrt{2} \) and \( \sqrt{120} \).
The square root of 120, written in radical form as \( \sqrt{120} \), is an example of an irrational number. This is because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating:
\[ \sqrt{120} \approx 10.954451150103 \]
Here's a step-by-step breakdown of why \( \sqrt{120} \) is irrational:
- Prime Factorization: First, factorize 120 into its prime components:
- 120 = 2 × 60
- 60 = 2 × 30
- 30 = 2 × 15
- 15 = 3 × 5
- Simplifying the Radical: Extract pairs of primes from under the radical sign: \[ \sqrt{120} = \sqrt{2^3 × 3 × 5} = \sqrt{4 × 30} = 2\sqrt{30} \] Since \( \sqrt{30} \) is not a perfect square and cannot be simplified further, the expression remains in its simplified radical form.
This confirms that \( \sqrt{30} \) is also irrational, and thus \( 2\sqrt{30} \) or \( \sqrt{120} \) is an irrational number.
Understanding the nature of rational and irrational numbers helps in grasping more complex mathematical concepts and ensures a solid foundation in number theory.
Simplifying the Square Root of 120
The square root of 120 can be simplified by expressing 120 as a product of its prime factors. This method helps to break down the number under the square root into simpler components.
- Prime Factorization: First, we find the prime factors of 120. We have:
\( 120 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 5 \)
- Grouping Pairs: Next, we group the pairs of prime factors under the square root:
\( \sqrt{120} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 3 \times 5} \)
- Simplifying: We take out the pairs from under the square root:
\( \sqrt{120} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 3 \times 5} \)
\( = 2 \sqrt{2 \times 3 \times 5} \)
\( = 2 \sqrt{30} \)
Therefore, the simplified radical form of the square root of 120 is \( 2\sqrt{30} \).
| Number | Prime Factors | Simplified Radical Form |
|---|---|---|
| 120 | 2, 2, 2, 3, 5 | 2\(\sqrt{30}\) |
Prime Factorization Method
To simplify the square root of 120 using the prime factorization method, follow these steps:
Find the prime factors of 120. Start by dividing by the smallest prime number, 2, and continue dividing by prime numbers until you reach 1.
- 120 ÷ 2 = 60
- 60 ÷ 2 = 30
- 30 ÷ 2 = 15
- 15 ÷ 3 = 5
- 5 ÷ 5 = 1
Write the prime factorization of 120.
120 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
Group the prime factors into pairs.
(2 × 2) × 2 × 3 × 5
Simplify the pairs by taking one factor from each pair outside the square root.
\(\sqrt{120} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times 2 \times 3 \times 5}\)
\(\sqrt{120} = 2 \sqrt{2 \times 3 \times 5}\)
Multiply the remaining factors inside the square root.
\(\sqrt{2 \times 3 \times 5} = \sqrt{30}\)
Combine the simplified factors.
\(\sqrt{120} = 2 \sqrt{30}\)
Therefore, the square root of 120 in its simplest radical form is \(2 \sqrt{30}\).
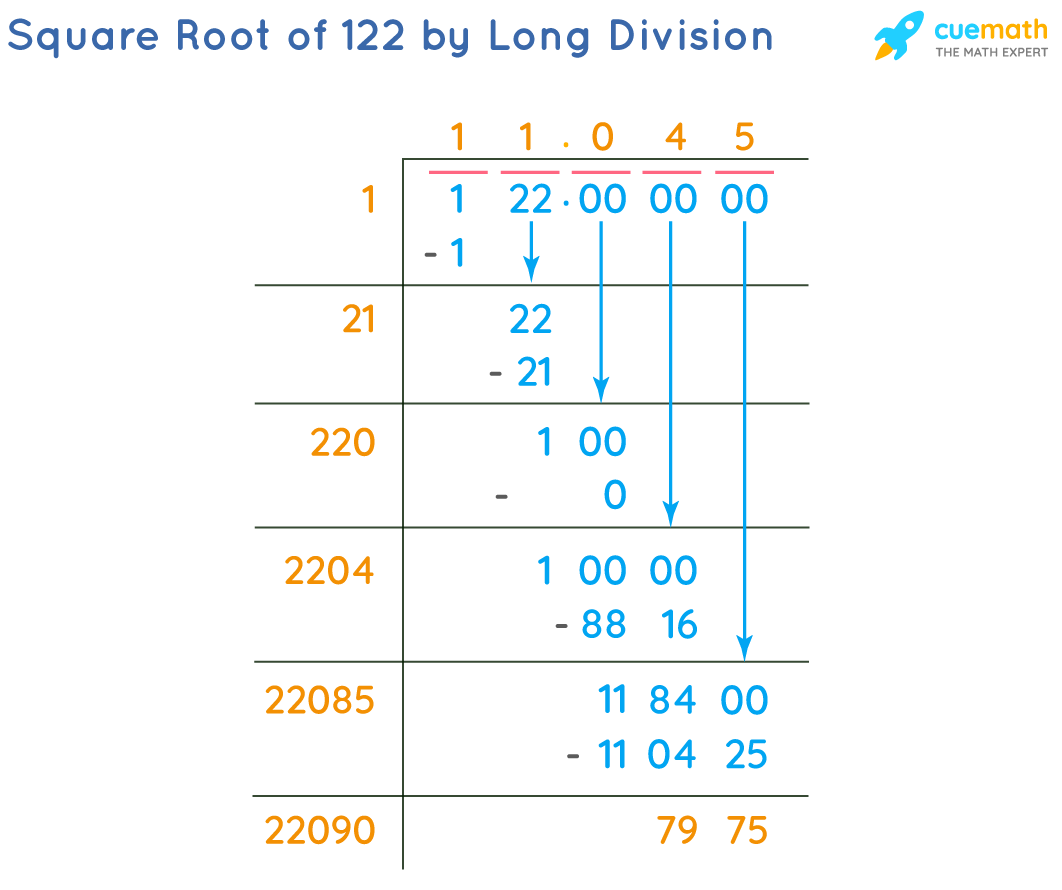
Calculating with a Calculator
Finding the square root of 120 using a calculator is straightforward. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Turn on your calculator.
- Enter the number 120.
- Press the square root (√) button. This is typically labeled as
√orsqrton most calculators. - Read the result displayed on the screen. The calculator will show the square root of 120 as approximately 10.9545.
For a more detailed explanation:
- The square root of 120 in decimal form is approximately 10.9545. This means that if you multiply 10.9545 by itself, you get a number very close to 120.
- If you need the square root of 120 in its simplest radical form, it is expressed as \(2\sqrt{30}\). This form is more exact and is often used in algebraic calculations.
- Using an online calculator can also help you visualize the steps and understand the calculation better. Websites like and provide tools to find square roots and simplify radical expressions.
Using a calculator is a quick and efficient way to find the square root, especially for numbers that are not perfect squares like 120.

Using Computers for Calculation
Calculating the square root of 120 using a computer is a straightforward process, thanks to various software tools and online calculators. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to do it:
Using Online Calculators
- Open a web browser and go to a reliable online calculator website such as Mathway, Symbolab, or Cuemath.
- Locate the square root calculator function. This is usually found in the algebra or basic math section.
- Enter the number 120 into the calculator.
- Click the "Calculate" button. The calculator will provide the result, which includes both the decimal form and the simplest radical form.
Using Math Software
- MATLAB or Octave:
- Open MATLAB or Octave.
- In the command window, type
sqrt(120)and press Enter. - The software will output the square root of 120.
- Wolfram Alpha:
- Open Wolfram Alpha in your web browser.
- Type "sqrt(120)" into the search bar and press Enter.
- Wolfram Alpha will display the result, including the exact form and the decimal approximation.
Using Programming Languages
- Python:
- Open a Python IDE or a Jupyter notebook.
- Use the following code to calculate the square root of 120:
import math result = math.sqrt(120) print(result) - Run the code to get the result.
- JavaScript (in a web browser console):
- Open the web browser's developer console (usually by pressing F12 or right-clicking on the page and selecting "Inspect").
- Enter the following code:
let result = Math.sqrt(120); console.log(result); - Press Enter to see the result.
These methods demonstrate how easily computers can handle the calculation of the square root of 120, providing both exact and approximate results efficiently.
Rounded Values of √120
The square root of 120 is an irrational number, meaning it has a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansion. For practical purposes, we often round this value to a certain number of decimal places.
Here are some common rounded values of √120:
- To 1 decimal place: √120 ≈ 11.0
- To 2 decimal places: √120 ≈ 10.95
- To 3 decimal places: √120 ≈ 10.954
- To 4 decimal places: √120 ≈ 10.9545
These rounded values are often used depending on the level of precision required in various applications. For example, when using the square root of 120 in scientific calculations, you might use the value rounded to more decimal places, while in simpler calculations, fewer decimal places might suffice.
Using a calculator or a computer, you can obtain more precise values. For instance, many scientific calculators and computer programs will give the square root of 120 as approximately 10.9544511501 when rounded to ten decimal places.
Square Root of 120 as a Fraction
To express the square root of 120 as a fraction, we first need to understand that √120 is an irrational number. However, we can approximate it as a fraction for practical purposes. Here’s a step-by-step method to represent √120 in a simplified radical form and then approximate it as a fraction.
Simplified Radical Form
First, let's simplify the square root of 120:
- Prime factorize 120: 120 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 5
- Group the prime factors in pairs: 120 = (2 × 2) × 2 × 3 × 5
- Take out the pairs from under the radical: √120 = √((2 × 2) × 2 × 3 × 5) = 2√(30)
So, the simplified radical form of √120 is 2√30.
Approximating √30 as a Fraction
Since √30 is still an irrational number, we approximate it for practical use:
- The approximate value of √30 is around 5.477
- Thus, √120 ≈ 2 × 5.477 = 10.954
Converting to Fraction
To express 10.954 as a fraction, we can use the continued fraction method or a simple fraction approximation:
- Recognize that 10.954 is close to 11, but slightly less.
- Approximate 10.954 ≈ 11 - 0.046.
- Since 0.046 is small, we can approximate it using a simple fraction such as 1/22.
- Therefore, 10.954 ≈ 11 - 1/22 = 10 + 21/22 = 241/22.
So, the square root of 120 can be approximately written as a fraction 241/22.
Exact Form
For exact calculations, remember to use the radical form 2√30 as it is the precise representation of the square root of 120 in its simplest form.
Exponential Representation
To express the square root of 120 using exponential notation, we first need to understand the basic relationship between radicals and exponents. The square root of a number can be written as the number raised to the power of 1/2. For example, the square root of \( x \) can be written as \( x^{1/2} \).
For the square root of 120, this can be represented as:
\[ \sqrt{120} = 120^{1/2} \]
To further simplify the expression, we can use the properties of exponents and the prime factorization of 120:
- Prime factorization of 120 is \( 120 = 2^3 \times 3 \times 5 \).
Using the property of exponents that \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \), we can write:
\[ \sqrt{120} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3 \times 5} \]
Next, we can separate the factors under the radical:
\[ \sqrt{120} = \sqrt{2^3} \times \sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{5} \]
Since \( \sqrt{2^3} = \sqrt{(2^2 \times 2)} = 2 \sqrt{2} \), we can further simplify the expression:
\[ \sqrt{120} = 2 \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{3} \times \sqrt{5} \]
Thus, the exponential representation of the square root of 120 is:
\[ \sqrt{120} = 2 \times 2^{1/2} \times 3^{1/2} \times 5^{1/2} \]
Finally, combining these terms gives us:
\[ \sqrt{120} = 2 \times (2 \times 3 \times 5)^{1/2} = 2 \times (30)^{1/2} = 2 \times 30^{1/2} \]
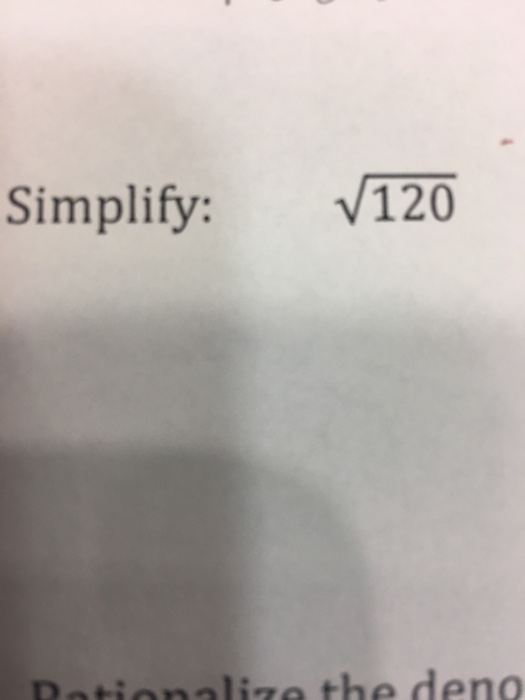
Practical Applications and Examples
The square root of 120, expressed in its simplest radical form as \(2\sqrt{30}\), has various practical applications in different fields. Here are some examples:
- Geometry and Trigonometry:
Square roots are often used in geometry and trigonometry to calculate the lengths of sides in right triangles. For instance, in the Pythagorean Theorem \(a^2 + b^2 = c^2\), if one side and the hypotenuse are known, the length of the other side can be found using the square root. Suppose we need to find a side \(a\) of a right triangle where the hypotenuse \(c\) is 13 and the other side \(b\) is 7:
\(a = \sqrt{c^2 - b^2} = \sqrt{13^2 - 7^2} = \sqrt{169 - 49} = \sqrt{120} = 2\sqrt{30}\).
- Construction:
In construction, the diagonal length of rectangular components, such as frames and supports, can be determined using the square root. For example, if a rectangular support has sides of 6 feet and 8 feet, the diagonal (hypotenuse) can be found as:
\(\sqrt{6^2 + 8^2} = \sqrt{36 + 64} = \sqrt{100} = 10\) feet.
- Physics:
Square roots appear in various physics equations. For instance, in calculating the height of a projectile or the distance traveled. If the equation of motion is given, solving for distance often involves square roots.
- Graphics and Design:
In computer graphics, the distance formula is used to calculate the distance between points in a 2D or 3D space, which involves square roots. The distance \(D\) between points \((x_1, y_1)\) and \((x_2, y_2)\) in 2D is:
\(D = \sqrt{(x_2 - x_1)^2 + (y_2 - y_1)^2}\).
- Quadratic Equations:
Square roots are crucial in solving quadratic equations using the quadratic formula \(x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a}\). The discriminant \((b^2 - 4ac)\) determines the nature of the roots, whether they are real or complex.
Interactive Tools and Calculators
Understanding and calculating the square root of 120 can be made much easier with the help of online interactive tools and calculators. These tools not only provide the square root but also show the step-by-step simplification process, making learning more engaging and effective. Below are some recommended online tools:
-
Mathway:
Mathway's square root calculator is a versatile tool that allows you to enter any number and find its square root. It provides results in both exact and decimal forms. You can access this tool at .
-
MathWarehouse:
MathWarehouse offers a free square root calculator that simplifies any square root to its simplest radical form and provides a decimal approximation. It's a user-friendly tool for quick calculations. Visit the calculator at .
-
Omni Calculator:
Omni Calculator simplifies the process of finding square roots by offering detailed explanations and examples. It is particularly useful for educational purposes as it explains the underlying math concepts. You can explore this tool at .
These tools are incredibly useful for students and anyone looking to understand square roots better. They not only provide immediate answers but also help in visualizing the step-by-step process, which is essential for learning and retention.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions about the square root of 120:
-
What is the square root of 120?
The square root of 120 is approximately 10.954451.
-
Is the square root of 120 a rational number?
No, the square root of 120 is an irrational number because its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
-
Can the square root of 120 be simplified?
Yes, the square root of 120 can be simplified to \(2\sqrt{30}\).
-
Is the square root of 120 a real number?
Yes, the square root of 120 is a real number.
-
How can I calculate the square root of 120 using a calculator?
On most calculators, you can find the square root by entering 120 and pressing the square root (√) button.
-
What is the square root of 120 as a fraction?
The square root of 120 cannot be exactly expressed as a fraction, but it can be approximated. For example, \(\sqrt{120} \approx \frac{1095}{100}\).
-
What is the exponential representation of the square root of 120?
The square root of 120 can be written in exponential form as \(120^{1/2}\).
Conclusion
The square root of 120, expressed in its simplest radical form as \(2\sqrt{30}\), is a valuable mathematical concept with various practical applications. Through our exploration, we've understood that \( \sqrt{120} \) is an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. Despite this, we can approximate it to any desired level of precision.
We have learned different methods to calculate and simplify the square root of 120, such as using prime factorization to express it in radical form, using calculators and computers for accurate computation, and understanding its representation in exponential form. Additionally, the use of interactive tools and calculators enhances our ability to visualize and work with this irrational number efficiently.
In practical scenarios, knowing how to simplify and approximate the square root of 120 helps in various fields such as engineering, physics, and everyday problem-solving. By breaking down complex concepts into understandable steps, we can apply mathematical principles more effectively in real-world situations.
The comprehensive guide on the square root of 120 showcases the importance of understanding both the theoretical and practical aspects of square roots. Whether you are a student, a professional, or someone with a keen interest in mathematics, grasping these concepts will undoubtedly enhance your analytical and problem-solving skills.
We hope this guide has provided you with a thorough understanding of the square root of 120 and its various facets. Continue to explore and apply these mathematical insights to broaden your knowledge and proficiency.

Hướng dẫn đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 120: sqrt(120). Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ cách thực hiện và áp dụng vào bài toán cụ thể.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai Của 120: sqrt(120)
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn đơn giản hóa căn thức thành dạng căn. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ cách thực hiện và áp dụng vào bài toán cụ thể.
Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Thức Thành Dạng Căn