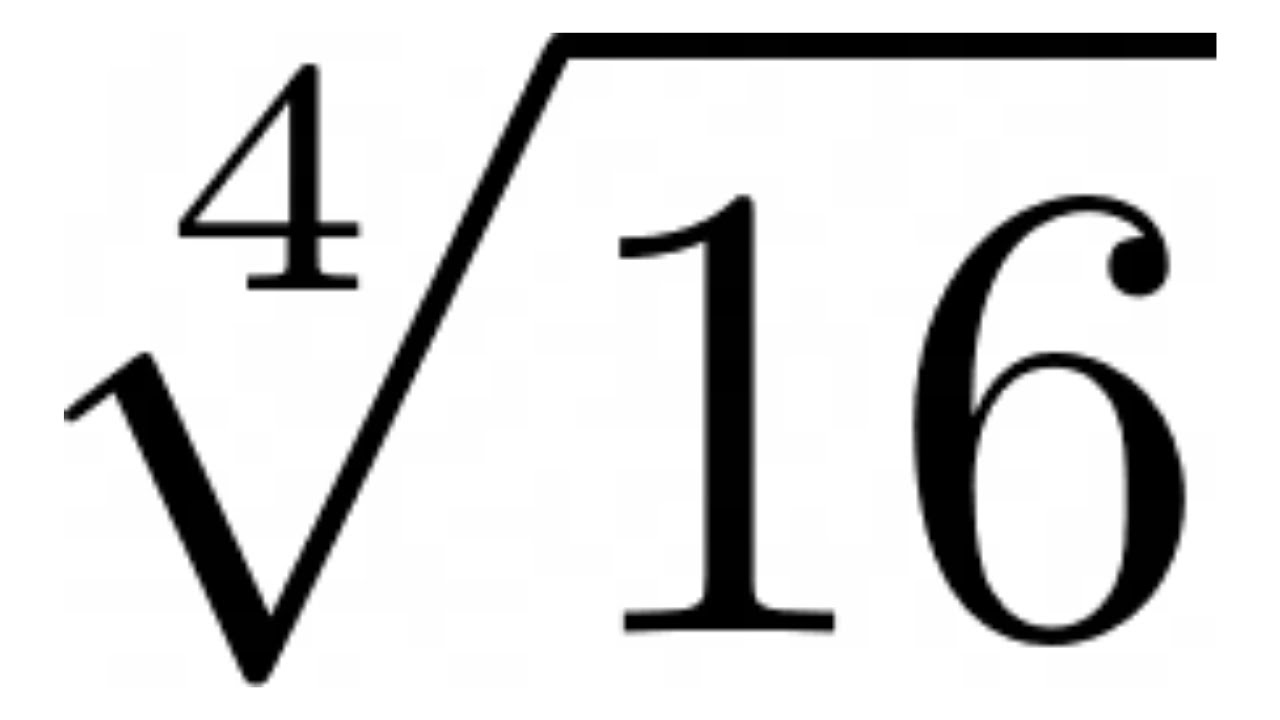Topic square root of 16 is a rational number: The square root of 16 is a rational number, offering a clear example of fundamental mathematical principles. This article explores why √16 equals 4, making it a rational number, and delves into various methods to calculate and understand this essential concept. Discover the simplicity and logic behind this perfect square.
Table of Content
- Understanding the Square Root of 16
- Introduction
- Definition of Square Root
- Understanding the Square Root of 16
- Why 16 is a Perfect Square
- Rational and Irrational Numbers
- Applications of Square Root of 16
- Solved Examples
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Conclusion
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá căn bậc hai của 16 trong video này. Tìm hiểu các phương pháp tính toán và ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai.
Understanding the Square Root of 16
The square root of 16 is a fundamental mathematical concept that is both simple and insightful. This article explores various aspects of the square root of 16, including its value, rationality, and methods of calculation.
Value of the Square Root of 16
The square root of 16 is 4. This is because 4 multiplied by itself (4 × 4) equals 16. Mathematically, this is represented as:
\[\sqrt{16} = 4\]
Why is the Square Root of 16 Rational?
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction of two integers. Since the square root of 16 is 4, which can be written as 4/1, it is considered a rational number. Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Prime factorization of 16: \(2^4\)
- The square root is: \(2^2 = 4\)
- Since 4 is an integer, the square root of 16 is rational.
Methods to Find the Square Root of 16
- Prime Factorization Method:
Prime factorization involves breaking down 16 into its prime factors:
\[16 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 = (2^2)^2\]
Taking the square root gives us:
\[\sqrt{16} = \sqrt{(2^2)^2} = 2^2 = 4\]
- Long Division Method:
The long division method involves dividing 16 into smaller parts to find the square root. Here are the steps:
- Pair the digits from right to left (16).
- Find a number that, when squared, is less than or equal to 16 (4 × 4 = 16).
- Since 4 × 4 equals 16 exactly, the quotient is 4.
Examples
- Example 1: Simplify the expression \(7\sqrt{16} + 15\).
Solution:
Since \(\sqrt{16} = 4\), we substitute:
\[7\sqrt{16} + 15 = 7 \times 4 + 15 = 28 + 15 = 43\]
- Example 2: If the area of a square is 16 square units, find the length of one side.
The area \(A\) of a square is given by \(A = s^2\), where \(s\) is the side length. Given \(A = 16\):
\[s = \sqrt{16} = 4\]
Thus, each side of the square is 4 units long.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the value of the square root of 16?
- Why is the square root of 16 a rational number?
Because it can be expressed as a whole number, which is 4.
Understanding the square root of 16 helps in grasping broader mathematical concepts and illustrates the beauty and simplicity of numbers.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 16 is a fundamental concept in mathematics, highlighting its nature as a rational number. Understanding why the square root of 16 is rational involves exploring its definition, calculation methods, and properties. This section will guide you through these aspects, ensuring a clear and detailed understanding.
First, let's define the square root of a number. The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For 16, this value is 4 because 4 × 4 = 16. This makes √16 = 4.
The square root of 16 can be expressed in various forms:
- Radical form: √16
- Exponential form: 16^(1/2)
To determine if the square root of 16 is rational, we consider the nature of rational numbers. A rational number can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, where the denominator is not zero. Since 4 is an integer, √16 = 4 is a rational number.
Several methods can be used to calculate the square root of 16:
- Prime Factorization: By breaking down 16 into its prime factors (2 × 2 × 2 × 2), we pair the factors to get (2 × 2) × (2 × 2). Simplifying, we find √16 = 4.
- Long Division Method: This traditional method involves dividing the number and finding its average, ensuring accuracy.
- Using a Calculator: Simply input 16 and press the square root function to get the result, √16 = 4.
Understanding these methods provides a comprehensive view of why the square root of 16 is a rational number and how it can be calculated efficiently.
Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical notation, the square root of a number a is denoted as √a. The square root function is the inverse operation of squaring a number. For example, since \(4^2 = 16\), the square root of 16 is 4, symbolically written as \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
The principal square root is the nonnegative root. For any positive real number a, its principal square root is denoted by \( \sqrt{a} \) and is always nonnegative.
Key points about square roots:
- The symbol √ is called the radical sign.
- The number under the radical sign is called the radicand.
- A square root can be either positive or negative because both \((4)^2\) and \((-4)^2\) equal 16. However, the principal square root is the nonnegative value.
For example, the square root of 16 can be found as follows:
- Using prime factorization: \( \sqrt{16} = \sqrt{2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2} = 2 \times 2 = 4 \).
- Using a calculator: Enter 16 and press the square root key to get 4.
Therefore, \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), which is a rational number because it can be expressed as a fraction (4/1).
Understanding the Square Root of 16
The square root of 16 is a fundamental mathematical concept that illustrates the idea of a number which, when multiplied by itself, results in 16. In this section, we will explore the definition, properties, and methods to calculate the square root of 16 in a detailed manner.
Definition of Square Root
Mathematically, the square root of a number \(n\) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number \(n\). The square root of 16 can be represented as:
\(\sqrt{16} = 4\)
Why 16 is a Perfect Square
A perfect square is an integer that can be expressed as the product of another integer with itself. Since \(4 \times 4 = 16\), 16 is a perfect square. This property makes its square root an integer.
Rationality of the Square Root of 16
The square root of 16 is a rational number. A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction \(\frac{p}{q}\) where \(p\) and \(q\) are integers and \(q \neq 0\). Since 4 can be expressed as \(\frac{4}{1}\), it is a rational number.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 16
- Prime Factorization Method:
Factorize 16 into prime factors:
\(16 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2\)
Group the prime factors into pairs of two identical factors:
\(\sqrt{16} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2) \times (2 \times 2)} = 2 \times 2 = 4\)
- Long Division Method:
- Pair the digits of 16 starting from the decimal point.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 16, which is 4.
- The quotient obtained is 4, hence the square root of 16 is 4.
- Using Exponents:
The square root can also be represented as an exponent:
\(\sqrt{16} = 16^{1/2} = 4\)
Applications and Examples
Understanding square roots is essential in various fields such as engineering, physics, and statistics. For instance, simplifying expressions like \(7\sqrt{16} + 15\) becomes straightforward when you know that \(\sqrt{16} = 4\).
Example: Simplify \(7\sqrt{16} + 15\).
Solution: \(7 \times 4 + 15 = 28 + 15 = 43\).
Conclusion
The square root of 16 is a simple yet powerful example of mathematical principles in action. By understanding its properties and methods of calculation, we can appreciate the elegance and utility of mathematics in solving real-world problems.
Why 16 is a Perfect Square
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. In other words, if \( n \) is an integer, then \( n^2 \) is a perfect square. For 16, it can be written as:
\[
16 = 4^2
\]
Since 4 is an integer, 16 is the product of an integer multiplied by itself, making 16 a perfect square.
Let's understand why 16 is a perfect square through different methods:
Prime Factorization Method
Prime factorization involves breaking down a number into its prime factors. For 16, the prime factorization is:
\[
16 = 2 \times 2 \times 2 \times 2 = 2^4
\]
To find the square root, we take the square root of both sides:
\[
\sqrt{16} = \sqrt{2^4} = 2^2 = 4
\]
Since 4 is an integer, 16 is confirmed to be a perfect square.
Visual Representation
Another way to understand why 16 is a perfect square is through a visual representation. If we arrange 16 objects in a square formation, we can form a 4x4 grid:
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
This visual clearly shows that the area of this square is \(4 \times 4 = 16\), reinforcing that 16 is a perfect square.
Properties of Perfect Squares
- A perfect square always has an integer as its square root.
- Perfect squares result from multiplying an integer by itself.
- In prime factorization, a perfect square will have even powers of all its prime factors.
Thus, since 16 meets all these criteria, it is indeed a perfect square.
Conclusion
From the prime factorization, visual representation, and properties of perfect squares, it is clear that 16 is a perfect square because it can be expressed as \(4 \times 4\), where 4 is an integer. This makes the square root of 16 a rational number, further confirming its status as a perfect square.
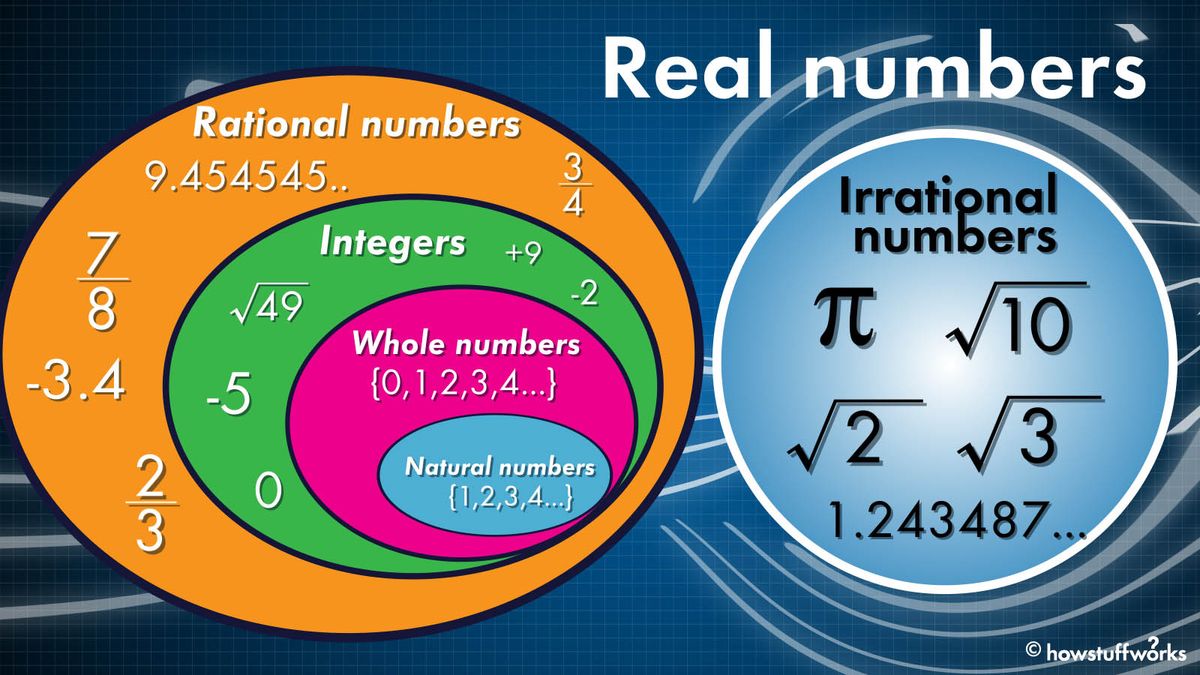
Rational and Irrational Numbers
Numbers can be classified into two main categories: rational and irrational numbers. Understanding these categories helps in comprehending the nature of numbers and their properties.
Rational Numbers
A rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction p/q of two integers, where p and q are integers and q is not zero. In other words, if a number can be written as a fraction with both numerator and denominator as integers, it is a rational number. Examples of rational numbers include:
- 5 (which can be written as 5/1)
- 1.75 (which can be written as 7/4)
- 0.5 (which can be written as 1/2)
- -3 (which can be written as -3/1)
Rational numbers can be either positive or negative, and they include both whole numbers and fractions. They can also be represented as either terminating or repeating decimals.
Irrational Numbers
An irrational number, on the other hand, cannot be written as a simple fraction. These numbers have non-terminating and non-repeating decimal expansions. Examples of irrational numbers include:
- \(\sqrt{2}\)
- \(\pi\)
- \(e\) (Euler's number)
These numbers cannot be accurately expressed as fractions or ratios of integers, which distinguishes them from rational numbers.
Why the Square Root of 16 is Rational
The square root of 16 is a rational number. This is because 16 is a perfect square, and its square root is an integer. Mathematically:
\[
\sqrt{16} = 4
\]
Since 4 can be expressed as the fraction \(\frac{4}{1}\), it is a rational number. Additionally, -4 is also a square root of 16, and since \(\frac{-4}{1}\) is also a rational number, both roots of 16 are rational.
In summary, rational numbers include integers, fractions, and terminating or repeating decimals, while irrational numbers cannot be expressed as simple fractions and have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions.
Applications of Square Root of 16
The square root of 16, which is 4, has a variety of practical applications across different fields. Here are some key applications:
-
Geometry:
In geometry, the square root of 16 is used to determine the side length of a square when the area is known. For example, a square with an area of 16 square units has each side equal to 4 units, because \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
-
Engineering:
Engineers use the square root of 16 in various calculations, such as determining dimensions of components where a square relationship is involved. For instance, in load distribution calculations where areas of square plates or sections are critical, knowing the side length from the area (16 square units) simplifies the process.
-
Architecture:
Architects use the square root of 16 in designing spaces and structures. For example, creating a square garden plot of 16 square meters will have each side measuring 4 meters, ensuring accurate and proportional designs.
-
Everyday Math:
In everyday life, the square root of 16 can be useful in practical situations such as arranging tiles. If you need to tile a square area of 16 square feet, you would need 4 tiles along each side.
-
Finance:
In finance, square roots can be used in various formulas and models, such as calculating the standard deviation in risk assessments. The square root of 16, being 4, could be part of these calculations when evaluating variances and volatilities.
-
Technology:
Technologists and computer scientists use square roots in algorithms and problem-solving. For instance, the square root function is a common operation in graphics and simulation software where precise calculations are necessary.
Understanding the square root of 16 is fundamental in these applications and many others, highlighting its significance in both theoretical and practical contexts.
Solved Examples
Here are some solved examples that illustrate the applications of the square root of 16 in different scenarios:
- Example 1: Arranging Cubes
Imagine you have 16 small cubes and you want to arrange them into a larger square. To find the side length of the larger square, you need to find the square root of 16.
- Calculate the square root of 16: \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
- Therefore, the side length of the larger square is 4 units.
- Example 2: Flower Bed Arrangement
You have a square flower bed with an area of 16 square meters. To find the length of one side of the flower bed, you need to find the square root of the area.
- Calculate the square root of 16: \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \).
- Thus, each side of the flower bed is 4 meters long.
- Example 3: Equilateral Triangle
Suppose you need to find the height of an equilateral triangle with a side length of 4 units (since the side length equals the square root of 16).
- The formula for the height of an equilateral triangle is \( h = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times \text{side length} \).
- Substitute the side length: \( h = \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} \times 4 = 2\sqrt{3} \).
- Therefore, the height of the equilateral triangle is \( 2\sqrt{3} \) units.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is the value of the square root of 16?
The square root of 16 is 4.
-
Why is the square root of 16 a rational number?
When you prime factorize 16, you get \( 2^4 \). Since all the prime factors are in even power, the square root of 16 is a positive integer (4), making it a rational number.
-
How do you evaluate 19 plus 17 times the square root of 16?
The expression is \( 19 + 17 \sqrt{16} \). Knowing that \( \sqrt{16} = 4 \), the calculation is \( 19 + 17 \times 4 = 19 + 68 = 87 \).
-
Is the number 16 a perfect square?
Yes, the prime factorization of 16 is \( 2^4 \), which shows that it is a perfect square because its square root is a whole number (4).
-
What is the value of 17 times the square root of 16?
The square root of 16 is 4. Therefore, \( 17 \sqrt{16} = 17 \times 4 = 68 \).
-
If the square root of 16 is 4, what is the square root of 0.16?
The square root of 0.16 is represented as \( \sqrt{0.16} = \sqrt{\frac{16}{100}} = \frac{\sqrt{16}}{\sqrt{100}} = \frac{4}{10} = 0.4 \).

Conclusion
The square root of 16 is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications. As we've explored, the square root of 16 is 4, a rational number, since it can be expressed as the quotient of two integers. This value is pivotal in various mathematical calculations and real-world scenarios.
We have delved into methods for finding the square root of 16, including the prime factorization method and the long division method. These methods highlight the systematic approach to breaking down and solving square root problems. Additionally, we discussed the significance of 16 being a perfect square, which simplifies its square root to an integer.
Understanding the properties of rational and irrational numbers further clarifies why the square root of 16 is a rational number. This knowledge is essential for comprehending more complex mathematical concepts and for practical applications such as geometry, algebra, and various fields of engineering.
The applications of the square root of 16 extend beyond theoretical mathematics into practical use cases such as calculating areas, dimensions, and optimizing arrangements. Through solved examples, we illustrated how the square root of 16 can be applied to everyday problems, demonstrating its utility and relevance.
In conclusion, mastering the concept of square roots, especially of perfect squares like 16, is crucial for mathematical proficiency. It serves as a building block for more advanced topics and provides a foundation for problem-solving in various disciplines. We hope this comprehensive guide has enhanced your understanding and appreciation of the square root of 16.
Khám phá căn bậc hai của 16 trong video này. Tìm hiểu các phương pháp tính toán và ứng dụng thực tế của căn bậc hai.
Căn Bậc Hai của 16
READ MORE:
Xem video để tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của một số hữu tỉ. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của Một Số Hữu Tỉ