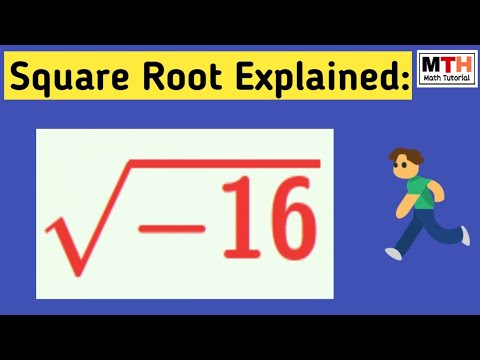
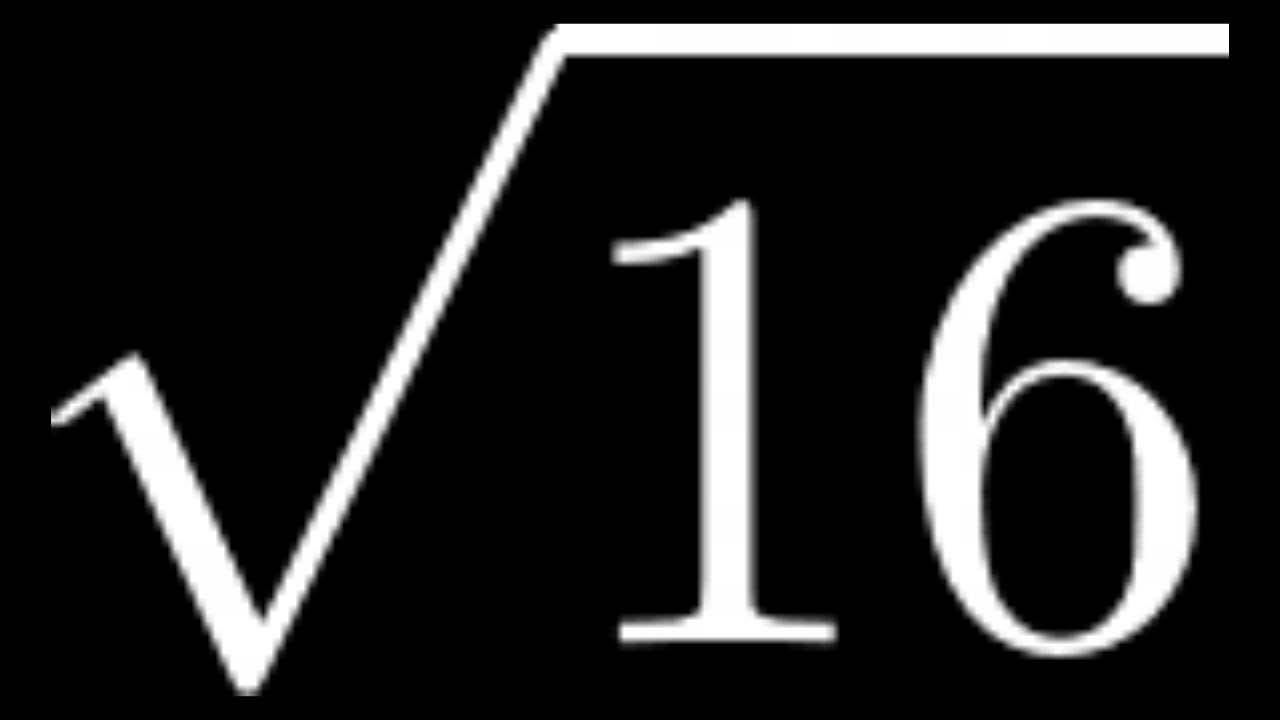Topic square root of 16 rational or irrational: Determining whether the square root of 16 is rational or irrational is a fundamental mathematical question. In this article, we will explore the properties of square roots, the distinction between rational and irrational numbers, and why the square root of 16 is indeed a rational number, simplifying mathematical concepts along the way.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 16: Rational or Irrational?
- Understanding the Square Root of 16
- What is a Square Root?
- Definition and Properties
- Calculation Methods
- Is 16 a Perfect Square?
- Rational vs. Irrational Numbers
- Why the Square Root of 16 is Rational
- Using Long Division to Find Square Roots
- Applications of the Square Root of 16
- FAQs on the Square Root of 16
- YOUTUBE:
Square Root of 16: Rational or Irrational?
The square root of 16 is a commonly discussed topic in mathematics. Let's explore its properties, including whether it is a rational or irrational number, and methods to calculate it.
Definition and Calculation
The square root of a number \( n \) is a value \( x \) such that \( x^2 = n \). For 16, we have:
\[\sqrt{16} = 4\]
This is because \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \).
Perfect Square
A perfect square is a number that has an integer as its square root. Since 16 is a perfect square, its square root is an integer.
Rational or Irrational?
A rational number can be expressed as a fraction of two integers, whereas an irrational number cannot. Since 4 is an integer, the square root of 16 is a rational number.
Methods to Find the Square Root
- Prime Factorization: Breaking down 16 into its prime factors gives us \(2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\). Grouping the pairs, we have \(\sqrt{16} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2)^2} = 4\).
- Long Division Method: This traditional method involves dividing the number into pairs of digits from right to left and finding the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 16.
- Calculator: Simply inputting 16 and pressing the square root button yields 4.
- Exponentiation: Using the exponent form, \(\sqrt{16} = 16^{1/2} = 4\).
Examples
- Example 1: If Noah has a bag with 16 cubes and arranges them into a square, each side will have \(\sqrt{16} = 4\) cubes.
- Example 2: If Jake arranges 16 flower plants in a square bed, each side of the square bed will have 4 plants.
Frequently Asked Questions
| Question | Answer |
| Is the square root of 16 rational? | Yes, it is rational because it equals 4. |
| What is the value of \(\sqrt{0.16}\)? | \(\sqrt{0.16} = 0.4\) |
| Is 16 a perfect square? | Yes, because its square root is 4, which is an integer. |
Understanding the properties of the square root of 16 helps in grasping broader mathematical concepts. The value \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) is a fundamental example of a perfect square and a rational number.

READ MORE:
Understanding the Square Root of 16
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For 16, the square root is denoted as . Here, we will delve into the concept and calculation of the square root of 16 and why it is considered a rational number.
First, let's understand some key terms:
- Square Root: A number that produces a specified quantity when multiplied by itself.
- Rational Number: A number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction , where and are integers and is not zero.
- Irrational Number: A number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
To determine the square root of 16, consider the following:
- Calculate: The square root of 16 is 4, since .
- Rational Check: The result, 4, can be expressed as the fraction , proving it is a rational number.
In conclusion, the square root of 16 is 4, which is a rational number because it can be represented as the fraction . Understanding this concept helps in distinguishing between rational and irrational numbers, and in simplifying mathematical problems involving square roots.
What is a Square Root?
A square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, results in the original number. The square root is denoted by the radical symbol . For example, the square root of 16 is represented as .
Key properties of square roots include:
- Positive and Negative Roots: Every positive number has two square roots: one positive and one negative. For 16, these are 4 and -4, since and .
- Principal Square Root: The non-negative square root of a number is called the principal square root. For 16, the principal square root is 4.
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 16, 25, and 36 are perfect squares because their square roots are integers.
To find the square root of a number, several methods can be used:
- Prime Factorization: Break down the number into its prime factors and pair them. For 16, the prime factors are 2 × 2 × 2 × 2, so the square root is 2 × 2 = 4.
- Long Division Method: A manual calculation method for finding square roots, especially useful for non-perfect squares.
- Using Calculators: Most calculators have a square root function to quickly find the square root of any number.
In summary, understanding square roots involves recognizing their properties, knowing that every positive number has both a positive and negative square root, and using various methods to calculate them. This foundational knowledge is crucial in many areas of mathematics.
Definition and Properties
The square root of a number is defined as a value which, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. Mathematically, for a number , its square root is denoted as . For example, the square root of 16 is 4, since .
Important properties of square roots include:
- Existence: Every non-negative real number has a non-negative square root. For instance, the square root of 16 is 4.
- Unique Principal Root: The principal square root is the non-negative root of a non-negative number. For 16, the principal square root is 4.
- Perfect Squares: Numbers such as 1, 4, 9, 16, etc., are perfect squares because their square roots are integers.
- Rational and Irrational Roots: A number is a perfect square if its square root is a rational number. The square root of 16 is 4, which is a rational number. If the square root is not a perfect square, it is an irrational number.
Consider the following table for better understanding:
| Number | Square Root | Rational or Irrational |
|---|---|---|
| 4 | 2 | Rational |
| 9 | 3 | Rational |
| 16 | 4 | Rational |
| 2 | 1.414... | Irrational |
In summary, the square root is a fundamental concept in mathematics with distinct properties that help in determining whether a number is rational or irrational. Perfect squares have rational square roots, while non-perfect squares have irrational roots.
Calculation Methods
Calculating the square root of a number can be done using various methods. Here, we explore three common methods to find the square root of 16.
1. Prime Factorization Method
- Break down the number into its prime factors. For 16, the prime factorization is 2 × 2 × 2 × 2.
- Pair the prime factors. For 16, we have (2 × 2) and (2 × 2).
- Take one number from each pair and multiply them. So, 2 × 2 = 4.
- Therefore, the square root of 16 is 4.
2. Long Division Method
- Group the digits of the number in pairs from right to left. For 16, we have only one pair: 16.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair. For 16, this number is 4 because 4 × 4 = 16.
- The quotient obtained is the square root of the number. Here, it is 4.
3. Using a Calculator
- Turn on the calculator and enter the number 16.
- Press the square root (√) button.
- The display shows the result, which is 4.
Comparison of Methods:
| Method | Steps | Result |
|---|---|---|
| Prime Factorization | Factorize, pair factors, multiply pairs | 4 |
| Long Division | Group digits, find largest square, divide | 4 |
| Calculator | Input number, press √ button | 4 |
Each of these methods confirms that the square root of 16 is 4. Understanding these methods not only helps in manual calculations but also enhances comprehension of the mathematical concepts behind square roots.

Is 16 a Perfect Square?
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the square of an integer. In mathematical terms, a number is a perfect square if there exists an integer such that . To determine if 16 is a perfect square, we need to find an integer that, when squared, equals 16.
Steps to check if 16 is a perfect square:
- Identify the integer that, when multiplied by itself, gives 16. This means finding .
- Calculate the square root of 16. We know that equals 4 because .
- Verify that the result is an integer. Since 4 is an integer, 16 is indeed a perfect square.
Another way to understand this is through the concept of prime factorization:
- Factorize 16 into prime factors: 2 × 2 × 2 × 2.
- Group the prime factors into pairs: (2 × 2) and (2 × 2).
- Each pair corresponds to a square of 2, and multiplying these pairs together gives us 4, which is an integer.
Perfect squares have several important properties:
- They are always non-negative.
- The number of factors of a perfect square is always odd.
- The square root of a perfect square is always an integer.
Based on these points, we can confidently say that 16 is a perfect square. The integer 4, when squared, equals 16, fulfilling the criteria of a perfect square.
Rational vs. Irrational Numbers
Understanding the difference between rational and irrational numbers is fundamental in mathematics. These two categories of numbers have distinct properties and characteristics.
Rational Numbers:
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. In other words, a number is rational if it can be written in the form , where and are integers and is not zero.
- Examples include 1/2, -3, 4.75 (which is 19/4), and 0 (which is 0/1).
- Rational numbers can be positive, negative, or zero.
- They can be expressed as terminating or repeating decimals.
Irrational Numbers:
An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction of two integers. Irrational numbers cannot be written in the form . Their decimal expansions are non-terminating and non-repeating.
- Examples include (pi), (Euler's number), and .
- Irrational numbers are also real numbers.
- They cannot be expressed as exact fractions.
Consider the following comparison:
| Property | Rational Numbers | Irrational Numbers |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Cannot be expressed as | |
| Decimal Expansion | Terminating or repeating | Non-terminating, non-repeating |
| Examples | 1/2, -3, 4.75, 0 | , , |
Given these definitions, we can confirm that the square root of 16 is a rational number because it equals 4, which can be expressed as the fraction . Therefore, it meets the criteria for rational numbers, being both an integer and expressible as a fraction of two integers.
Why the Square Root of 16 is Rational
A rational number is defined as any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. To determine if the square root of 16 is rational, we need to see if it can be written in the form , where and are integers.
Steps to demonstrate why the square root of 16 is rational:
- Calculate the square root of 16. We know that equals 4.
- Check if 4 can be expressed as a fraction. Indeed, 4 can be written as .
- Both 4 and 1 are integers, and the denominator is not zero.
Because the square root of 16 (which is 4) can be expressed as the fraction , it meets the definition of a rational number.
Let's summarize the properties and verification:
- Perfect Square: 16 is a perfect square because it can be written as .
- Integer Result: The square root of 16 is an integer (4).
- Expressible as a Fraction: The integer 4 can be expressed as .
- Rational Number: Since 4 can be written as a fraction of two integers, it is a rational number.
Based on these points, we can conclusively state that the square root of 16 is rational. The number 4, being both an integer and expressible as a fraction, fulfills all the criteria for rational numbers.
Using Long Division to Find Square Roots
The long division method is a systematic approach to finding the square root of a number. Here, we will demonstrate how to find the square root of 16 using this method step by step.
Pair the Digits: Begin by grouping the digits of the number in pairs, starting from the decimal point and moving both to the left and the right. For the number 16, we have one pair: 16.
Find the Largest Square: Determine the largest square that is less than or equal to the first pair (16). The largest perfect square less than or equal to 16 is 16 (4 x 4 = 16).
Subtract and Bring Down the Next Pair: Subtract the square from the first pair and bring down the next pair of digits. Since there are no more digits in 16, this step is not needed further.
- 16 - 16 = 0
Double the Quotient: Double the current quotient (which is 4), giving 8, and use this as the starting part of our divisor in the next step.
Find the Next Digit: Determine the next digit by finding a number that, when appended to the current divisor (80), and multiplied by the same number, gives a product less than or equal to the remainder. In this case, since the remainder is 0, the next digit is 0.
Repeat: Since the remainder is zero and there are no more digits, the process stops here. The square root of 16 is 4.
The steps above illustrate the long division method for finding the square root of 16. Since we found a whole number (4), it confirms that the square root of 16 is rational.

Applications of the Square Root of 16
The square root of 16, which is 4, finds applications in various fields. Here are some practical uses:
-
Geometry:
In geometry, the square root of 16 is used to calculate the side length of squares and rectangles. For example, if the area of a square is 16 square units, the length of each side is 4 units because \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
-
Algebra:
In algebra, the square root of 16 is used to solve quadratic equations. For instance, the equation \( x^2 = 16 \) has solutions \( x = 4 \) and \( x = -4 \).
-
Physics:
In physics, the square root of 16 can be used to determine distances and velocities in various problems. For example, if an object travels a distance of 16 meters in a given time, the calculation of its velocity might involve finding the square root of 16.
-
Engineering:
Engineers use the square root of 16 in various calculations, such as determining the load distribution on structures. For example, if a load of 16 units is equally distributed over four points, the load per point is \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) units.
-
Everyday Mathematics:
In everyday life, knowing that \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \) can help with tasks such as determining the dimensions of a room or garden plot when the area is known.
-
Technology:
In computer graphics and digital imaging, the square root of 16 might be used to optimize algorithms for rendering images, where calculations involving perfect squares simplify processing.
Overall, the square root of 16 is a fundamental value that is widely applicable in many practical and theoretical contexts.
FAQs on the Square Root of 16
Here are some frequently asked questions about the square root of 16:
- What is the value of the square root of 16?
- Why is the square root of 16 a rational number?
- How is 16 a perfect square?
- What is the value of 17 times the square root of 16?
- Is the number 16 a perfect square?
- What is the value of the square root of 0.16?
- What are some applications of the square root of 16?
- Determining the side length of a square with an area of 16 square units.
- Calculating dimensions in geometric problems.
- Solving algebraic equations where the square root function is involved.
The square root of 16 is 4.
The square root of 16 is rational because 16 is a perfect square, and its square root is an integer (4). A number is considered rational if it can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Since 4 can be written as 4/1, it is a rational number.
A number is a perfect square if it can be expressed as the square of an integer. Since 4 * 4 = 16, 16 is a perfect square.
The square root of 16 is 4, so 17 times the square root of 16 is 17 * 4 = 68.
Yes, 16 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as 4².
The square root of 0.16 is 0.4. This can be derived from the square root of 16/100, which is 4/10, or 0.4.
The square root of 16 is used in various real-world applications, including:
Căn Bậc Hai của 16
READ MORE:
Xem máy tính con người giải quyết bài toán dài nhất thế giới. Một video thú vị để khám phá kỹ năng tính toán đáng kinh ngạc.
Máy Tính Con Người Giải Quyết Bài Toán Dài Nhất Thế Giới #shorts