Topic what is the square root of zero: The square root of zero is a fundamental concept in mathematics that often sparks curiosity. This article explores the meaning and properties of zero, its square root, and its significance in various mathematical contexts. Dive in to understand why the square root of zero is both simple and profound.
Table of Content
- What is the Square Root of Zero?
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding the Concept of Zero
- Mathematical Definition of Square Root
- Calculating the Square Root of Zero
- Properties of Zero
- Applications of Square Roots in Mathematics
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Common Misconceptions about Square Roots
- YOUTUBE: The square root of zero là gì? Tìm hiểu trong một phút về các surds và bài toán liên quan đến căn bậc hai của số không.
What is the Square Root of Zero?
The square root of zero is a simple yet fundamental concept in mathematics. Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{0} = 0
\]
Explanation
To understand why the square root of zero is zero, consider the definition of the square root. The square root of a number \( x \) is a number \( y \) such that:
\[
y^2 = x
\]
For zero, this means finding a number \( y \) such that:
\[
y^2 = 0
\]
The only number that satisfies this equation is \( y = 0 \) because:
\[
0 \times 0 = 0
\]
Properties of the Square Root of Zero
- Zero is the only number that, when squared, equals zero.
- The square root of zero is unique; no other number has this property.
Applications in Mathematics
The concept of square roots is widely used in various areas of mathematics, including algebra, geometry, and calculus. Understanding the square root of zero helps in simplifying equations and solving problems involving square roots and exponents.
Table of Nth Roots of Zero
| Index | Radicand | Root Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 0 | ²√0 | 0 |
| 3 | 0 | ³√0 | 0 |
| 4 | 0 | ⁴√0 | 0 |
| 5 | 0 | ⁵√0 | 0 |
| 6 | 0 | ⁶√0 | 0 |
| 7 | 0 | ⁷√0 | 0 |
| 8 | 0 | ⁸√0 | 0 |
| 9 | 0 | ⁹√0 | 0 |
| 10 | 0 | ¹⁰√0 | 0 |
Summary
The square root of zero is a fundamental concept, simply defined as zero. It is unique and forms the basis for understanding more complex mathematical principles.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
Square roots are a fundamental concept in mathematics, representing a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of a number \( x \) is denoted as \( \sqrt{x} \) or \( x^{1/2} \).
Key properties of square roots include:
- Non-negative result: The square root of any non-negative number is also non-negative.
- Product rule: \( \sqrt{a \times b} = \sqrt{a} \times \sqrt{b} \)
- Quotient rule: \( \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}} \)
- Zero property: \( \sqrt{0} = 0 \)
Understanding square roots is crucial for solving equations, simplifying expressions, and many applications in science and engineering.
Let's delve deeper into how square roots are defined and calculated, with a special focus on the intriguing case of the square root of zero.
Understanding the Concept of Zero
Zero is a unique and fundamental number in mathematics. It serves as the additive identity, meaning that adding zero to any number does not change the value of that number. Zero is represented by the symbol \(0\) and has several important properties:
- Additive Identity: For any number \(a\), \(a + 0 = a\).
- Multiplicative Property: For any number \(a\), \(a \times 0 = 0\).
- Divisibility: Any number divided by zero is undefined, while zero divided by any non-zero number is zero.
- Neutral Element in Subtraction: For any number \(a\), \(a - 0 = a\).
- Square Root: The square root of zero is zero, \( \sqrt{0} = 0 \).
Zero plays a critical role in various mathematical operations and serves as a cornerstone for more advanced mathematical concepts. Understanding zero is essential for grasping the basics of arithmetic, algebra, and calculus.
Next, we will explore the mathematical definition of square roots, providing a deeper understanding of how they are calculated and their significance in various contexts.
Mathematical Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is denoted by the radical symbol √. The square root of a number x is written as √x.
Mathematically, for a given non-negative number x, the square root of x is a number y such that:
\(y = \sqrt{x}\)
or equivalently,
\(y^2 = x\)
Here are some key points about square roots:
- The square root of 0 is 0: \(\sqrt{0} = 0\).
- The square root of a positive number is always positive.
- Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative, represented as \(\pm \sqrt{x}\).
- The square root of a negative number is not a real number; it is an imaginary number, denoted as \(i\sqrt{|x|}\) where \(i\) is the imaginary unit.
Let's look at some examples:
| Number (x) | Square Root (\(\sqrt{x}\)) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| -1 | i |
Therefore, the square root is a fundamental concept in mathematics, providing the basis for more complex mathematical operations and applications.
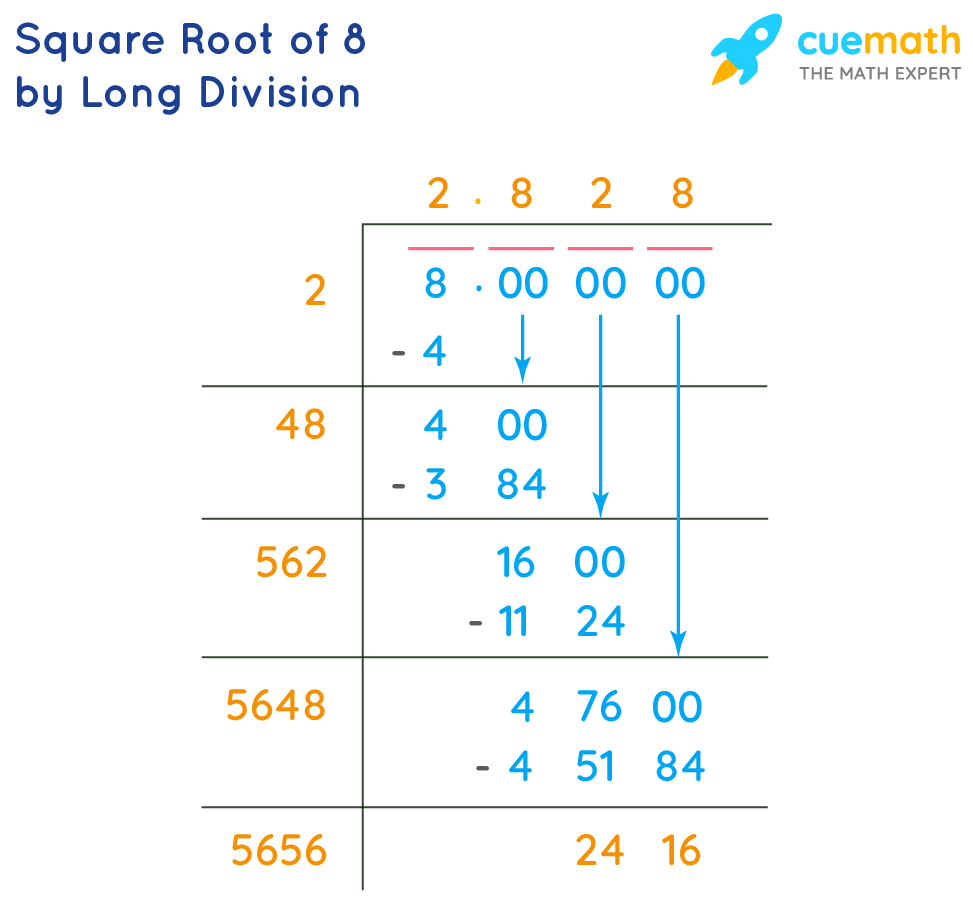
Calculating the Square Root of Zero
To calculate the square root of zero, we start with the basic understanding that the square root of a number \( x \) is a value \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). For zero, this means finding a number \( y \) such that \( y^2 = 0 \).
The solution to this equation is straightforward: the only number that satisfies \( y^2 = 0 \) is \( y = 0 \). This is because any non-zero number squared results in a positive number, and negative numbers squared yield positive results as well.
Therefore, the square root of zero, \( \sqrt{0} \), is simply \( 0 \).

Properties of Zero
Zero, often represented as \( 0 \), holds several unique properties in mathematics:
- Additive Identity: When added to any number \( x \), zero leaves the number unchanged: \( x + 0 = x \).
- Multiplicative Annihilator: When multiplied by any number \( x \), zero results in zero: \( x \cdot 0 = 0 \).
- Neutral Element in Operations: In both addition and multiplication, zero serves as a neutral element: \( x + 0 = x \) and \( x \cdot 0 = 0 \).
- Special Case in Division: Division by zero is undefined in arithmetic due to the impossibility of finding a number \( y \) such that \( y \cdot 0 = x \neq 0 \).
- Non-Negative Nature: Zero is non-negative and serves as a reference point between positive and negative numbers on the number line.
Applications of Square Roots in Mathematics
Square roots are fundamental in various mathematical applications:
- Geometric Formulas: Square roots appear in formulas for calculating distances, areas, and volumes. For instance, in geometry, the distance between two points in a coordinate plane is found using the Pythagorean theorem, which involves square roots.
- Engineering: Engineers use square roots in fields such as electrical engineering (root mean square calculations) and structural engineering (calculating forces and stresses).
- Physics: In physics, square roots are prevalent in equations related to waveforms, quantum mechanics, and fluid dynamics.
- Statistics: Square roots play a role in statistical analysis, particularly in calculating standard deviation and variance.
- Computer Graphics: Square roots are essential in computer graphics for calculating distances between points and for transformations.
- Financial Modeling: In finance, square roots are used in the Black-Scholes model for option pricing and in other risk management calculations.
- Mathematical Modeling: Square roots are crucial in mathematical models across various disciplines, including biology (population growth models) and economics (macroeconomic models).
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the square root of zero?
The square root of zero, denoted as \( \sqrt{0} \), is equal to zero. This is because zero multiplied by itself (0 × 0) equals zero.
- Why is the square root of zero important?
The concept of the square root of zero is fundamental in mathematics as it helps define the properties of numbers and serves as a basis for understanding higher mathematical concepts.
- Can the square root of zero be negative?
No, by convention, the square root function \( \sqrt{x} \) for real numbers is defined to yield a non-negative result. Therefore, \( \sqrt{0} = 0 \) and not \( -0 \).
- What are some practical uses of knowing the square root of zero?
Understanding the square root of zero is important in various scientific and engineering applications, such as in physics equations involving energy and momentum calculations.
- Is the square root of zero an imaginary number?
No, the square root of zero is a real number, specifically zero itself. Imaginary numbers are defined as the square roots of negative numbers.
Common Misconceptions about Square Roots
- Square roots of negative numbers:
One common misconception is that square roots of negative numbers do not exist. In fact, they do exist and are called imaginary numbers. For example, \( \sqrt{-1} = i \), where \( i \) is the imaginary unit.
- Square root of zero is undefined:
Another misconception is that the square root of zero is undefined or cannot be calculated. In reality, the square root of zero is defined and equals zero, because \( 0 \times 0 = 0 \).
- Square roots are always positive:
While it's true that the principal (non-negative) square root of a non-negative real number is positive, square roots can be positive or negative depending on the context, especially in complex numbers.
- Square roots are only used in basic arithmetic:
Many believe that square roots are limited to elementary arithmetic. However, they have extensive applications in advanced mathematics, physics, engineering, statistics, and various scientific fields.

The square root of zero là gì? Tìm hiểu trong một phút về các surds và bài toán liên quan đến căn bậc hai của số không.
The square root of zero || One Minute Math || surds
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu về phép tính căn bậc hai của số không và các bước cụ thể để tính toán. Video hướng dẫn chi tiết về √0.
Tìm Căn Bậc Hai: √0