Topic what is the square root of 16: What is the square root of 16? Discover the answer and its significance in mathematics. This article delves into the concept of square roots, the value of the square root of 16, and various methods to calculate it, offering practical examples and applications to enhance your understanding.
Table of Content
Understanding the Square Root of 16
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the number 16, its square root is 4. This can be represented in several mathematical forms and can be understood through various methods.
Value of the Square Root of 16
In mathematical notation, the square root of 16 is written as:
\(\sqrt{16} = 4\)
This means that \(4 \times 4 = 16\). The value of the square root of 16 is therefore both positive and negative, which can be expressed as:
\(\sqrt{16} = \pm 4\)
Methods to Find the Square Root of 16
- Prime Factorization Method: The prime factorization of 16 is \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\). Grouping the prime factors in pairs and multiplying gives us \(4\).
- Long Division Method: This method involves dividing 16 in a systematic way to find its square root. This confirms that the square root of 16 is 4.
Examples and Applications
Here are a few examples to understand the practical application of finding the square root of 16:
- Example 1: Simplifying the expression \((7\sqrt{16}) + 15\).
Solution: Given \((7\sqrt{16}) + 15\), substituting the value of \(\sqrt{16}\) as 4, we get:
\(7 \times 4 + 15 = 28 + 15 = 43\)
- Example 2: Determine the value of \(m\) if \(m + \sqrt{16} = 20\).
Solution: Given \(m + \sqrt{16} = 20\), substituting the value of \(\sqrt{16}\) as 4, we get:
\(m + 4 = 20 \rightarrow m = 20 - 4 = 16\)
Further Information
The square root of 16 is an important concept in mathematics, and it can be explored in various ways such as through illustrations, examples, and different problem-solving methods. Understanding this concept helps in grasping more complex mathematical principles and applications.
Learn more about square roots and practice with interactive tools and examples on educational websites.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical terms, the square root of 16 is written as √16, which equals 4. This fundamental concept in mathematics not only helps in solving equations but also in understanding various real-life applications. Here, we explore what the square root of 16 means, its properties, and how to find it step by step.
- Definition of Square Root
- Properties of Square Root of 16
- Methods to Find the Square Root of 16
- Using Perfect Squares
- Long Division Method
- Babylonian Method
- Examples and Practice Problems
- Applications of Square Roots in Real Life
Understanding the square root of 16 provides a basis for further exploration of mathematical concepts and problem-solving techniques.
Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical terms, if \(x\) is the square root of \(y\), then \(x^2 = y\). The square root is denoted using the radical symbol \( \sqrt{} \).
The concept of square roots extends to both perfect squares, which are numbers like 16, 25, and 36 whose square roots are whole numbers, and imperfect squares, which are numbers like 20, 30, and 45 whose square roots include fractions or decimals.
For instance, the square root of 16 is represented as \( \sqrt{16} \). Since \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \), it follows that \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
Here is the step-by-step process to understand the square root of 16:
- Identify the number: 16.
- Find a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 16. In this case, \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- Therefore, the square root of 16 is 4, which can be written as \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
Square roots can also be found using methods such as prime factorization and long division. For prime factorization, the steps are:
- Factorize 16 into its prime factors: \( 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \).
- Group the factors into pairs: \( (2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2) \).
- Take one factor from each pair: \( 2 \times 2 = 4 \).
- Hence, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
The long division method involves dividing the number into smaller steps, which makes it easier to handle larger numbers. By following these methods, we can find the square roots of both perfect and imperfect squares effectively.
Examples
Understanding the square root of 16 can be reinforced through various examples. Here, we explore different instances and methods to elucidate this concept.
-
Basic Example:
The square root of 16 is represented as √16. Since 4 × 4 = 16, we conclude that √16 = 4.
-
Using Repeated Subtraction:
By repeatedly subtracting odd numbers from 16 until zero is reached, we determine the square root. For instance:
- 16 - 1 = 15
- 15 - 3 = 12
- 12 - 5 = 7
- 7 - 7 = 0
Since we performed 4 subtractions, √16 = 4.
-
Prime Factorization:
Breaking down 16 into its prime factors, we have:
16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 Pairing the prime factors and selecting one from each pair:
2 × 2 This gives us √16 = 4.
-
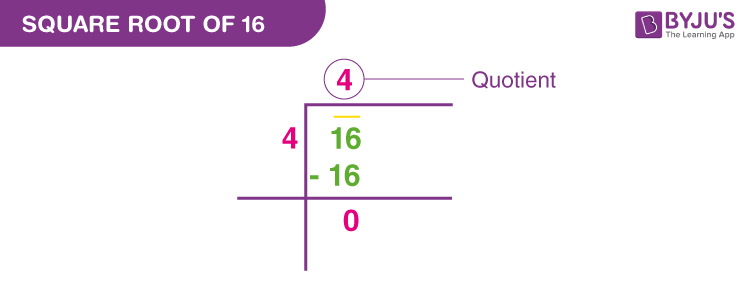
Division Method:
Applying the division method:
- Group digits in pairs from the right: 16
- Find the largest number whose square is ≤ 16, which is 4.
- Thus, √16 = 4.
-
Example Problems:
- What is √64? Since 8 × 8 = 64, √64 = 8.
- If the area of a square garden is 16 m², its side length is √16 = 4 meters.
Visual Learning
Visual learning can significantly enhance understanding of mathematical concepts such as square roots. Below are some visual methods to understand and calculate the square root of 16:
Graphical Representation
Consider a number line to visualize the square root of 16:
- Plot the points 0, 4, and 16 on the number line.
- The square root of 16 is the point at which the square of a number equals 16, which is 4.
Below is a graphical representation:
Geometric Interpretation
A square with an area of 16 square units can be used to find the square root:
- Draw a square and divide it into 16 smaller squares.
- Each smaller square has an area of 1 square unit.
- The side length of the large square is the square root of 16, which is 4 units.
Here is a visual representation of the square:
Using MathJax for Mathematical Representation
We can use MathJax to represent the square root of 16 mathematically:
\[ \sqrt{16} = 4 \]
Step-by-Step Calculation
Below is a table showing step-by-step calculations using the prime factorization method:
| Step | Calculation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 16 = 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 | Prime factors of 16 |
| 2 | Group the prime factors in pairs | (2 × 2) × (2 × 2) |
| 3 | Take one factor from each pair | 2 × 2 |
| 4 | Multiply the factors | 4 |
Interactive Learning
Use online interactive tools to visualize and manipulate the square root concept:
- Interactive number lines where you can drag points to see the effect.
- Geometric tools to draw squares and other shapes to understand areas and side lengths.
- MathJax-enabled platforms to input and solve square root equations.
These visual aids can help in developing a deeper understanding of the concept of square roots and make learning more engaging and effective.
FAQs
-
What is the Value of the Square Root of 16?
The value of the square root of 16 is 4. This is because 4 multiplied by itself (4 × 4) equals 16.
-
Is the Square Root of 16 a Rational Number?
Yes, the square root of 16 is a rational number. This is because it can be expressed as the fraction 4/1, where both the numerator and the denominator are integers.
-
Is 16 a Perfect Square?
Yes, 16 is a perfect square. A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer. In this case, 4 × 4 = 16, so 16 is the square of 4.
-
How to Represent the Square Root of 16?
The square root of 16 can be represented in several forms:
- Radical form: √16
- Exponential form: 161/2
-
How Do You Calculate the Square Root of 16?
There are various methods to calculate the square root of 16:
- Using a calculator: Enter 16 and press the square root (√) button to get 4.
- Using the prime factorization method: Express 16 as 24, then take the square root of each factor pair, which results in 4.
- Using the long division method: Perform long division to find that the square root of 16 is 4.
-
Why Does 16 Have Two Square Roots?
Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. Therefore, the square roots of 16 are 4 and -4. However, the principal square root is the positive one, which is 4.
-
Is the Square Root of 0.16 Related to the Square Root of 16?
Yes, the square root of 0.16 is related to the square root of 16. Since 0.16 is 16/100, the square root of 0.16 is √(16/100) = √16 / √100 = 4 / 10 = 0.4.
Giá Trị Căn Bậc Hai Của 16
READ MORE:
Làm Thế Nào Để Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai Của 16: sqrt(16)