Topic what is the square root of 320: Understanding what the square root of 320 is can be fascinating and useful for various applications. In this article, we will explore the decimal and simplified radical forms of the square root of 320, explain the methods to calculate it, and discuss its practical uses. Dive in to learn all about the square root of 320!
Table of Content
- Square Root of 320
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding the Square Root of 320
- Decimal Form of the Square Root of 320
- Simplified Radical Form of the Square Root of 320
- Prime Factorization Method
- Applications of the Square Root of 320
- Comparing Square Roots of Similar Numbers
- FAQs about the Square Root of 320
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của 320 trong video này. Tìm hiểu các phương pháp đơn giản hóa và ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai của 320.
Square Root of 320
The square root of 320 is a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the product 320. This value can be expressed in both its simplified radical form and its decimal form.
Decimal Form
The square root of 320 in decimal form is approximately:
\(\sqrt{320} \approx 17.88854381999832\)
Simplified Radical Form
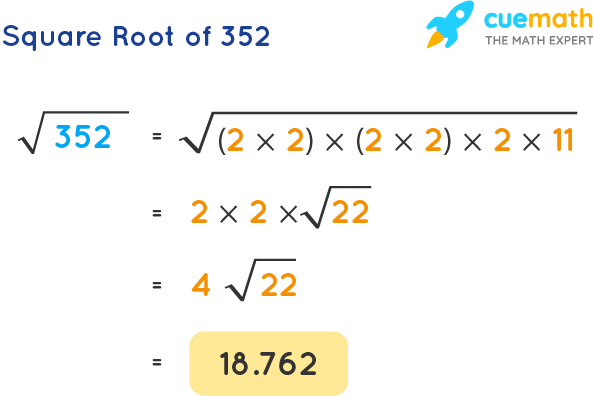
To express the square root of 320 in its simplest radical form, we factorize 320 into its prime factors:
This allows us to simplify the radical:
\(\sqrt{320} = \sqrt{2^6 \times 5} = \sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5} = 2^3 \times \sqrt{5} = 8\sqrt{5}\)
Therefore, the simplified radical form of the square root of 320 is:
Step-by-Step Simplification
- Factorize 320 to find its prime factors: \(320 = 2^6 \times 5\).
- Rewrite the expression under the square root: \(\sqrt{320} = \sqrt{2^6 \times 5}\).
- Simplify the square root by separating perfect squares: \(\sqrt{2^6 \times 5} = \sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5}\).
- Extract the square root of the perfect square: \(\sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5} = 2^3 \times \sqrt{5}\).
- Express the final simplified form: \(\sqrt{320} = 8\sqrt{5}\).
Conclusion
The square root of 320 can be represented both as a decimal, approximately \(17.89\), and in its simplified radical form as \(8\sqrt{5}\). Understanding both forms can be useful depending on the context in which the square root is needed.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. It is a fundamental concept in mathematics and is widely used in various fields such as science, engineering, and finance.
Understanding square roots involves recognizing both their practical applications and theoretical foundations. Here, we will cover the basics of square roots, including their properties and methods for calculating them.
- Definition: If \( x^2 = a \), then \( x \) is the square root of \( a \).
- Notation: The square root of a number \( a \) is denoted as \( \sqrt{a} \).
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots, one positive and one negative, denoted as \( \sqrt{a} \) and \( -\sqrt{a} \) respectively.
For example, the square roots of 16 are 4 and -4, since \( 4^2 = 16 \) and \( (-4)^2 = 16 \).
Square roots can be categorized into two types based on the nature of the number:
- Perfect Squares: These are numbers whose square roots are integers. Examples include 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25.
- Non-Perfect Squares: These are numbers whose square roots are not integers and are often irrational numbers. Examples include 2, 3, 5, and 320.
Calculating square roots can be done using various methods, including:
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down a number into its prime factors to simplify the square root calculation.
- Estimation: Approximating the square root by finding the closest perfect squares.
- Using a Calculator: The most common and straightforward method for finding the square root of any number.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the specific methods for calculating the square root of 320, both in its decimal and simplified radical forms.
Understanding the Square Root of 320
The square root of 320 is a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 320. This can be expressed in both decimal and simplified radical forms. Understanding the square root of 320 involves several steps, including factorization and simplification.
Decimal Form
In its decimal form, the square root of 320 is approximately:
\(\sqrt{320} \approx 17.88854381999832\)
Simplified Radical Form
To express the square root of 320 in its simplest radical form, we need to factorize 320 into its prime factors:
- Step 1: Find the prime factors of 320.
- Step 2: Express 320 as a product of its prime factors.
Prime factorization of 320:
\(320 = 2 \times 160\)
\(320 = 2 \times 2 \times 80\)
\(320 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 40\)
\(320 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 20\)
\(320 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 10\)
\(320 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5\)
\(320 = 2^6 \times 5\)
Using the prime factorization, we can simplify the square root:
\(\sqrt{320} = \sqrt{2^6 \times 5} = \sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5} = 2^3 \times \sqrt{5} = 8\sqrt{5}\)
Step-by-Step Simplification
- Factorize 320 into its prime factors: \(320 = 2^6 \times 5\).
- Rewrite the square root expression: \(\sqrt{320} = \sqrt{2^6 \times 5}\).
- Simplify the square root by separating perfect squares: \(\sqrt{2^6 \times 5} = \sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5}\).
- Extract the square root of the perfect square: \(\sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5} = 2^3 \times \sqrt{5}\).
- Express the final simplified form: \(\sqrt{320} = 8\sqrt{5}\).
Thus, the square root of 320 can be represented in two forms: its decimal form, approximately \(17.88854381999832\), and its simplified radical form, \(8\sqrt{5}\). Both representations are useful depending on the context in which the square root is needed.
Decimal Form of the Square Root of 320
The decimal form of the square root of 320 provides an approximate value that is often easier to use in practical applications. Calculating the square root of 320 in decimal form involves finding the non-repeating, non-terminating decimal that, when squared, equals 320.
Calculation Process
- Estimate the square root: Identify two perfect squares between which 320 falls. For instance, \(16^2 = 256\) and \(18^2 = 324\), so the square root of 320 lies between 16 and 18.
- Refine the estimate: Narrow down the estimate by checking closer values. Since \(17^2 = 289\) and \(18^2 = 324\), the square root of 320 is closer to 18.
- Use a calculator for precision: For a more accurate value, use a calculator to find the decimal approximation of \(\sqrt{320}\).
Using a calculator, we find that:
\(\sqrt{320} \approx 17.88854381999832\)
Applications of Decimal Form
The decimal form of the square root of 320 is useful in various scenarios:
- Engineering: Precise measurements often require the decimal form for accuracy in calculations.
- Science: Scientific experiments and data analysis benefit from using the decimal approximation for precision.
- Everyday Use: In practical applications such as construction or crafts, the decimal form provides a clear and usable value.
Comparison with Other Numbers
Understanding the decimal form also helps in comparing the square root of 320 with other numbers. For instance:
- \(\sqrt{300} \approx 17.320508075688775\)
- \(\sqrt{350} \approx 18.708286933869708\)
Such comparisons can be crucial in contexts where relative magnitudes matter.
Conclusion
The decimal form of the square root of 320 is approximately 17.88854381999832. This precise value is essential in many fields where accuracy is paramount. Understanding how to calculate and use this decimal form enhances both practical applications and theoretical knowledge.
Simplified Radical Form of the Square Root of 320
The simplified radical form of the square root of 320 provides an exact representation using prime factors. This form is often preferred in algebraic manipulations and theoretical work because it maintains the precise value without decimal approximations.
Prime Factorization Method
To simplify the square root of 320, we start by finding its prime factors:
- Begin with the number 320 and divide by the smallest prime number, 2:
- \(320 \div 2 = 160\)
- \(160 \div 2 = 80\)
- \(80 \div 2 = 40\)
- \(40 \div 2 = 20\)
- \(20 \div 2 = 10\)
- \(10 \div 2 = 5\)
- So, the prime factorization of 320 is:
\(320 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 = 2^6 \times 5\)
Simplifying the Square Root
Next, we simplify the square root using the prime factorization:
\(\sqrt{320} = \sqrt{2^6 \times 5}\)
We can separate the perfect square factor from the non-perfect square factor:
\(\sqrt{320} = \sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5} = 2^3 \times \sqrt{5} = 8\sqrt{5}\)
Step-by-Step Simplification
- Factorize 320 into its prime factors: \(320 = 2^6 \times 5\).
- Rewrite the square root expression: \(\sqrt{320} = \sqrt{2^6 \times 5}\).
- Separate the perfect square factor: \(\sqrt{2^6 \times 5} = \sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5}\).
- Simplify the square root of the perfect square: \(\sqrt{(2^3)^2} = 2^3\).
- Combine the simplified terms: \(2^3 \times \sqrt{5} = 8\sqrt{5}\).
Conclusion
Thus, the simplified radical form of the square root of 320 is:
\(\sqrt{320} = 8\sqrt{5}\)
This exact form is useful for algebraic operations, ensuring precision without relying on decimal approximations. Understanding both the simplified radical form and the decimal form of square roots enhances your mathematical flexibility and accuracy.

Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a systematic approach to simplifying the square root of a number by breaking it down into its prime factors. This method ensures an exact representation and helps in understanding the structure of the number. Here’s how to use the prime factorization method to find the square root of 320:
Step-by-Step Process
- Identify the smallest prime number: Start with the smallest prime number, which is 2.
- Divide the number: Divide 320 by 2 repeatedly until it is no longer divisible by 2.
- \(320 \div 2 = 160\)
- \(160 \div 2 = 80\)
- \(80 \div 2 = 40\)
- \(40 \div 2 = 20\)
- \(20 \div 2 = 10\)
- \(10 \div 2 = 5\)
- Prime factorization result: Once 320 is fully divided by 2, the remaining number is 5, which is also a prime number. Thus, the prime factorization of 320 is:
\(320 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 5 = 2^6 \times 5\)
Simplifying the Square Root
Using the prime factorization, we can simplify the square root of 320:
\(\sqrt{320} = \sqrt{2^6 \times 5}\)
We can rewrite the expression by separating the perfect square from the non-perfect square:
\(\sqrt{2^6 \times 5} = \sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5} = 2^3 \times \sqrt{5} = 8\sqrt{5}\)
Conclusion
The prime factorization method provides a clear and systematic way to simplify the square root of 320. By breaking down 320 into its prime factors, we find that:
\(\sqrt{320} = 8\sqrt{5}\)
This method ensures an exact and simplified radical form, useful in various mathematical contexts and applications.
Applications of the Square Root of 320
The square root of 320, which is approximately 17.888, finds its applications in various fields. Here are some practical uses:
- Geometry and Area Calculation: The square root is crucial in geometry, especially when dealing with areas and side lengths. For instance, if a square has an area of 320 square units, each side length can be found by calculating the square root of 320, which gives approximately 17.888 units. This is essential for architectural designs and land measurements.
- Physics and Engineering: In physics, the square root is used to calculate different parameters, such as in the equations involving gravity and acceleration. For example, if an object falls from a height where the distance is represented as a function involving 320, the square root helps determine the time it takes to hit the ground.
- Statistics: In statistical analysis, square roots are used in standard deviation calculations, which measure the dispersion or variation in a set of values. If a dataset involves a sum of squares equal to 320, the square root helps in computing the standard deviation.
- Computer Science: Algorithms in computer graphics often require square root calculations for rendering images and simulations. Calculating distances between points in a space or normalizing vectors often involves taking square roots, including numbers like 320.
- Economics and Finance: In financial mathematics, square roots are used in various formulas, including those for calculating volatility and risk assessment. For example, if a financial model involves a variance of 320, the standard deviation, which is the square root of variance, becomes approximately 17.888, helping in risk management.
Comparing Square Roots of Similar Numbers
When comparing square roots of similar numbers, it's important to understand their relative sizes. Here, we compare the square root of 320 with the square roots of nearby numbers.
Consider the following numbers: 300, 310, 320, 330, and 340. Their square roots can be approximated as follows:
- \(\sqrt{300} \approx 17.32\)
- \(\sqrt{310} \approx 17.61\)
- \(\sqrt{320} \approx 17.89\)
- \(\sqrt{330} \approx 18.17\)
- \(\sqrt{340} \approx 18.44\)
From these approximations, we can see how the square roots increase with the numbers:
- \(\sqrt{300} < \sqrt{310}\)
- \(\sqrt{310} < \sqrt{320}\)
- \(\sqrt{320} < \sqrt{330}\)
- \(\sqrt{330} < \sqrt{340}\)
To make comparisons more visually clear, consider the following number line representation:
| \(\sqrt{300}\) | \(\sqrt{310}\) | \(\sqrt{320}\) | \(\sqrt{330}\) | \(\sqrt{340}\) |
| 17.32 | 17.61 | 17.89 | 18.17 | 18.44 |
It's evident from the table that as the numbers increase, their square roots increase in a non-linear fashion. The differences between consecutive square roots become smaller as the numbers increase, reflecting the properties of the square root function.
Using this knowledge, you can compare any two square roots by either approximating their values or using a number line for a more visual comparison.
FAQs about the Square Root of 320
- What is the square root of 320?
The square root of 320 is approximately \( \sqrt{320} \approx 17.888 \). It can also be expressed in simplified radical form as \( 8\sqrt{5} \).
- Is 320 a perfect square?
No, 320 is not a perfect square. A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer, but there is no integer that, when squared, equals 320.
- What is the decimal value of the square root of 320?
The decimal value of the square root of 320 is approximately 17.88854382.
- Is the square root of 320 a rational number?
No, the square root of 320 is not a rational number. Rational numbers are numbers that can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, but the square root of 320 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
- Can we find the square root of 320 by the repeated subtraction method?
No, the repeated subtraction method can only be used to find the square root of perfect squares, and since 320 is not a perfect square, this method does not apply.
- How do you simplify the square root of 320?
To simplify the square root of 320, we can use its prime factorization. The prime factors of 320 are \(2^6 \times 5\). This can be written as:
\[
\sqrt{320} = \sqrt{2^6 \times 5} = \sqrt{(2^3)^2 \times 5} = 2^3 \times \sqrt{5} = 8\sqrt{5}
\]Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 320 is \( 8\sqrt{5} \).

Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của 320 trong video này. Tìm hiểu các phương pháp đơn giản hóa và ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai của 320.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 320
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của 320 trong video này. Tìm hiểu các phương pháp đơn giản hóa và ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai của 320 để nâng cao kiến thức toán học của bạn.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 320