Topic square root of 266: Discover the fascinating world of the square root of 266. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore its mathematical properties, calculation methods, and practical applications. Whether you're a student, educator, or math enthusiast, learn how this intriguing number plays a crucial role in various fields. Dive in to expand your mathematical knowledge!
Table of Content
- Square Root of 266
- Introduction to the Square Root of 266
- Mathematical Definition
- Approximate Value of the Square Root of 266
- Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 266
- Rational and Irrational Numbers
- Historical Context and Interesting Facts
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá căn bậc hai của 266 với hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Tìm hiểu các ứng dụng và tính chất của căn bậc hai này.
Square Root of 266
The square root of 266 is represented as \( \sqrt{266} \).
Approximate Value
The approximate value of the square root of 266 is:
\[
\sqrt{266} \approx 16.308
\]
Steps to Calculate the Square Root of 266
-
Initial Guess: Start with an initial guess close to the actual value. For example, let's start with 16.
\[
16^2 = 256
\] -
Divide and Average: Divide 266 by your initial guess and average the result with the initial guess.
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{16 + \frac{266}{16}}{2} \approx 16.3125
\] -
Refine the Guess: Repeat the divide and average steps with the new guess.
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{16.3125 + \frac{266}{16.3125}}{2} \approx 16.308
\]
Properties of the Square Root of 266
- The square root of 266 is an irrational number.
- It cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- Its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating.
Alternative Method: Using a Calculator
For a quick and precise result, use a scientific calculator:
\[
\sqrt{266} \approx 16.308
\]
Applications of the Square Root of 266
- Used in various mathematical computations and geometric calculations.
- Common in engineering and physics problems involving quadratic equations.
The square root of 266, approximately 16.308, is an important irrational number with various practical applications.

READ MORE:
Introduction to the Square Root of 266
The square root of 266 is a mathematical value that, when multiplied by itself, equals 266. It is represented as \( \sqrt{266} \) and is an important concept in various fields, including algebra, geometry, and engineering. Understanding the square root of 266 involves exploring its properties, calculation methods, and practical applications.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Approximate Value: The square root of 266 is approximately 16.308.
- Mathematical Properties: It is an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
Let's delve deeper into the steps to calculate the square root of 266 and its significance:
- Initial Guess: Start with a reasonable initial guess close to the expected value. For instance, a good starting point could be 16.
- Refinement: Use the divide-and-average method to refine the guess. This involves dividing 266 by the initial guess and averaging the result with the initial guess.
- Iteration: Repeat the refinement process until the desired level of accuracy is achieved.
Mathematically, the refinement process can be expressed as:
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{\text{Initial guess} + \frac{266}{\text{Initial guess}}}{2}
\]
This iterative method helps in achieving a more accurate approximation of the square root.
In summary, the square root of 266 is a fundamental mathematical concept with diverse applications. By understanding its properties and calculation methods, one can appreciate its role in various mathematical and practical contexts.
Mathematical Definition
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. For the number 266, the square root is denoted as \( \sqrt{266} \).
Mathematically, the definition can be expressed as:
\[
\sqrt{266} \times \sqrt{266} = 266
\]
Key points to understand the square root of 266 include:
- Radical Form: The expression \( \sqrt{266} \) is in its radical form.
- Approximate Value: The approximate decimal value of \( \sqrt{266} \) is 16.308.
- Irrational Number: Since 266 is not a perfect square, \( \sqrt{266} \) is an irrational number. This means its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
To further understand the mathematical properties of \( \sqrt{266} \), consider the following steps for approximation:
- Initial Guess: Begin with an initial guess close to the square root, such as 16.
- Refinement Process: Use the iterative method known as the "Babylonian method" or "Heron's method" to refine the guess. This method is calculated as follows:
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{\text{Initial guess} + \frac{266}{\text{Initial guess}}}{2}
\] - Repeat: Repeat the refinement process until the guess converges to a stable value. For instance, starting with an initial guess of 16:
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{16 + \frac{266}{16}}{2} \approx 16.3125
\]
By continuing this iterative process, you can achieve a more accurate approximation of \( \sqrt{266} \).
Understanding the mathematical definition of the square root of 266 provides a foundation for further exploration into its properties and applications in various fields of mathematics and science.
Approximate Value of the Square Root of 266
The square root of 266, denoted as \( \sqrt{266} \), is an irrational number. This means that its exact value cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. However, we can find an approximate value to a desired level of accuracy.
The approximate value of \( \sqrt{266} \) is:
\[
\sqrt{266} \approx 16.308
\]
To understand how this approximation is derived, let's look at the steps involved in calculating the square root using the iterative method known as the "Babylonian method" or "Heron's method":
- Initial Guess: Start with an initial guess close to the expected value. A reasonable initial guess might be 16.
- First Iteration: Use the formula to refine the guess:
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{16 + \frac{266}{16}}{2} \approx 16.3125
\] - Second Iteration: Repeat the refinement process:
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{16.3125 + \frac{266}{16.3125}}{2} \approx 16.308
\] - Convergence: Continue the iteration until the value converges to a stable number. For practical purposes, we can stop at a few decimal places of precision.
Using a scientific calculator or a computer, we can find that:
\[
\sqrt{266} \approx 16.308
\]
Here are some properties of the approximate value:
- Non-Terminating Decimal: The decimal representation goes on infinitely without repeating.
- Irrational Number: Since it cannot be expressed as a fraction, \( \sqrt{266} \) is classified as an irrational number.
Understanding the approximate value of \( \sqrt{266} \) is crucial for practical applications in fields such as engineering, physics, and various branches of mathematics where precise calculations are necessary.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 266
Calculating the square root of 266 can be approached through various methods, each with its own level of complexity and precision. Here, we'll explore some common techniques, including the Babylonian method, long division method, and using a calculator.
Babylonian Method (Heron's Method)
The Babylonian method, also known as Heron's method, is an iterative technique that starts with an initial guess and refines it to get closer to the actual square root. Here's how it works:
- Initial Guess: Choose an initial guess close to the square root. For example, 16.
- Iterate: Apply the formula:
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{\text{Old guess} + \frac{266}{\text{Old guess}}}{2}
\]For the initial guess of 16:
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{16 + \frac{266}{16}}{2} \approx 16.3125
\] - Repeat: Continue the process with the new guess:
\[
\text{New guess} = \frac{16.3125 + \frac{266}{16.3125}}{2} \approx 16.308
\] - Convergence: Repeat until the value stabilizes. The value converges to approximately 16.308.
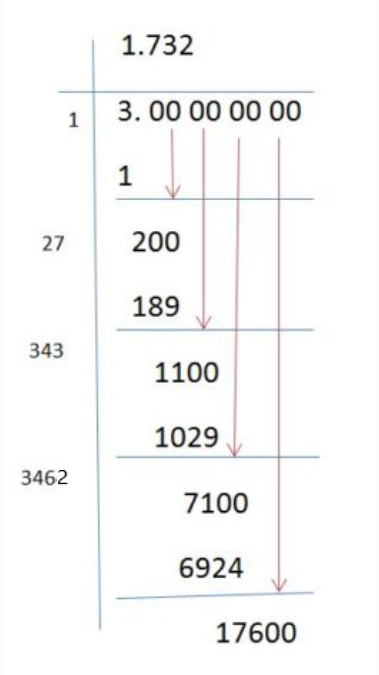
Long Division Method
The long division method is a manual technique that provides a step-by-step process to find the square root. Here’s a simplified overview:
- Pair Digits: Start from the decimal point and pair the digits of the number. For 266, consider it as 2|66.
- Initial Divisor: Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair (2). The largest number is 1 (since \(1^2 = 1\)).
- Subtract and Bring Down: Subtract 1 from 2 and bring down the next pair (66), making it 166.
- Double and Estimate: Double the divisor (1 becomes 2) and find a digit that, when added to 20 and multiplied by the same digit, gives a product less than or equal to 166. The digit is 6, since \(26 \times 6 = 156\).
- Repeat: Continue the process to achieve the desired precision.
Using a Calculator
For a quick and precise result, a scientific calculator can be used:
- Step 1: Enter 266.
- Step 2: Press the square root (√) button.
- Result: The calculator will display \( \sqrt{266} \approx 16.308 \).
Each method offers a different balance of simplicity, effort, and precision. The Babylonian method is effective for manual calculations with a high degree of accuracy, while the long division method provides a systematic approach for precise manual calculations. Using a calculator is the quickest and most straightforward method for obtaining an accurate result.

Rational and Irrational Numbers
Understanding the concepts of rational and irrational numbers is essential for grasping the nature of the square root of 266 and its mathematical significance.
Rational Numbers
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, where the numerator is an integer, and the denominator is a non-zero integer. In other words, a rational number can be written in the form:
\[
\frac{a}{b}
\]
where \( a \) and \( b \) are integers and \( b \neq 0 \).
- Examples of Rational Numbers:
- \( \frac{1}{2} \) (0.5)
- \( \frac{3}{4} \) (0.75)
- \( 5 \) (which can be written as \( \frac{5}{1} \))
- \( -\frac{2}{3} \) (-0.666...)
- Properties:
- Rational numbers can be either positive, negative, or zero.
- The decimal expansion of a rational number either terminates or repeats periodically.
Irrational Numbers
An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction of two integers. The decimal representation of an irrational number is non-terminating and non-repeating. These numbers cannot be written in the form:
\[
\frac{a}{b}
\]
where \( a \) and \( b \) are integers and \( b \neq 0 \).
- Examples of Irrational Numbers:
- \( \pi \) (Pi, approximately 3.14159...)
- \( e \) (Euler's number, approximately 2.71828...)
- \( \sqrt{2} \) (approximately 1.414...)
- \( \sqrt{3} \) (approximately 1.732...)
- Properties:
- Irrational numbers cannot be precisely represented as a fraction of two integers.
- The decimal expansion of an irrational number goes on forever without repeating.
Square Root of 266: An Irrational Number
The square root of 266, \( \sqrt{266} \), is an irrational number. This is because 266 is not a perfect square, meaning there are no two identical rational numbers that multiply to give 266. The decimal expansion of \( \sqrt{266} \) is non-terminating and non-repeating, approximately equal to 16.308.
Understanding the distinction between rational and irrational numbers helps in recognizing the unique characteristics and behaviors of numbers like \( \sqrt{266} \). This knowledge is crucial in various fields of mathematics, science, and engineering.
Historical Context and Interesting Facts
The concept of square roots has a long and fascinating history that spans several ancient civilizations. The square root of 266, while not as prominently discussed as the square roots of perfect squares, still plays a role in the broader history of mathematics.
Square roots were understood and utilized by ancient Babylonians, who created clay tablets like the Yale Babylonian Collection tablet YBC 7289 around 1800-1600 BC. This tablet shows an accurate calculation of the square root of 2, highlighting the advanced mathematical knowledge of that era.
In ancient Egypt, the Rhind Mathematical Papyrus, dated around 1650 BC, demonstrates methods for extracting square roots using inverse proportion techniques. This indicates a practical approach to mathematics that was essential for architectural and engineering purposes.
The ancient Indians also made significant contributions to the understanding of square roots. The Sulba Sutras, dating back to 800-500 BC, provide detailed methods for calculating square roots. These texts include remarkably accurate approximations for the square roots of numbers like 2 and 3, showcasing the precision of early Indian mathematicians.
In Greece, the mathematician Euclid proved that the square roots of non-perfect squares are irrational numbers, a concept that dates back to around 300 BC. This foundational work laid the groundwork for future explorations in number theory.
While the specific calculation of the square root of 266 might not have been a focal point in historical texts, the principles and methods developed by these ancient mathematicians apply universally. The square root of 266, approximately 16.3095064303, exemplifies the intricate relationship between numbers and their roots that has been explored for millennia.
In modern times, the calculation of square roots, including that of 266, is fundamental in various scientific fields, engineering, and computer science. Understanding these roots allows for solving quadratic equations, optimizing systems, and performing statistical analyses.
The journey of square roots from ancient clay tablets to contemporary algorithms illustrates the timeless nature of mathematical inquiry and its ongoing importance in advancing human knowledge and technology.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- What is the square root of 266?
The square root of 266 is approximately 16.3095. In mathematical notation, it is represented as \( \sqrt{266} \approx 16.3095 \).
- Is 266 a perfect square?
No, 266 is not a perfect square. A perfect square is an integer that is the square of another integer. Since the square root of 266 is not an integer, 266 is not a perfect square.
- Is the square root of 266 rational or irrational?
The square root of 266 is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction, and its decimal form is non-repeating and non-terminating.
- How can the square root of 266 be calculated manually?
The square root of 266 can be calculated manually using methods such as the long division method or the Babylonian method (also known as Hero's method). These methods involve iterative steps to approximate the value.
- Can the square root of 266 be simplified?
No, the square root of 266 cannot be simplified further. It is already in its simplest radical form, \( \sqrt{266} \).
- How can the square root of 266 be calculated using a calculator?
To calculate the square root of 266 using a calculator, enter 266 and then press the square root (√) button. The result should be approximately 16.3095.
- How is the square root of 266 represented with an exponent?
The square root of 266 can be expressed using an exponent as \( 266^{1/2} \).
- Can the square root of 266 be expressed as a fraction?
Since the square root of 266 is an irrational number, it cannot be expressed exactly as a fraction. However, it can be approximated as a fraction, such as \( \frac{1631}{100} \).
Conclusion
The square root of 266, approximately 16.30951, is a fascinating number with various properties and applications. As an irrational number, it cannot be precisely expressed as a simple fraction, and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. This characteristic makes it an interesting subject in mathematical studies and real-world applications.
Understanding the square root of 266 can enhance comprehension of various mathematical concepts such as irrational numbers, prime factorization, and the methods of computing square roots. It also finds relevance in geometry, physics, and engineering, where precise calculations are crucial.
In summary, the exploration of the square root of 266 not only enriches our mathematical knowledge but also demonstrates the beauty and complexity of numbers. It serves as a reminder of the intricate patterns and structures that underpin the world of mathematics.

Khám phá căn bậc hai của 266 với hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Tìm hiểu các ứng dụng và tính chất của căn bậc hai này.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 266 - Hướng Dẫn Toàn Diện
READ MORE:
Khám phá căn bậc hai của 266 với hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Tìm hiểu các ứng dụng và tính chất của căn bậc hai này.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 266 - Hướng Dẫn Chi Tiết