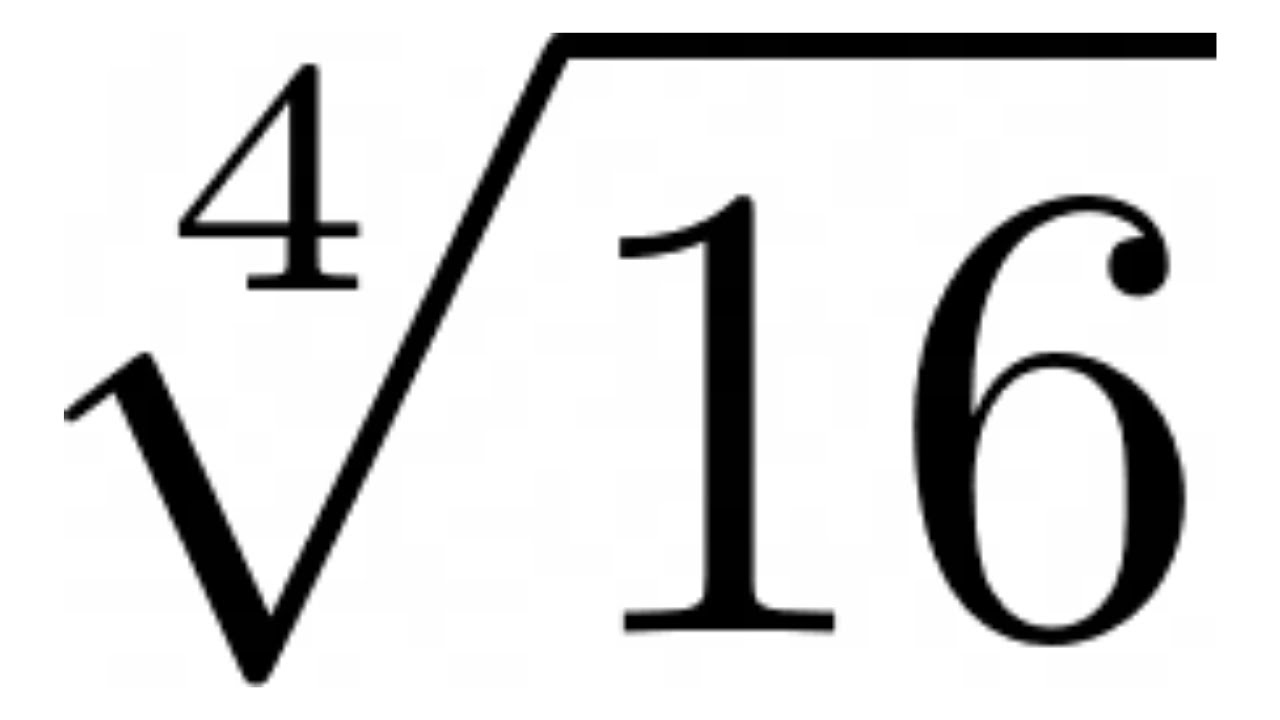Topic square root of 1620: The square root of 1620 is a fascinating mathematical concept. In this article, we delve into its calculation, methods to simplify it, and practical applications. Whether you're a student, educator, or math enthusiast, you'll find valuable insights and easy-to-follow explanations to enhance your understanding of this topic.
Table of Content
Square Root of 1620
The square root of 1620 is an interesting mathematical problem with several facets. Below, you will find detailed information about the square root of 1620, including its value, how it is calculated, and some additional insights.
Value of the Square Root of 1620
The square root of 1620, expressed in decimal form, is approximately:
Simplifying the Square Root of 1620
To simplify the square root of 1620, we use prime factorization:
Thus, the square root of 1620 in its simplest radical form is:
Properties and Additional Information
- The square root of 1620 is an irrational number, as it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- It has both a positive and negative root, but the principal square root is the positive one.
- Using the long division method or a calculator is a common approach to finding the square root of 1620.
Table of Roots
| Index | Root |
|---|---|
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 |
For more detailed calculations and examples, you can visit the sources used in this compilation, which include various math-focused websites and online calculators.

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 1620 is an interesting mathematical concept that finds application in various fields. The square root, denoted as \( \sqrt{1620} \), is approximately equal to 40.249223595. This number, when multiplied by itself, results in 1620. The principal square root refers to the positive value, which is most commonly used in calculations.
In this article, we will explore the methods to calculate the square root of 1620, its properties, and its applications. We will also discuss how to determine whether it is a rational or irrational number, and provide step-by-step instructions for calculating it using different tools.
- Understanding the Square Root
- Methods of Calculation
- Using a Calculator
- Using Excel or Google Sheets
- Manual Calculation
- Properties of the Square Root
- Applications of the Square Root
- Conclusion
Let's begin our journey into the fascinating world of square roots by understanding the basic concept and methods of calculation.
Definition and Calculation
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. The square root of 1620 is approximately 40.249. This value is derived from the fact that 40.249 multiplied by itself equals 1620.
To calculate the square root of 1620, you can use several methods, including:
- Using a calculator or mathematical software that has a square root function.
- Using the long division method to find the square root manually.
- Using prime factorization to simplify the square root.
Here's a step-by-step process for the long division method:
- Pair the digits of 1620 from right to left: 16 and 20.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 16, which is 4 (since 42 = 16).
- Subtract 16 from 16, bringing down the next pair of digits (20) to get 020.
- Double the divisor (4) to get 8, and determine the largest digit (x) such that 8x multiplied by x is less than or equal to 020.
- The process continues, bringing down pairs of digits and finding the next digit of the quotient until the desired precision is achieved.
Using the prime factorization method, 1620 can be expressed as:
\[
1620 = 2^2 \times 3^4 \times 5^1
\]
The square root of 1620 in its simplest radical form is:
\[
\sqrt{1620} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 3^4 \times 5} = 2 \times 3^2 \times \sqrt{5} = 18\sqrt{5}
\]
Thus, \(\sqrt{1620}\) can be expressed as \(18\sqrt{5}\) in radical form.
Whether you use a calculator, manual methods, or prime factorization, understanding these steps ensures a comprehensive grasp of finding square roots.
Methods of Calculation
The square root of 1620 can be calculated using various methods. Below are detailed steps to find the square root using different approaches.
-
Prime Factorization Method
Prime factorization is one of the methods to simplify the square root of 1620. Follow these steps:
- Find the prime factors of 1620: \( 1620 = 2^2 \times 3^4 \times 5 \)
- Group the factors into pairs: \( (2^2) \times (3^4) \times (5) \)
- Take one factor from each pair and multiply them: \( \sqrt{1620} = \sqrt{(2^2) \times (3^4) \times (5)} = 18\sqrt{5} \)
-
Using a Calculator
For a quick and accurate calculation, you can use a scientific calculator:
- Enter 1620 and press the square root (√) button.
- The result is approximately 40.249223594996.
-
Using Excel or Google Sheets
Another efficient method is to use spreadsheet software:
- In a cell, type
=SQRT(1620)and press Enter. The result will be displayed as 40.249223594996. - You can also use the
=POWER(1620, 1/2)function to get the same result.
- In a cell, type
-
Manual Calculation Using Approximation
To manually approximate the square root:
- Identify two perfect squares between which 1620 lies. For example, \( 40^2 = 1600 \) and \( 41^2 = 1681 \).
- Estimate that the square root of 1620 is slightly more than 40 but less than 41.
- Refine your estimate using the average method or another iterative method to get closer to the exact value.
Prime Factorization Method
The prime factorization method is an effective way to simplify the square root of a number by breaking it down into its prime factors. Here’s how you can simplify the square root of 1620 using this method:
- First, find the prime factors of 1620.
- 1620 can be factorized as 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 5.
- Group the factors into pairs of identical numbers.
- The pairs are: (2 × 2), (3 × 3), and (3 × 3). The remaining factor is 5.
- Take one factor from each pair and multiply them together.
- 2 × 3 × 3 = 18
- Multiply the result by the square root of any remaining factors.
- The remaining factor is 5, so √1620 = 18√5.
Thus, the square root of 1620, simplified using the prime factorization method, is 18√5. This method ensures you break down the number into its simplest radical form, making calculations more manageable.

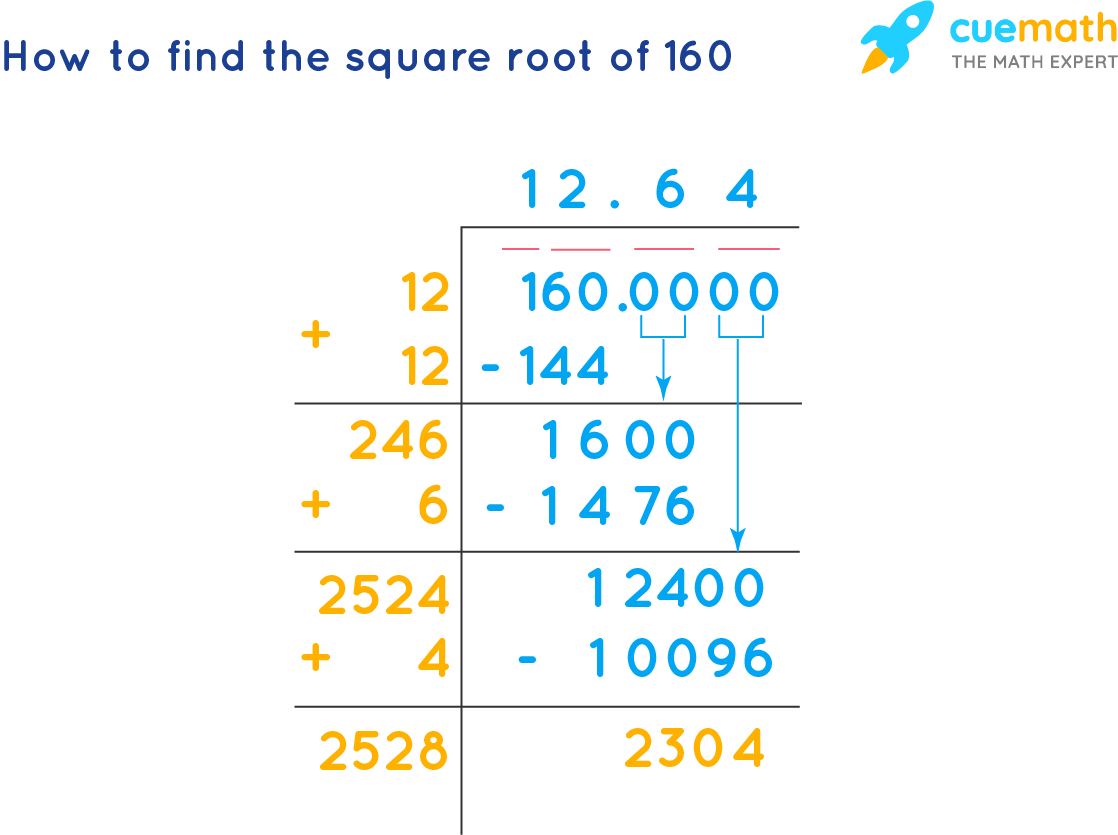
Long Division Method
The long division method is a systematic approach for finding the square root of any number, whether it is a perfect square or not. Here is a detailed, step-by-step guide to using this method to find the square root of 1620.
-
Pair the Digits: Separate the digits of the number into pairs, starting from the decimal point. For 1620, pair the digits as (16)(20).
-
Estimate the Largest Digit: Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair (16). The largest such number is 4, because \(4^2 = 16\).
Current root: 4
-
Subtract and Bring Down: Subtract the square of 4 from 16 to get 0, then bring down the next pair of digits (20), giving you 020.
-
Double the Quotient: Double the current quotient (4) to get 8.
New divisor: 8_
-
Find the Next Digit: Find the digit to complete the new divisor such that when it is multiplied by itself, the product is less than or equal to the new dividend (020). The largest digit that works is 0.
New quotient: 40
-
Repeat Steps: Bring down pairs of zeros and repeat the steps to get more precise decimal values. For example, bring down 00 to make it 0200, and continue with the process.
By repeating the steps, you will refine the approximation of the square root of 1620 to the desired number of decimal places.
Simplification Process
The simplification of the square root of 1620 involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and then simplifying the square root based on these factors. Here is the detailed step-by-step process:
- First, find the prime factors of 1620. The prime factorization of 1620 is \(2^2 \times 3^4 \times 5\).
- Next, identify pairs of prime factors, as pairs can be taken out of the square root. For 1620, we have:
- A pair of 2s (\(2^2\))
- Two pairs of 3s (\(3^4\))
- For each pair of prime factors outside the square root, take one instance of the factor. Thus, we take one 2 from \(2^2\) and two 3s from \(3^4\).
- Multiply these factors taken out of the square root: \(2 \times 3 \times 3 = 18\).
- The remaining prime factor inside the square root is 5, which cannot be paired. Thus, the simplified form of \(\sqrt{1620}\) is \(18\sqrt{5}\).
Therefore, the square root of 1620 simplified is \(18\sqrt{5}\). This simplification process not only makes the square root easier to understand but also aids in further mathematical operations.
Examples of Simplification
Let's simplify the square root of 1620 using the prime factorization method. The prime factorization of 1620 is as follows:
- First, we find the prime factors of 1620.
- 1620 can be factored into 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 5.
- This can be written as \( 2^2 \times 3^4 \times 5 \).
- To simplify, we pair the prime factors:
\[
\sqrt{1620} = \sqrt{2^2 \times 3^4 \times 5}
\]
We take one factor out of each pair of prime factors:
\[
\sqrt{2^2} = 2, \quad \sqrt{3^4} = 3^2 = 9
\]
Thus, we can write:
\[
\sqrt{1620} = 2 \times 9 \times \sqrt{5} = 18 \sqrt{5}
\]
Therefore, the simplified form of the square root of 1620 is \( 18 \sqrt{5} \).
To convert this into a decimal, we multiply 18 by the square root of 5:
\[
18 \times \sqrt{5} \approx 18 \times 2.236 = 40.249223594996
\]
Here are the steps illustrated in a table format:
| Step | Operation | Result |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prime factorization of 1620 | \(2^2 \times 3^4 \times 5\) |
| 2 | Pair the factors | \( (2^2) \), \( (3^4) \), \( (5) \) |
| 3 | Take one factor from each pair | 2, 9, \(\sqrt{5}\) |
| 4 | Multiply the results | \(18 \sqrt{5}\) |
| 5 | Convert to decimal form | 40.249223594996 |
By following these steps, we have successfully simplified and calculated the square root of 1620.
Applications and Related Concepts
Square roots, including the square root of 1620, find practical application in various fields, showcasing the utility of this mathematical concept in our daily lives and various industries. Here are some examples:
- Architecture and Engineering:
In architecture, square roots are essential for calculating areas and dimensions. Engineers use them to determine natural frequencies of structures, such as bridges and buildings, to predict how they will respond to different loads, such as wind or traffic.
- Physics:
Square roots are critical in physics for formulas related to motion, energy, and gravity. They help scientists solve complex problems, such as calculating the velocity of moving objects or the intensity of sound waves.
- Finance:
In finance, square roots are used to calculate the standard deviation, a key metric in risk assessment and portfolio management. They help investors understand the volatility of stocks and make informed investment decisions.
- Computer Graphics:
Square roots are used in computer graphics to calculate distances and angles, which are essential for rendering realistic 3D models and environments. They play a vital role in game development and animation.
- Navigation:
In navigation, square roots are used to calculate the shortest distance between points, which is vital for GPS technology and mapping. Pilots and sailors use them to determine the best routes for travel.
- Statistics:
Square roots are fundamental in statistics for calculating variance and standard deviation, which describe how data deviates from the mean. These metrics are crucial for data analysis and interpretation.
- Geometry:
In geometry, square roots are used to compute areas, perimeters, and solve problems involving right triangles. The Pythagorean theorem, for example, relies on square roots to determine the length of triangle sides.
- Electrical Engineering:
Square roots are used in electrical engineering to compute power, voltage, and current in circuits. They are essential for designing and analyzing electrical systems, such as power grids and communication networks.

Additional Resources
Explore more examples and resources to deepen your understanding of square roots and their applications:
Here are some additional resources to expand your knowledge:
Căn Bậc Hai của 1620 | Toán Học
READ MORE:
Căn bậc hai của 1620 là bao nhiêu?