Topic what's the square root of 10: What's the square root of 10? This fascinating mathematical concept is more than just a number. In this article, we'll explore its value, methods to calculate it, and its real-world applications. Whether you're a student, educator, or math enthusiast, understanding the square root of 10 can enhance your knowledge and problem-solving skills.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 10
- Introduction
- Definition of Square Root
- Mathematical Representation of Square Root of 10
- Decimal Approximation of Square Root of 10
- Methods for Approximating Square Roots
- Applications of the Square Root of 10
- Importance of Square Roots in Mathematics
- Frequently Asked Questions about Square Root of 10
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu cách tính căn bậc hai của 10 trong video này. Khám phá các phương pháp và ứng dụng của căn bậc hai trong toán học.
Square Root of 10
The square root of 10 is a mathematical concept that can be represented in several ways. The most common representation is using the radical symbol, which looks like this:
The square root of 10 is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. The approximate value of the square root of 10 is:
Steps to Calculate the Square Root of 10
- Estimation: Begin by finding two perfect squares between which 10 lies. These are 9 (\(3^2\)) and 16 (\(4^2\)), so \(\sqrt{10}\) is between 3 and 4.
- Refinement: Use methods such as the average of the upper and lower bounds, or apply the Newton-Raphson method for better precision.
- Decimal Approximation: Continue the refinement to several decimal places. For practical purposes, \(\sqrt{10} \approx 3.162\) is often sufficient.
Representation of \(\sqrt{10}\) in Different Forms
- Fractional Form: Since it is irrational, it cannot be exactly represented as a fraction. However, it can be approximated by fractions such as \(3.162\).
- Decimal Form: \(\sqrt{10} \approx 3.162277660168379\).
- Exponential Form: \((10)^{0.5}\).
Applications of \(\sqrt{10}\)
The square root of 10 is used in various mathematical and scientific calculations, including geometry, algebra, and physics. It is often encountered in problems involving quadratic equations, optimization, and theoretical physics.
Understanding and approximating the square root of 10 can help in solving real-world problems where precise measurements and calculations are required.
READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 10 is an intriguing mathematical concept that falls between the integers 3 and 4. It is represented symbolically as √10 and is known to be an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. The value of the square root of 10 is approximately 3.162277660168379, which is often rounded to 3.162 for simplicity.
Calculating the square root of 10 involves understanding both its mathematical significance and practical applications. Historically, various methods have been developed to approximate square roots, including ancient techniques used by cultures such as the Babylonians and the Indians. Today, we use more refined mathematical methods and tools to find these values accurately.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the definition and representation of the square root of 10, delve into its decimal approximation, outline the steps to calculate it, and discuss various methods for approximating square roots. Additionally, we will examine the practical applications of √10 in different fields and highlight its importance in mathematics. Whether you are a student, educator, or simply a math enthusiast, this guide aims to provide you with a thorough understanding of the square root of 10.
Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. Mathematically, if x is the square root of y, then it is represented as \( x = \sqrt{y} \). This can also be expressed as \( x^2 = y \).
The square root symbol is '√', called the radical symbol. For example, the square root of 9 is written as \( \sqrt{9} \), which equals 3 because \( 3 \times 3 = 9 \).
Here are some key properties of square roots:
- If a number is a perfect square, then it has an integer as its square root. For example, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
- Negative numbers do not have real square roots because the product of two negative numbers is positive.
- Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. However, the radical symbol denotes only the principal (non-negative) square root. For example, \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \) and \( -5 \).
- The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots of the factors, i.e., \( \sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b} \), provided both a and b are non-negative.
Square roots play a vital role in various mathematical calculations and have applications in fields such as geometry, algebra, and calculus.
Mathematical Representation of Square Root of 10
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical terms, the square root of a number \( x \) is represented as \( \sqrt{x} \). The square root symbol is also known as a radical sign, and the number inside the symbol is called the radicand.
For the number 10, its square root is expressed as \( \sqrt{10} \). This value is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be exactly expressed as a fraction of two integers, and it has an infinite number of non-repeating decimals.
Using MathJax, we can represent the square root of 10 as follows:
\[
\sqrt{10}
\]
We can approximate the value of \( \sqrt{10} \) using the decimal form. The approximate value of \( \sqrt{10} \) is 3.162, which can be written as:
\[
\sqrt{10} \approx 3.162
\]
Derivation of \( \sqrt{10} \)
The square root of 10 can be derived through various methods. One common method is the prime factorization approach, though in this case, since 10 is not a perfect square, it cannot be simplified using integer factorization. Instead, it remains in its simplest radical form:
\[
\sqrt{10} = \sqrt{2 \times 5} = \sqrt{2} \times \sqrt{5}
\]
Using approximate values for \( \sqrt{2} \) and \( \sqrt{5} \), we get:
\[
\sqrt{2} \approx 1.414 \quad \text{and} \quad \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236
\]
Thus,
\[
\sqrt{10} \approx 1.414 \times 2.236 = 3.162
\]
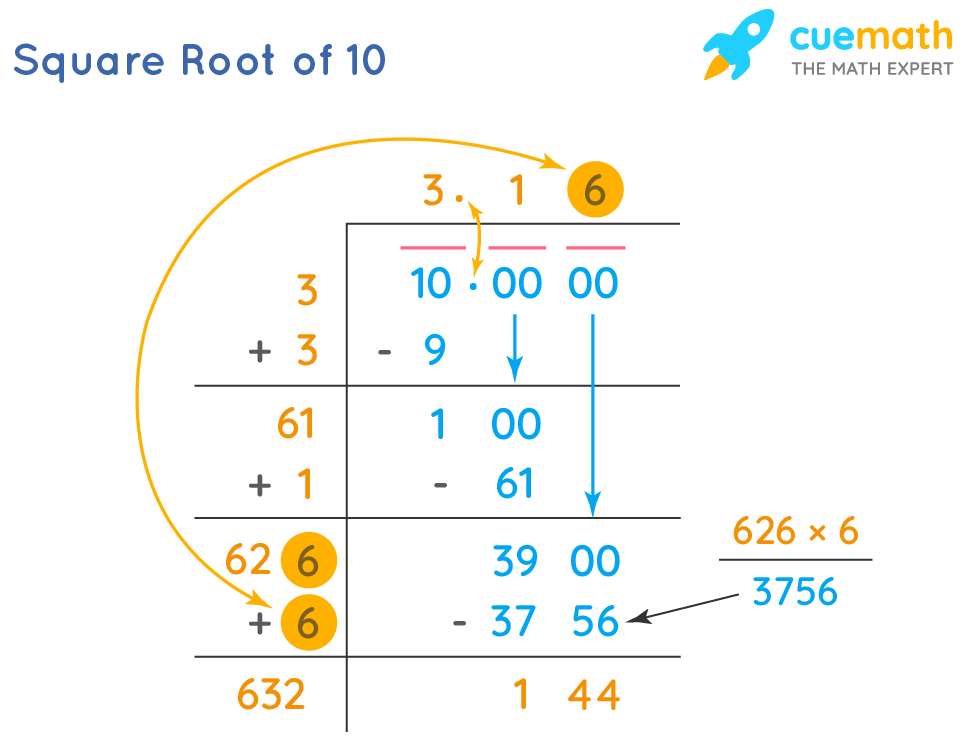
Long Division Method
The long division method is another technique to find the square root of a number. It is a step-by-step procedure that helps in finding the square root of non-perfect squares, providing a more accurate decimal value.
To find \( \sqrt{10} \) using the long division method, we perform the following steps:
- Pair the digits of the number from right to left.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair.
- Subtract the square of this number from the first pair and bring down the next pair.
- Double the quotient obtained so far and determine the next digit by trial and error.
- Repeat the process until the desired accuracy is achieved.
Properties of Square Roots
- Square roots of positive numbers can be positive or negative. For example, both 3.162 and -3.162 are square roots of 10.
- The square root of zero is zero.
- Square roots of negative numbers are not real numbers; they are complex numbers.
In summary, the square root of 10, denoted as \( \sqrt{10} \), is an irrational number approximately equal to 3.162, and it plays a crucial role in various mathematical and real-world applications.
Decimal Approximation of Square Root of 10
The square root of 10 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed exactly as a simple fraction. Instead, its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. Using various mathematical methods, we can approximate the square root of 10 to several decimal places.
One of the most common methods to find this approximation is the long division method, which involves a series of steps to get increasingly accurate decimal places:
- Start by making an initial guess. Since 32 = 9 and 42 = 16, we know that √10 is between 3 and 4.
- Using the long division method, we can narrow this range to get a more precise value. Begin with the number 10.0 and divide it by 3, giving us an initial quotient of 3.333.
- Square the quotient and adjust as necessary, adding decimal places and recalculating until the desired precision is achieved.
- After several iterations, we find that √10 ≈ 3.1622.
Using a calculator, we can find that the decimal approximation of the square root of 10 is approximately:
\(\sqrt{10} \approx 3.162277660168379\)
For most practical purposes, it is often sufficient to use a rounded value:
\(\sqrt{10} \approx 3.162\)
This approximation is accurate to four decimal places, which is usually enough for most mathematical and scientific calculations.
In summary, the decimal approximation of the square root of 10 is an essential value in various fields, from geometry to engineering, providing a useful tool for calculations involving this non-perfect square.

Methods for Approximating Square Roots
There are several methods for approximating square roots, each with its own advantages and applications. Here are some common methods:
- Babylonian Method (Heron's Method)
The Babylonian Method is an ancient technique for finding square roots, which involves iteratively averaging the number with its quotient. It is based on the formula:
\[
x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{a}{x_n} \right)
\]where \(a\) is the number you want to find the square root of, and \(x_n\) is the current approximation. This method converges rapidly to the accurate square root.
- Long Division Method
This method is similar to the long division technique used for regular division. It involves the following steps:
- Pair the digits of the number starting from the decimal point.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair.
- Subtract this square from the first pair and bring down the next pair of digits.
- Double the current root and find the next digit by trial and error, ensuring the product is less than or equal to the current number.
- Repeat the steps until the desired precision is achieved.
This method can be used to find square roots to any degree of accuracy by continuing the process.
- Newton's Method
Newton's Method, or the Newton-Raphson Method, is another iterative method used to approximate square roots. For the function \(f(x) = x^2 - a\), the iterative formula is:
\[
x_{n+1} = x_n - \frac{f(x_n)}{f'(x_n)} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{a}{x_n} \right)
\]This formula is essentially the same as the Babylonian Method and is used for its fast convergence.
- Estimations and Approximations
For quick approximations, one can use the fact that the square root of a number lies between the square roots of the perfect squares surrounding it. For example, \(\sqrt{10}\) is between \(\sqrt{9} = 3\) and \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
Applications of the Square Root of 10
The square root of 10, like other square roots, finds its application in various fields. Here are some key areas where it is utilized:
- Geometry: The square root of 10 is often used in geometry to calculate distances and dimensions. For instance, it can help determine the diagonal length of a rectangle with sides of length 1 and 3 units using the Pythagorean theorem.
- Physics: In physics, square roots are essential for calculations involving energy, force, and motion. For example, the root mean square (RMS) speed of gas particles is derived from the square root of the average velocity squared.
- Finance: In finance, the volatility of stock prices, which measures the degree of variation of a trading price series over time, can be calculated using square roots. This helps investors understand the risk associated with a stock.
- Statistics: In statistics, square roots are crucial for computing standard deviation, which measures the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values. The standard deviation is the square root of the variance, providing insight into data variability.
- Engineering: Engineers use square roots in various calculations, including signal processing and electrical engineering. For instance, the square root function is used to determine the power of an electrical signal from its RMS value.
- Computer Science: Algorithms in computer science often involve square roots, especially in fields like cryptography, where they are used in algorithms for encryption and decryption to ensure secure communication.
These applications illustrate the wide-ranging importance of square roots in different scientific, technical, and practical domains.
Importance of Square Roots in Mathematics
Square roots are fundamental in mathematics and play a crucial role in various mathematical concepts and real-world applications. They are important for the following reasons:
-
Solving Quadratic Equations:
Square roots are essential in solving quadratic equations of the form \( ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \). The quadratic formula, which is used to find the roots of such equations, involves the square root operation: \( x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 - 4ac}}{2a} \). -
Geometry and Trigonometry:
In geometry, the Pythagorean theorem involves square roots to determine the lengths of sides in right-angled triangles: \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \). In trigonometry, square roots appear in various identities and formulas. -
Calculus:
Square roots are important in calculus for finding the lengths of curves and in the computation of integrals and derivatives involving root functions. -
Physics and Engineering:
Many physical laws and engineering principles involve square roots. For example, the formula for the period of a pendulum \( T = 2\pi \sqrt{\frac{L}{g}} \) involves a square root. -
Statistics:
In statistics, the standard deviation, which measures the spread of data points, is calculated using the square root of the variance. -
Computer Science:
Algorithms for computer graphics, cryptography, and numerical methods often involve square root calculations.
Understanding square roots helps in grasping more complex mathematical concepts and enhances problem-solving skills. They are not only theoretical constructs but also have practical applications that are vital in various scientific and engineering fields.
Frequently Asked Questions about Square Root of 10
Here are some common questions and answers about the square root of 10:
- What is the square root of 10?
The square root of 10 is approximately \( \sqrt{10} \approx 3.162 \).
- Is the square root of 10 a rational number?
No, the square root of 10 is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating.
- How do you find the square root of 10?
The square root of 10 can be found using methods such as the long division method or by using a calculator. For a manual approach, the long division method is commonly used.
- Can the square root of 10 be simplified?
No, the square root of 10 cannot be simplified further as 10 is not a perfect square.
- What are some applications of the square root of 10?
The square root of 10 is used in various fields such as engineering, physics, and mathematics to solve problems involving area, volume, and other calculations requiring precision.
- Why is it important to understand the square root of 10?
Understanding the square root of 10 helps in comprehending more complex mathematical concepts and is useful in various scientific and engineering calculations.
Conclusion
Understanding the square root of 10 provides a foundation for comprehending more complex mathematical concepts and their applications. The square root of 10 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 3.162, and it plays a significant role in various fields including engineering, physics, and computer science.
Through methods such as the long division method, Newton's method, and using calculators or software, we can approximate the square root of 10 with high accuracy. Recognizing the importance of square roots in mathematics helps us appreciate their utility in solving equations, analyzing scientific data, and understanding the geometry of shapes.
The study of square roots, including that of 10, not only enhances our numerical skills but also our logical reasoning and problem-solving abilities. As we delve deeper into the mathematical world, the fundamental concept of square roots will continue to be a crucial tool in our analytical toolkit.
In conclusion, the square root of 10 exemplifies the beauty and complexity of mathematics, demonstrating the interconnectedness of mathematical principles and their practical applications in the real world.
Tìm hiểu cách tính căn bậc hai của 10 trong video này. Khám phá các phương pháp và ứng dụng của căn bậc hai trong toán học.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 10
READ MORE:
Xem video này để hiểu về khái niệm gốc bình phương và cách nó áp dụng trong toán học.
Gốc Bình Phương là Gì? | Toán cùng Thầy J