Topic kite perimeter calculator: Discover how to use the kite perimeter calculator to effortlessly determine the perimeter of a kite. This tool simplifies complex geometric calculations, making it ideal for students, educators, and enthusiasts. Learn the formulas, steps, and practical applications of kite perimeter calculations to enhance your mathematical skills and understanding.
Table of Content
- Kite Perimeter Calculator
- Introduction
- Definition of a Kite
- Basic Properties of a Kite
- Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
- Formulas for Calculating Area
- Step-by-Step Calculation Example
- Online Kite Perimeter Calculators
- Applications in Geometry
- Measurement Units and Conversion
- YOUTUBE: Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của một cánh diều bằng cách sử dụng định lý Pythagoras. Học cách tính chu vi một cách dễ dàng và chính xác.
Kite Perimeter Calculator
Use the formulas and examples provided below to calculate the perimeter of a kite.
Formulas for Kite Perimeter
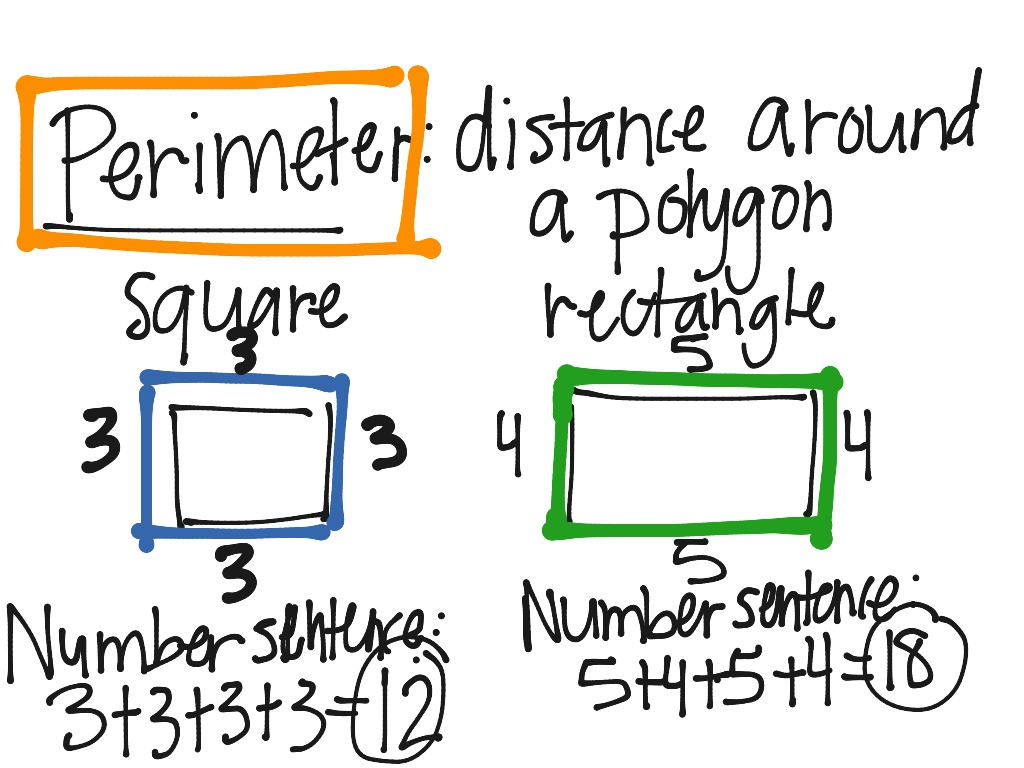
The perimeter \(P\) of a kite can be calculated using the following formula:
\[
P = 2 \times (a + b)
\]
where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the two distinct pairs of adjacent sides of the kite.
Example Calculation
Let's consider an example where the lengths of the sides are given:
- Side \(a\) = 8 units
- Side \(b\) = 6 units
Using the formula:
\[
P = 2 \times (a + b) = 2 \times (8 + 6) = 2 \times 14 = 28 \text{ units}
\]
Alternative Calculation Using Diagonals
If the diagonals of the kite are known, the side lengths can be calculated using the following steps:
- Let the lengths of the diagonals be \(d_1\) and \(d_2\).
- Calculate half-lengths: \(d_1/2\) and \(d_2/2\).
- Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the side lengths: \[ a = \sqrt{\left(\frac{d_1}{2}\right)^2 + \left(\frac{d_2}{2}\right)^2} \] \li>Sum the lengths of all sides to find the perimeter.
Example with Diagonals
Consider a kite with diagonals of 10 units and 8 units:
- Half-length of first diagonal \(d_1/2 = 5\) units
- Half-length of second diagonal \(d_2/2 = 4\) units
Calculate the side lengths:
\[
a = \sqrt{(5)^2 + (4)^2} = \sqrt{25 + 16} = \sqrt{41} \approx 6.4 \text{ units}
\]
The perimeter is:
\[
P = 2 \times (a + b) = 2 \times (6.4 + 6.4) = 2 \times 12.8 = 25.6 \text{ units}
\]
Useful Tools
- Online calculators for kite perimeter and area.
- Geometric formulas and their applications.
Conclusion
By using the formulas and methods described, you can easily calculate the perimeter of a kite whether you know the side lengths or the diagonals.

READ MORE:
Introduction
A kite is a unique quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of adjacent sides that are equal in length. The kite perimeter calculator is a handy tool for determining the perimeter of this shape, essential for various mathematical and practical applications. Using the kite perimeter calculator, you can quickly and accurately find the perimeter by inputting the lengths of the kite's sides or its diagonals. This tool simplifies complex calculations, making it accessible for students, teachers, and professionals in fields like engineering and design.
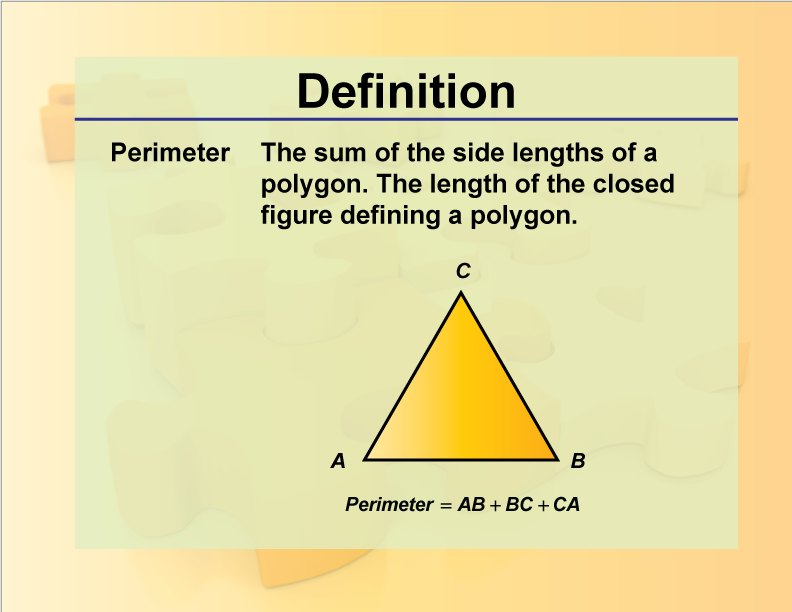
Definition of a Kite
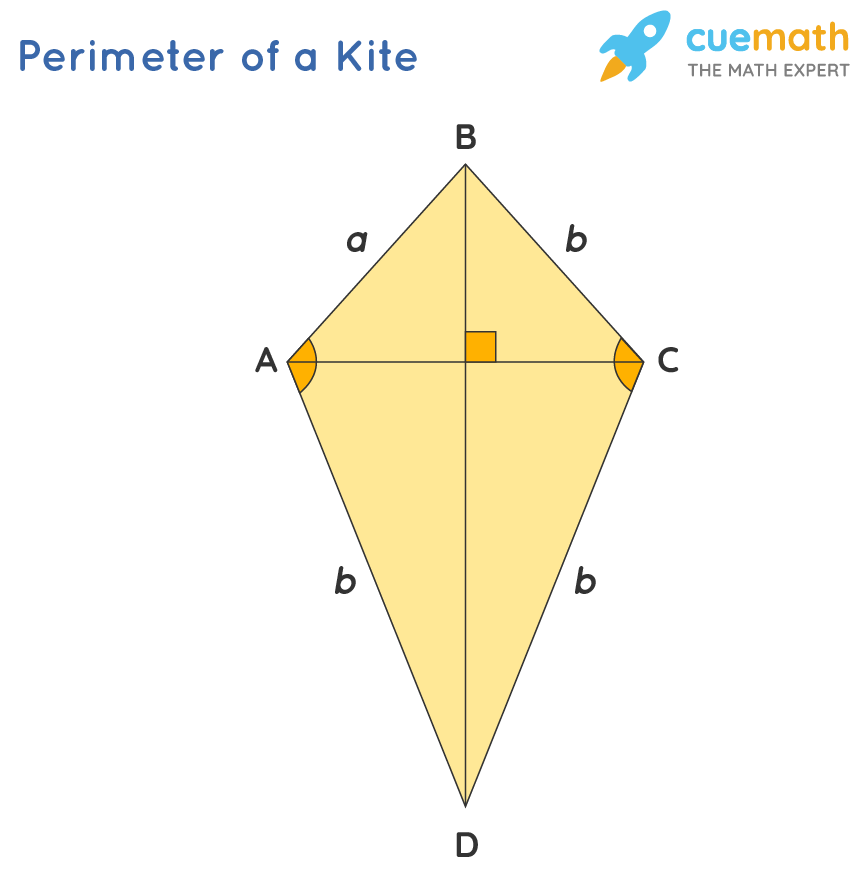
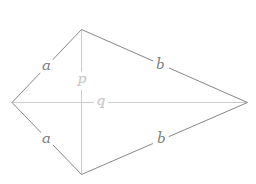
A kite in geometry is a special type of quadrilateral with two distinct pairs of adjacent sides that are equal in length. The main characteristics of a kite are:
- Pairs of Equal Sides: Two pairs of adjacent sides (neighboring sides) are of equal length. This means that one pair of shorter sides is equal, and one pair of longer sides is equal.
- Diagonals: A kite has two diagonals that intersect at a right angle. The longer diagonal bisects the shorter one.
- Angles: The angles between unequal sides are equal. The angles where the two pairs of equal sides meet are called vertex angles, and these are generally different from the other two angles, known as non-vertex angles.
The perimeter of a kite is calculated by summing up the lengths of all its sides. If the lengths of the pairs of equal sides are denoted as \(a\) and \(b\), the perimeter \(P\) is given by:
\[
P = 2(a + b)
\]
Understanding these properties helps in calculating various parameters of a kite, such as its perimeter and area, and is essential in solving related geometric problems.
Basic Properties of a Kite
A kite is a unique type of quadrilateral that has several distinct properties. Understanding these properties is essential for calculations related to its perimeter and area. Here are the basic properties of a kite:
- Two Pairs of Adjacent Sides: A kite has two pairs of sides. Each pair consists of adjacent sides that are equal in length.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a kite intersect at right angles (90 degrees). One diagonal bisects the other, dividing the kite into two congruent triangles.
- Angles: The angles where the two pairs of equal-length sides meet are equal. The other pair of opposite angles are also equal.
- Symmetry: A kite has an axis of symmetry along the longer diagonal. This axis divides the kite into two mirror-image halves.
- Area: The area of a kite can be calculated using the formula: \[ A = \frac{d_1 \cdot d_2}{2} \] where \(d_1\) and \(d_2\) are the lengths of the diagonals.
- Perimeter: The perimeter of a kite is given by the sum of all its sides, which can be expressed as: \[ P = 2(a + b) \] where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the two pairs of equal-length sides.
These properties make the kite a versatile and interesting shape in geometry, useful in various mathematical calculations and real-world applications.
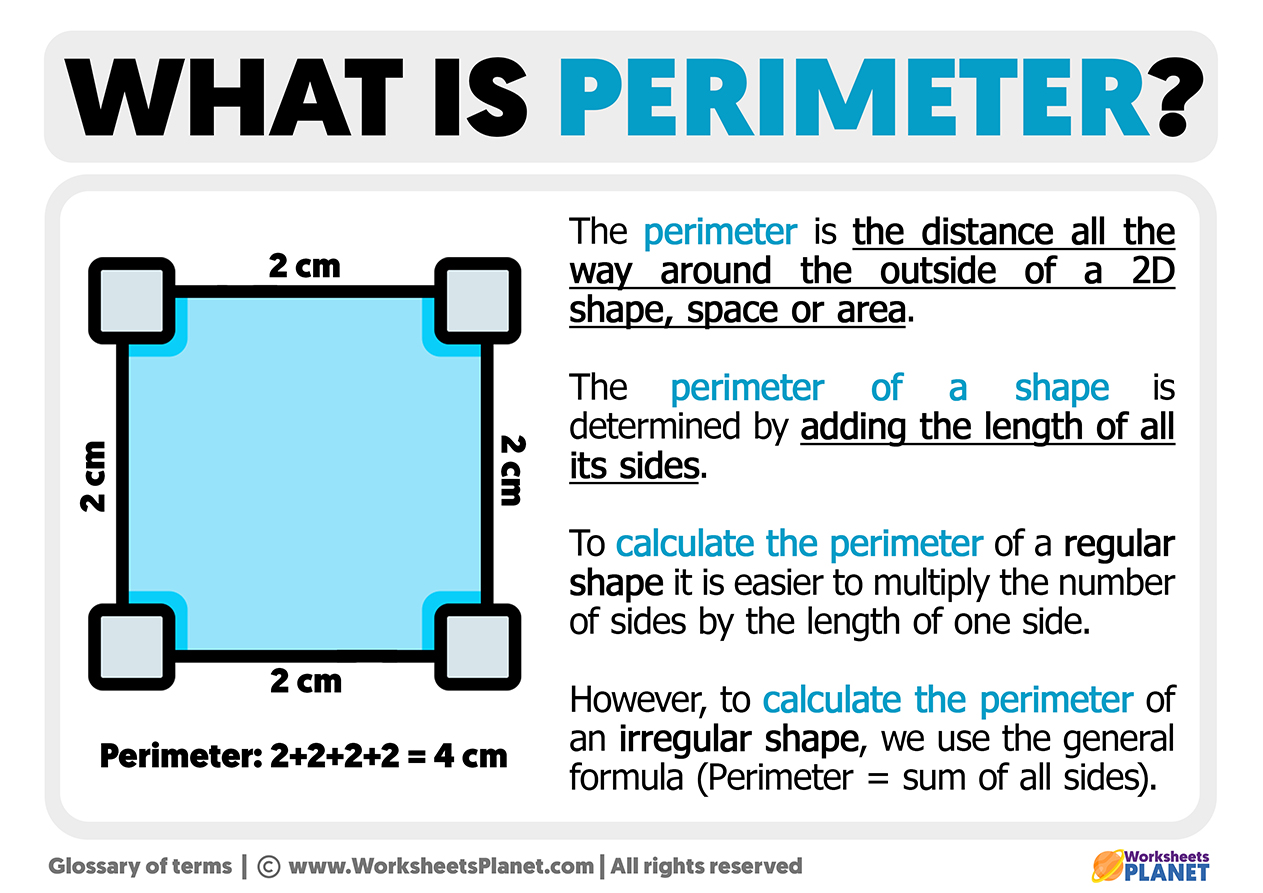
Formulas for Calculating Perimeter
The perimeter of a kite is calculated by adding the lengths of all its sides. A kite has two pairs of adjacent sides that are equal in length. The formula for the perimeter \( P \) of a kite can be expressed as:
- \( P = 2 \times (a + b) \)
Where:
- \( a \) is the length of one pair of adjacent sides.
- \( b \) is the length of the other pair of adjacent sides.
Let's consider an example where the lengths of the sides are given as follows:
- \( a = 5 \, \text{units} \)
- \( b = 7 \, \text{units} \)
Using the formula:
\( P = 2 \times (5 + 7) \)
\( P = 2 \times 12 \)
\( P = 24 \, \text{units} \)
Therefore, the perimeter of the kite is 24 units.
Formulas for Calculating Area
Calculating the area of a kite can be done using different formulas based on the known measurements. The area can be derived using the lengths of the diagonals or using trigonometric principles if the side lengths and the angle between them are known. Here are the detailed formulas:
-
Using Diagonals:
If the lengths of the diagonals are known, the area of the kite can be calculated using the formula:
\[
\text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times d_1 \times d_2
\]Where \(d_1\) and \(d_2\) are the lengths of the diagonals.
-
Using Trigonometry:
If the lengths of two adjacent sides \(a\) and \(b\), and the angle \(\theta\) between them are known, the area can be calculated using trigonometric functions:
\[
\text{Area} = a \times b \times \sin(\theta)
\]Where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the adjacent sides, and \(\theta\) is the angle between them.
These formulas provide flexible methods to find the area of a kite based on available measurements. Whether using the lengths of the diagonals or applying trigonometric principles, each method ensures accurate calculation of the kite's area.
Step-by-Step Calculation Example
To understand how to calculate the perimeter and area of a kite, let's go through a detailed example step by step.
-
Step 1: Identify the given dimensions
Suppose we have a kite with the following diagonal lengths:
- Diagonal 1 (\(d_1\)) = 8 cm
- Diagonal 2 (\(d_2\)) = 6 cm
-
Step 2: Calculate the area
The formula to calculate the area of a kite is:
\[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times d_1 \times d_2 \]
Substitute the given values into the formula:
\[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times 8 \, \text{cm} \times 6 \, \text{cm} = 24 \, \text{cm}^2 \]
-
Step 3: Calculate the perimeter
If we know the lengths of the sides, we can calculate the perimeter. For instance, if the kite's two pairs of adjacent sides are 5 cm and 7 cm, the perimeter is:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2(a + b) \]
Where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the adjacent sides:
\[ \text{Perimeter} = 2(5 \, \text{cm} + 7 \, \text{cm}) = 2 \times 12 \, \text{cm} = 24 \, \text{cm} \]
Online Kite Perimeter Calculators
Online kite perimeter calculators are a convenient tool for quickly finding the perimeter of a kite by simply inputting the lengths of the sides. These calculators are designed to save time and reduce errors in manual calculations. Below, we outline some of the popular online kite perimeter calculators and their features.
-
Kite Perimeter Calculator by Calculator.net
This calculator allows users to input the lengths of the two pairs of adjacent sides of the kite. It then automatically calculates the perimeter using the formula:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2(a + b)
\]
where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the two pairs of adjacent sides. -
Kite Perimeter Calculator by Omni Calculator
Omni Calculator offers a user-friendly interface where you can input the side lengths. It also provides a detailed explanation of the steps involved in the calculation, which enhances understanding. The formula used is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2(a + b)
\] -
Kite Perimeter Calculator by Math Warehouse
Math Warehouse provides a simple yet effective kite perimeter calculator. Users need to enter the lengths of the sides, and the tool will calculate the perimeter. Additionally, it offers visual aids to help users better understand the shape and properties of the kite.
-
Kite Perimeter Calculator by Geometry Calculator
This calculator is designed specifically for geometric shapes, including kites. Users input the side lengths, and the calculator provides the perimeter along with a brief explanation of the calculation process. The formula used is:
\[
\text{Perimeter} = 2(a + b)
\]
These online calculators are highly useful for students, teachers, and anyone needing to perform quick geometric calculations. They simplify the process and provide accurate results, making them an essential tool in geometry.
Applications in Geometry
The kite shape has several interesting applications in the field of geometry, both in theoretical concepts and practical problems. Understanding the properties and calculations related to kites can enhance one's comprehension of geometric principles and improve problem-solving skills. Here are some detailed applications of kites in geometry:
-
Geometric Proofs
Kites are often used in geometric proofs to demonstrate properties of quadrilaterals. For example, the diagonals of a kite are perpendicular to each other, which can be used to prove the Pythagorean theorem in certain contexts.
The properties of a kite, such as congruent adjacent sides and symmetry, are frequently leveraged to solve complex geometric problems and construct rigorous proofs.
-
Symmetry and Transformations
Kites exhibit line symmetry, meaning they can be divided into two congruent halves by a line through their diagonals. This property is useful in studying symmetry and transformations in geometry.
Students can learn about reflections and rotational symmetry through the kite's structure, enhancing their understanding of these concepts in the broader context of geometric transformations.
-
Tiling and Tessellation
Kites can be used in tiling and tessellation patterns, where they cover a plane without gaps or overlaps. This application is particularly valuable in architectural design and art, where geometric patterns are essential.
The ability to use kites in tessellation helps in exploring the principles of plane geometry and the properties of polygons when used in repeated patterns.
-
Area and Perimeter Calculations
Calculating the area and perimeter of kites is a practical application in various fields such as engineering, architecture, and design. The formulas for these calculations are:
- Perimeter: \[ \text{Perimeter} = 2(a + b) \] where \(a\) and \(b\) are the lengths of the two pairs of adjacent sides.
- Area: \[ \text{Area} = \frac{1}{2} \times d_1 \times d_2 \] where \(d_1\) and \(d_2\) are the lengths of the diagonals.
-
Problem Solving and Competitions
Kites are often featured in mathematical problem-solving competitions and exams. Understanding the properties of kites can provide a strategic advantage in tackling these problems.
Students are encouraged to explore various geometric figures, including kites, to develop their analytical and deductive reasoning skills, which are crucial for success in competitive mathematics.
Overall, the study of kites in geometry offers a rich field of exploration, combining theoretical knowledge with practical applications. By mastering the properties and calculations related to kites, one can gain a deeper understanding of geometric principles and their real-world applications.
Measurement Units and Conversion
When calculating the perimeter of a kite, it is important to understand the various measurement units and how to convert between them. This ensures accuracy and consistency in geometric calculations. Below, we provide a comprehensive guide on measurement units commonly used in geometry and the conversion processes.
Common Measurement Units
- Millimeters (mm)
- Centimeters (cm)
- Meters (m)
- Inches (in)
- Feet (ft)
- Yards (yd)
Conversion Formulas
Understanding how to convert between these units is crucial. Below are some key conversion formulas:
-
Millimeters to Centimeters
1 mm = 0.1 cm
-
Centimeters to Meters
1 cm = 0.01 m
-
Meters to Inches
1 m = 39.3701 in
-
Inches to Feet
1 in = 0.0833333 ft
-
Feet to Yards
1 ft = 0.333333 yd
Step-by-Step Conversion Examples
Here are some examples to illustrate the conversion process:
-
Example 1: Converting 150 cm to meters
Formula: \( 1 \, \text{cm} = 0.01 \, \text{m} \)
Calculation: \( 150 \, \text{cm} \times 0.01 = 1.5 \, \text{m} \)
-
Example 2: Converting 3 feet to inches
Formula: \( 1 \, \text{ft} = 12 \, \text{in} \)
Calculation: \( 3 \, \text{ft} \times 12 = 36 \, \text{in} \)
-
Example 3: Converting 2 meters to yards
Formula: \( 1 \, \text{m} = 1.09361 \, \text{yd} \)
Calculation: \( 2 \, \text{m} \times 1.09361 = 2.18722 \, \text{yd} \)
Using Conversion Tools
Online conversion tools can also assist in quickly converting between different measurement units. These tools are particularly useful for complex conversions or when working with multiple units. Some recommended online conversion tools include:
- UnitConverter.net: Offers a wide range of conversion categories and units.
- ConvertUnits.com: Provides detailed conversion steps and explanations.
- Metric Conversions: User-friendly interface with accurate conversion results.
By understanding and utilizing measurement units and conversion methods, you can ensure precision in geometric calculations, particularly when determining the perimeter of a kite. Accurate conversions are essential for consistency and reliability in both academic and practical applications.
Video hướng dẫn cách tính chu vi của một cánh diều bằng cách sử dụng định lý Pythagoras. Học cách tính chu vi một cách dễ dàng và chính xác.
Kite: Tìm Chu Vi Bằng Cách Sử Dụng Pythagoras
READ MORE:
Video hướng dẫn công thức toán học để tính diện tích và chu vi của cánh diều. Tìm hiểu cách tính toán một cách chính xác và dễ dàng.
Công Thức Toán Học - Tính Diện Tích và Chu Vi Của Cánh Diều