Topic square root of 1625: Discover the fascinating world of the square root of 1625. Learn how to calculate it, understand its properties, and explore its various applications in mathematics and beyond. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, this comprehensive guide will enhance your knowledge and appreciation of this intriguing number.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 1625
- Introduction
- Value of the Square Root of 1625
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root
- Is the Square Root of 1625 Irrational?
- Applications of the Square Root of 1625
- Examples and Practice Problems
- FAQs on the Square Root of 1625
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tìm căn bậc hai của số 1625 bằng phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố. Phù hợp với những ai đang tìm kiếm phương pháp tính toán hiệu quả và dễ hiểu.
Square Root of 1625
The square root of 1625 is approximately 40.311288741493. It is not a perfect square, making it an irrational number.
Mathematical Representation
The square root of 1625 can be expressed using the radical symbol as follows:
\[\sqrt{1625} \approx 40.311288741493\]
This can also be written in exponential form as:
\[1625^{\frac{1}{2}} \approx 40.311288741493\]
Prime Factorization Method
To simplify the square root of 1625 using prime factorization:
- Find the prime factors of 1625: \(1625 = 5^3 \times 13\)
- Group the factors into pairs: \(1625 = 5^2 \times 5 \times 13\)
- Take one factor from each pair: \(\sqrt{1625} = 5 \sqrt{65}\)
Therefore, the simplified form is:
\[5 \sqrt{65} \approx 40.311288741493\]
Properties of the Square Root of 1625
- The square root of 1625 is an irrational number.
- It has both positive and negative values: \(±40.311288741493\).
- The principal square root is the positive value: \(40.311288741493\).
Calculation Methods
You can calculate the square root of 1625 using various methods, including:
- Using a calculator: Enter 1625 and press the square root (√) button.
- Using Excel or Google Sheets: Enter
=SQRT(1625)or=POWER(1625, 1/2)in a cell.
Table of Nth Roots of 1625
| Index (N) | Root | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 2 | Square Root (²√1625) | 40.311 |
| 3 | Cube Root (³√1625) | 11.757 |
| 4 | Fourth Root (⁴√1625) | 6.349 |
| 5 | Fifth Root (⁵√1625) | 4.387 |
| 6 | Sixth Root (⁶√1625) | 3.429 |
| 7 | Seventh Root (⁷√1625) | 2.875 |
| 8 | Eighth Root (⁸√1625) | 2.520 |
| 9 | Ninth Root (⁹√1625) | 2.274 |
| 10 | Tenth Root (¹⁰√1625) | 2.095 |

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 1625 is a fascinating mathematical concept that has various applications. The value of the square root of 1625 is approximately 40.311, which can be determined through different methods such as long division or prime factorization. This article will explore the definition, calculation methods, and applications of the square root of 1625 in detail.
- The square root of 1625 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- Using the long division method, the approximate value is found to be 40.311.
- Prime factorization of 1625 (5^3 × 13) shows that it is not a perfect square, further indicating its irrationality.
- Practical applications include solving quadratic equations and determining geometric properties such as the side length of a square with an area of 1625 square units.
Understanding the square root of 1625 involves exploring both its numerical value and its role in various mathematical and real-world contexts.
Value of the Square Root of 1625
The square root of 1625 is a value which, when multiplied by itself, equals 1625. Mathematically, this can be expressed as:
\\(\sqrt{1625} = 40.3112887415\\)
Here's a detailed breakdown of this value:
- The square root of 1625 is approximately 40.3112887415.
- This value is derived using the long division method, which is a common technique for finding the square root of non-perfect squares.
- Alternatively, the square root can also be calculated using the Babylonian method, also known as Hero's method, which involves iteratively averaging guesses to converge on the accurate value.
The square root of 1625 can be represented in mathematical notation as follows:
\\[ \sqrt{1625} = 40.3112887415 \\]
For practical purposes, this value is often rounded to a suitable degree of precision, such as 40.31 or 40.311, depending on the context in which it is used.
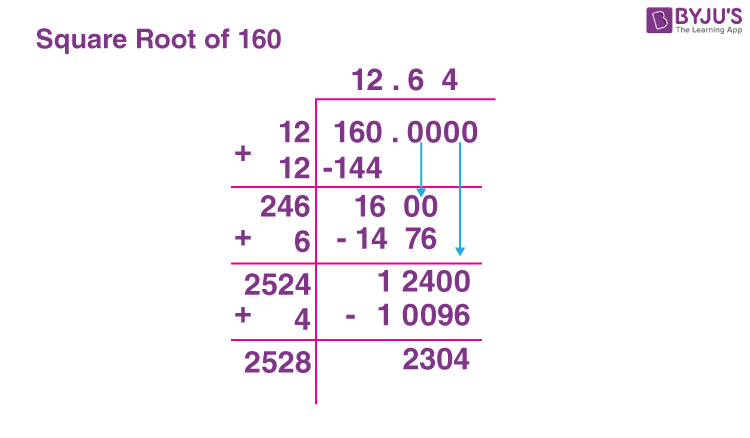
Methods to Calculate the Square Root
Calculating the square root of a number, such as 1625, can be approached through various methods. Here, we outline some common and effective techniques:
- Prime Factorization Method
- Find the prime factors of 1625. In this case, 1625 = 5^2 * 65.
- Rewrite the number as the product of its prime factors: √(5^2 * 65).
- Take the square root of each factor: √(5^2) * √65 = 5√65.
- The simplified square root of 1625 is thus 5√65.
- Long Division Method
- Pair the digits of the number from right to left.
- Estimate the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to the leftmost pair.
- Use this number as the divisor and the quotient in the division process.
- Repeat the process for each pair of digits, adjusting the divisor and quotient accordingly.
- This iterative process yields a decimal approximation of the square root.
- Using a Calculator
- Input the number 1625 into the calculator.
- Press the square root function (√) to get the result.
- The calculator provides an accurate decimal value: √1625 ≈ 40.311288741493.
Each of these methods has its own advantages. The prime factorization method provides an exact value in its simplest radical form, while the long division and calculator methods offer precise decimal approximations.
Is the Square Root of 1625 Irrational?
The square root of 1625 can be expressed in different forms, including its simplified radical form and decimal form. By examining these forms, we can determine whether the square root is irrational.
The decimal representation of the square root of 1625 is approximately 40.311288741493. This non-repeating, non-terminating decimal indicates that the square root is irrational.
To confirm, let's simplify the square root of 1625 step-by-step:
- Prime factorize 1625: 1625 = 5 × 5 × 5 × 13 = 5^2 × 5 × 13.
- Express in square root form: √1625 = √(5^2 × 5 × 13).
- Simplify: √1625 = 5√65.
The simplified form, 5√65, still contains a square root, showing it cannot be simplified to a rational number. Hence, √1625 is indeed an irrational number.

Applications of the Square Root of 1625
The square root of 1625, approximately 40.31, finds its applications in various fields. Understanding these applications helps appreciate the practical utility of mathematical concepts in real-world scenarios. Below are detailed examples of how the square root of 1625 can be used:
- Geometry: In geometric calculations, the square root of 1625 can be used to determine the side length of a square with an area of 1625 square units. If you know the area of a square, you can find the side length by taking the square root of the area.
- Physics: Square roots often appear in physics formulas, such as those involving gravitational force calculations. For instance, if an object is dropped from a height, the time taken to hit the ground can be calculated using square root functions.
- Engineering: Engineers use square roots in various design and analysis calculations. For example, when determining the stress on a particular material or component, square roots can be part of the equations used.
- Construction: In construction, calculating dimensions accurately is crucial. The square root function helps in determining distances and measurements that are not straightforward, such as the diagonal length of a square area.
- Computer Graphics: In computer graphics, algorithms often use square roots to calculate distances between points in a coordinate system. This is vital for rendering accurate images and animations.
- Statistics: Square roots are used in statistical calculations, such as standard deviation, which measures the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values.
By understanding these applications, one can see the diverse use cases of the square root of 1625 across different fields, enhancing both theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
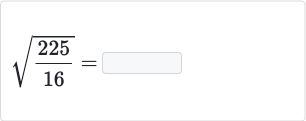
Examples and Practice Problems
Understanding the square root of 1625 through practical examples and problems is essential for mastering the concept. Here, we provide step-by-step examples and practice problems to solidify your understanding.
- Example 1: Calculate the square root of 1625 using the prime factorization method.
- Step 1: Find the prime factors of 1625. 1625 = 5 x 5 x 13 x 5.
- Step 2: Pair the prime factors: (5 x 5) x 13.
- Step 3: Extract the square root from the pairs: 5.
- Step 4: The remaining factor, 13, is not a perfect square, so the exact value remains \(5 \sqrt{13}\).
- Example 2: Use the estimation method to find the square root of 1625.
- Step 1: Identify the perfect squares closest to 1625. They are 1600 (40^2) and 1681 (41^2).
- Step 2: Since 1625 is closer to 1600, the approximate square root lies between 40 and 41.
- Step 3: Refine the estimation by testing values between 40 and 41 to get a more precise result.
- Practice Problems:
- Problem 1: Find the square root of 1444 using the long division method.
- Problem 2: Determine if the square root of 2025 is rational or irrational.
- Problem 3: Estimate the square root of 2500 and verify using a calculator.
These examples and problems provide a comprehensive approach to understanding and calculating square roots. Practice these methods to enhance your mathematical skills.
FAQs on the Square Root of 1625
-
What is the simplest radical form of √1625?
The simplest radical form of √1625 is 5√65. This is derived by performing prime factorization, where 1625 = 5^2 * 65, and simplifying it to 5√65.
-
Why is the square root of 1625 an irrational number?
The square root of 1625 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Its decimal form, approximately 40.31128874149274826183307..., is non-terminating and non-repeating, which are the characteristics of irrational numbers.
-
What are the applications of square roots in real life?
Square roots are used in various real-life applications including:
- Solving quadratic equations in algebra.
- Calculating dimensions in geometry, such as finding the side length of a square given its area.
- Understanding physical concepts such as acceleration, area, and volume in physics and engineering.
- Financial calculations, including determining the standard deviation in statistics.
Video hướng dẫn cách tìm căn bậc hai của số 1625 bằng phương pháp phân tích thừa số nguyên tố. Phù hợp với những ai đang tìm kiếm phương pháp tính toán hiệu quả và dễ hiểu.
Tìm Căn Bậc Hai Bằng Phương Pháp Phân Tích Thừa Số Nguyên Tố, Căn Bậc Hai của 1625 (√1625)
READ MORE:
Xem video này để hiểu về khái niệm về bình phương và căn bậc hai, cùng những ví dụ minh họa và ứng dụng trong cuộc sống hàng ngày.
Bình phương & Căn bậc hai