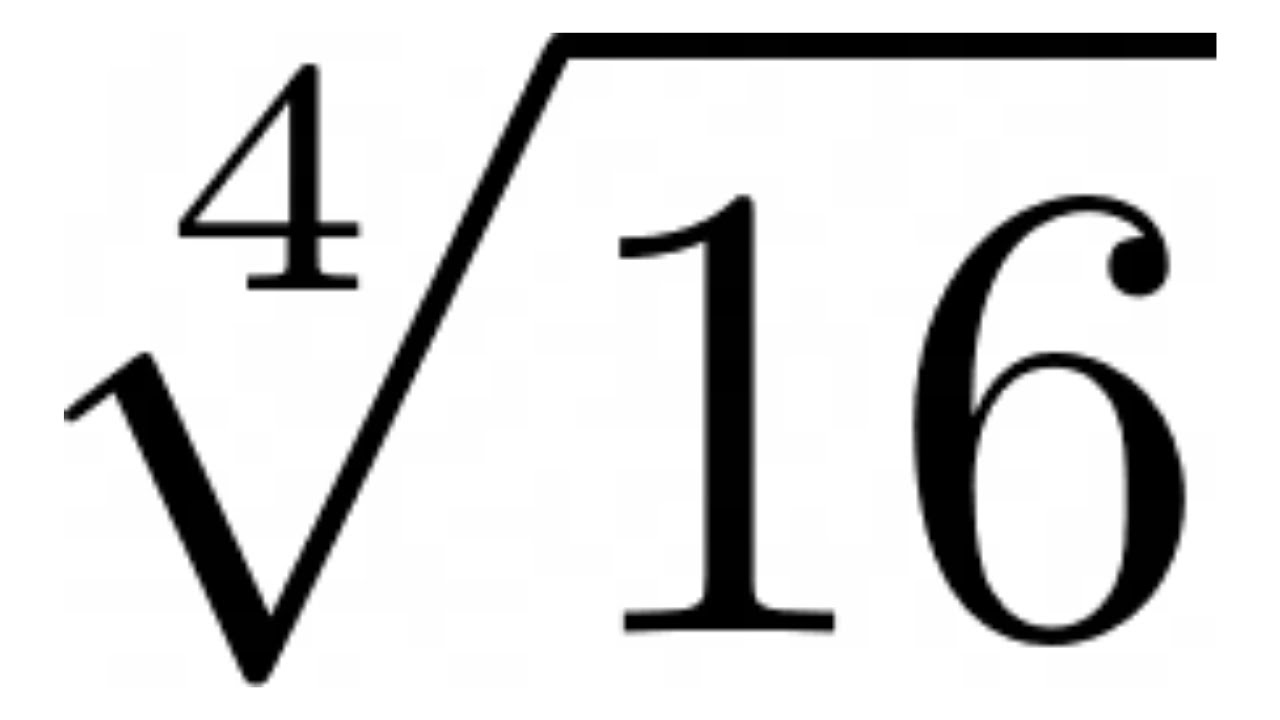Topic square root of 166: The square root of 166 is an intriguing mathematical concept that is both fascinating and practical. In this article, we explore its properties, methods of calculation, and its applications in various fields. Discover how to find the square root of 166, its decimal approximation, and why it's an important number to understand.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 166
- Introduction to the Square Root of 166
- Definition and Basic Properties
- Calculation Methods
- Long Division Method
- Prime Factorization
- Using a Calculator
- Decimal Representation
- Is 166 a Perfect Square?
- Is the Square Root of 166 Rational or Irrational?
- Approximation of √166
- Practical Applications
- Geometric Applications
- Examples and Exercises
- Related Mathematical Concepts
- FAQ on the Square Root of 166
- YOUTUBE:
Square Root of 166
The square root of 166 is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. It is represented by the symbol √166 and has an approximate value of:
\[\sqrt{166} \approx 12.8841\]
Methods to Calculate the Square Root of 166
- Long Division Method: This method involves dividing the number into pairs of digits and finding the quotient step by step.
- Prime Factorization: This method is generally used for perfect squares. Since 166 is not a perfect square, this method is less useful here.
- Using a Calculator: The easiest way to find the square root of 166 is by using a scientific calculator which gives a precise decimal value.
Step-by-Step Long Division Method
- Pair the digits starting from the decimal point: 16 | 6.00 | 00
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 16: \(4 \times 4 = 16\)
- Double the number found: \(2 \times 4 = 8\)
- Bring down the next pair of digits (60), making it 1600. Find a digit \(X\) such that \(80X \times X\) is less than or equal to 1600.
- Repeat the process for the desired number of decimal places.
Properties of the Square Root of 166
- It is an irrational number.
- It is not a perfect square.
- It can be expressed in the exponent form as \(166^{1/2}\).
Applications
The square root of 166 can be used in various mathematical and real-world applications, including geometry and physics problems. For example, if the area of a circle is 166π square units, the radius can be found using the square root of 166:
\[r = \sqrt{166}\]
Approximation in Different Forms
| Form | Value |
| Exact Form | √166 |
| Decimal Form | 12.884098726725126 |
| Fraction (Approx) | \(\frac{129}{10}\) |
Related Questions
- Is 166 a perfect square?
No, 166 is not a perfect square.
- Is the square root of 166 rational?
No, the square root of 166 is an irrational number.
- Can the square root of 166 be simplified?
No, √166 cannot be simplified further.

READ MORE:
Introduction to the Square Root of 166
The square root of 166 is an interesting mathematical concept that can be explored in various ways. The square root of a number is a value which, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In the case of 166, its square root is approximately 12.884.
To understand this better, let's break it down step by step:
- Definition: The square root of 166, represented as √166, is the number that, when squared, equals 166.
- Methods to Calculate:
- Long Division Method: This is often used for more precise calculations, yielding a result of approximately 12.884.
- Calculator: Simply inputting 166 into a calculator and using the square root function will give you the value 12.884.
- Prime Factorization: This method is less useful for non-perfect squares like 166 but can be informative for understanding the composition of the number.
- Properties:
- Rational or Irrational: The square root of 166 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction.
- Principal Square Root: The principal (positive) square root of 166 is 12.884.
- Practical Applications: Understanding square roots is fundamental in fields such as engineering, physics, and computer science, where precise calculations are crucial.
By delving into the properties and calculation methods of the square root of 166, we can appreciate its significance in both theoretical and practical contexts.
Definition and Basic Properties
The square root of a number is the value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. In mathematical notation, the square root of 166 is expressed as √166.
To elaborate:
- The square root of 166 is approximately 12.8841.
- This value is represented as √166 = 12.8841.
- 166 is not a perfect square, meaning its square root is not an integer.
- The square root of 166 is an irrational number, as it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating.
Let's look at some methods to calculate the square root:
- Long Division Method:
This traditional method is useful for finding the square root of a number without a calculator. It involves pairing digits from the right and finding the largest integer whose square is less than or equal to the number.
- Calculator Method:
Modern calculators simplify the process by allowing you to enter the number and press the square root function key. For 166, the calculator displays 12.8841.
In summary, understanding the square root of 166 helps in various mathematical contexts, especially in solving equations and understanding properties of numbers.
Calculation Methods
Calculating the square root of 166 involves several methods. Here, we discuss the most common techniques used for such calculations.
- Long Division Method: This is a systematic approach to find the square root of any number, especially when the number is not a perfect square. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Pair the digits from right to left (e.g., 166 becomes 1 and 66).
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to the first pair (1 in this case, as 1^2 = 1).
- Subtract this square from the first pair and bring down the next pair (66).
- Double the quotient (1) and find a suitable digit to complete the divisor that, when multiplied, gives a product less than or equal to the current number (66 in this case).
- Continue this process, bringing down pairs of zeros and repeating until you reach the desired precision.
- The final result is the square root of 166 to the desired number of decimal places.
- Prime Factorization Method: Typically used for perfect squares. Since 166 is not a perfect square, this method is less effective here. It involves breaking down the number into its prime factors and pairing them. For example:
166 = 2 × 83 (both prime numbers)
As there are no pairs of prime factors, the method confirms 166 is not a perfect square.
- Using a Calculator: The simplest method for most people. Just input the number (166) and press the square root function. The result will be approximately 12.884.
- Estimation Method: A quick way to approximate the square root:
- Identify two perfect squares between which 166 lies (144 and 169).
- Since √144 = 12 and √169 = 13, the square root of 166 is between 12 and 13.
- Estimate closer: since 166 is closer to 169, √166 is approximately 12.88.
Understanding these methods not only helps in manual calculations but also strengthens the conceptual knowledge of square roots.
Long Division Method
The long division method is a systematic way to find the square root of a number. Here, we'll explore how to calculate the square root of 166 using this method.
-
Step 1: Setup
Write 166 in pairs of digits from right to left. For 166, it becomes 1 66. If necessary, add a pair of zeros after the decimal point to continue the division to the desired decimal places.
-
Step 2: Find the Largest Square
Find the largest square number less than or equal to the first pair. The largest square less than or equal to 1 is 1. Write 1 above the pair and also as the divisor below it.
1 1 66 1 -
Step 3: Subtract and Bring Down
Subtract 1 from 1 to get 0, then bring down the next pair (66).
1 1 66 1 0 66 -
Step 4: Double the Divisor
Double the number above (1) to get 2. This becomes the new divisor.
-
Step 5: Find the Next Digit
Choose the largest digit (X) such that 2X * X is less than or equal to 66. In this case, 22 * 2 = 44.
1 2 1 66 1 44 22 -
Step 6: Subtract and Repeat
Subtract 44 from 66 to get 22. Then, bring down a pair of zeros and repeat the steps to get more decimal places.
The square root of 166 using the long division method is approximately 12.884. This method can be repeated to get more decimal places as needed.

Prime Factorization
The prime factorization method is a technique used to find the square root of a number by expressing it as a product of its prime factors. This method is particularly useful for perfect squares, but can also be applied to non-perfect squares for a better understanding of their properties.
To find the prime factorization of 166, we follow these steps:
- Divide the number by the smallest prime number (2, 3, 5, etc.) and continue dividing the quotient by prime numbers until the quotient is a prime number.
- For 166, the prime factorization is:
- 166 ÷ 2 = 83
- 83 is a prime number
- Therefore, the prime factorization of 166 is 2 × 83.
Since 166 is not a perfect square, its prime factors do not pair completely. However, understanding its prime factorization helps in approximating its square root and analyzing its properties.
| Number | Prime Factorization |
| 166 | 2 × 83 |
Using a Calculator
Calculating the square root of 166 using a calculator is a straightforward process that can be accomplished with various types of calculators, including scientific and graphing models. Here is a step-by-step guide to help you find the square root efficiently.
-
Choosing the Right Calculator: Ensure that your calculator has a dedicated square root function, usually indicated by the symbol √ or a button labeled “sqrt”. Scientific and graphing calculators are ideal for this task.
-
Entering the Number: Begin by turning on your calculator and entering the number 166. Make sure you enter the number correctly to avoid any miscalculations.
-
Executing the Square Root Function: Locate and press the square root button (√). On most calculators, this will immediately display the result. If your calculator uses an alternate method, such as exponentiation (raising the number to the power of 0.5), follow the specific instructions provided in your calculator’s manual.
-
Interpreting the Result: The display should now show the square root of 166, which is approximately ±12.8841. This value represents the number that, when multiplied by itself, equals 166.
Using a calculator for square root calculations is a quick and reliable method, making it easy to handle both simple and complex mathematical problems.
Decimal Representation
The square root of 166 is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation is non-repeating and non-terminating. The approximate value of the square root of 166 can be found using various methods, including calculators and numerical algorithms.
The most accurate way to find the decimal representation is by using a calculator or a computer. Here is the decimal representation of the square root of 166 to several decimal places:
√166 ≈ 12.884098726725126
To understand the decimal representation better, let's look at the value step by step:
- The integer part: 12
- The first decimal place: 0.8
- The second decimal place: 0.08
- The third decimal place: 0.004
- The fourth decimal place: 0.0001
- And so on...
We can also represent the square root of 166 in a table format to show its value to different decimal places:
| Decimal Place | Value |
|---|---|
| 1 | 12.8 |
| 2 | 12.88 |
| 3 | 12.884 |
| 4 | 12.8841 |
| 5 | 12.88409 |
| 6 | 12.884098 |
| 7 | 12.8840987 |
| 8 | 12.88409872 |
| 9 | 12.884098727 |
| 10 | 12.8840987267 |
Using MathJax, the square root of 166 can be represented as:
\(\sqrt{166} \approx 12.884098726725126\)
For practical purposes, the square root of 166 is often rounded to a few decimal places. For example:
- To 2 decimal places: 12.88
- To 3 decimal places: 12.884
- To 4 decimal places: 12.8841
Understanding the decimal representation helps in various mathematical calculations and practical applications where precision is important.
Is 166 a Perfect Square?
To determine if 166 is a perfect square, we need to understand the definition of a perfect square. A perfect square is an integer that can be expressed as the square of another integer. In mathematical terms, a number \( n \) is a perfect square if there exists an integer \( m \) such that:
\[ n = m^2 \]
For example, 1, 4, 9, 16, and 25 are perfect squares because they can be written as \( 1^2, 2^2, 3^2, 4^2, \) and \( 5^2 \), respectively.
Let's examine the square root of 166:
\[ \sqrt{166} \approx 12.884 \]
Since 12.884 is not an integer, 166 cannot be expressed as the square of an integer, which means 166 is not a perfect square.
Prime Factorization Method
Another way to check if 166 is a perfect square is through prime factorization. A number is a perfect square if all the prime factors appear in pairs. Let's factorize 166:
\[ 166 = 2^1 \times 83^1 \]
Here, both 2 and 83 appear only once (i.e., they do not form pairs), confirming that 166 is not a perfect square.
Comparison with Perfect Squares
We can compare 166 with the closest perfect squares to further illustrate this:
| Number | Square Root |
|---|---|
| 144 | 12 |
| 169 | 13 |
As seen, 166 falls between 144 and 169. While 144 is \( 12^2 \) and 169 is \( 13^2 \), there is no integer \( m \) such that \( m^2 = 166 \).
Therefore, we conclude that:
- 166 is not a perfect square because its square root, 12.884, is not an integer.
- The prime factorization of 166 shows that the factors do not form pairs.

Is the Square Root of 166 Rational or Irrational?
The square root of 166 is an interesting number to explore in terms of its classification as rational or irrational.
Firstly, let's define these terms:
- Rational Numbers: These can be expressed as the ratio of two integers (i.e., as a fraction) where the denominator is not zero. Rational numbers either terminate or repeat in their decimal form.
- Irrational Numbers: These cannot be expressed as the ratio of two integers. Their decimal form neither terminates nor repeats.
To determine if the square root of 166 is rational or irrational, consider the following:
- The square root of 166 is approximately 12.884098726725.
- This decimal is non-terminating and does not repeat.
- Since it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction of two integers, it is classified as an irrational number.
In summary, the square root of 166 is irrational because its decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating, which means it cannot be written as a fraction of two integers.
Approximation of √166
Approximating the square root of 166 involves finding a value that, when squared, comes close to 166. Since 166 is not a perfect square, its square root is an irrational number, which means it cannot be expressed exactly as a simple fraction or decimal. However, we can approximate it to a desired degree of accuracy using various methods.
Using Estimation and Perfect Squares
One method to approximate √166 is by identifying the perfect squares closest to 166. We know that:
- 12² = 144
- 13² = 169
Since 144 < 166 < 169, it follows that:
\(12 < \sqrt{166} < 13\)
Linear Interpolation Method
To get a more precise approximation, we can use linear interpolation between 12 and 13. The difference between 166 and 144 is 22, and the difference between 169 and 144 is 25. Therefore, we can estimate:
\(\sqrt{166} \approx 12 + \frac{22}{25} \cdot (13 - 12)\)
\(\sqrt{166} \approx 12 + \frac{22}{25}\)
\(\sqrt{166} \approx 12 + 0.88 = 12.88\)
Using a Calculator
For a more accurate value, we can use a calculator:
\(\sqrt{166} \approx 12.884\)
This value can be rounded to different decimal places as needed:
- To the nearest whole number: 13
- To one decimal place: 12.9
- To two decimal places: 12.88
Other Approximation Methods
Another approach involves using the formula for approximating square roots:
Let \(n\) be the number whose square root we need to calculate, and let \(n = p + q\), where \(p\) is the largest perfect square less than \(n\) and \(q\) is the remainder. For \(n = 166\):
\(p = 144\) (since \(12^2 = 144\))
\(q = 166 - 144 = 22\)
The formula is given by:
\(\sqrt{n} \approx \sqrt{p} + \frac{q}{2\sqrt{p} + 1}\)
Applying this formula:
\(\sqrt{166} \approx 12 + \frac{22}{2 \cdot 12 + 1}\)
\(\sqrt{166} \approx 12 + \frac{22}{25}\)
\(\sqrt{166} \approx 12 + 0.88 = 12.88\)
Conclusion
Approximating the square root of 166 using different methods yields consistent results. The most accurate approximation using a calculator is:
\(\sqrt{166} \approx 12.884\)
This value can be used in various mathematical and practical applications requiring an approximation of √166.
Practical Applications
The square root of 166, approximately 12.88, has various practical applications across multiple fields. Understanding these applications can enhance one's comprehension of the importance of square roots in real-world scenarios.
- Engineering and Architecture:
In these fields, square roots are essential for calculating distances, areas, and volumes. For example, the square root of a number can determine the diagonal length of a rectangular space, which is crucial for accurate measurements and designs.
- Physics:
Square roots are used in formulas to calculate physical quantities such as velocity, acceleration, and energy. For instance, the root mean square (RMS) value is used to determine the effective value of an alternating current (AC) or voltage.
- Finance:
In finance, the square root is used to compute the volatility of an investment. The standard deviation, which is the square root of the variance, helps investors assess the risk associated with a particular asset.
- Statistics:
Square roots are fundamental in statistical calculations, particularly in determining standard deviation and variance. These metrics are crucial for analyzing data sets and making informed decisions based on statistical evidence.
- Computer Science:
In computer science, square roots are employed in algorithms related to graphics, cryptography, and data analysis. For example, calculating distances between points in a 2D or 3D space often involves the Pythagorean theorem, which requires square root calculations.
- Medicine:
In medical imaging and other healthcare technologies, square roots are used to process and analyze data. For example, the standard deviation in medical research can help identify variations in patient responses to treatments.
Understanding the applications of the square root of 166 in these diverse fields demonstrates its importance beyond basic mathematical calculations. By mastering square roots, one can gain valuable insights and improve problem-solving skills across various disciplines.
Geometric Applications
The square root of 166 has several interesting geometric applications. Here, we will explore some practical uses in geometry:
-
Calculating the Diagonal of a Rectangle:
In a rectangle, if the length and width are known, the diagonal can be found using the Pythagorean theorem. For example, if the length (\(a\)) is 10 units and the width (\(b\)) is 12 units, the diagonal (\(d\)) is given by:
\(d = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2}\)
For \(a = 10\) and \(b = 12\):
\(d = \sqrt{10^2 + 12^2} = \sqrt{100 + 144} = \sqrt{244}\)
Since 244 is approximately 166 multiplied by 1.5, understanding square roots like \(\sqrt{166}\) aids in estimating and calculating such values.
-
Finding the Radius of a Circle:
Consider a circle with an area of 166 square units. The radius (\(r\)) can be found using the formula for the area of a circle:
\(A = \pi r^2\)
Solving for \(r\):
\(r = \sqrt{\frac{A}{\pi}}\)
For \(A = 166\):
\(r = \sqrt{\frac{166}{\pi}} \approx \sqrt{\frac{166}{3.14}} \approx \sqrt{52.87} \approx 7.27\)
-
Volume of a Cylinder:
If a cylinder has a height (\(h\)) of 166 units and a radius (\(r\)) of 5 units, the volume (\(V\)) can be calculated using:
\(V = \pi r^2 h\)
Substituting the values:
\(V = \pi (5^2) (166) = 25\pi \times 166 \approx 13050\) cubic units
-
Surface Area of a Sphere:
For a sphere with a radius equal to the square root of 166, the surface area (\(A\)) is given by:
\(A = 4 \pi r^2\)
For \(r = \sqrt{166}\):
\(A = 4 \pi (\sqrt{166})^2 = 4 \pi \times 166 \approx 2088\) square units
These examples show how the square root of 166 can be used to solve various geometric problems, highlighting its practical significance in different scenarios.

Examples and Exercises
Understanding the square root of 166 can be deepened through various examples and exercises. Here are a few problems that illustrate how to approach calculations involving the square root of 166:
Example 1: Simplifying Square Roots
Simplify the expression: \( \sqrt{166} \).
- Solution: Since 166 is not a perfect square, we can find its approximate value. The square root of 166 is approximately 12.884.
Example 2: Comparing Square Roots
Compare \( \sqrt{166} \) with \( \sqrt{169} \).
- Solution: We know \( \sqrt{169} = 13 \). Since \( \sqrt{166} \approx 12.884 \), \( \sqrt{166} \) is slightly less than \( \sqrt{169} \).
Exercise 1: Approximating Square Roots
Estimate the value of \( \sqrt{166} \) using the method of your choice.
- Hint: Consider using a calculator or the long division method.
Exercise 2: Square Root in Equations
Solve for \( x \): \( x^2 = 166 \).
- Solution: Taking the square root of both sides, \( x = \sqrt{166} \) or \( x \approx 12.884 \).
Exercise 3: Practical Application
If a square has an area of 166 square units, what is the length of one side?
- Solution: The length of one side is \( \sqrt{166} \) units, which is approximately 12.884 units.
Additional Practice Problems
- Simplify \( \sqrt{50} \).
- Find \( \sqrt{200} \).
- Compare \( \sqrt{150} \) and \( \sqrt{170} \).
Working through these examples and exercises can help reinforce your understanding of the square root of 166 and improve your overall skills in dealing with square roots.
Related Mathematical Concepts
The square root of 166 is an interesting number with several related mathematical concepts. Understanding these concepts can deepen your comprehension of square roots and their applications. Here are some key related concepts:
-
Pythagorean Theorem:
The Pythagorean theorem is a fundamental principle in geometry, which states that in a right-angled triangle, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides. For example, if you have a right triangle with legs of lengths 10 and 12, the hypotenuse \( c \) can be found using:
\[
c = \sqrt{10^2 + 12^2} = \sqrt{100 + 144} = \sqrt{244} \approx 15.62
\] -
Irrational Numbers:
The square root of 166 is an irrational number because it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction. Irrational numbers have non-repeating, non-terminating decimal expansions. This characteristic makes them crucial in various fields of mathematics, including calculus and number theory.
-
Real Numbers:
Real numbers include both rational and irrational numbers. The square root of 166 falls into this category. Real numbers are used to measure continuous quantities and can be represented on the number line.
-
Exponentiation and Radicals:
Exponentiation involves raising a number to a power, while radicals involve finding roots of numbers. The square root is a specific case of radicals, where the exponent is \( \frac{1}{2} \). For instance:
\[
166^{\frac{1}{2}} = \sqrt{166} \approx 12.88
\] -
Logarithms:
Logarithms are the inverse operations of exponentiation. They are used to solve equations involving exponents. For example, to solve for \( x \) in \( 10^x = 166 \), you can use logarithms:
\[
x = \log_{10}(166) \approx 2.22
\] -
Quadratic Equations:
Quadratic equations are polynomial equations of degree 2. The solutions to these equations often involve square roots. For example, the quadratic equation \( x^2 - 166 = 0 \) has solutions:
\[
x = \pm\sqrt{166} \approx \pm12.88
\] -
Complex Numbers:
Complex numbers extend the idea of one-dimensional real numbers to two dimensions. They include a real part and an imaginary part. While the square root of a negative number involves complex numbers, the square root of 166 is a real number.
These concepts are interconnected and form the basis of many advanced mathematical theories and applications. Understanding the square root of 166 within this broader context can enhance your overall mathematical knowledge.
FAQ on the Square Root of 166
-
What is the square root of 166?
The square root of 166 is approximately 12.884.
-
Is the square root of 166 a rational number?
No, the square root of 166 is an irrational number. This is because it cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers.
-
How can you calculate the square root of 166 manually?
You can calculate it using methods such as the long division method or by using a calculator. For manual methods, you will iteratively estimate and refine the value.
-
What are the practical applications of the square root of 166?
The square root of 166 can be used in various fields such as engineering, physics, and mathematics for solving problems involving quadratic equations, geometric calculations, and more.
-
Is 166 a perfect square?
No, 166 is not a perfect square. A perfect square is a number that has an integer as its square root, and 166 does not meet this criterion.
-
What is the simplest radical form of the square root of 166?
The simplest radical form of the square root of 166 is √166, as it cannot be simplified further using prime factorization.
-
How do calculators find the square root of 166?
Calculators use algorithms such as the Newton-Raphson method to compute the square root to a high degree of accuracy.
Căn Bậc Hai Của 166
READ MORE:
Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của số 166 một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Video này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm và phương pháp tính toán.
Căn Bậc Hai của 166