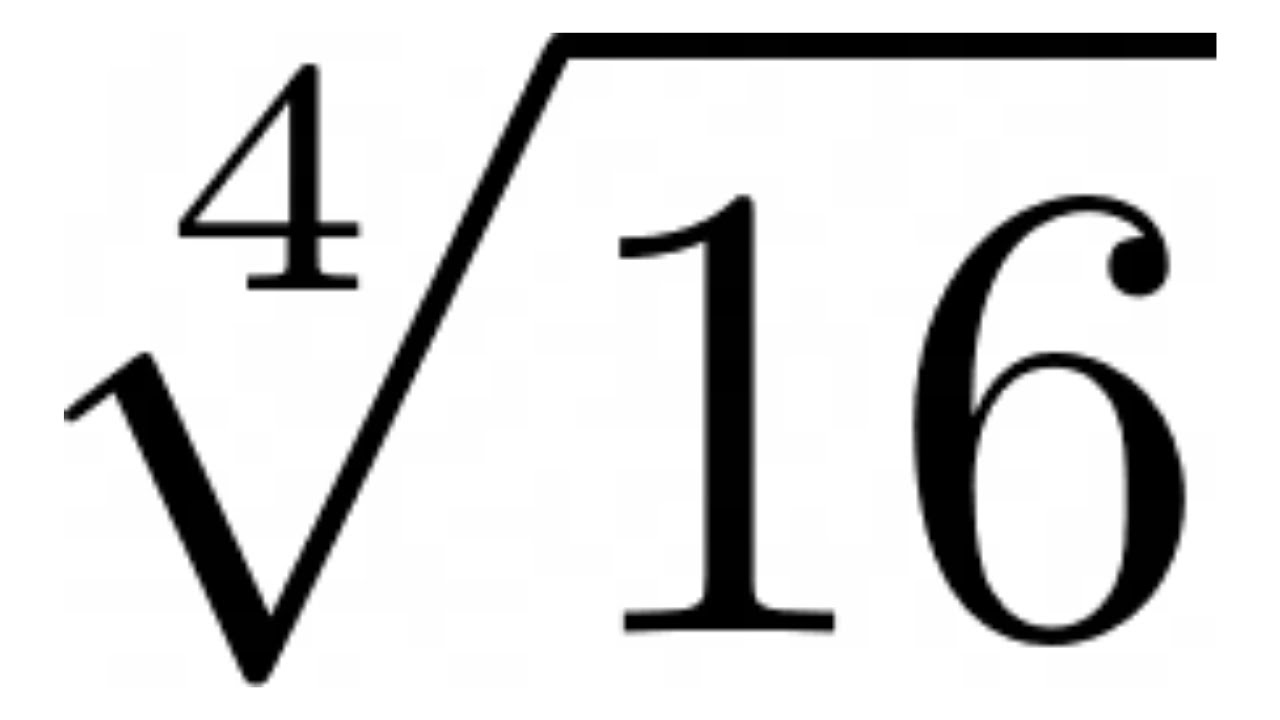Topic square root of 1640: The square root of 1640 is an interesting mathematical concept. It is approximately 40.4969, a value which, when multiplied by itself, equals 1640. This article will explore various methods to calculate the square root of 1640, its properties, and its applications in different contexts, ensuring a comprehensive understanding for learners and enthusiasts.
Table of Content
Square Root of 1640
The square root of 1640 is a number that, when multiplied by itself, gives the result of 1640. Mathematically, this can be represented as:
\[\sqrt{1640} = 40.4969134626\]
Definition
The square root of 1640 can be expressed using the radical sign, like this: \(\sqrt{1640}\). This number, approximately 40.497, is not a perfect square and hence is considered an irrational number.
Calculation Methods
To calculate the square root of 1640, you can use various methods:
- Calculator: Simply enter 1640 and press the square root (√) key to get the result.
- Spreadsheet Software: Use the SQRT function in Excel or Google Sheets:
=SQRT(1640). - Manual Calculation: Use the long division method or iterative approximation techniques.
Simplified Radical Form
The square root of 1640 in its simplest radical form is:
\[\sqrt{1640} = 2\sqrt{410}\]
Rational or Irrational?
Since 1640 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number. This means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
Approximation and Rounding
The square root of 1640 rounded to different decimal places is:
- To the nearest tenth: 40.5
- To the nearest hundredth: 40.50
- To the nearest thousandth: 40.497
Table of nth Roots
| Index | Radicand | Root Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 1640 | \(\sqrt[2]{1640}\) | ±40.4969134626 |
| 3 | 1640 | \(\sqrt[3]{1640}\) | 11.7927370799 |
| 4 | 1640 | \(\sqrt[4]{1640}\) | ±6.3637185248 |
| 5 | 1640 | \(\sqrt[5]{1640}\) | 4.3951000886 |
| 6 | 1640 | \(\sqrt[6]{1640}\) | ±3.4340554859 |
| 7 | 1640 | \(\sqrt[7]{1640}\) | 2.8791441343 |
| 8 | 1640 | \(\sqrt[8]{1640}\) | ±2.5226411803 |
| 9 | 1640 | \(\sqrt[9]{1640}\) | 2.2761709276 |
| 10 | 1640 | \(\sqrt[10]{1640}\) | ±2.0964494004 |
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 1640
The square root of 1640 is a number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 1640. This value is approximately 40.4969134626. Understanding the square root of a number is crucial in various mathematical contexts, from solving equations to understanding geometric properties.
Here are some key details about the square root of 1640:
- Notation: The square root of 1640 can be written as √1640 or 16401/2.
- Principal Square Root: The principal square root is the positive value, approximately 40.497.
- Negative Square Root: There is also a negative square root, which is -40.497.
- Rational or Irrational: The square root of 1640 is an irrational number, as it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
To find the square root of 1640 manually, one could use methods such as prime factorization or the long division method. However, with modern tools, using a calculator or a computer program like Excel (using the formula =SQRT(1640)) makes this calculation straightforward and quick.
The value of the square root of 1640 is significant in various applications, from scientific calculations to everyday problem-solving, demonstrating the importance and utility of understanding square roots in mathematics.
Definition and Calculation
The square root of 1640 is a mathematical operation that finds a number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 1640. This can be represented as \( \sqrt{1640} \). The square root of 1640 is approximately 40.4969134626.
To find the square root of 1640, you can use various methods such as using a calculator, applying the long division method, or using mathematical software like Excel or Google Sheets.
Here is a step-by-step guide to calculate the square root of 1640:
- List the factors of 1640: 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20, 40, 41, 82, 164, 205, 328, 410, 820, 1640.
- Identify the perfect squares among the factors: In this case, the perfect squares are 1 and 4.
- Divide 1640 by the largest perfect square: \( 1640 / 4 = 410 \).
- Calculate the square root of the perfect square: \( \sqrt{4} = 2 \).
- Combine the results: \( \sqrt{1640} = 2 \sqrt{410} \).
This shows that \( \sqrt{1640} \) can be simplified to \( 2 \sqrt{410} \).
You can also find the square root using a calculator by simply entering 1640 and pressing the square root button, giving you the result of approximately 40.4969134626.
In exponential form, the square root of 1640 is represented as \( 1640^{\frac{1}{2}} \).
Properties of the Square Root
The square root of 1640 is a fascinating number with various properties. Understanding these properties helps in grasping the significance and applications of square roots in mathematics. Below, we detail some key properties of the square root of 1640:
- Definition: The square root of 1640, denoted as √1640, is the number which, when multiplied by itself, equals 1640. Mathematically, √1640 ≈ 40.4969.
- Principal Square Root: The principal square root of 1640 is the positive value, approximately 40.4969.
- Negative Square Root: The negative counterpart is -40.4969, since both (40.4969)^2 and (-40.4969)^2 equal 1640.
- Irrational Number: The square root of 1640 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has an infinite, non-repeating decimal expansion.
- Radical Form: In its simplified radical form, the square root of 1640 can be expressed as 2√410, showing that 1640 can be broken down into factors of 4 and 410.
- Exponent Form: The exponent form of the square root of 1640 is 16401/2, a common way to denote roots in algebra.
Below is a table illustrating different properties and forms of the square root of 1640:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Principal Square Root | 40.4969 |
| Negative Square Root | -40.4969 |
| Radical Form | 2√410 |
| Exponent Form | 16401/2 |
Understanding these properties aids in comprehending how square roots function and their relevance in various mathematical contexts.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root
Calculating the square root of 1640 can be done using various methods, both manually and with technological tools. Below are the detailed steps and methods:
- Using a Calculator: The simplest method is to use a calculator. Enter 1640 and press the square root (√) button. The result is approximately 40.4969.
- Using a Computer: Software like Excel or Google Sheets can be used to calculate the square root by using the SQRT function. For example, in Excel, type
=SQRT(1640)to get the result 40.4969134626. - Long Division Method:
- Pair the digits of 1640 from right to left: 16 and 40.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 16, which is 4.
- Subtract 16 from 16 to get 0 and bring down the next pair of digits (40).
- Double the number (4) and find the largest digit (X) such that 8X * X is less than or equal to 40. The digit is 0.
- Repeat the process with additional decimal places as needed.
- Prime Factorization: Break down 1640 into its prime factors and simplify under the square root. However, 1640 is not a perfect square, so it simplifies as
2√410.
Each method provides a way to understand and verify the square root calculation, ensuring accuracy and comprehension.

Perfect Square Check
Calculating the square root of a number, such as 1640, can be approached using several methods. Below, we outline two common techniques: the Long Division Method and the Prime Factorization Method.
Long Division Method
The Long Division Method is particularly useful for finding the square root of non-perfect squares. Here are the steps:
- Pair the Digits: Starting from the decimal point, pair the digits of the number 1640. If there is an odd number of digits, the leftmost digit will form a pair with a zero.
- Find the Largest Square: Determine the largest square smaller than or equal to the leftmost pair. Subtract this square from the pair and bring down the next pair of digits.
- Double the Quotient: Double the quotient found so far. This is used as part of the divisor in the next step.
- Form the New Divisor: Determine a digit to append to the doubled quotient such that the new number, when multiplied by this digit, is less than or equal to the dividend.
- Repeat: Continue this process until you have processed all digit pairs.
The result after using the Long Division Method for √1640 is approximately 40.497.
Prime Factorization Method
The Prime Factorization Method is often used for perfect squares. Since 1640 is not a perfect square, this method is less applicable, but here's a brief outline:
- Prime Factors: Factorize the number into its prime factors. For example, \( 1640 = 2^3 \times 5 \times 41 \).
- Pair the Factors: Pair the prime factors to simplify. If each factor can be paired, the number is a perfect square.
- Simplify: Calculate the product of the pairs to find the square root.
Since 1640 cannot be perfectly paired into squares, it confirms that the number is not a perfect square, making this method less straightforward for non-perfect squares.
Using a calculator or software tools such as Excel or Google Sheets can also help quickly determine square roots:
- Excel/Google Sheets: Use the formula
=SQRT(1640)or=POWER(1640, 1/2)to get the result, 40.496913462633.
These methods provide a comprehensive understanding of how to calculate and verify the square root of 1640.
Decimal and Fractional Representation
The square root of 1640 can be represented both in decimal and fractional forms. Let's explore these representations step by step:
Decimal Representation
The decimal representation of the square root of 1640 can be found using a calculator or computer:
- Enter 1640 into the calculator or use a software tool like Excel or Google Sheets.
- Use the square root function to find the result.
The square root of 1640 in decimal form is approximately:
\(\sqrt{1640} \approx 40.49691\)
Fractional Representation
To express the square root of 1640 in fractional form, we consider the simplified radical form obtained earlier and approximate it:
- The simplified radical form is \(2\sqrt{410}\).
- Approximate \(\sqrt{410}\) to a fraction:
- \(\sqrt{410} \approx 20.248\)
- Thus, \(2\sqrt{410} \approx 2 \times 20.248 = 40.496\)
- We can write \(40.496\) as a fraction:
- Convert the decimal to a fraction: \(\frac{40496}{1000}\)
- Simplify the fraction by finding the greatest common divisor (GCD) of 40496 and 1000, which is 8.
- \(\frac{40496 \div 8}{1000 \div 8} = \frac{5062}{125}\)
So, the square root of 1640 can be approximated as a fraction:
\(\sqrt{1640} \approx \frac{5062}{125}\)
Exponent Representation
Representing the square root of 1640 using exponents involves expressing it in the form of a power. Let's explore this representation step by step:
In general, the square root of a number can be written as that number raised to the power of \( \frac{1}{2} \). For the square root of 1640, we have:
\[\sqrt{1640} = 1640^{\frac{1}{2}}\]
Simplified Exponent Form
We can also express 1640 in terms of its prime factors and then apply the exponent:
- First, recall the prime factorization of 1640:
- 1640 = 2^3 \times 5 \times 41
- Next, apply the exponent \( \frac{1}{2} \) to each prime factor:
\[\sqrt{1640} = (2^3 \times 5 \times 41)^{\frac{1}{2}}\]
- Distribute the exponent \( \frac{1}{2} \) to each factor:
\[(2^3)^{\frac{1}{2}} \times 5^{\frac{1}{2}} \times 41^{\frac{1}{2}}\]
- Simplify the expression:
\[2^{3 \cdot \frac{1}{2}} \times 5^{\frac{1}{2}} \times 41^{\frac{1}{2}}\]
\[2^{1.5} \times 5^{0.5} \times 41^{0.5}\]
Thus, the exponent representation of the square root of 1640 is:
\[1640^{\frac{1}{2}} = 2^{1.5} \times 5^{0.5} \times 41^{0.5}\]
Practical Applications
The square root of 1640 has several practical applications across different fields. Let's explore some of these applications step by step:
1. Engineering and Architecture
Engineers and architects often use square roots in their calculations to determine various measurements and dimensions. For instance:
- Calculating the diagonal length of a square or rectangular component.
- Determining the magnitude of forces acting at different angles.
In these cases, the square root of 1640 might be used to calculate specific lengths or forces in design and structural analysis.
2. Physics
In physics, the square root is frequently used in formulas involving energy, velocity, and distance. Some examples include:
- Determining the root mean square speed of gas molecules in thermodynamics.
- Calculating the displacement in wave mechanics where the square root function is involved.
For example, if a calculation involves the square root of 1640, it might relate to specific energy levels or wave properties in a physical system.
3. Finance and Economics
In finance, the square root function is used to model different economic phenomena. Applications include:
- Calculating standard deviation and variance in portfolio management.
- Modeling the growth rate of investments over time.
Using the square root of 1640 in these calculations helps financial analysts assess risk and predict future financial performance.
4. Computer Science
Square roots are essential in computer algorithms, particularly in areas such as cryptography, graphics, and numerical methods:
- Optimizing search algorithms that require distance calculations.
- Generating random numbers and encryption keys in cryptographic protocols.
For example, the square root of 1640 might be used in a program to compute distances between points in a multidimensional space or in secure data transmission protocols.
5. Everyday Life
Square roots are also used in various everyday scenarios, such as:
- Estimating the time required to travel a certain distance based on speed.
- Calculating the dimensions of a piece of land or a garden plot.
Understanding the square root of 1640 can help in making quick and accurate estimations in daily activities, contributing to more efficient problem-solving.
Overall, the square root of 1640 is a valuable tool across numerous domains, helping professionals and individuals perform accurate calculations and make informed decisions.
100615-1640_230615-1016_230615-1332 - Video Hướng Dẫn Toàn Diện
READ MORE:
100615-1640_230615-1016_230615-1332 - Video Hướng Dẫn Chi Tiết