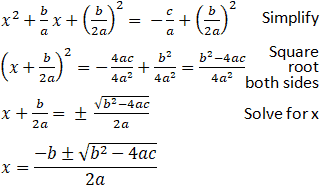Topic square root 99: Discover the comprehensive guide to the square root of 99 (√99). Learn calculation methods, properties, and real-life applications of this intriguing mathematical constant. Explore whether √99 is rational or irrational, and delve into its historical significance and estimation techniques. This article equips you with all the essential insights into √99.
Table of Content
- Square Root of 99
- Introduction to Square Root of 99
- Calculation Methods for √99
- Decimal Representation of √99
- Is √99 a Rational or Irrational Number?
- Estimation Techniques for √99
- Properties of √99
- Real-Life Applications of the Square Root of 99
- Historical Significance of the Number 99 and Its Square Root
- YOUTUBE: Xem video để học cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 99 (sqrt(99)).
Square Root of 99
The square root of 99 is approximately $\sqrt{99} \approx 9.95$.
Calculation Steps
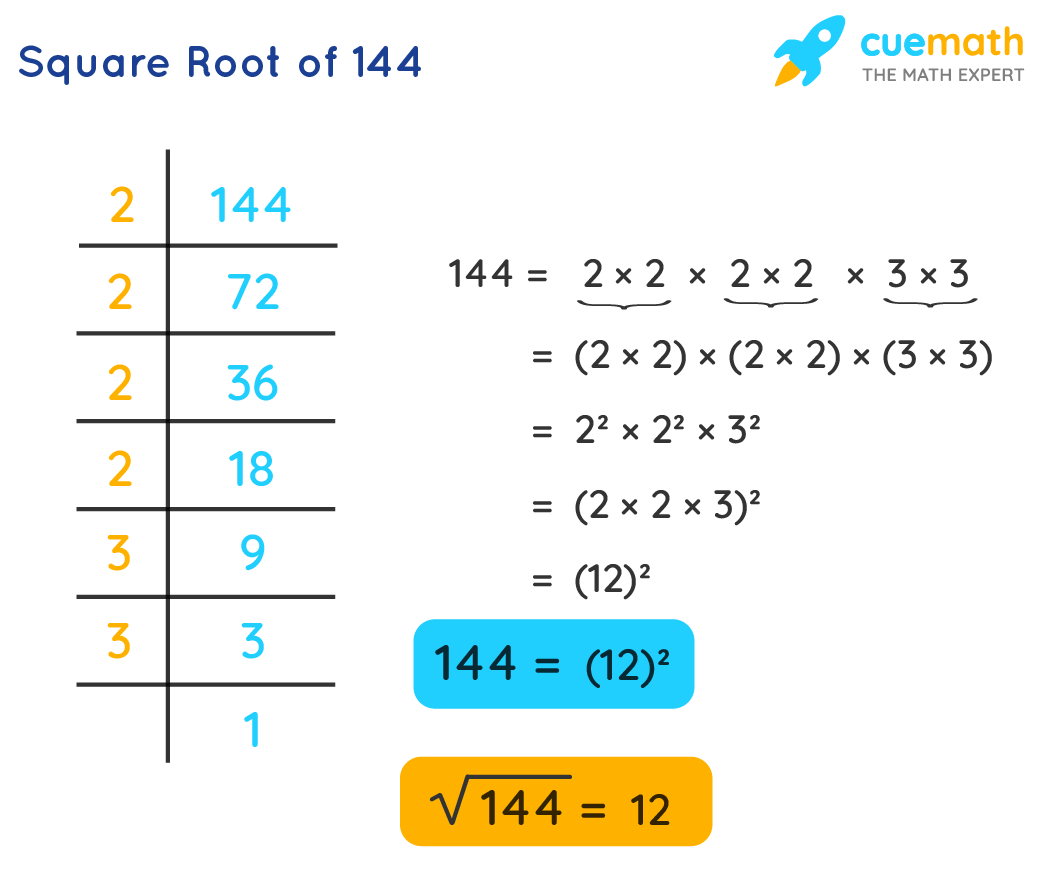
- Factorize 99 into prime factors: $99 = 3 \times 3 \times 11 = 3^2 \times 11$.
- Take the square root of each factor: $\sqrt{99} = \sqrt{3^2 \times 11} = 3\sqrt{11}$.
- Estimate $\sqrt{11} \approx 3.3166$.
- Multiply to find the approximate value: $3 \times 3.3166 \approx 9.95$.
Decimal Approximation
| Exact Value: | $\sqrt{99}$ |
| Approximation: | 9.949874 |
Further Information
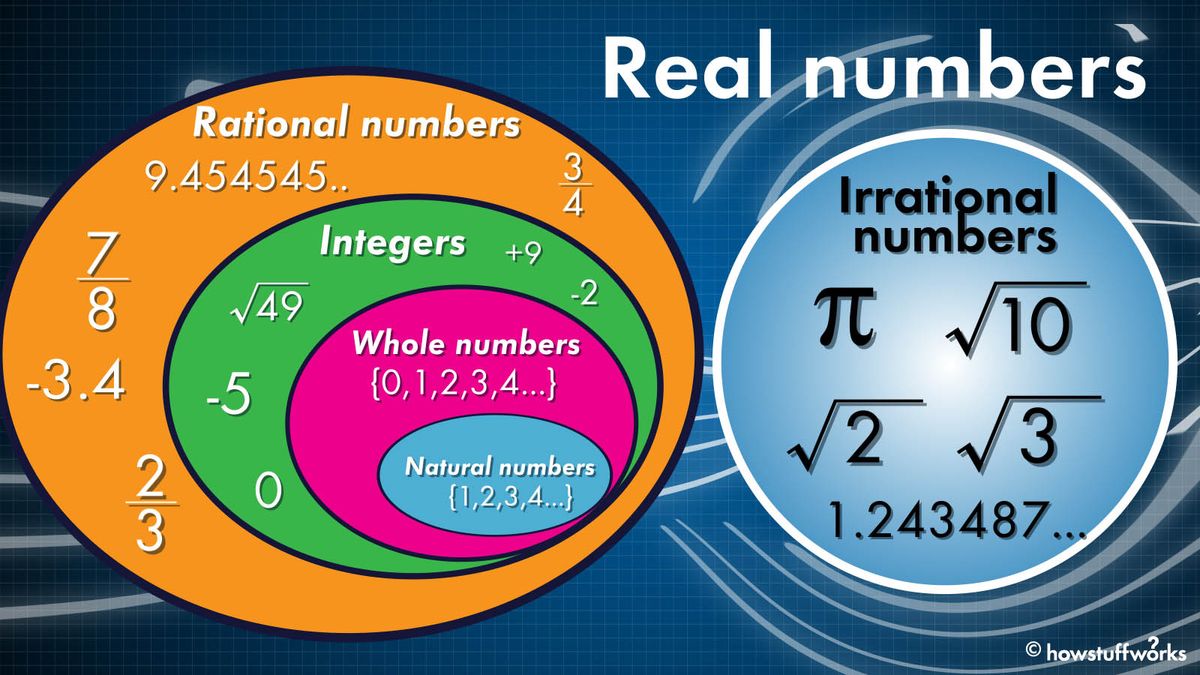
The square root of 99 is an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation goes on forever without repeating.

READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root of 99
The square root of 99, denoted as √99, is a mathematical constant that represents the number which, when multiplied by itself, gives the product 99. Understanding the square root of 99 involves exploring its properties, calculation methods, and its place in mathematics.
Here are key points to introduce you to the concept of √99:
- Definition: √99 is the positive real number that satisfies the equation \( x \times x = 99 \).
- Approximation: The approximate value of √99 is around 9.95.
- Nature: √99 is an irrational number, meaning its decimal representation goes on indefinitely without repeating.
- Calculation: Methods to calculate √99 include using numerical approximation techniques or algebraic methods such as factoring or the quadratic formula.
- Properties: It is a non-negative number, and its square is exactly equal to 99.
- Applications: In real-world applications, √99 appears in various fields including physics, engineering, and economics where calculations involving area or distance often require precise values.
Exploring √99 provides insights into fundamental mathematical concepts and practical applications, showcasing its importance in both theoretical and applied contexts.
Calculation Methods for √99
Calculating the square root of 99 (√99) involves several methods, each suited to different contexts:
- Numerical Approximation: Using iterative methods such as Newton's method to approximate √99 to a desired precision.
- Algebraic Methods: Applying algebraic techniques such as factoring or the quadratic formula, where √99 can be expressed in terms of its prime factors.
- Estimation Techniques: Utilizing approximation methods such as the Babylonian method, which iteratively improves the estimate of √99.
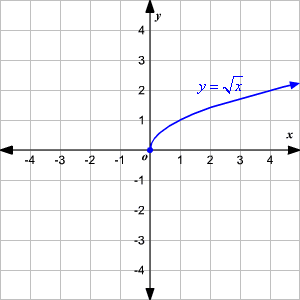
- Graphical Methods: Representing √99 graphically to find intersections or approximate values from the graph of the function \( f(x) = x^2 - 99 \).
- Computational Methods: Leveraging computational tools or software to calculate √99 with high precision, using algorithms designed for square root computation.
Each method offers unique advantages depending on the required accuracy, available resources, and mathematical background, ensuring flexibility in calculating √99 across various disciplines and applications.
Decimal Representation of √99
The decimal representation of √99, an irrational number, extends infinitely without repeating:
Here are the initial digits of √99:
| √99 ≈ | 9.949874 |
As an irrational number, √99 cannot be expressed exactly as a finite decimal or fraction. The decimal expansion continues indefinitely without settling into a repeating pattern, showcasing the unique and unending nature of irrational numbers like √99.
Is √99 a Rational or Irrational Number?
√99 is an irrational number. Here’s why:
- Definition: An irrational number cannot be expressed as a fraction of integers where the denominator is not zero.
- Calculation: √99 does not yield a terminating or repeating decimal, confirming its irrational nature.
- Proof by Contradiction: Assuming √99 is rational leads to a contradiction, as it contradicts the fundamental definition of irrationality.
- Prime Factorization: The prime factorization of 99 (3 × 3 × 11) shows that √99 cannot simplify to a rational number, reinforcing its irrationality.
- Real-Life Applications: In practical scenarios, irrational numbers like √99 are essential for precise measurements and calculations in fields such as geometry, physics, and engineering.
Understanding that √99 is irrational underscores its unique mathematical properties and its significance in both theoretical and applied contexts.

Estimation Techniques for √99
Estimating the square root of 99 can be approached using several methods:
- Comparison Method: Compare √99 with known square roots of nearby perfect squares, such as √100 = 10 and √81 = 9, to estimate its value between these two.
- Linear Interpolation: Given that 99 is closer to 100 than to 81, use linear interpolation to estimate √99 as closer to 9.9, considering the linear progression between √81 and √100.
- Using Approximation Formulas: Utilize approximation formulas such as the binomial approximation or iterative approximation methods to refine the estimation of √99.
- Calculating by Parts: Break down 99 into simpler components, such as 100 - 1, and approximate √99 based on the known values of √100 and √1.
These techniques provide varying degrees of accuracy depending on the level of precision required for the estimation of √99.
Properties of √99
The square root of 99, denoted as √99, possesses the following properties:
- Number Type: √99 is an irrational number, meaning it cannot be expressed as a simple fraction and its decimal representation goes on infinitely without repeating.
- Numerical Value: √99 is approximately 9.94987437...
- Relationship with Perfect Squares: √99 lies between √81 = 9 and √100 = 10, illustrating its position between consecutive perfect squares.
- Factorization: The factorization of 99 as 3 × 3 × 11 influences its square root, as √99 can be expressed as √(3^2 × 11) = 3√11.
- Decimal Digits: The decimal expansion of √99 begins as 9.949 and continues infinitely without a pattern.
Real-Life Applications of the Square Root of 99
The square root of 99, √99, finds practical applications in various real-life scenarios:
- Engineering and Construction: In structural engineering, √99 helps in calculating diagonal distances across rectangular spaces and determining lengths of certain geometric shapes.
- Mathematical Modeling: √99 appears in mathematical models that involve estimating values between known square roots, aiding in interpolation techniques.
- Financial Analysis: In financial modeling, √99 can be used to estimate volatility in market returns and in risk assessment calculations.
- Scientific Calculations: Physicists and chemists use √99 in calculations involving wave propagation, particle motion, and other phenomena where distance or scaling plays a crucial role.
- Education and Problem Solving: Understanding √99 helps students grasp concepts related to irrational numbers, square roots, and their applications in solving complex problems.
Historical Significance of the Number 99 and Its Square Root
The number 99 and its square root, √99, hold historical significance in various contexts:
- Ancient Mathematics: In ancient civilizations, √99 was a subject of mathematical exploration, contributing to the development of numerical systems and geometric principles.
- Cultural Symbolism: In some cultures, the number 99 symbolizes completeness or perfection, influencing philosophical and religious beliefs.
- Scientific Influence: √99 played a role in early scientific inquiries into irrational numbers and their properties, shaping the foundations of modern mathematics.
- Numerical Mysticism: The number 99 and its square root have been subjects of numerological studies and mystical interpretations across different cultures throughout history.
- Historical Calculations: Mathematicians throughout history used √99 in practical calculations related to geometry, astronomy, and engineering, reflecting its utility in ancient scientific pursuits.

Xem video để học cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của số 99 (sqrt(99)).
Cách đơn giản hóa căn bậc hai của 99: sqrt(99)
READ MORE:
Xem video để học về căn bậc hai của số 99.
Căn bậc hai của số 99