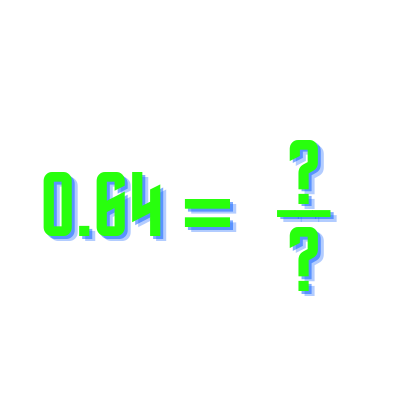Topic square root of 216 in radical form: The square root of 216 in radical form is a fascinating mathematical topic. Understanding how to simplify it provides valuable insights into algebraic principles. Learn how to express √216 in its simplest radical form and explore various methods to calculate and approximate this value efficiently.
Table of Content
Square Root of 216 in Radical Form
The square root of 216 can be simplified using its prime factorization.
Prime Factorization Method
First, express 216 in terms of its prime factors:
\( 216 = 2^3 \times 3^3 \)
Taking the square root of both sides:
\( \sqrt{216} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^3} = \sqrt{(2 \times 3)^2 \times 6} = 6\sqrt{6} \)
Thus, the square root of 216 in radical form is \( 6\sqrt{6} \).
Decimal Form
When calculated, the square root of 216 is approximately 14.697.
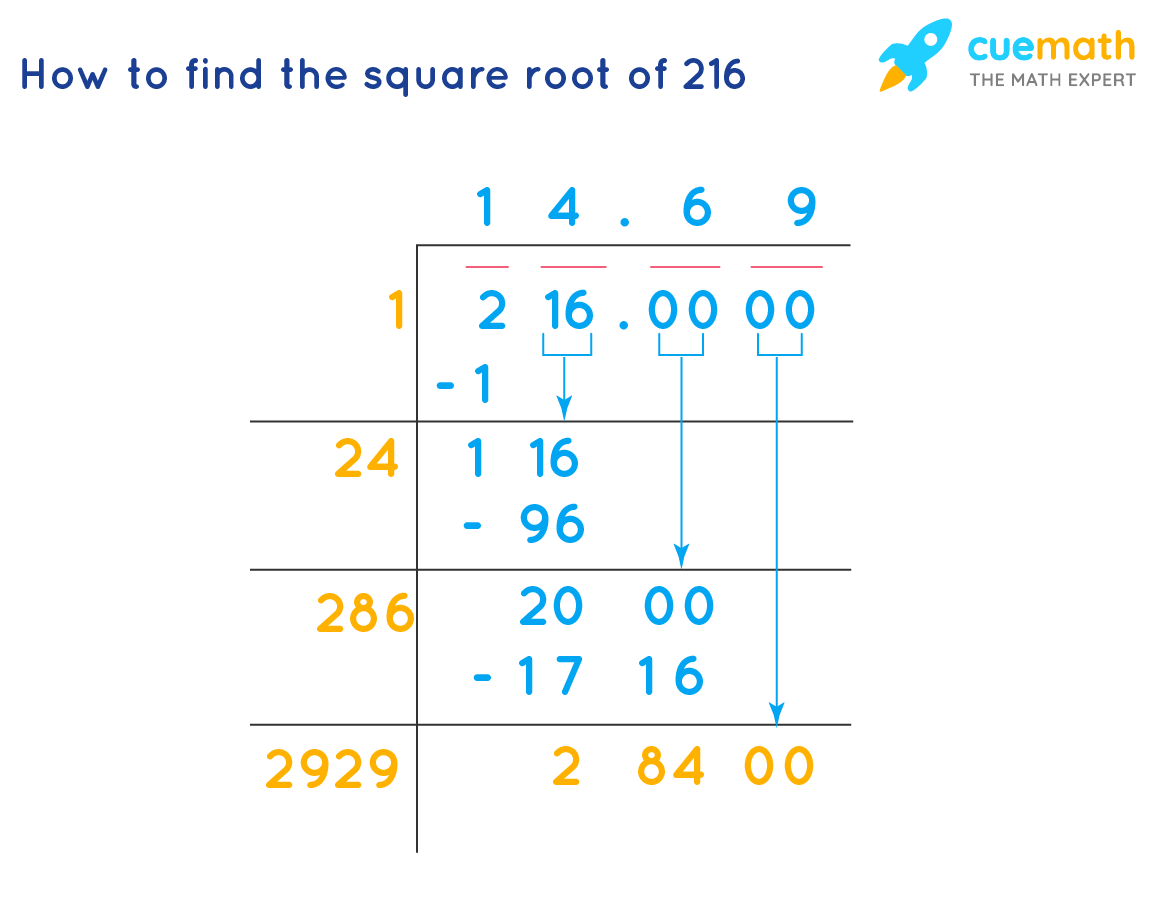
Steps to Find the Square Root of 216 Using Long Division Method
- Write 216 in decimal form as 216.0000 and pair the digits from right to left.
- Find a number which, when multiplied by itself, is less than or equal to 2. The number is 1.
- Subtract 1 from 2, bringing down the next pair to get 116.
- Double the quotient (1) to get 2 and find a number that, when multiplied by (20 + number), is less than or equal to 116. The number is 4.
- Continue this process to get the quotient 14.697.
Applications and Examples
Consider an example where Amy wants to find the side length of a square garden with an area of 216 square feet:
\( x^2 = 216 \)
\( x = \sqrt{216} = 14.697 \) (approximately)
The side length of the garden is approximately 14.7 feet.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is 216 a perfect square? No, 216 is not a perfect square because it cannot be expressed as the product of two equal integers.
- Is the square root of 216 a rational number? No, the square root of 216 is not a rational number because it is a non-terminating and non-repeating decimal.
- What is the decimal value of the square root of 216? The approximate decimal value is 14.697.
- Is 216 a perfect cube? Yes, 216 is a perfect cube since \( 6^3 = 216 \).

READ MORE:
Introduction
The square root of 216 in radical form is a fundamental concept in mathematics, often simplified to its simplest radical form for ease of understanding and computation. The simplest radical form of the square root of 216 is expressed as \( 6\sqrt{6} \). This form is derived through prime factorization, which breaks down 216 into its prime factors. The steps to simplify the square root of 216 involve factoring the number, grouping the factors, and then simplifying the expression under the radical. This method helps in understanding the properties of numbers and their roots, making calculations more manageable.
Understanding the Square Root
The square root of a number is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives the original number. For instance, the square root of 216 is a number which, when squared, equals 216. This concept is fundamental in various fields such as algebra, geometry, and real-world problem solving.
Let's explore the square root of 216 in radical form:
- The square root of 216 can be simplified by factorizing 216 into its prime factors. The prime factorization of 216 is \(2^3 \times 3^3\).
- To express the square root of 216 in its simplest radical form, we can group the prime factors: \( \sqrt{216} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^3} \).
- By taking the square root of each factor group, we get \( \sqrt{216} = \sqrt{(2^3 \times 3^3)} = \sqrt{(2 \times 2 \times 2) \times (3 \times 3 \times 3)} \).
- Simplifying further, \( \sqrt{(2^2 \times 2) \times (3^2 \times 3)} = \sqrt{(4 \times 2) \times (9 \times 3)} \).
- Taking the square root of the perfect squares: \( \sqrt{4} \times \sqrt{9} \times \sqrt{6} = 2 \times 3 \times \sqrt{6} = 6\sqrt{6} \).
Thus, the simplest radical form of the square root of 216 is \( 6\sqrt{6} \).
Additionally, the approximate decimal value of the square root of 216 is 14.697, when rounded to three decimal places.
Understanding these steps can help in solving various mathematical problems involving square roots and their applications.
Calculation Methods
Calculating the square root of 216 involves several methods, each providing a clear understanding of the process. Here are the most common techniques:
1. Prime Factorization
The prime factorization method simplifies the square root by breaking down 216 into its prime factors:
- First, express 216 as a product of its prime factors: 216 = 23 × 33.
- Apply the square root to each factor: √216 = √(23 × 33).
- Simplify the expression: √216 = 6√6.
- Thus, the simplified radical form of the square root of 216 is 6√6.
2. Long Division Method
The long division method is a step-by-step technique to find the square root manually:
- Set up the number 216 in pairs of two digits from right to left: 2, 16, 00.
- Find the largest number whose square is less than or equal to 2, which is 1. Place 1 on top.
- Subtract 1 from 2, bring down the next pair to get 116.
- Double the quotient (1), which is 2, and find a digit X such that 2X × X ≤ 116. The correct digit is 4.
- Continue the process to reach the desired accuracy, resulting in √216 ≈ 14.6969.
3. Using a Calculator
For a quick and accurate result, use a calculator:
- Input 216 and press the square root button (√).
- The calculator will display the result as approximately 14.6969.
4. Using Computer Software
Computer software such as Excel or Google Sheets can also calculate square roots:
- Use the function =SQRT(216) in the software.
- The result will be approximately 14.6969.
5. Rounding the Square Root
Sometimes, the square root needs to be rounded to a specific decimal place:
- To the nearest tenth: √216 ≈ 14.7.
- To the nearest hundredth: √216 ≈ 14.70.
- To the nearest thousandth: √216 ≈ 14.697.
6. Fractional Form
Although √216 is an irrational number and cannot be expressed as an exact fraction, it can be approximated:
- As a fraction: √216 ≈ 14.7/1 ≈ 1470/100 ≈ 14 7/10.
7. Exponential Form
The square root can also be written with a fractional exponent:
- √216 = 2161/2.
Is 216 a Perfect Square?
A perfect square is a number that can be expressed as the product of an integer with itself. To determine whether 216 is a perfect square, we need to see if there is an integer that, when multiplied by itself, equals 216.
To check this, let's factorize 216:
- Prime factorization of 216: \(216 = 2^3 \times 3^3\)
We notice that the prime factors do not pair evenly. For 216 to be a perfect square, all the prime factors must pair evenly (i.e., each exponent in the prime factorization should be even). Since the exponents of both 2 and 3 are odd, 216 is not a perfect square.
Therefore, 216 cannot be expressed as the square of an integer, confirming that it is not a perfect square.
Rational or Irrational?
To determine whether the square root of 216 is rational or irrational, we need to understand the nature of rational and irrational numbers. A number is rational if it can be expressed as the quotient of two integers, i.e., in the form p/q where p and q are integers and q ≠ 0. An irrational number cannot be written as a simple fraction; its decimal form is non-repeating and non-terminating.
To find the square root of 216 in its simplest radical form, we use prime factorization:
- Prime factorization of 216: \(216 = 2^3 \times 3^3\)
- Taking the square root of both sides: \(\sqrt{216} = \sqrt{2^3 \times 3^3} = \sqrt{(2 \times 3)^3} = 6\sqrt{6}\)
The simplified form of the square root of 216 is \(6\sqrt{6}\). Since \(\sqrt{6}\) is not a perfect square and cannot be simplified to a fraction, it is an irrational number.
Therefore, the square root of 216 is irrational, because its simplified radical form includes \(\sqrt{6}\), which is irrational. The decimal approximation of the square root of 216 is 14.6969, a non-terminating and non-repeating decimal, further confirming its irrationality.
Conclusion
Exploring the square root of 216 in radical form reveals its significance across various mathematical applications. Whether calculating areas, dimensions, or diagonals in geometric shapes, understanding √216 as 6√6 enhances problem-solving capabilities. This knowledge not only aids in theoretical mathematics but also finds practical utility in fields requiring precise measurements and calculations.
Khám phá cách tính căn bậc hai của số 216 một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Hướng dẫn này sẽ giúp bạn hiểu rõ hơn về khái niệm này.
Căn Bậc Hai của 216
READ MORE:
Tìm hiểu cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 216 một cách chi tiết và dễ hiểu. Hướng dẫn này sẽ giúp bạn nắm rõ phương pháp thực hiện.
Đơn Giản Hóa Căn Bậc Hai của 216