Topic square root of 116 simplified: Unlock the mystery of simplifying the square root of 116 with our step-by-step guide. Learn the prime factorization method to effortlessly transform \(\sqrt{116}\) into its simplest form, making complex calculations a breeze. Dive in to enhance your mathematical skills and boost your confidence in handling square roots!
Table of Content
- Simplified Square Root of 116
- Introduction to Square Roots
- Understanding Square Roots
- Definition of Simplified Square Roots
- Prime Factorization Method
- Steps to Simplify the Square Root of 116
- Breaking Down 116 into Prime Factors
- Simplifying Using Perfect Squares
- Detailed Calculation Process
- Alternate Methods to Simplify Square Roots
- Examples of Other Simplified Square Roots
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Xem video này để tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 116 và cách áp dụng nó vào bài toán với từ khóa 'square root of 116 simplified'.
Simplified Square Root of 116
The square root of 116 can be simplified by factoring it into its prime components. The process is outlined below:
Step-by-Step Simplification
- Factor 116 into its prime factors: \(116 = 2^2 \times 29\).
- Express the square root of 116 using its prime factors: \(\sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29}\).
- Simplify the square root by taking the square root of the perfect square factor: \(\sqrt{2^2 \times 29} = 2\sqrt{29}\).
Final Result
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 116 is:
\[\sqrt{116} = 2\sqrt{29}\]
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics, playing a crucial role in various calculations and problem-solving scenarios. A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For example, the square root of 9 is 3, because \(3 \times 3 = 9\).
Square roots are commonly represented using the radical symbol (√). The number under the radical symbol is called the radicand. For instance, in \(\sqrt{116}\), 116 is the radicand.
Here is a step-by-step guide to understanding square roots:
- Identify Perfect Squares: Perfect squares are numbers that have integer square roots. Examples include 1, 4, 9, 16, and so on.
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down a number into its prime factors can simplify the process of finding its square root. For instance, 116 can be factored into \(2^2 \times 29\).
- Simplify Using Perfect Squares: If the radicand includes a perfect square factor, it can be simplified. For example, \(\sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29} = 2\sqrt{29}\).
Understanding and simplifying square roots can greatly enhance your mathematical abilities and provide a solid foundation for more advanced topics.
Understanding Square Roots
Square roots are a fundamental concept in mathematics, essential for various computations and problem-solving techniques. A square root of a number is a value which, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. For instance, the square root of 25 is 5 because \(5 \times 5 = 25\).
The notation for the square root is the radical symbol (√), followed by the radicand (the number under the radical sign). For example, in \(\sqrt{116}\), 116 is the radicand.
To understand square roots more thoroughly, let's consider the following steps:
- Identify the Radicand: This is the number inside the radical symbol. In \(\sqrt{116}\), 116 is the radicand.
- Determine Perfect Squares: Perfect squares are numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, etc., which have whole numbers as their square roots. Recognizing these can simplify calculations.
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down the radicand into its prime factors can help simplify the square root. For example, 116 can be factored into \(2^2 \times 29\).
- Simplify the Square Root: Use the prime factorization to simplify the square root. For example, \(\sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29} = 2\sqrt{29}\).
By understanding and practicing these steps, you can master the concept of square roots and apply them effectively in various mathematical contexts.
Definition of Simplified Square Roots
A simplified square root is the most reduced form of a square root expression. Simplifying a square root involves expressing it in a way that no perfect square factors other than 1 remain under the radical sign. This process makes the expression easier to work with in mathematical calculations.
To simplify a square root, follow these steps:
- Prime Factorization: Begin by factoring the number under the radical into its prime factors. For instance, the prime factorization of 116 is \(2^2 \times 29\).
- Identify Perfect Squares: Look for pairs of prime factors, as they can be simplified. In the case of 116, the pair is \(2^2\).
- Simplify the Radical: Take the square root of the perfect square factors and move them outside the radical. For example, \(\sqrt{2^2 \times 29} = 2\sqrt{29}\).
Thus, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{116}\) is \(2\sqrt{29}\). This form is easier to interpret and use in further mathematical operations.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is a systematic approach to simplifying square roots by breaking down the radicand into its prime factors. This method is particularly useful for large numbers or when dealing with non-perfect squares. Here is a detailed, step-by-step guide to using the prime factorization method:
- Find the Prime Factors: Begin by identifying the prime factors of the number under the radical sign. For example, for 116:
- 116 is even, so divide by 2: \(116 \div 2 = 58\).
- 58 is also even, so divide by 2 again: \(58 \div 2 = 29\).
- 29 is a prime number, so the prime factorization of 116 is \(2^2 \times 29\).
- Group the Prime Factors: Group the prime factors in pairs. Each pair of identical factors represents a perfect square. In the case of 116, the factor \(2^2\) forms a perfect square.
- So, \(116 = 2^2 \times 29\).
- Rewrite the Square Root: Express the square root of the number using the prime factors. For \(\sqrt{116}\), this becomes:
- \(\sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29}\).
- Simplify the Expression: Take the square root of the perfect square factor and move it outside the radical sign. The non-perfect square factor remains inside the radical. Therefore:
- \(\sqrt{2^2 \times 29} = 2\sqrt{29}\).
Using the prime factorization method, we have simplified \(\sqrt{116}\) to \(2\sqrt{29}\). This method is effective for breaking down complex square roots into simpler, more manageable forms.

Steps to Simplify the Square Root of 116
Simplifying the square root of 116 involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and identifying perfect squares. Here are the detailed steps:
-
First, find the prime factorization of 116:
- 116 can be divided by 2: \(116 \div 2 = 58\)
- 58 can also be divided by 2: \(58 \div 2 = 29\)
- 29 is a prime number.
So, the prime factorization of 116 is \(2^2 \times 29\).
-
Next, rewrite the square root of 116 using its prime factors:
\(\sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29}\)
-
Identify and separate the perfect squares from the prime factors:
\(\sqrt{2^2 \times 29} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{29}\)
-
Simplify the perfect square:
\(\sqrt{2^2} = 2\)
-
Combine the simplified perfect square with the remaining square root:
\(\sqrt{116} = 2 \sqrt{29}\)
Therefore, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{116}\) is \(2 \sqrt{29}\).
Breaking Down 116 into Prime Factors
Breaking down 116 into its prime factors is a crucial step in simplifying its square root. Here are the detailed steps:
-
Start by checking the smallest prime number, which is 2:
- 116 is an even number, so it is divisible by 2.
- Divide 116 by 2:
\(116 \div 2 = 58\)
-
Next, check if 58 is divisible by 2:
- 58 is also an even number, so it is divisible by 2.
- Divide 58 by 2:
\(58 \div 2 = 29\)
-
Finally, check the number 29:
- 29 is a prime number, meaning it cannot be divided by any other numbers except 1 and itself.
-
Now, list the prime factors of 116:
Prime factorization of 116 is \(2 \times 2 \times 29\) or \(2^2 \times 29\).
This prime factorization is essential for further steps in simplifying the square root of 116.
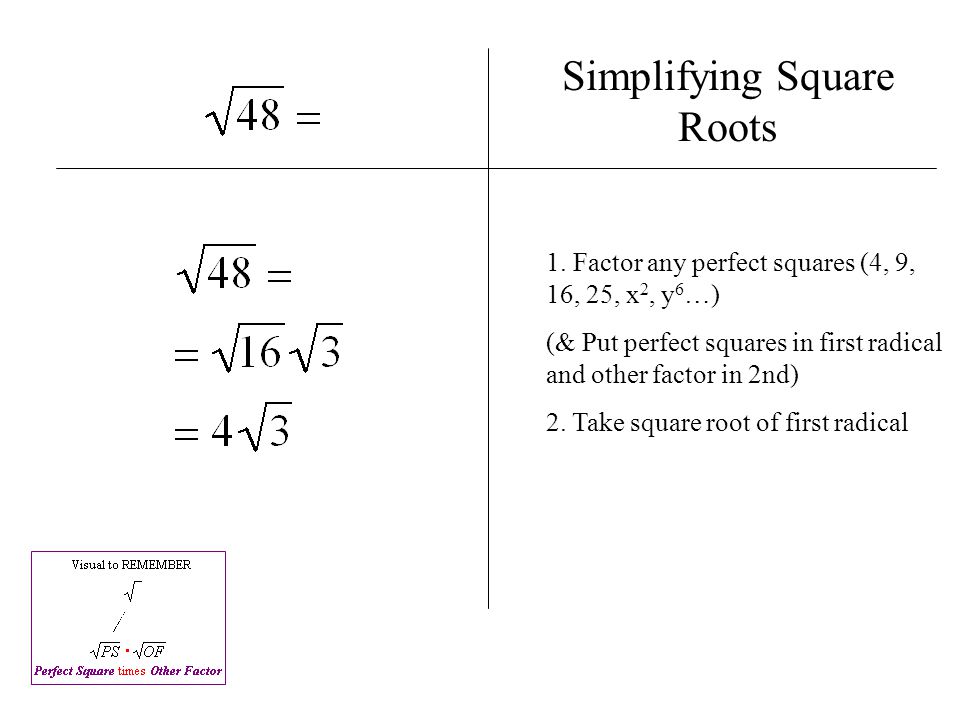
Simplifying Using Perfect Squares
To simplify the square root of 116 using perfect squares, follow these steps:
Identify Perfect Square Factors: List the factors of 116 and identify the perfect square among them. The factors of 116 are 1, 2, 4, 29, 58, and 116. The largest perfect square factor is 4.
Rewrite 116 Using Its Factors: Express 116 as a product of its perfect square factor and another factor. In this case, 116 can be written as:
\[
116 = 4 \times 29
\]Apply the Square Root to Each Factor: Use the property of square roots that allows you to take the square root of each factor separately:
\[
\sqrt{116} = \sqrt{4 \times 29} = \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{29}
\]Simplify the Square Root of the Perfect Square: Calculate the square root of the perfect square factor. The square root of 4 is 2:
\[
\sqrt{4} = 2
\]Combine the Results: Multiply the square root of the perfect square by the square root of the other factor to get the simplified form:
\[
\sqrt{116} = 2 \times \sqrt{29}
\]Thus, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{116}\) is \(2\sqrt{29}\).
Detailed Calculation Process
To find the simplified form of the square root of 116, we will go through a detailed calculation process step by step using the prime factorization method and the identification of perfect squares.
-
Prime Factorization: First, we perform prime factorization of 116.
- 116 is an even number, so it can be divided by 2.
- 116 ÷ 2 = 58
- 58 is also an even number, so it can be divided by 2.
- 58 ÷ 2 = 29
- 29 is a prime number and cannot be divided further.
Thus, the prime factorization of 116 is: \( 116 = 2^2 \times 29 \)
-
Identify Perfect Squares: Look for pairs of prime factors. Here, \( 2^2 \) is a perfect square.
So, we have: \( \sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29} \)
-
Simplify: Split the square root into two parts and simplify.
- \( \sqrt{116} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 29} = \sqrt{2^2} \times \sqrt{29} \)
- \( \sqrt{2^2} = 2 \)
- So, \( \sqrt{116} = 2\sqrt{29} \)
-
Approximate Decimal Value: If you need a decimal approximation:
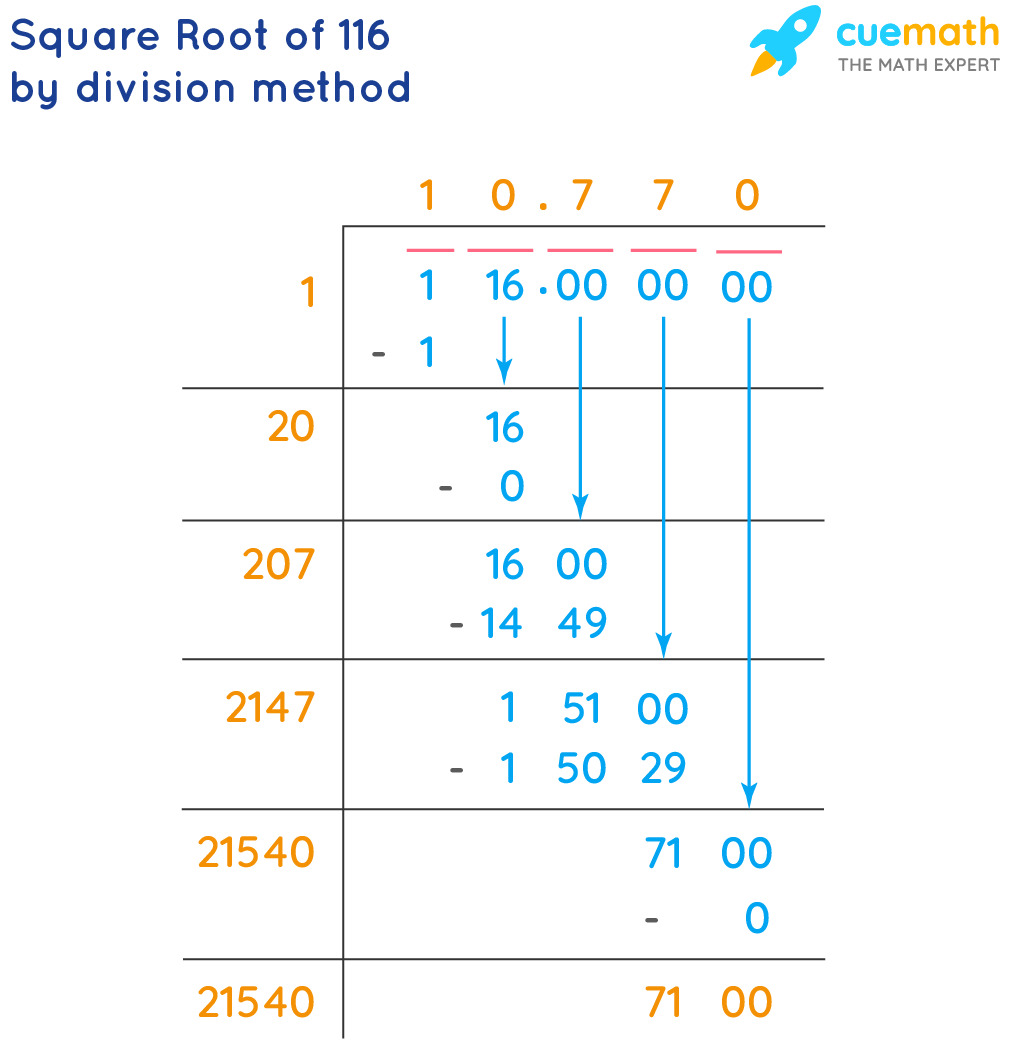
\( 2\sqrt{29} \approx 2 \times 5.385 = 10.770 \)
Thus, the simplified form of \( \sqrt{116} \) is \( 2\sqrt{29} \) and its approximate decimal value is 10.770.
Alternate Methods to Simplify Square Roots
While the prime factorization method is widely used to simplify square roots, there are alternative approaches that can be employed. These methods can provide quicker solutions or offer different perspectives on simplification. Let's explore some of these alternatives:
- Estimation Technique: One approach is to estimate the square root of the number and then refine the approximation through successive iterations. This method can be particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers or when a quick approximation is needed.
- Trigonometric Methods: Trigonometric functions, such as the arctangent function, can be used to approximate square roots. By utilizing trigonometric identities and series expansions, square roots can be expressed in terms of trigonometric functions, providing an alternative way to simplify them.
- Iterative Algorithms: Iterative algorithms, such as Newton's method, can be applied to find the square root of a number. These algorithms iteratively refine an initial guess until a satisfactory approximation is obtained. While they may require more computational resources, they can be effective in finding precise solutions.
- Binomial Expansion: The binomial theorem can be employed to expand expressions involving square roots. By using the binomial expansion, square roots can be expressed as infinite series, allowing for alternative representations and simplification techniques.
- Special Cases and Identities: Certain special cases and mathematical identities can simplify square roots. For example, the difference of squares identity or the Pythagorean theorem can be utilized to simplify expressions involving square roots. Understanding these identities can provide shortcuts in the simplification process.
These alternate methods offer diverse approaches to simplifying square roots, catering to different preferences and mathematical contexts. Depending on the specific problem at hand, one method may be more efficient or insightful than others.
Examples of Other Simplified Square Roots
Here are some examples of other simplified square roots, showcasing various techniques and strategies:
- √100: The square root of 100 is a perfect square, equal to 10.
- √121: Similarly, the square root of 121 is also a perfect square, equal to 11.
- √64: Another example is the square root of 64, which is 8.
- √144: The square root of 144 is a perfect square, resulting in 12.
- √225: Lastly, the square root of 225 simplifies to 15, being a perfect square.
These examples illustrate how various numbers can be simplified to obtain their square roots, often by identifying perfect squares or employing other mathematical techniques.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some frequently asked questions about simplifying the square root of 116:
- What is the square root of 116?
- Can the square root of 116 be simplified?
- What is the simplified form of the square root of 116?
- Are there alternate methods to simplify the square root of 116?
- Why is simplifying square roots important?
The square root of 116 is an irrational number, approximately equal to 10.7703. It cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
Yes, the square root of 116 can be simplified. It can be simplified using the prime factorization method or other mathematical techniques to obtain a more concise expression.
The simplified form of the square root of 116 can be expressed as 2√29. This form represents the square root of 116 in terms of its prime factors, where 2 is the square root of 4 and √29 remains in its radical form.
Yes, besides the prime factorization method, there are alternative approaches to simplify the square root of 116. Techniques such as estimation, trigonometric methods, iterative algorithms, and special identities can be employed to simplify square roots.
Simplifying square roots helps in making calculations more manageable and understandable. It allows for easier comparison of values and facilitates further mathematical operations.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the square root of 116 can be simplified using various methods, with the prime factorization method being a common approach. By breaking down 116 into its prime factors and identifying perfect squares, we can simplify the square root expression. Additionally, alternate methods such as estimation, trigonometric techniques, iterative algorithms, and special identities offer alternative avenues for simplification.
Understanding how to simplify square roots not only enhances mathematical skills but also fosters a deeper comprehension of number properties and mathematical relationships. Whether it's for practical calculations or academic pursuits, mastering the art of simplifying square roots is a valuable asset in the realm of mathematics.

Xem video này để tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 116 và cách áp dụng nó vào bài toán với từ khóa 'square root of 116 simplified'.
Hướng dẫn Cách Rút Gọn Căn bậc 2 của 116: sqrt(116)
READ MORE:
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai / Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của Các Số Không Phải Số Chính Phương