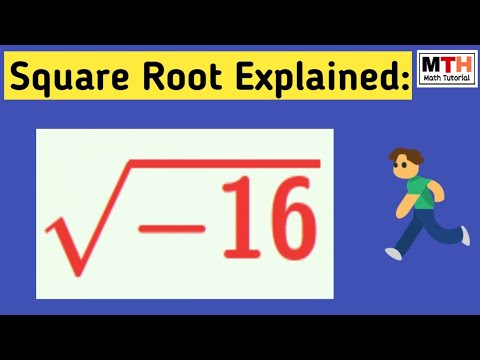
Topic square root of 16 in radical form: Understanding the square root of 16 in its radical form is fundamental in mathematics. This guide explores the various methods to simplify and calculate the square root of 16, explains its properties, and provides practical examples. Dive in to learn how the simplest radical form, √16, is simplified to the number 4.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of 16 in Radical Form
- Introduction to Square Roots and Radical Form
- What is the Square Root of 16?
- Understanding Radical Form
- Calculating the Square Root of 16
- Simplification of the Radical Form √16
- Using Prime Factorization to Find the Square Root
- Perfect Squares and Their Square Roots
- Is the Square Root of 16 Rational or Irrational?
- Applications of the Square Root of 16 in Real Life
- Examples and Problem-Solving
- Visualizing the Square Root of 16
- Comparing Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 16
- Exploring Related Concepts: Exponents and Roots
- FAQs about the Square Root of 16
- Common Misconceptions about Square Roots
- YOUTUBE: Xem video để khám phá bí ẩn của căn bậc hai 16 và cách biểu diễn nó dưới dạng gốc.
Understanding the Square Root of 16 in Radical Form
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For the number 16, its square root in radical form is expressed as .
Calculation and Simplification
The radical form simplifies to:
- First, identify that 16 is a perfect square.
- Since , we can simplify to 4.
Therefore, .
Prime Factorization Method
We can also determine the square root of 16 using prime factorization:
- Prime factorize 16: .
- Group the factors in pairs: and .
- Each pair’s square root is .
So, by prime factorization.
Long Division Method
The long division method can also be used to find the square root of 16:
- Start by pairing the digits of the number from right to left. For 16, we consider it as a whole number.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 16. This number is 4, because .
- Therefore, the quotient 4 is the square root of 16.
Hence, using long division.
Properties of the Square Root of 16
- The square root of 16 is a rational number because it simplifies to a whole number, 4.
- Since 16 is a perfect square, its square root is a positive integer.
- The simplified radical form remains .
Examples and Applications
- Example 1: Simplify the expression .
Solution: Substituting gives . - Example 2: Solve for in the equation .
Solution: Simplifying , we get . Thus, . - Example 3: Simplify the expression .
Solution: Substituting gives .

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Roots and Radical Form
The concept of square roots is fundamental in mathematics. The square root of a number is a value which, when multiplied by itself, yields the original number. In radical form, the square root is represented using the radical symbol (√). For instance, the square root of 16 in radical form is written as .
Here are key points to understand about square roots and radical form:
- Definition: The square root of a number \( x \) is a number \( y \) such that \( y^2 = x \). In radical form, it is expressed as .
- Perfect Squares: Numbers like 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because their square roots are whole numbers (e.g., ).
- Non-Perfect Squares: Numbers that do not have whole numbers as their square roots. Their square roots are often expressed in simplified radical form or as decimals.
The radical form provides a compact way to represent roots, especially useful when dealing with non-perfect squares. To simplify a square root in radical form:
- Identify Perfect Squares: Check if the number is a perfect square. For example, 16 is a perfect square because \( 4 \times 4 = 16 \).
- Simplify: If the number is a perfect square, its square root is an integer. Thus, .
- Use Prime Factorization: For non-perfect squares, factorize the number into primes and simplify the radicals accordingly.
The use of radical form extends beyond simple square roots to other roots and is a crucial tool in algebra and higher-level mathematics.
What is the Square Root of 16?
The square root of 16 is a fundamental concept in mathematics that provides insight into how numbers work. The square root function, denoted by the radical symbol √, asks for a number which, when multiplied by itself, results in the given number. For 16, the square root is 4 because 4 × 4 equals 16. This relationship is crucial in various areas of mathematics, including algebra and geometry.
Understanding Square Roots
Square roots are essential in solving quadratic equations and analyzing geometric shapes. They help in understanding the properties of numbers and their behavior under multiplication. The square root of any positive number has two values: one positive and one negative. For example, both 4 and -4 are square roots of 16, but in most practical applications, the positive root is used.
Expressing Square Root of 16 in Radical Form
- The simplest radical form of the square root of 16 is √16.
- Simplifying √16, we find that it equals 4, as 16 is a perfect square (4² = 16).
Steps to Find the Square Root of 16
- Start by identifying the number whose square root is required, which is 16.
- Look for a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 16. This number is 4 because 4 × 4 = 16.
- Express this in the simplest radical form as √16 = 4.
Applications of the Square Root of 16
Understanding the square root of 16 is useful in various practical contexts. For instance, it is crucial in geometry for calculating the side length of a square with an area of 16 square units. It is also used in algebra for simplifying equations and understanding the nature of numbers.
Additional Insights
- 16 is a perfect square because its square root is an integer.
- The square root of 16 is also used in higher mathematics, including calculus and number theory.
- When using the square root in calculations, always consider both the positive and negative roots, especially in equations.
In conclusion, the square root of 16 is 4, a fundamental mathematical fact with wide-ranging applications and significance.
Understanding Radical Form
The radical form is a way of expressing numbers that involve roots, such as square roots or cube roots. It uses the radical symbol (√) to denote the root and simplifies the representation of these values. For example, the square root of 16 in radical form is written as . This notation is especially useful in various mathematical contexts, from basic algebra to advanced calculus.
Components of Radical Form
- Radical Symbol (√): The symbol used to denote the root.
- Radicand: The number under the radical symbol. In , the radicand is 16.
- Index: Indicates the degree of the root. For square roots, the index is typically 2 and is often omitted. For cube roots, the index is 3, written as .
Steps to Simplify Radical Form
- Identify the Radicand: Start by examining the number under the radical sign. For example, in , the radicand is 16.
- Prime Factorization: Break down the radicand into its prime factors. For 16, we have .
- Pair the Factors: Group the factors into pairs. Each pair will simplify to a single number outside the radical. In this case, simplifies to 4.
- Rewrite the Radicand: Any factors not paired remain under the radical. Since all factors of 16 are paired, it simplifies completely to 4.
Thus, because 16 is a perfect square.
Examples of Radical Form
- Square Root of 25: Written as , it simplifies to 5 since .
- Cube Root of 27: Expressed as , it simplifies to 3 since .
- Fourth Root of 16: Represented as , it simplifies to 2 because .
Uses and Applications
Radical forms are prevalent in many fields of mathematics and science. They are used to solve equations, simplify expressions, and model real-world phenomena. Understanding how to work with radicals is crucial for progressing in mathematical studies and solving complex problems efficiently.
Calculating the Square Root of 16
The process of calculating the square root of a number, such as 16, involves finding a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 16 is 4 because 4 × 4 equals 16. Here's a step-by-step guide to understanding and calculating the square root of 16 using different methods:
Method 1: Direct Calculation
- Identify the Number: Start with the number for which you want to find the square root, which is 16.
- Perfect Square Recognition: Recognize that 16 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as 4 × 4.
- Write in Radical Form: The square root of 16 is written in radical form as .
- Simplify: Since 16 is a perfect square, its square root simplifies to 4. Therefore, .
Method 2: Prime Factorization
- Factorize the Number: Break down 16 into its prime factors. The prime factorization of 16 is .
- Pair the Factors: Group the factors into pairs: .
- Extract the Pairs: Each pair of factors simplifies to a single factor outside the radical. So, .
- Conclude the Result: Thus, the square root of 16, using prime factorization, is 4.
Method 3: Estimation and Refinement
- Estimate: Start with a rough estimate. Since 16 is close to 4², we estimate the square root of 16 to be around 4.
- Refine the Estimate: Use the method of successive averages. For 16, since our initial guess is 4 and 16/4 equals 4, the average remains 4.
- Iterate if Necessary: Repeat the averaging process if the estimate was not precise. In this case, since 16/4 is exactly 4, no further iteration is needed.
- Confirm the Result: Therefore, the refined estimate confirms that the square root of 16 is 4.
Understanding the Result
The result of the square root of 16, which is 4, can be visualized and confirmed through various methods. Whether by direct calculation, prime factorization, or iterative refinement, the value consistently simplifies to 4. Recognizing 16 as a perfect square simplifies the process considerably.
This foundational concept is not only useful in arithmetic and algebra but also forms the basis for more advanced mathematical theories and applications. Knowing how to calculate and simplify square roots is a key skill in mathematics.
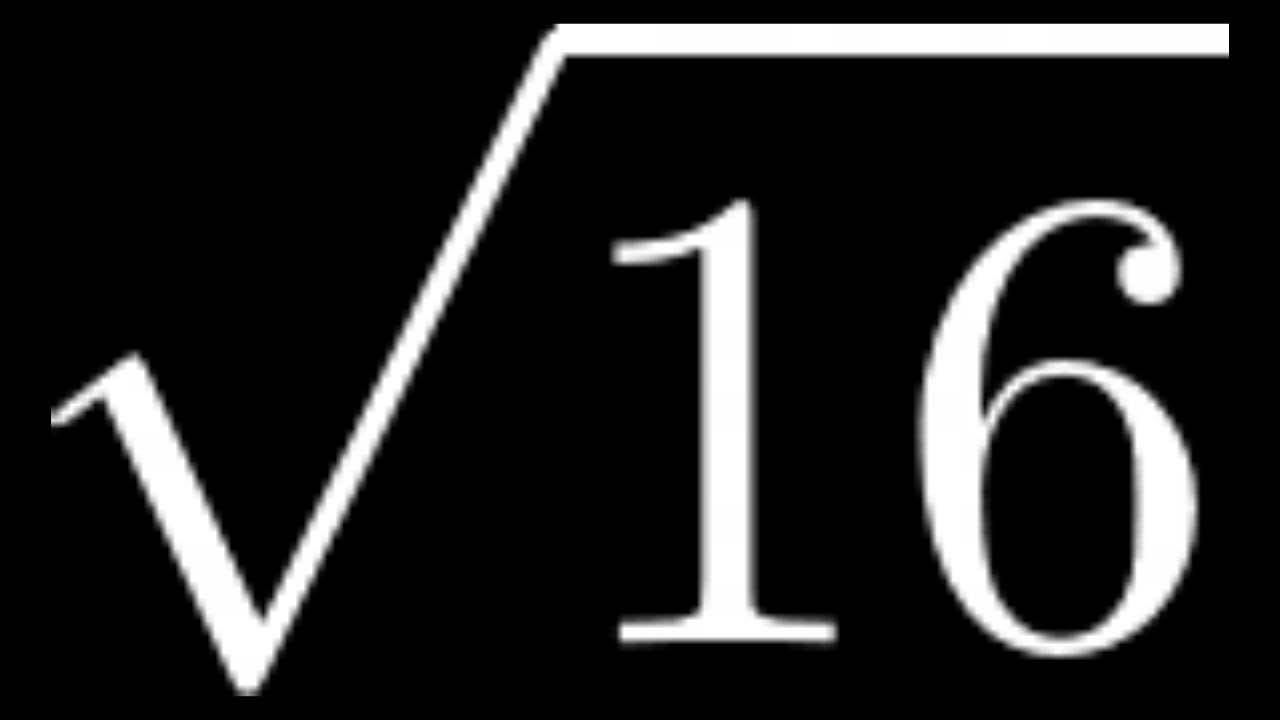
Simplification of the Radical Form √16
Simplifying the radical form of a number involves reducing the expression to its simplest form. For the square root of 16, this process is straightforward because 16 is a perfect square. Here's a detailed step-by-step guide to simplify √16:
Step-by-Step Simplification
- Write the Radical Form:
Start by expressing the number in radical form: .
- Identify the Perfect Square:
Determine if the number under the radical, known as the radicand, is a perfect square. In this case, 16 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as the square of an integer: .
- Simplify the Radical:
Apply the property of square roots which states that . Since , we have .
- Express the Simplified Form:
Therefore, the simplified form of is 4. This simplification shows that the square root of 16 is an integer.
Visual Representation
To further understand the simplification, consider the visual representation of the square root:
- Geometric Interpretation:
In geometry, the square root of 16 represents the side length of a square with an area of 16 square units. Since the area of a square is given by side × side, and , the side length is 4.
Alternative Methods for Simplification
Beyond direct calculation, other methods can simplify the radical form:
- Prime Factorization:
Break down 16 into its prime factors: . Group these into pairs: . Taking the square root of each pair yields .
- Using Exponents:
Express 16 as a power of 2: . Applying the square root to an exponent, we use the rule . Therefore, .
Applications and Relevance
Understanding the simplification of radicals is vital in various fields of mathematics and science. It simplifies solving equations, facilitates computations in algebra, and aids in understanding geometric properties. The ability to simplify radicals quickly and accurately is a fundamental skill that supports more advanced mathematical learning and problem-solving.
Using Prime Factorization to Find the Square Root
Prime factorization is a method used to express a number as the product of its prime factors. This method is particularly useful for simplifying square roots, as it allows us to break down the radicand into smaller components. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide to finding the square root of 16 using prime factorization:
Step-by-Step Guide
- Identify the Number:
Begin with the number whose square root you want to find, in this case, 16.
- Factorize the Number into Prime Factors:
Break down 16 into its prime factors. The prime factorization of 16 is:
. - Group the Prime Factors:
Next, group the prime factors into pairs. For 16, the prime factors are paired as:
. - Simplify Each Pair:
Take one factor from each pair out of the radical. Since we have two pairs of 2s, each pair simplifies to a single 2:
. - Express the Simplified Form:
Therefore, the square root of 16 simplifies to 4:
.
Visual Representation
To better understand the process, consider the following table that shows the step-by-step prime factorization and simplification of 16:
| Step | Prime Factors | Grouping | Simplification |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identify the Number | 16 | — | — |
| Factorize into Primes | — | — | |
| Group the Factors | — | — | |
| Simplify Each Pair | — | — |
Advantages of Prime Factorization
- Systematic Approach: Prime factorization provides a structured way to simplify square roots, especially when dealing with larger numbers.
- Applicable to Non-Perfect Squares: While 16 is a perfect square, prime factorization is also helpful for simplifying the square roots of non-perfect squares.
- Foundation for Advanced Concepts: Understanding prime factorization is essential for higher-level mathematics, including algebra and number theory.
By mastering prime factorization, you can simplify square roots and other radicals efficiently, providing a strong foundation for further mathematical exploration and problem-solving.
Perfect Squares and Their Square Roots
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer multiplied by itself. For example, 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because they are the squares of 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 respectively.
The square root of a perfect square is the value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original perfect square. For instance, the square root of 16 is 4 because 4 multiplied by itself equals 16.
Here's a list of some common perfect squares and their corresponding square roots:
| Perfect Square | Square Root |
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
| 25 | 5 |
| 36 | 6 |
| 49 | 7 |
| 64 | 8 |
It's important to familiarize yourself with these perfect squares and their square roots as they are fundamental in various mathematical concepts and applications.
Is the Square Root of 16 Rational or Irrational?
The square root of 16, denoted as √16, is rational. This is because 16 is a perfect square, meaning it can be expressed as the square of an integer, which in this case is 4.
When a number is a perfect square, its square root is rational, as it can be expressed as a fraction of two integers. In the case of √16, it equals 4, which can be written as 4/1, making it a rational number.

Applications of the Square Root of 16 in Real Life
The square root of 16 has numerous applications in real-life scenarios, particularly in fields such as:
- Engineering: In engineering, the square root of 16 is used in calculations involving measurements, dimensions, and geometric properties. For example, it can be used to calculate the dimensions of a square with an area of 16 square units.
- Construction: In construction, understanding the square root of 16 is essential for determining measurements, angles, and proportions. It helps architects and builders ensure accuracy and precision in their designs and constructions.
- Finance: In finance, the square root of 16 may be utilized in various financial calculations, such as determining interest rates, mortgage payments, or investment returns. It aids in understanding the relationships between different financial variables.
- Technology: In technology, the square root of 16 can be involved in programming algorithms, signal processing, and digital image processing. It plays a role in data analysis, encryption techniques, and error correction.
- Education: Understanding the square root of 16 is crucial in mathematics education, particularly for teaching basic concepts of square roots, perfect squares, and numerical operations. It forms the foundation for more advanced mathematical topics.
These are just a few examples of how the square root of 16 is applied in real-life situations, highlighting its significance across various fields and disciplines.
Examples and Problem-Solving
Let's explore some examples and problem-solving scenarios involving the square root of 16:
- Example 1: Calculate the square root of 16.
- Example 2: Find the length of one side of a square with an area of 16 square units.
- Example 3: Determine if 16 is a perfect square.
- Example 4: Express √16 in radical form.
We know that the square root of 16 is 4 because 4 multiplied by itself equals 16.
To find the length of one side, we take the square root of the area. Therefore, the length of one side is √16, which equals 4 units.
Yes, 16 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as 4 multiplied by 4, making it a square of the integer 4.
√16 can be expressed as 4 in radical form.
These examples demonstrate the practical application of the square root of 16 and how it can be utilized in various problem-solving situations.
Visualizing the Square Root of 16
Visualizing the square root of 16 can help in understanding its significance and properties. Here are some ways to visualize it:
- Geometrically: Imagine a square with an area of 16 square units. Each side of the square would measure 4 units since 4 multiplied by 4 equals 16. The square root of 16, represented as √16, corresponds to the length of one side of this square.
- On a Number Line: On a number line, you can locate √16 at the point where the value is 4. This illustrates that the square root of 16 is 4, indicating the distance from zero on the number line.
- Using Math Concepts: Understanding the properties of perfect squares can aid in visualizing the square root of 16. Recognizing that 16 is the result of 4 multiplied by 4 helps in comprehending that the square root of 16 is 4.
Visualizing the square root of 16 enhances conceptual understanding and facilitates problem-solving in various mathematical contexts.
Comparing Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 16
Various methods can be employed to calculate the square root of 16. Let's compare some common approaches:
- Using Multiplication: One straightforward method is to find a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 16. In this case, it's evident that 4 multiplied by 4 equals 16, so the square root of 16 is 4.
- Prime Factorization: Another method involves prime factorization. By breaking down 16 into its prime factors (2 × 2 × 2 × 2), we can pair them up to find the square root. Since there are two pairs of 2s, the square root is 2 × 2 = 4.
- Estimation: Estimation can also be used to approximate the square root of 16. By recognizing that 16 is between the squares of 3 and 4 (9 and 16, respectively), we can infer that the square root is closer to 4.
- Using Calculator: For quick and accurate results, a calculator can be used to directly compute the square root of 16. Most calculators will yield 4 as the square root.
These methods offer different approaches to calculating the square root of 16, catering to varying preferences and situations.

Exploring Related Concepts: Exponents and Roots
Understanding the relationship between exponents and roots is crucial in mathematics. Here's how exponents and roots are related:
- Exponents: An exponent represents the number of times a base is multiplied by itself. For example, 23 means 2 multiplied by itself three times, resulting in 8.
- Roots: A root, such as a square root (√) or cube root (∛), is the inverse operation of raising a number to a certain exponent. It finds the original number that was raised to the given power. For instance, √16 is the number that, when squared, equals 16.
- Relationship: The relationship between exponents and roots can be expressed as follows: Taking the square root (√) of a number is equivalent to raising that number to the power of 1/2. Similarly, taking the cube root (∛) is equivalent to raising the number to the power of 1/3.
- Application: Understanding exponents and roots is essential for various mathematical operations, such as simplifying expressions, solving equations, and calculating areas and volumes in geometry.
By exploring these related concepts, you can deepen your understanding of the fundamental principles underlying mathematical operations involving exponents and roots.
FAQs about the Square Root of 16
Here are some frequently asked questions about the square root of 16:
- What is the square root of 16?
- Is the square root of 16 a whole number?
- Is the square root of 16 rational or irrational?
- What is the radical form of the square root of 16?
- How is the square root of 16 useful in real life?
The square root of 16 is 4. This is because 4 multiplied by itself equals 16.
Yes, the square root of 16 is a whole number. It is precisely 4, which is an integer.
The square root of 16 is rational. This is because 16 is a perfect square, and its square root can be expressed as a fraction of two integers.
The radical form of the square root of 16 is √16, which equals 4.
The square root of 16 has various applications in fields such as engineering, construction, finance, technology, and education. It helps in calculations, measurements, and problem-solving tasks.
These FAQs provide insights into the square root of 16 and its significance in mathematics and real-world contexts.
Common Misconceptions about Square Roots
Despite being a fundamental mathematical concept, square roots can sometimes be misunderstood. Here are some common misconceptions:
- Square roots always result in two answers:
- Square roots of negative numbers are not real:
- Square roots are always irrational:
- Square roots only apply to whole numbers:
This is not true. While every positive number has two square roots (one positive and one negative), when referring to the principal square root, we typically mean the positive square root. For example, the principal square root of 16 is 4, not -4.
Although the square root of a negative number is not a real number, it is still a valid mathematical concept. These roots are called imaginary numbers and play a crucial role in advanced mathematics, particularly in fields like complex analysis and electrical engineering.
While many square roots are indeed irrational (meaning they cannot be expressed as a simple fraction), there are exceptions. The square roots of perfect squares, such as √4 or √9, are rational numbers. In fact, the square root of 16, which is 4, is also rational.
This is not accurate. Square roots can be applied to any non-negative real number, including fractions and decimals. For example, the square root of 0.25 is 0.5.
By dispelling these misconceptions, we can gain a clearer understanding of square roots and their significance in mathematics.
Xem video để khám phá bí ẩn của căn bậc hai 16 và cách biểu diễn nó dưới dạng gốc.
Canh Bạc Của 16: Sự Hấp Dẫn Của Căn Bậc Hai
READ MORE:
Xem video để tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 16 và biểu diễn nó dưới dạng gốc.
Cách Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 16: sqrt(16)