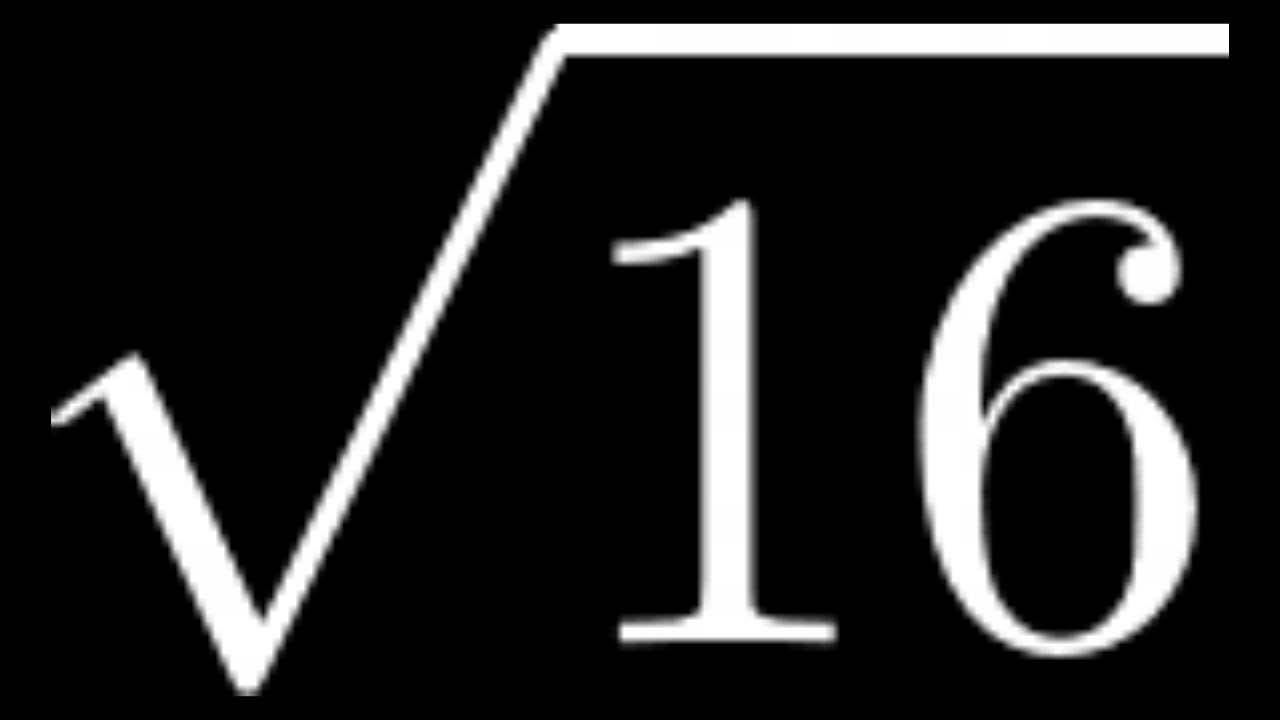Topic what is the principal square root of 16: The principal square root of 16 is a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing the non-negative root that, when multiplied by itself, equals 16. In this article, we explore the principal square root, its significance, and how it is applied in various mathematical problems. Join us as we uncover the simplicity and beauty of this mathematical principle.
Table of Content
- What is the Principal Square Root of 16?
- Definition of Principal Square Root
- Calculation of Principal Square Root of 16
- Mathematical Explanation
- Properties of the Principal Square Root
- Applications in Real Life
- Examples and Solved Problems
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá căn bậc hai của 16 trong video này. Tìm hiểu cách tính toán và các ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai.
What is the Principal Square Root of 16?
The principal square root of a number is its non-negative square root. For the number 16, this can be calculated as follows:
When a number \( a \) is squared, it gives a product \( b \). The square root of \( b \), denoted as \( \sqrt{b} \), is the value that, when multiplied by itself, results in \( b \).
Calculation of the Square Root of 16
To find the square root of 16, we need a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 16:
\[
\sqrt{16} = 4
\]
This is because:
\[
4 \times 4 = 16
\]
Understanding Principal Square Root
Although both 4 and -4 are square roots of 16, the principal square root is defined to be the non-negative value. Hence:
\[
\sqrt{16} = 4
\]
Properties and Definitions
- The symbol \( \sqrt{} \) denotes the square root.
- The principal square root is always non-negative.
- For any non-negative real number \( a \), \( \sqrt{a} \) is the principal square root of \( a \).
Examples of Square Roots
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
| 36 | 6 |
Why is the Principal Square Root Important?
In mathematical operations, using the principal square root helps to maintain consistency and avoid ambiguity, especially in algebra and higher-level mathematics.

READ MORE:
Definition of Principal Square Root
The principal square root of a number is defined as the unique nonnegative square root of a nonnegative real number. For any nonnegative number \( a \), the principal square root is denoted by \( \sqrt{a} \), where the symbol \( \sqrt{} \) is known as the radical sign. This means that the principal square root of \( a \) is the positive number that, when squared, gives \( a \).
For example:
- The principal square root of 16 is 4, since \( 4^2 = 16 \).
- The principal square root of 25 is 5, since \( 5^2 = 25 \).
It is important to note that while a positive number \( a \) has two square roots, one positive and one negative, the principal square root refers only to the positive root. Therefore:
- The square roots of 9 are 3 and -3, but the principal square root of 9 is 3.
- The square roots of 16 are 4 and -4, but the principal square root of 16 is 4.
In mathematical notation, this is expressed as:
- \(\sqrt{a} = r\) where \( r \) is the principal square root of \( a \) and \( r \ge 0 \).
- \(r^2 = a\).
Calculation of Principal Square Root of 16
To find the principal square root of 16, follow these detailed steps:
- Identify the number to find the square root of: 16.
- Understand that the principal square root of a number is its non-negative root.
- Find the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to 16. In this case, it is 4 because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- Express the square root in radical form: \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
Let's break it down step-by-step:
-
Step 1: Write 16 as shown in the figure. Start grouping the number in pairs from the right end. For 16, both the numbers will be grouped under one bar.
16 -
Step 2: Find the largest number that when multiplied with itself will give 16 or a smaller number closest to 16.
- 4 is the required number since \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
-
Step 3: Perform division on the dividend 16, using 4 as the divisor.
4 |16 - Step 4: The quotient obtained from the long division is the square root of 16.
Thus, the principal square root of 16 is 4. This is expressed as \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
Mathematical Explanation
The principal square root of a number is the positive value that, when squared, equals the original number. For 16, this value is 4. Here's a detailed explanation:
-
Understanding Square Roots:
The square root of a number \( x \) is a number \( r \) such that \( r^2 = x \). In the case of 16, we seek \( r \) such that \( r^2 = 16 \).
-
Calculating the Square Root of 16:
- Identify \( x \): Here, \( x = 16 \).
- Find \( r \) such that \( r^2 = 16 \). We observe that \( 4^2 = 16 \) and \( (-4)^2 = 16 \). Thus, both 4 and -4 are square roots of 16.
- Select the Principal Square Root: By definition, the principal square root is the positive value. Hence, the principal square root of 16 is 4.
-
Mathematical Notation:
The principal square root of 16 is denoted as \( \sqrt{16} \). This simplifies to:
\[
\sqrt{16} = 4
\]However, when considering both square roots, we write:
\[
\pm \sqrt{16} = \pm 4
\] -
Importance of the Principal Square Root:
The principal square root is essential in various mathematical contexts, including solving equations and performing operations involving exponents and radicals.
In summary, while 16 has two square roots, 4 and -4, the principal square root is the positive value, 4.
Properties of the Principal Square Root
The principal square root of a number is its nonnegative square root, which simplifies many mathematical operations and properties. Below are key properties of the principal square root:
- Uniqueness: Every nonnegative real number \( a \) has a unique nonnegative square root, denoted as \( \sqrt{a} \).
- Multiplicative Property: The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots:
\[
\sqrt{ab} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b} \quad \text{for} \quad a, b \geq 0.
\] - Quotient Property: The square root of a quotient is equal to the quotient of the square roots:
\[
\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \quad \text{for} \quad b \neq 0.
\] - Nonnegativity: The principal square root of any nonnegative number is always nonnegative.
- Exponentiation: The principal square root can be expressed using exponentiation:
\[
\sqrt{a} = a^{1/2}.
\]
These properties are fundamental in simplifying and solving equations involving square roots. For example, they are essential in algebra and calculus for operations such as integration and differentiation of functions involving square roots.

Applications in Real Life
The principal square root of 16, which is 4, finds numerous applications in everyday life. Understanding and using square roots is essential in various fields such as construction, art, and science. Here are some practical applications:
- Construction and Design: Architects and engineers use square roots to calculate areas and dimensions of structures. For example, if a square-shaped plot of land has an area of 16 square meters, each side of the plot would be 4 meters.
- Carpentry: When creating square components, such as tabletops or frames, knowing the square root helps in determining the length of each side when the area is known.
- Gardening: Gardeners might arrange plants in a square grid. For a grid of 16 plants, each row and column would have 4 plants, utilizing the principal square root for optimal layout.
- Art and Design: Artists use the square root to maintain proportions and symmetry in their work, especially when dealing with square canvases or design elements.
- Mathematics Education: Teaching square roots helps students understand fundamental concepts in algebra and geometry, laying the groundwork for more advanced mathematical studies.
These applications highlight the importance of understanding square roots and their practical utility in a wide range of disciplines.
Examples and Solved Problems
Understanding the principal square root of 16 through examples and solved problems helps solidify the concept. Here are some practical examples:
- Example 1: If you have 16 small square tiles and want to arrange them to form a larger square, you need to find the side length of this larger square. Since the principal square root of 16 is 4, the side length of the larger square is 4 tiles.
- Example 2: A square garden has an area of 16 square meters. To find the length of one side of the garden, calculate the principal square root of 16, which is 4 meters.
- Example 3: In a school project, students need to create a square-shaped board with an area of 16 square inches. They will determine the side length of the board by finding the principal square root of 16, resulting in a side length of 4 inches.
Let's look at detailed steps to solve these problems:
Step-by-Step Solution for Example 1
- Identify the area of the square: 16 square tiles.
- Calculate the principal square root of 16: \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
- The side length of the larger square is 4 tiles.
Step-by-Step Solution for Example 2
- Identify the area of the garden: 16 square meters.
- Calculate the principal square root of 16: \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
- The side length of the garden is 4 meters.
Step-by-Step Solution for Example 3
- Identify the area of the square board: 16 square inches.
- Calculate the principal square root of 16: \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
- The side length of the board is 4 inches.
These examples illustrate how to apply the concept of the principal square root in real-life situations. The key is to understand that the principal square root provides a positive value that is practical for measurements and arrangements.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is the principal square root of 16?
The principal square root of 16 is 4. It is the non-negative number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 16.
-
Why is 4 the principal square root of 16 and not -4?
While both 4 and -4 are square roots of 16, the principal square root is defined as the non-negative root. Therefore, 4 is the principal square root.
-
How do you calculate the principal square root of a number?
The principal square root of a number \( x \) is calculated using the symbol \( \sqrt{x} \). For example, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
-
Can the principal square root of a negative number be calculated?
No, the principal square root of a negative number is not defined in the set of real numbers. It requires the use of imaginary numbers. For example, the principal square root of -16 is \( 4i \).
-
What are some properties of the principal square root?
- The principal square root is always non-negative.
- If \( x \) is a positive number, then \( \sqrt{x^2} = x \).
- The principal square root function is continuous for all non-negative values of \( x \).
-
Why is the principal square root important?
The principal square root is used in various mathematical calculations, scientific formulas, and engineering problems where a non-negative value is required.
-
Are there real-life applications of the principal square root?
Yes, principal square roots are used in calculating areas, solving quadratic equations, and in various fields such as physics, engineering, and finance.
-
What is the difference between a square root and the principal square root?
A square root of a number \( x \) can be both positive and negative, while the principal square root is the non-negative root. For example, the square roots of 16 are 4 and -4, but the principal square root is only 4.
Khám phá căn bậc hai của 16 trong video này. Tìm hiểu cách tính toán và các ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 16
READ MORE:
Khám phá căn bậc hai chính trong video này. Tìm hiểu định nghĩa và cách tính toán căn bậc hai chính.
Căn Bậc Hai Chính