Topic what square root equals 8: The square root of 8 is a fascinating topic in mathematics. The value, approximately 2.828, offers insights into numerical properties and calculation methods. Understanding how to derive this root through techniques like the approximation method or the long division method can enhance your math skills. Explore the intriguing world of square roots and their practical applications!
Table of Content
Square Root of 8
The square root of 8 is a number which, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number 8. Since 8 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number.
Exact and Decimal Forms
The square root of 8 can be expressed in several forms:
- Exact form: \( \sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2} \)
- Decimal form: \( \sqrt{8} \approx 2.82842712475 \)
Simplification Process
To simplify the square root of 8, follow these steps:
- Express 8 as a product of its prime factors: \( 8 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \).
- Rewrite the square root of 8: \( \sqrt{8} = \sqrt{4 \times 2} \).
- Simplify using the property of square roots: \( \sqrt{4 \times 2} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{2} = 2\sqrt{2} \).
Calculation Methods
There are different methods to calculate the square root of 8:
- Using a calculator to find \( \sqrt{8} \approx 2.82842712475 \).
- Using the long division method to obtain a more accurate decimal value.
Examples and Applications
Let's consider a practical example:
- Example 1: If the area of a square is 8 square feet, find the length of each side.
- Solution: The side length of the square is the square root of the area. Thus, the side length is \( \sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2} \approx 2.828 \) feet.
Properties
- The square root of 8 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- It lies between the square roots of 4 (which is 2) and 9 (which is 3).
Visual Representation
The square root of 8 can also be visualized on a number line or through geometric representation by considering the side length of a square with an area of 8 square units.
Additional Information
For further reading and detailed calculations, you can explore more on the following websites:
READ MORE:
Introduction
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, providing a foundation for various calculations and problem-solving scenarios. When we talk about the square root of a number, we are referring to a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4 because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
In this article, we will focus on the square root of 8. Understanding the square root of 8 involves exploring its exact value, its properties, and its applications in both theoretical and practical contexts. By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of what the square root of 8 is and how it can be used effectively in various mathematical and real-world scenarios.
Definition of Square Root
A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root is denoted by the radical symbol "√". For a given number \(x\), the square root is expressed as \(\sqrt{x}\).
The mathematical definition can be stated as:
- \(\sqrt{x} = y\) if and only if \(y^2 = x\)
For example, the square root of 16 is 4 because \(4^2 = 16\). Mathematically, this is represented as \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
Square roots can be classified into two categories:
- Perfect Squares: Numbers whose square roots are integers. For instance, \(\sqrt{9} = 3\) and \(\sqrt{25} = 5\).
- Imperfect Squares: Numbers whose square roots are not integers and often result in irrational numbers. For example, \(\sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2} \approx 2.828\).
Additionally, the square root of a positive number has both a positive and a negative value. This is because both \(y\) and \(-y\) satisfy the equation \(y^2 = x\). Thus, \(\sqrt{x}\) can be expressed as \(\pm y\).
For the number 8, the square root is written as:
- \(\sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2} \approx 2.828\)
Here, \(2\sqrt{2}\) is an exact value, while 2.828 is an approximation.
Methods to Calculate Square Root of 8
There are several methods to calculate the square root of 8. Below, we will discuss two common methods: the Long Division Method and the Approximation Method.
Long Division Method
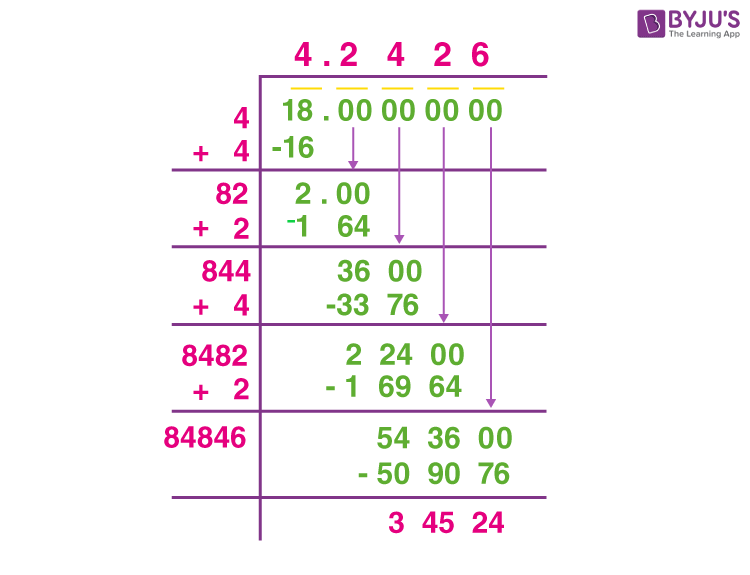
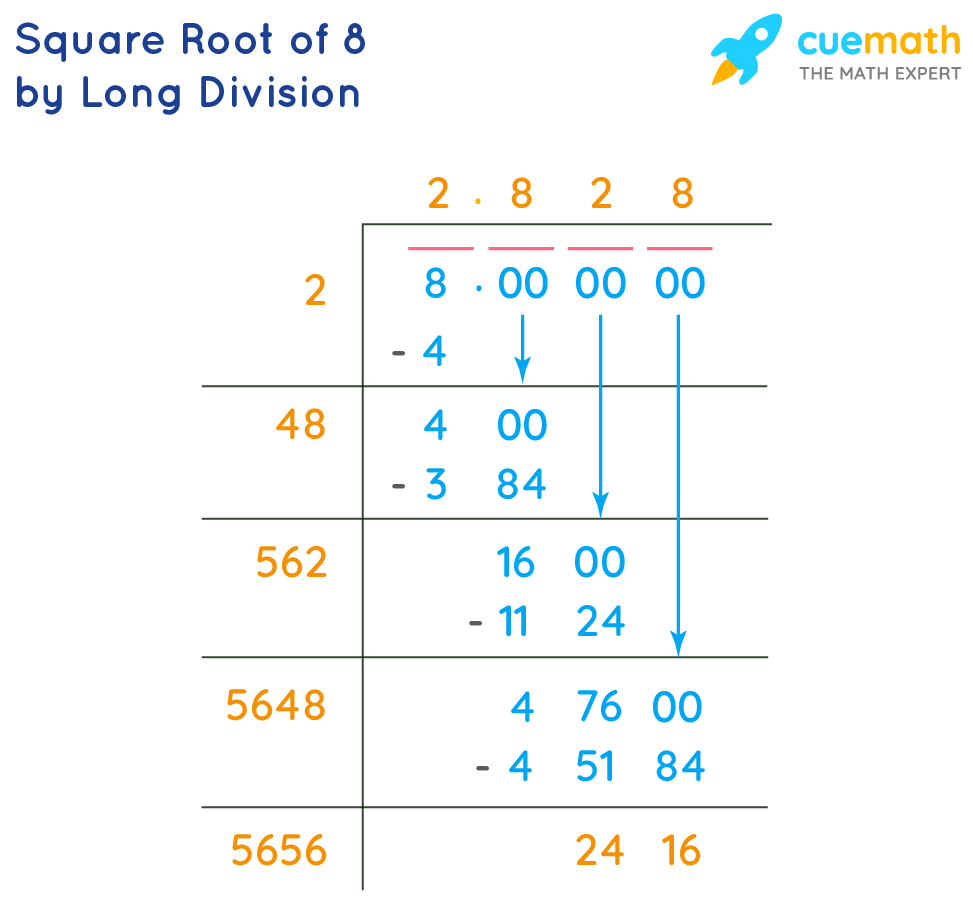
- First, write the number 8 under the division symbol.
- Pair the digits from right to left. Here, 8 has only one digit, so we consider it as one pair.
- Find a number whose square is less than or equal to 8. The closest number is 2, because 22 = 4.
- Use 2 as the quotient and also as the divisor. Divide 8 by 2, giving a quotient of 2 and a remainder of 4.
- Bring down two zeros to the right of the remainder, making it 400.
- Double the quotient (which is 2), giving 4. Use 4 as the new divisor's first digit.
- Find a digit x such that 4x multiplied by x is less than or equal to 400. The closest value is 8 (since 48 × 8 = 384).
- Subtract 384 from 400, giving a remainder of 16. Bring down two more zeros, making it 1600.
- Repeat the process to find more decimal places. The quotient obtained after repeating these steps is approximately 2.828.
Approximation Method
- Select a perfect square number close to 8. The nearest perfect square less than 8 is 4 (since 22 = 4).
- Divide 8 by the square root of 4, which is 2. So, 8 ÷ 2 = 4.
- Take the average of 2 and 4. (2 + 4) / 2 = 3.
- Repeat the steps using the new approximation to get closer to the actual square root. The more iterations you perform, the closer you get to the accurate value of √8 ≈ 2.828.
By using these methods, we can determine that the square root of 8 is approximately 2.828. These methods highlight the principles of precision and approximation in mathematics.
Value of Square Root of 8
The square root of 8 is a value that, when multiplied by itself, equals 8. This value can be represented in both exact and decimal forms.
- Exact Value: The square root of 8 in its simplest radical form is expressed as \( \sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2} \).
- Decimal Value: The approximate decimal value of \( \sqrt{8} \) is 2.828. This can be calculated to more decimal places, but is often rounded to three decimal places for simplicity.
Let's break down these values further:
| Form | Representation | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Exact Value | \( \sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2} \) | The exact value is derived from the factorization of 8, which is \( 8 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \). Simplifying the radical, we get \( \sqrt{8} = \sqrt{4 \times 2} = 2\sqrt{2} \). |
| Decimal Value | 2.828 | Using methods such as long division or a calculator, the square root of 8 is approximately 2.828 up to three decimal places. This provides a practical numerical value for everyday use. |
The square root of 8 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. As an irrational number, \( \sqrt{8} \) plays a significant role in various mathematical and real-world applications, including geometry and engineering.
Properties of Square Root of 8
The square root of 8, denoted as \( \sqrt{8} \) or \( 2\sqrt{2} \), has several notable properties:
- Rational or Irrational: The square root of 8 is an irrational number. This is because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. Specifically, \( \sqrt{8} \approx 2.82842712475 \).
- Perfect Square or Not: The number 8 is not a perfect square. A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer. Since there is no integer that, when squared, equals 8, it is classified as a non-perfect square.
- Expression in Exponential Form: The square root of a number can also be written in exponential form. Therefore, \( \sqrt{8} \) can be expressed as \( 8^{1/2} \) or \( (2^3)^{1/2} = 2^{3/2} \).
- Multiplication Property: The square root of a product is equal to the product of the square roots. For example, \( \sqrt{8} = \sqrt{4 \times 2} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{2} = 2\sqrt{2} \).
- Negative Roots: For any positive number, there are always two square roots: one positive and one negative. Thus, the square roots of 8 are \( \pm 2\sqrt{2} \).
- Even and Odd Properties: The square root of an even number is always even, and the square root of an odd number is always odd. Since 8 is an even number, its square root (in terms of whole number factors) also involves even numbers.
- Real and Complex Numbers: The square root of a positive number is a real number, while the square root of a negative number is a complex number. Therefore, \( \sqrt{8} \) is a real number.
- Addition Property: The sum of the square roots of two numbers is not necessarily equal to the square root of the sum of those numbers. For instance, \( \sqrt{4} + \sqrt{4} \neq \sqrt{8} \). Instead, \( \sqrt{4} + \sqrt{4} = 4 \), while \( \sqrt{8} = 2\sqrt{2} \).
Applications of Square Root of 8
The square root of 8 (\(\sqrt{8}\)) has various applications in both theoretical and practical contexts. Here are some common applications:
- Geometry:
In geometry, the square root of 8 is often used to find the side length of a square when its area is known. For example, if a square garden has an area of 8 square feet, each side would be \(\sqrt{8}\) or \(2\sqrt{2}\) feet long.
- Construction:
In construction, \(\sqrt{8}\) can be used to determine the lengths of diagonal supports or the sides of right triangles. For instance, in a right triangle with one leg measuring 2 feet, the hypotenuse could be calculated using the square root of 8 for certain configurations.
- Physics:
Square roots are used in physics to solve problems involving area, distance, and other measurements. For example, the time it takes for an object to fall from a certain height can be determined using square root calculations.
- Real-World Problems:
Everyday applications include calculating the dimensions of various objects and spaces. For example, the diagonal distance in a square-shaped room with an area of 8 square meters can be found using \(\sqrt{8}\).
- Engineering:
In engineering, square roots are used to compute various parameters, such as stresses and strains in materials. The square root of 8 might be used in formulas to determine tolerances or capacities.
These applications demonstrate the versatility and importance of understanding and utilizing square roots in different fields and real-life situations.
Common Questions
-
What is the Square Root of -8?
The square root of a negative number is not a real number. In mathematics, the square root of -8 is expressed using the imaginary unit \(i\), where \(i\) is defined as \(\sqrt{-1}\). Thus, the square root of -8 can be written as \(\sqrt{-8} = \sqrt{8} \times \sqrt{-1} = 2\sqrt{2}i\).
-
Is 8 a Perfect Square?
No, 8 is not a perfect square. A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the square of an integer. Since there is no integer \(n\) such that \(n^2 = 8\), 8 is not a perfect square. Instead, the square root of 8 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 2.828.
-
Is the Square Root of 8 Rational or Irrational?
The square root of 8 is an irrational number. An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. The decimal representation of \(\sqrt{8}\) is non-terminating and non-repeating, approximately equal to 2.82842712475...
-
What Methods Can Be Used to Calculate the Square Root of 8?
- Long Division Method: This traditional method involves a step-by-step division process to approximate the square root to the desired decimal places.
- Approximation Method: This method uses iterative techniques such as the Newton-Raphson method to find a close approximation of the square root.
READ MORE:
Giúp Toán Học: Cách Giải Phương Trình Căn Bậc Hai