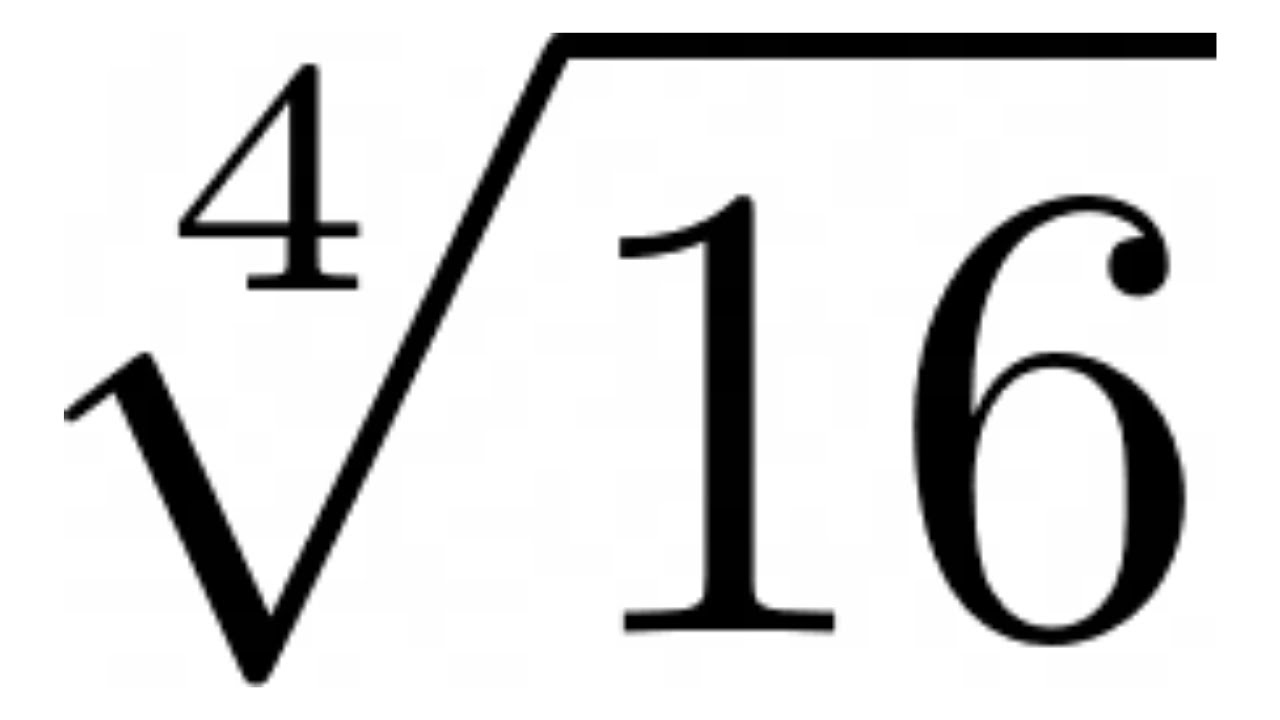Topic square root of 496: The square root of 496 is 22.271. This article delves into the calculation methods, its significance in mathematics, and practical applications. Explore how to compute it manually or using tools like calculators and spreadsheets. Learn why it's an irrational number and its role in various mathematical contexts.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 496
- Introduction
- Definition of Square Root
- Decimal Representation of the Square Root of 496
- Applications of Square Roots
- Calculating Square Roots in Excel and Google Sheets
- Babylonian Method for Finding Square Roots
- Table of Nth Roots of 496
- Table of Square Roots of Numbers Around 496
- YOUTUBE: Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của 496 và ứng dụng của nó trong toán học và cuộc sống hàng ngày. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Square Root of 496
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 496 is approximately 22.27105745132.
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 496
-
Prime Factorization:
Using prime factorization, 496 can be expressed as 24 × 31. Thus, the square root of 496 can be simplified as:
\[\sqrt{496} = \sqrt{2^4 \times 31} = 4\sqrt{31} \approx 22.271\]
-
Long Division Method:
The long division method provides a way to find the square root of 496 by successive approximation, resulting in the value 22.27105745132.
Properties of the Square Root of 496
-
Irrational Number:
The square root of 496 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-terminating and non-repeating.
Examples
-
Solve the equation \(x^2 - 496 = 0\):
\(x = \pm \sqrt{496} \approx \pm 22.271\)
-
If the area of a square is 496 square inches, find the length of its side:
\( \text{Side length} = \sqrt{496} \approx 22.271 \text{ inches}\)
-
If the area of an equilateral triangle is \(496\sqrt{3}\) square inches, find the length of its side:
\( \text{Side length} = 2\sqrt{496} \approx 44.542 \text{ inches}\)
Square Root Calculation in Excel
To calculate the square root of 496 in Excel, you can use the formula:
=SQRT(496)This will return the value 22.27105745132.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 496 is a fundamental mathematical concept often explored in various educational contexts. Represented mathematically as √496, the square root of 496 is approximately 22.271. This value, when squared, returns the original number, 496. In this section, we will delve into the methods to compute the square root, its properties, and its applications in solving equations and geometric problems.
To find the square root of 496, we can use methods such as prime factorization or the long division method. Prime factorization involves breaking down 496 into its prime factors, which simplifies to 4√31. This indicates that 496 is not a perfect square, and its square root is an irrational number. The long division method provides a more precise decimal form, which is useful for practical calculations.
Understanding the square root of 496 is crucial for solving quadratic equations and finding dimensions in geometric shapes. For example, if we know the area of a square is 496 square units, the length of one side can be found using the square root, leading to real-world applications in construction and design.
Definition of Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical notation, if \( y = \sqrt{x} \), then \( y^2 = x \). For example, the square root of 25 is 5, because \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \), which is expressed as \( \sqrt{25} = 5 \).
Square roots are fundamental in various areas of mathematics and are represented using the radical symbol (√). The concept of square roots extends beyond perfect squares and can also be applied to non-perfect squares, resulting in irrational numbers. An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and has a non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansion.
For instance, the square root of 496 is approximately 22.271, denoted as \( \sqrt{496} \approx 22.271 \). This value is obtained through methods such as the long division method or using a calculator. The square root of 496 in simplest radical form is expressed as \( 4\sqrt{31} \).
Understanding square roots is crucial in solving equations, analyzing geometrical shapes, and many other mathematical applications. Here's a step-by-step outline of finding the square root of a number using the long division method:
- Start by pairing the digits of the number from right to left.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair.
- Subtract this square from the first pair and bring down the next pair of digits.
- Double the quotient obtained in step 2 and use it as the new divisor.
- Repeat the process until you reach the desired level of accuracy.
These steps help in determining the square root of non-perfect squares with precision. Knowing the square root is particularly useful in various real-world problems, such as finding the side length of a square given its area or solving quadratic equations.
Decimal Representation of the Square Root of 496
The square root of 496, denoted as \( \sqrt{496} \), is a number that when multiplied by itself gives the product 496. The precise decimal value of the square root of 496 is approximately 22.27105745132008768847789.
To understand this better, let's break it down step-by-step:
- Start with the number 496.
- Identify the square root symbol \( \sqrt{} \).
- Use a calculator or a long division method to determine the value of \( \sqrt{496} \).
- The result is 22.27105745132008768847789, which is the positive root.
This decimal representation indicates that \( \sqrt{496} \) is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal form is non-repeating and non-terminating.
In summary, the square root of 496 in decimal form is:
- \( \sqrt{496} \approx 22.271 \) (to three decimal places)
- \( \sqrt{496} \approx 22.27105745132008768847789 \) (to twenty decimal places)
Applications of Square Roots
The square root is a fundamental concept in mathematics with a variety of practical applications across different fields. Understanding and utilizing square roots can be essential in both academic and real-world scenarios. Here are some of the key applications:
- Geometry: Square roots are crucial in geometry, particularly when calculating the lengths of sides in right triangles using the Pythagorean theorem. For example, the length of a hypotenuse can be found using the formula \( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \).
- Physics: In physics, square roots are used to determine the magnitude of vectors, calculate distances, and solve equations involving acceleration and velocity.
- Engineering: Engineers use square roots in various calculations, such as determining stress and strain in materials, analyzing electrical circuits, and designing structures.
- Computer Graphics: Square roots are used in algorithms for rendering images, calculating distances between points, and simulating realistic motion in computer graphics and video games.
- Statistics: In statistics, square roots are used to compute standard deviations, which measure the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of values.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use square roots to calculate distances between celestial objects, such as stars and planets, by applying formulas derived from observations and measurements.
- Finance: In finance, square roots are used in the calculation of compound interest and in various risk management models to determine the volatility of asset prices.
These applications demonstrate the versatility and importance of square roots in various fields, making them a vital mathematical tool for solving a wide range of problems.

Calculating Square Roots in Excel and Google Sheets
Calculating the square root of a number in Excel and Google Sheets is straightforward and can be done using built-in functions. Below are step-by-step guides for both Excel and Google Sheets.
Using Excel
- Open Excel and enter the number for which you want to find the square root in a cell (e.g., A1).
- Click on an empty cell where you want the result to be displayed.
- Type the following formula:
=SQRT(A1)
- Press Enter. The square root of the number in cell A1 will be displayed in the selected cell.
You can also directly enter a number in the formula:
=SQRT(496)
Using Google Sheets
- Open Google Sheets and enter the number for which you want to find the square root in a cell (e.g., A1).
- Click on an empty cell where you want the result to be displayed.
- Type the following formula:
=SQRT(A1)
- Press Enter. The square root of the number in cell A1 will be displayed in the selected cell.
You can also directly enter a number in the formula:
=SQRT(496)
Alternative Methods
In both Excel and Google Sheets, you can also use the caret operator (^) to find the square root. The formula for calculating the square root using the caret operator is:
=A1^(1/2)
Or for a direct number:
=496^(1/2)
This will also return 22.271.
Calculating Other Roots
For calculating other roots, such as the cube root or the fourth root, you can use the following formulas:
- Cube Root:
=A1^(1/3)
=496^(1/3)
- Fourth Root:
=A1^(1/4)
=496^(1/4)
These methods work in both Excel and Google Sheets.
Using these steps and formulas, you can easily calculate the square root and other roots of any number in Excel and Google Sheets.
Babylonian Method for Finding Square Roots
The Babylonian method, also known as Heron's method, is an ancient algorithm used to approximate the square root of a number. This method is iterative and converges quickly to an accurate result.
To find the square root of a number \( S \) using the Babylonian method, follow these steps:
- Initial Guess: Start with an initial guess \( x_0 \). A reasonable guess might be \( x_0 = S/2 \).
- Iterative Step: Use the iterative formula: \[ x_{n+1} = \frac{1}{2} \left( x_n + \frac{S}{x_n} \right) \]
- Convergence Check: Continue iterating until the difference between successive approximations is smaller than a chosen tolerance \( \epsilon \). In other words, stop when: \[ |x_{n+1} - x_n| < \epsilon \]
Here is a step-by-step example of calculating the square root of 496:
- Initial Guess: Let's start with \( x_0 = 248 \) (since 496/2 = 248).
- First Iteration: \[ x_1 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 248 + \frac{496}{248} \right) = \frac{1}{2} \left( 248 + 2 \right) = 125 \]
- Second Iteration: \[ x_2 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 125 + \frac{496}{125} \right) = \frac{1}{2} \left( 125 + 3.968 \right) \approx 64.484 \]
- Third Iteration: \[ x_3 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 64.484 + \frac{496}{64.484} \right) \approx 35.743 \]
- Fourth Iteration: \[ x_4 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 35.743 + \frac{496}{35.743} \right) \approx 24.655 \]
- Fifth Iteration: \[ x_5 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 24.655 + \frac{496}{24.655} \right) \approx 22.556 \]
- Sixth Iteration: \[ x_6 = \frac{1}{2} \left( 22.556 + \frac{496}{22.556} \right) \approx 22.271 \]
After six iterations, we have an approximation of the square root of 496 as 22.271, which is very close to the actual value.
The Babylonian method is efficient and easy to implement, making it a popular technique for calculating square roots even in modern times.
Table of Nth Roots of 496
The table below provides an overview of the nth roots of 496. Each root is calculated to show how the value of 496 can be expressed as different powers. The nth root of a number x is a value that, when raised to the power n, gives x. Here, we display the values for roots from the square root to the tenth root.
| Index | Root | Value |
| 2 | Square Root of 496 | 22.271 |
| 3 | Cube Root of 496 | 7.916 |
| 4 | Fourth Root of 496 | 4.719 |
| 5 | Fifth Root of 496 | 3.460 |
| 6 | Sixth Root of 496 | 2.814 |
| 7 | Seventh Root of 496 | 2.427 |
| 8 | Eighth Root of 496 | 2.172 |
| 9 | Ninth Root of 496 | 1.993 |
| 10 | Tenth Root of 496 | 1.860 |
These values highlight the versatility of roots and their applications in various mathematical contexts. The nth roots can be calculated using mathematical software, calculators, or specific algorithms like the Newton-Raphson method for more precision.
Table of Square Roots of Numbers Around 496
The following table lists the square roots of numbers close to 496. These values can be useful for comparative analysis or approximation purposes.
| Number | Square Root |
| 491 | 22.1585 |
| 492 | 22.1807 |
| 493 | 22.2028 |
| 494 | 22.225 |
| 495 | 22.2472 |
| 496 | 22.271 |
| 497 | 22.2931 |
| 498 | 22.3152 |
| 499 | 22.3373 |
| 500 | 22.3607 |
These values are approximate and rounded to four decimal places. They can be verified using various methods such as prime factorization, long division, or calculator tools.

Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của 496 và ứng dụng của nó trong toán học và cuộc sống hàng ngày. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 496
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của 496 và ứng dụng của nó trong toán học và cuộc sống hàng ngày. Hướng dẫn chi tiết và dễ hiểu.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 496