Topic 3 square root of 16: Discover the fascinating process behind calculating 3 times the square root of 16. This straightforward mathematical expression holds intriguing applications and insights. In this article, we break down the steps and explore real-life examples to help you understand and appreciate the simplicity and utility of this calculation.
Table of Content
- Understanding 3 √16
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding 3 Square Root of 16
- Calculation Steps
- Examples and Applications
- Frequently Asked Questions
- YOUTUBE: Tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc ba của một số không phải lập phương, cụ thể là căn bậc ba của 16, để nắm vững các khái niệm toán học cơ bản.
Understanding 3 √16
The expression "3 square root of 16" refers to multiplying 3 by the square root of 16. Let's break this down step by step using Mathjax to show the calculations clearly.
Step-by-Step Calculation
The square root of 16 is calculated as follows:
\[\sqrt{16} = 4\]
Thus, the expression 3 √16 can be written as:
\[3 \times \sqrt{16} = 3 \times 4\]
So the final result is:
\[3 \times 4 = 12\]
Mathematical Explanation
- The square root function finds a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For 16, that number is 4 because \(4 \times 4 = 16\).
- Multiplying 3 by the square root of 16 involves performing the multiplication after finding the square root.
Using a Square Root Calculator
Online calculators can simplify finding the square root. Here is how to use them:
- Enter the number 16 into the calculator.
- Click the button to calculate the square root, which will yield 4.
- Multiply the result (4) by 3 to get 12.
Additional Information
For more information on calculating square roots and using online tools, check out resources like Mathway and Math Goodies.
| Expression | Result |
| \(3 \times \sqrt{16}\) | 12 |

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics and has various practical applications. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 16 is 4 because 4 multiplied by 4 equals 16.
Square roots are represented using the radical symbol (√). The principal square root is always non-negative, although every positive number actually has two square roots: one positive and one negative. For instance, while √16 = 4, it is also true that -4 × -4 = 16, so -4 is also a square root of 16.
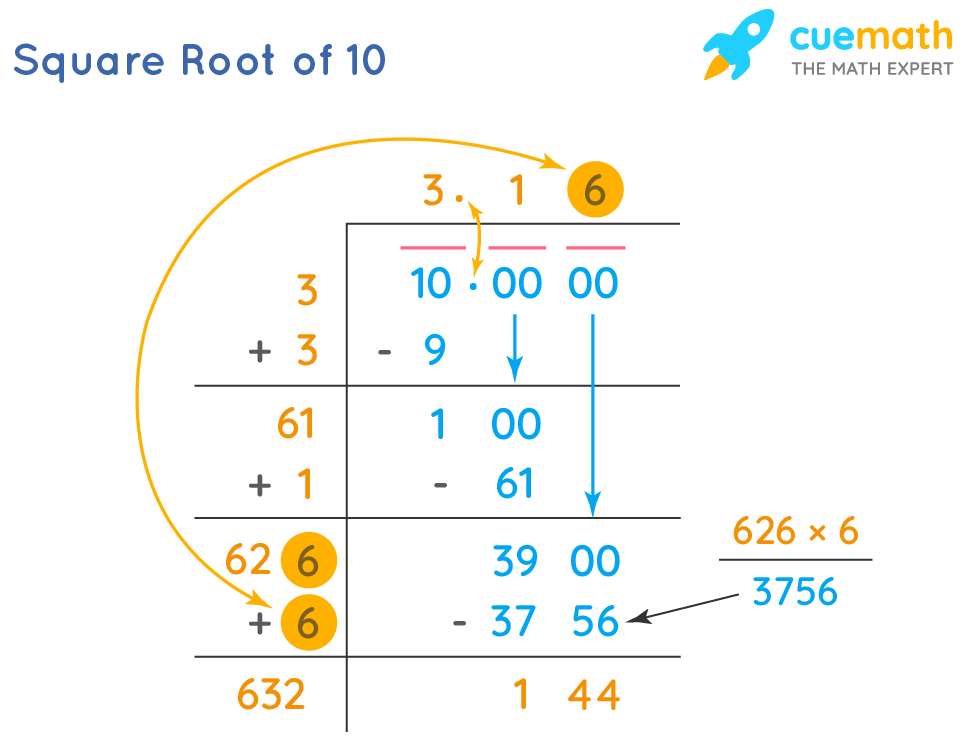
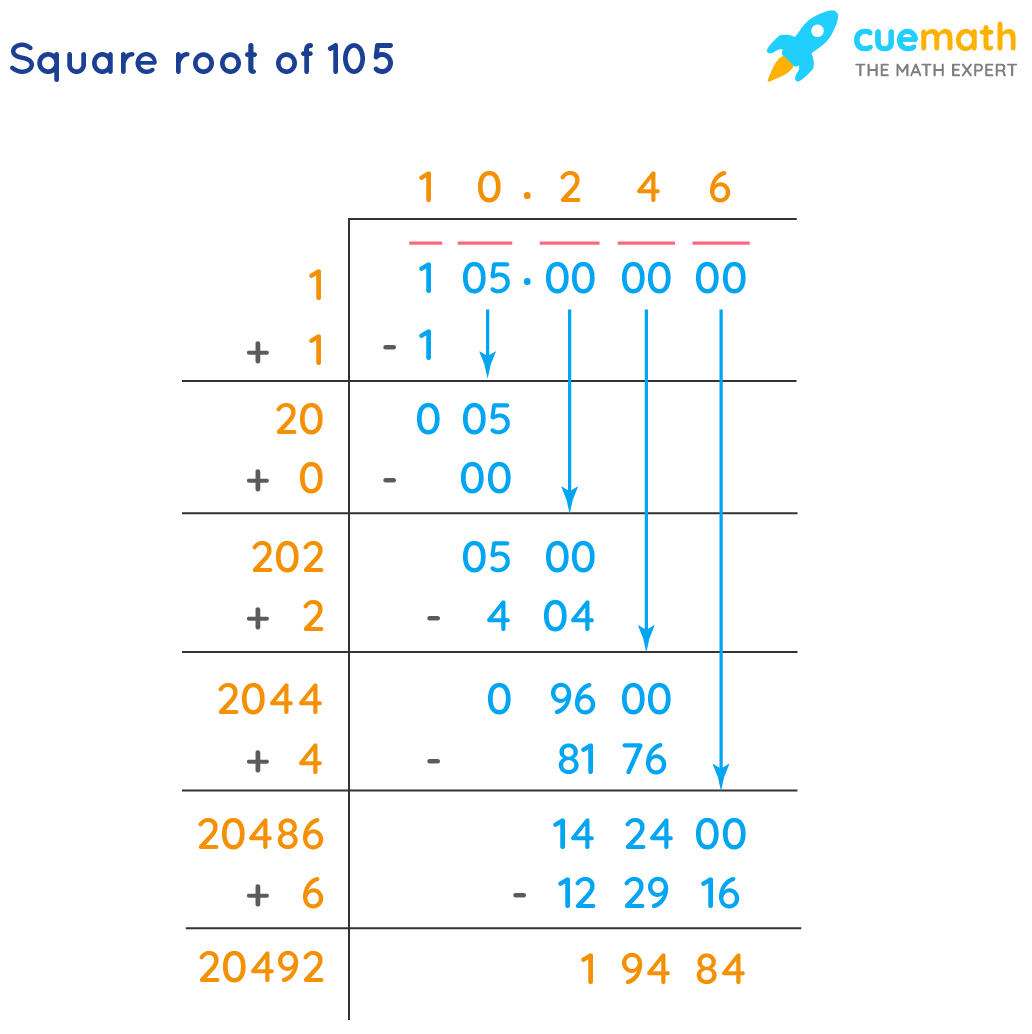
Square roots can be found for both perfect squares and non-perfect squares. Perfect squares are numbers whose square roots are integers, such as 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25. Non-perfect squares have square roots that are irrational numbers, meaning they cannot be expressed as exact fractions and their decimal forms are non-terminating and non-repeating.
To calculate the square root of a number manually, especially for perfect squares, you can use methods such as prime factorization or the long division method. For non-perfect squares, calculators or iterative methods such as the Newton-Raphson method are typically used to find approximate values.
- The square root symbol is called the radical symbol and looks like this: √.
- Perfect squares, such as 16, have square roots that are integers (e.g., √16 = 4).
- Non-perfect squares, like 10, have irrational square roots (e.g., √10 ≈ 3.162).
- The principal square root of a positive number is the non-negative root.
Understanding square roots is essential for solving quadratic equations, working with geometric shapes, and many other areas of mathematics and science.
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
| 36 | 6 |
In conclusion, square roots play a crucial role in various mathematical calculations and problem-solving scenarios. By mastering the concept of square roots, one can enhance their understanding of more complex mathematical concepts and improve their problem-solving skills.
Understanding 3 Square Root of 16
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, representing a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 16 is 4, because 4 × 4 = 16. When we talk about "3 square root of 16", we are referring to multiplying 3 by the square root of 16.
Here's how to break it down:
- Find the square root of 16:
- 16 can be written as 4² because 4 × 4 = 16.
- Thus, √16 = 4.
- Multiply 3 by the square root of 16:
- 3 × √16 = 3 × 4.
- The result is 12.
Therefore, the expression "3 square root of 16" simplifies to 12.
| Expression | Result |
| √16 | 4 |
| 3 × √16 | 12 |
This method can be applied to other numbers as well, and understanding the square root and multiplication principles is crucial for solving more complex mathematical problems.
Calculation Steps
To calculate the expression \(3 \sqrt{16}\), follow these detailed steps:
-
Identify the square root of 16: The square root of 16 is the number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 16. Therefore, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
-
Multiply by 3: Next, take the square root value found in step 1 and multiply it by 3. Thus, \( 3 \times 4 = 12 \).
Therefore, the value of \(3 \sqrt{16}\) is 12.
Examples and Applications
The concept of square roots is widely used in various fields. Below are some detailed examples and applications of the square root of 16 and how it's utilized in real-life scenarios:
-
Finance
In finance, the square root is used to calculate the volatility of stock returns. For example, to find the volatility, one might take the square root of the variance of a stock's returns. This helps investors assess the risk associated with the investment.
-
Architecture
Square roots are essential in architecture and engineering to determine natural frequencies of structures. For instance, calculating the natural frequency of a bridge involves using square roots, which helps in predicting how the structure will respond to different loads such as wind or traffic.
-
Science
Square roots are used in various scientific calculations, such as determining the speed of an object, the amount of radiation absorbed by materials, and the intensity of sound waves. These calculations help scientists understand and develop new technologies and solutions.
-
Statistics
In statistics, square roots are used to calculate standard deviation, a measure of how spread out numbers are in a dataset. The standard deviation is the square root of the variance and is crucial for analyzing data and making informed decisions.
-
Geometry
In geometry, square roots are used to calculate areas and perimeters of shapes. For example, using the Pythagorean theorem involves taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the sides of a right triangle to find the length of the hypotenuse.
-
Computer Science
Square roots are used in computer algorithms for encryption, image processing, and game physics. For instance, encryption algorithms use square roots to generate keys for secure data transmission.
-
Cryptography
In cryptography, square roots are used for digital signatures and secure communication channels. These techniques ensure the authenticity and security of data transactions.
-
Navigation
Square roots are used in navigation to calculate distances and directions between points. Pilots and sailors use these calculations to determine their course and position accurately.
-
Electrical Engineering
Square roots are used in electrical engineering to compute power, voltage, and current in circuits. These calculations are vital for designing and optimizing electrical systems.
-
Cooking
In cooking, square roots can be used to scale recipes. For instance, if you need to adjust a recipe for a larger or smaller serving size, using the square root of the scaling factor can help maintain the correct proportions of ingredients.
-
Photography
In photography, the f-number of a camera lens, which controls the aperture, is related to the square root of the aperture area. This relationship helps photographers control the amount of light entering the camera.
-
Computer Graphics
Square roots are used in computer graphics to calculate distances and lengths of vectors, essential for rendering images and animations.
-
Telecommunication
In telecommunication, the inverse square law describes how signal strength decreases with distance, using the square root to model this relationship.

Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some commonly asked questions about the 3 square root of 16:
-
What is the value of 3 times the square root of 16?
The square root of 16 is 4. Therefore, 3 times the square root of 16 is \(3 \times 4 = 12\).
-
Why is the square root of 16 a rational number?
The square root of 16 is a rational number because 16 is a perfect square. The square root of 16 is 4, which is an integer. Any integer is considered a rational number.
-
How do you find the square root of 16?
To find the square root of 16, you can use the following steps:
- Find the largest number that when multiplied by itself gives 16. This number is 4.
- Thus, the square root of 16 is 4.
-
Is 16 a perfect square?Yes, 16 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as \(4 \times 4\). Therefore, the square root of 16 is an integer.
-
What are some applications of square roots?
Square roots are used in various fields including geometry, physics, and engineering. For instance, calculating the side length of a square when given the area, determining the standard deviation in statistics, and solving quadratic equations in algebra.
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc ba của một số không phải lập phương, cụ thể là căn bậc ba của 16, để nắm vững các khái niệm toán học cơ bản.
Học Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Ba Của Số Không Phải Lập Phương, Căn Bậc Ba(16)