Topic 8 square root: The square root of 8, often expressed as √8, is a fascinating mathematical concept. This article delves into the various methods to calculate it, its applications, and its significance. Whether you're a student or a math enthusiast, understanding √8 can enhance your grasp of mathematical principles and their practical uses.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 8
- Introduction to Square Root of 8
- Understanding Square Roots
- Mathematical Representation
- Methods to Calculate Square Root of 8
- Decimal and Fractional Form
- Applications of Square Root of 8
- Comparison with Other Square Roots
- Visual Representations
- FAQs on Square Root of 8
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video về Gốc bậc hai của 8 để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này và xem liệu nó có phù hợp với bài viết về từ khóa '8 square root' hay không.
Square Root of 8
The square root of 8, denoted as \(\sqrt{8}\), is a number which, when multiplied by itself, results in the original number 8. The value of the square root of 8 can be expressed both in its simplest radical form and in decimal form.
Value of Square Root of 8
In simplest radical form:
\(\sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2}\)
In decimal form, it is approximately:
\(\sqrt{8} \approx 2.828\)
How to Calculate the Square Root of 8
To find the square root of 8, one can use various methods, including prime factorization and long division method.
Prime Factorization Method
- First, express 8 as the product of its prime factors: \(8 = 2 \times 2 \times 2\).
- Pair the prime factors: \(\sqrt{8} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 2} = 2\sqrt{2}\).
Examples
- If Mr. Smith wants to fence his square garden which has an area of 8 square feet, the length of each side of the garden will be \(2\sqrt{2}\) feet.
- For a square with an area of 8 square inches, the side length of the square will be approximately 2.828 inches.
Properties of the Square Root of 8
| Form | Value |
| Simplified Radical Form | 2\(\sqrt{2}\) |
| Decimal Form | 2.828 |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 8
The square root of 8, often written as √8, is a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 8. The value of the square root of 8 is approximately 2.828. It is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. In its simplest radical form, the square root of 8 is written as 2√2.
Here are some methods to calculate and understand the square root of 8:
- Using the prime factorization method: 8 can be broken down into its prime factors (2 × 2 × 2). Thus, √8 can be simplified as 2√2.
- Using the long division method: This technique is useful for finding more precise decimal values of the square root.
- Using estimation: By knowing that the square root of 4 is 2 and the square root of 9 is 3, we can estimate that the square root of 8 is between 2 and 3, closer to 3.
Mathematically, the principal square root of 8 can be represented as:
The value 2√2 is known as a surd, as it represents an irrational number in its simplest form.
Understanding Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is denoted by the radical symbol (√). For example, the square root of 9 is 3 because \(3 \times 3 = 9\).
Mathematically, the square root of a number \(x\) is represented as:
\[\sqrt{x}\]
Square roots can be both positive and negative because both \((+3) \times (+3)\) and \((-3) \times (-3)\) result in 9. However, in most contexts, we refer to the principal (positive) square root.
Key properties of square roots include:
- For any non-negative number \(x\), \(\sqrt{x^2} = x\).
- The square root of 0 is 0: \(\sqrt{0} = 0\).
- The square root of 1 is 1: \(\sqrt{1} = 1\).
- \(\sqrt{a \cdot b} = \sqrt{a} \cdot \sqrt{b}\), for any non-negative numbers \(a\) and \(b\).
- \(\sqrt{\frac{a}{b}} = \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}\), for any non-negative numbers \(a\) and \(b\), with \(b \ne 0\).
Square roots are widely used in various fields such as geometry, physics, engineering, and statistics to solve equations and analyze data.
Understanding the concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics as it lays the foundation for more advanced topics like solving quadratic equations, working with exponents, and understanding irrational numbers.
Mathematical Representation
The square root of 8 can be represented mathematically as follows:
- Symbolically: \( \sqrt{8} \)
- Numerically: approximately \( 2.82842712474619 \) (rounded to 14 decimal places)
To find the square root of 8, one can utilize various methods:
- Estimation Method: Using approximations and iterative techniques.
- Prime Factorization: Expressing 8 as a product of prime factors \( 2^3 \) and then simplifying.
- Long Division: A manual calculation method where 8 is divided by successive approximations.
The square root of 8 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed exactly as a fraction.
Methods to Calculate Square Root of 8
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 8. Here we will discuss three common methods: Long Division Method, Approximation Method, and Prime Factorization.
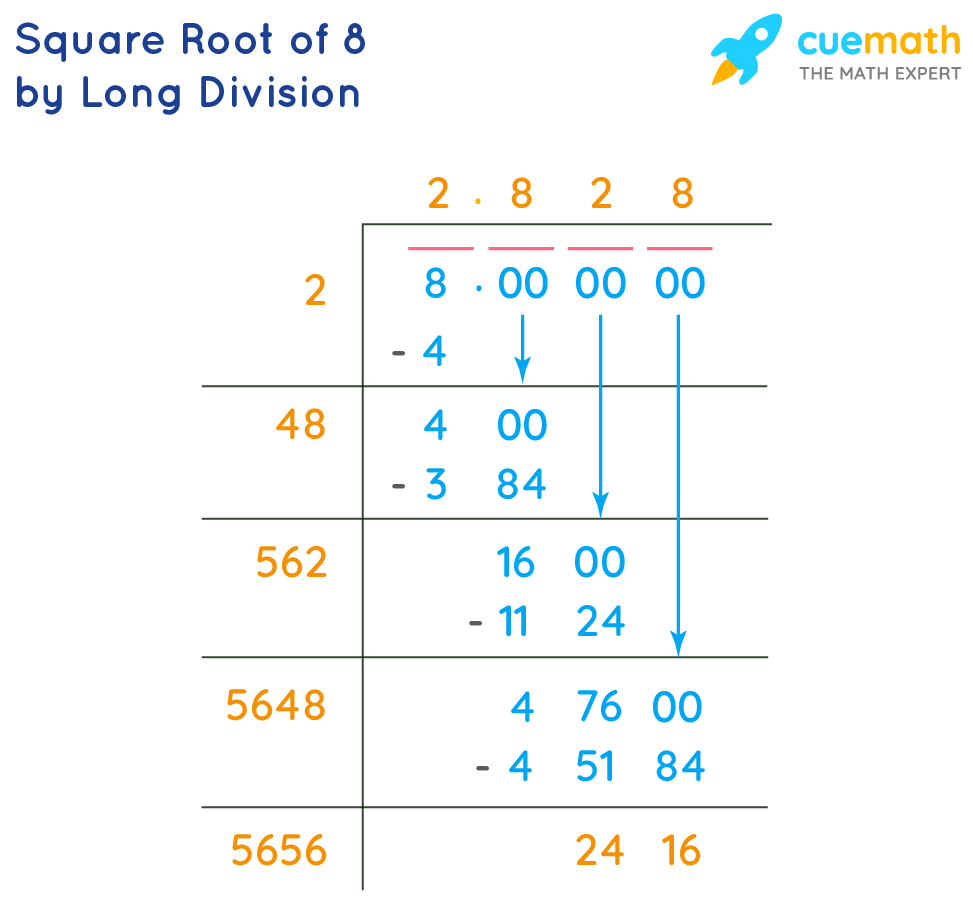
Long Division Method
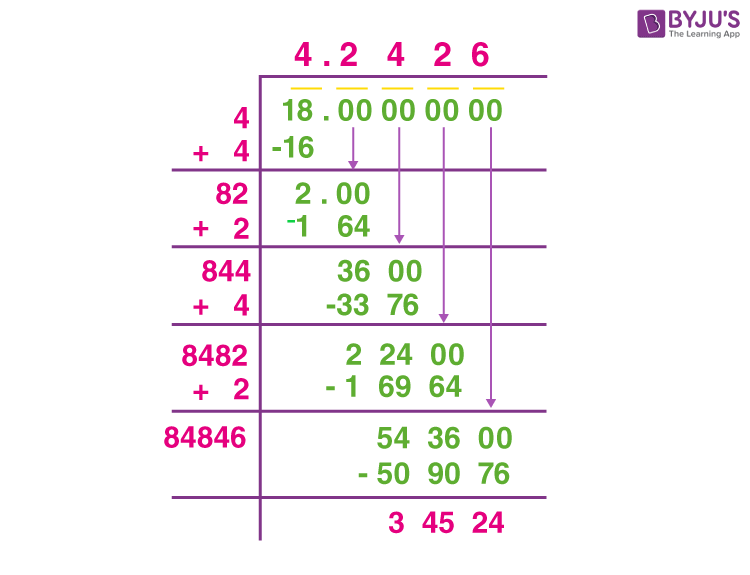
- Write 8 as 8.000000 to ensure accuracy to several decimal places.
- Pair the digits from right to left, starting with the decimal point. In this case, you get (8.00)(00)(00).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair (8). This number is 2 (since \(2^2 = 4\)). Write 2 as the first digit of the square root.
- Subtract \(4\) from \(8\) to get \(4\), then bring down the next pair (00) to make it 400.
- Double the current quotient (2) to get 4. Find a digit (x) such that \(4x \cdot x \leq 400\). The digit is 4 (since \(44 \cdot 4 = 176\)). Write 4 as the next digit of the quotient.
- Subtract 176 from 400 to get 224, then bring down the next pair (00) to make it 22400.
- Repeat the process until you reach the desired number of decimal places.
The approximate value of \( \sqrt{8} \) using this method is 2.8284.
Approximation Method
- Identify two perfect squares between which 8 lies. These are \(4\) (since \(2^2 = 4\)) and \(9\) (since \(3^2 = 9\)).
- Since 8 is closer to 9, start with 2.5 as a guess for \( \sqrt{8} \).
- Improve the approximation by using the formula: \( \text{New guess} = \frac{\text{Old guess} + \frac{8}{\text{Old guess}}}{2} \).
- Substitute 2.5 into the formula: \( \text{New guess} = \frac{2.5 + \frac{8}{2.5}}{2} = \frac{2.5 + 3.2}{2} = 2.85 \).
- Repeat the process until the guesses converge to a stable value. After a few iterations, the approximate value is 2.8284.
Prime Factorization
- Express 8 as a product of prime factors: \( 8 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 2^3 \).
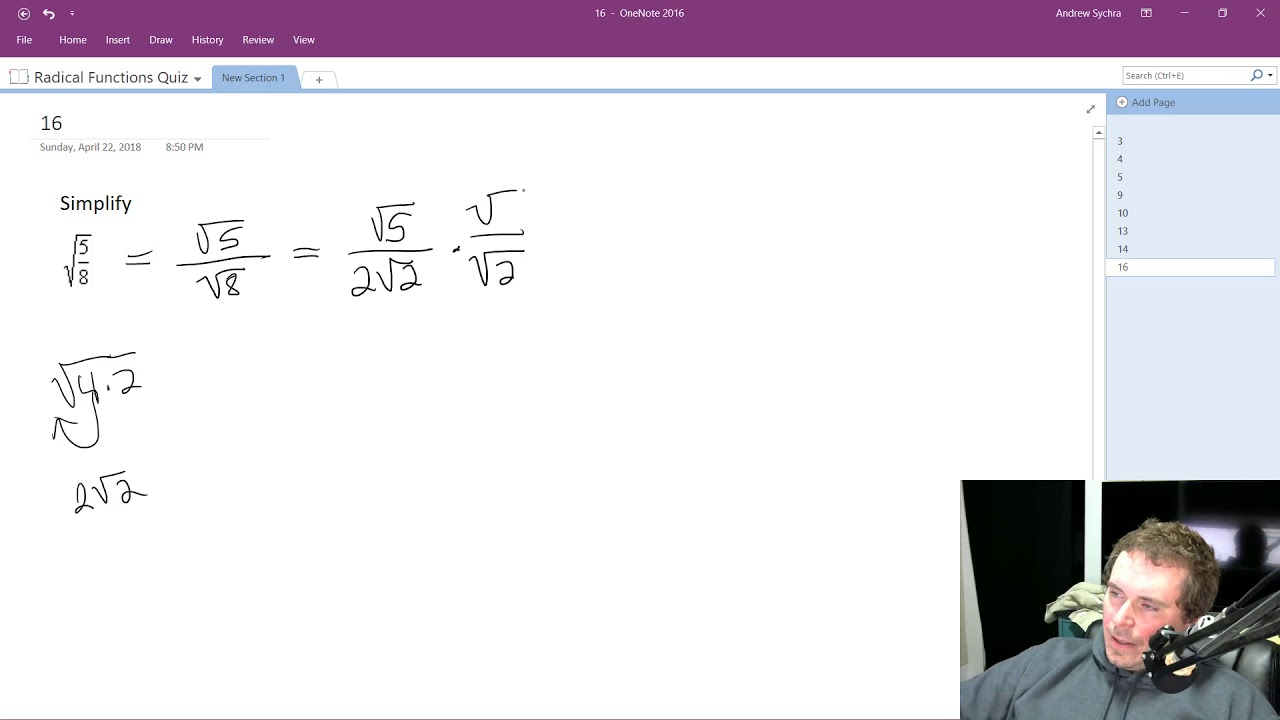
- Rewrite the expression to find the square root: \( \sqrt{8} = \sqrt{2^3} = \sqrt{4 \cdot 2} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{2} \).
- Since \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \), the expression simplifies to \( 2\sqrt{2} \).
- The exact value of \( \sqrt{8} \) is \( 2\sqrt{2} \), and its approximate value is 2.8284.
Each of these methods provides a way to understand and calculate the square root of 8, with varying levels of precision and complexity.
Decimal and Fractional Form
The square root of 8 is an irrational number, which means it cannot be exactly expressed as a simple fraction. However, we can represent it in both decimal and fractional approximations for practical purposes.
Decimal Form: The square root of 8 in decimal form is approximately:
\(\sqrt{8} \approx 2.82842712474619\)
This value is often rounded to 2.828 for simplicity in everyday calculations.
Fractional Form: While the exact square root of 8 cannot be represented as a fraction, we can use rational approximations to understand its value better. Here are a few fractional representations:
- Using a rough estimate, \(\sqrt{8} \approx \frac{8}{3}\), which equals approximately 2.6667.
- A more precise approximation is \(\sqrt{8} \approx \frac{141}{50}\), which equals approximately 2.82.
We can also express the square root of 8 using the simplest radical form:
\(\sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2}\)
This form highlights the relationship between 8 and 2, where 8 is 4 multiplied by 2, and the square root of 4 is 2.
To summarize, while \(\sqrt{8}\) is inherently an irrational number, its value can be closely approximated using decimal and fractional forms for practical applications.
Applications of Square Root of 8
- Engineering: In engineering calculations, the square root of 8 (√8) often appears in various formulas involving dimensions and scaling factors, such as in structural engineering for calculating dimensions of beams or columns.
- Physics: In physics, √8 is relevant in scenarios where quantities scale with the square root of the eighth power of other physical quantities, such as in wave propagation and energy dissipation calculations.
- Mathematics: √8 is used in mathematical contexts such as geometric constructions involving the diagonal of a square or as a component in trigonometric identities.
- Computer Science: In algorithms and programming, √8 can be utilized in numerical methods and simulations requiring accurate approximations or as a scaling factor in computational geometry.
Comparison with Other Square Roots
| Number | Square Root | Approximate Value | Comparison with √8 |
| 4 | √4 | 2 | √8 is approximately 1.414 times √4 |
| 9 | √9 | 3 | √8 is approximately 0.944 times √9 |
| 16 | √16 | 4 | √8 is approximately 0.707 times √16 |
- √8 falls between the square roots of 4 and 9, being closer in value to √9.
- Compared to √16, √8 is approximately 0.707 times its value.
- The ratio between √8 and √4 is approximately 1.414, indicating that √8 is larger than √4.
Visual Representations
Visual representations of the square root of 8 (√8) often include:
- Number Line: On a number line, √8 is located approximately between 2.8 and 2.9.
- Graphical Plot: Graphically, √8 is represented as a point on a Cartesian plane, typically plotted around (2.828, 0) or (0, 2.828), depending on the orientation.
- Geometric Construction: Geometrically, √8 can be depicted as the length of the diagonal across a square with each side of length 2 units.

FAQs on Square Root of 8
- What is the square root of 8 (√8)?
The square root of 8, denoted as √8, is an irrational number approximately equal to 2.82842712. - Is √8 a rational number?
No, √8 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. - How is √8 calculated?
√8 can be calculated using various methods including the long division method, approximation techniques, or using its prime factorization. - What are the applications of √8?
√8 finds applications in engineering for structural calculations, in physics for wave propagation studies, in mathematics for geometric constructions, and in computer science for algorithms and simulations. - How does √8 compare to other square roots?
√8 is approximately 1.414 times √4, 0.944 times √9, and 0.707 times √16, positioning it between these values on the number line. - Where does √8 appear in real-world problems?
√8 appears in various real-world problems involving scaling factors, dimensions, and calculations where the eighth power of quantities needs to be considered.
Conclusion
In conclusion, exploring the square root of 8 (√8) reveals its significance across various disciplines and applications. From its foundational role in mathematics and geometry to its practical applications in engineering, physics, and computer science, √8 proves to be a versatile value used in calculations ranging from structural dimensions to wave propagation studies. Its comparison with other square roots like √4, √9, and √16 illustrates its unique position on the number line, offering insights into scaling and proportionality in real-world scenarios. Visual representations further enhance our understanding, depicting √8 geometrically and graphically. Frequently asked questions highlight common queries about its nature, calculation methods, and real-world relevance. Overall, √8 stands as a fundamental mathematical concept with broad implications in both theoretical and applied contexts.
Xem video về Gốc bậc hai của 8 để hiểu rõ hơn về chủ đề này và xem liệu nó có phù hợp với bài viết về từ khóa '8 square root' hay không.
Gốc bậc hai của 8 - Tổng quan chi tiết
READ MORE:
Xem video về cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 8 để hiểu cách thức và phương pháp giản đơn nhất, và xem liệu nó có phù hợp với bài viết về từ khóa '8 square root' hay không.
Cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 8: sqrt(8)