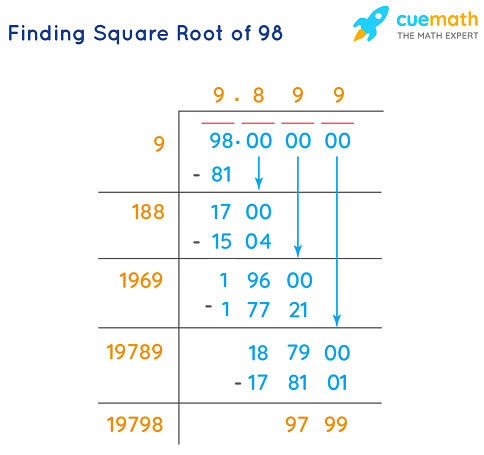
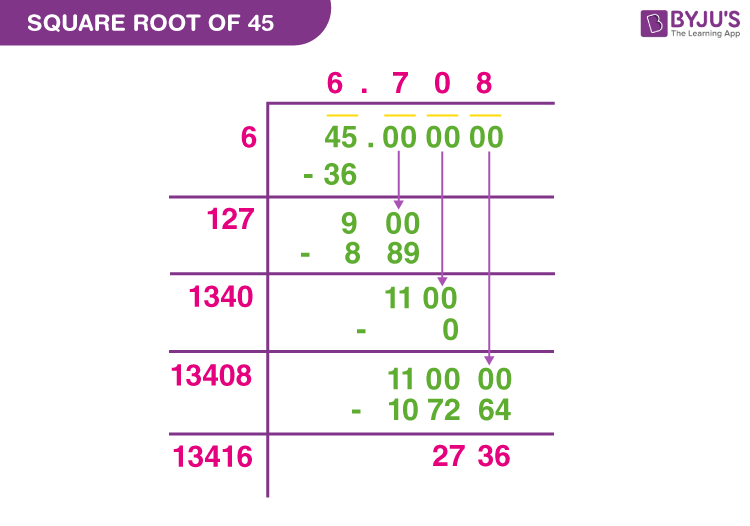
Topic square root graph calculator: Explore the fascinating world of mathematics with our comprehensive guide on using a square root graph calculator. Discover how to plot, interpret, and analyze square root functions effectively, making your learning experience both engaging and insightful.
Table of Content
- Square Root Graph Calculator
- Introduction to Square Root Functions
- Domain and Range of Square Root Functions
- Graphing Square Root Functions
- Examples of Square Root Function Graphs
- Using Online Graphing Calculators
- Popular Square Root Graph Calculators
- Step-by-Step Guide to Graphing Square Root Functions
- Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Advanced Features in Graphing Calculators
- Educational Resources for Learning Square Root Graphs
- Conclusion and Further Reading
- YOUTUBE: Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách vẽ đồ thị hàm căn bậc hai trên máy tính TI-84 Plus CE. Hữu ích cho những ai muốn học cách sử dụng máy tính đồ thị cho phép vẽ đồ thị căn bậc hai.
Square Root Graph Calculator
The "square root graph calculator" is a useful tool for visualizing the square root function and performing various mathematical calculations. Below is an overview of its features, functions, and some popular tools available online.
Popular Graphing Calculators
-
Desmos Graphing Calculator
Desmos offers an interactive graphing calculator that allows you to plot functions, including square root functions. It's user-friendly and widely used for educational purposes.
-
GeoGebra
GeoGebra provides a graphing calculator with powerful features for plotting square root functions and other mathematical expressions. It supports dynamic visualization and interactive geometry.
-
Symbolab
Symbolab's calculator not only graphs square root functions but also provides step-by-step solutions and explanations for various mathematical problems.
-
TI-84 Plus Graphing Calculator
The TI-84 Plus is a popular handheld calculator that supports graphing square root functions. It is often used in educational settings and standardized tests.
-
Casio fx-9750GII
This Casio graphing calculator is known for its affordability and functionality, including the ability to graph square root functions efficiently.
How to Graph Square Root Functions
Graphing a square root function involves plotting points that satisfy the equation \( y = \sqrt{x} \). Here's a step-by-step guide:
- Input the square root function \( y = \sqrt{x} \) into your graphing calculator.
- Adjust the viewing window to capture the necessary range of x and y values.
- Observe the plotted curve, which will start at the origin (0,0) and extend to the right.
- Use the trace feature to examine specific points on the graph.
Understanding the Square Root Function
The square root function is a type of radical function, represented as \( y = \sqrt{x} \). It is only defined for non-negative values of x because the square root of a negative number is not a real number.
The general properties of the square root function include:
- The domain is \( x \geq 0 \).
- The range is \( y \geq 0 \).
- The function is increasing, meaning as x increases, y also increases.
Example Calculations
| Expression | Result |
|---|---|
| \(\sqrt{4}\) | 2 |
| \(\sqrt{9}\) | 3 |
| \(\sqrt{16}\) | 4 |
| \(\sqrt{25}\) | 5 |
Additional Resources
- - Offers educational videos on graphing square root functions and other mathematical concepts.
- - Provides a variety of calculators, including ones for simplifying square roots and other functions.
- - Features an online calculator for various mathematical calculations, including square roots.
READ MORE:
Introduction to Square Root Functions
The square root function, denoted as \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \), is a fundamental mathematical function that maps a non-negative input \( x \) to its non-negative square root. This function is widely used in various fields such as mathematics, physics, engineering, and computer science.
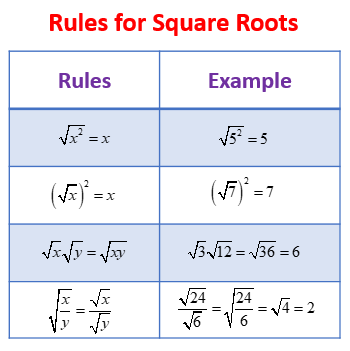
Definition: The square root of a number \( x \) is a value that, when multiplied by itself, gives \( x \). In other words, if \( y = \sqrt{x} \), then \( y^2 = x \).
Notation: The square root function is represented by the radical symbol \( \sqrt{} \). For example, \( \sqrt{9} = 3 \) because \( 3 \times 3 = 9 \).
Properties of the Square Root Function:
- The domain of \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) is \( x \geq 0 \).
- The range of \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) is \( y \geq 0 \).
- The function \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) is continuous and non-decreasing.
- The square root function has a unique output for each input within its domain.
Graphical Representation: The graph of \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) is a curve that starts at the origin (0,0) and increases gradually. The function’s graph is part of the parabola \( y^2 = x \), but only the upper half.
Applications:
- Geometry: The square root is used to find the side length of a square when the area is known.
- Statistics: Square root transformations are used to stabilize the variance of data.
- Physics: It is used in formulas to calculate speed and acceleration.
- Finance: The square root is used in calculating the volatility of financial instruments.
Understanding the square root function is essential for grasping more complex mathematical concepts and for solving various real-world problems.
Domain and Range of Square Root Functions
The domain and range of the square root function are fundamental concepts that describe the allowable inputs and resulting outputs of the function \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \).
Domain:
The domain of the square root function consists of all non-negative real numbers. This is because the square root of a negative number is not defined in the set of real numbers. Mathematically, the domain is represented as:
\[
\text{Domain} = \{ x \in \mathbb{R} \mid x \geq 0 \}
\]
In interval notation, this is written as:
\[
\text{Domain} = [0, \infty)
\]
Range:
The range of the square root function is also all non-negative real numbers. This is because the square root of any non-negative number is non-negative. Therefore, the range is:
\[
\text{Range} = \{ y \in \mathbb{R} \mid y \geq 0 \}
\]
In interval notation, this is:
\[
\text{Range} = [0, \infty)
\]
Examples:
| \( x \) | \( \sqrt{x} \) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
Graphical Interpretation:
The graph of \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) begins at the origin (0,0) and extends to the right, increasing gradually. It only exists in the first quadrant of the Cartesian plane, reflecting its non-negative domain and range. As \( x \) increases, the slope of the graph decreases, creating a curve that flattens as \( x \) moves towards infinity.
Real-World Applications:
- Geometry: Used to find side lengths of squares when the area is known.
- Physics: Helps in computing values for certain motion and energy equations.
- Statistics: Applied in data transformations to normalize distributions and stabilize variances.
- Finance: Utilized in various algorithms for risk and volatility assessments.
Understanding the domain and range of the square root function is essential for solving practical problems and interpreting its graph accurately.
Graphing Square Root Functions
Graphing the square root function \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) helps visualize how the function behaves and understand its characteristics. Below is a step-by-step guide to graphing this function:
Step-by-Step Guide:
- Identify the Function: The standard form of the square root function is \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \). This function starts at the origin and increases as \( x \) increases.
- Determine the Domain: As discussed, the domain of \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) is all non-negative real numbers (\( x \geq 0 \)). This means you will only plot points where \( x \geq 0 \).
- Create a Table of Values: Choose several non-negative values of \( x \) and calculate their corresponding \( y \) values:
\( x \) \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) 0 0 1 1 4 2 9 3 16 4 - Plot the Points: On a Cartesian plane, plot the points from your table. For example, (0,0), (1,1), (4,2), (9,3), and (16,4). Ensure that you only plot points where \( x \) is non-negative.
- Draw the Curve: Connect the plotted points smoothly. The graph will start at the origin and curve upwards, gradually flattening out as \( x \) increases. The resulting shape is the right half of a parabola, extending infinitely to the right.
- Label the Axes: Ensure the \( x \)-axis is labeled as the input (\( x \)) and the \( y \)-axis as the output (\( \sqrt{x} \)). Include appropriate scale and labels for clarity.
Graph Features:
- Origin Point: The graph of \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) passes through the origin (0,0).
- Non-negativity: The graph only exists in the first quadrant, where both \( x \) and \( y \) are non-negative.
- Shape: The graph starts steep and becomes less steep as \( x \) increases, forming a curve that flattens out.
- Behavior: As \( x \) approaches infinity, \( \sqrt{x} \) also approaches infinity but at a decreasing rate.
Graphing Tools:
Several online graphing calculators can assist in visualizing the square root function:
- Desmos: An intuitive and user-friendly graphing tool that allows plotting of the square root function and customization of the graph.
- GeoGebra: Provides dynamic graphing capabilities and interactive elements for deeper exploration.
- Symbolab: Offers detailed graphing and analysis of functions, including square roots.
Using these tools, you can easily graph the square root function and experiment with transformations and variations to gain a deeper understanding of its properties.
Examples of Square Root Function Graphs
Examining examples of square root function graphs helps illustrate their properties and how they can be transformed. Here are some key examples:
1. Basic Square Root Function:
The basic square root function is \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \). Its graph is a smooth curve starting at the origin (0,0) and extending to the right:
| \( x \) | \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 9 | 3 |
| 16 | 4 |
The graph starts steep and flattens as \( x \) increases.
2. Vertical Shift: \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} + c \)
Adding a constant \( c \) shifts the graph vertically:
\[
f(x) = \sqrt{x} + 2
\]
This shifts the graph of \( \sqrt{x} \) up by 2 units. Each \( y \)-value increases by 2:
| \( x \) | \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} + 2 \) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 2 |
| 1 | 3 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 9 | 5 |
| 16 | 6 |
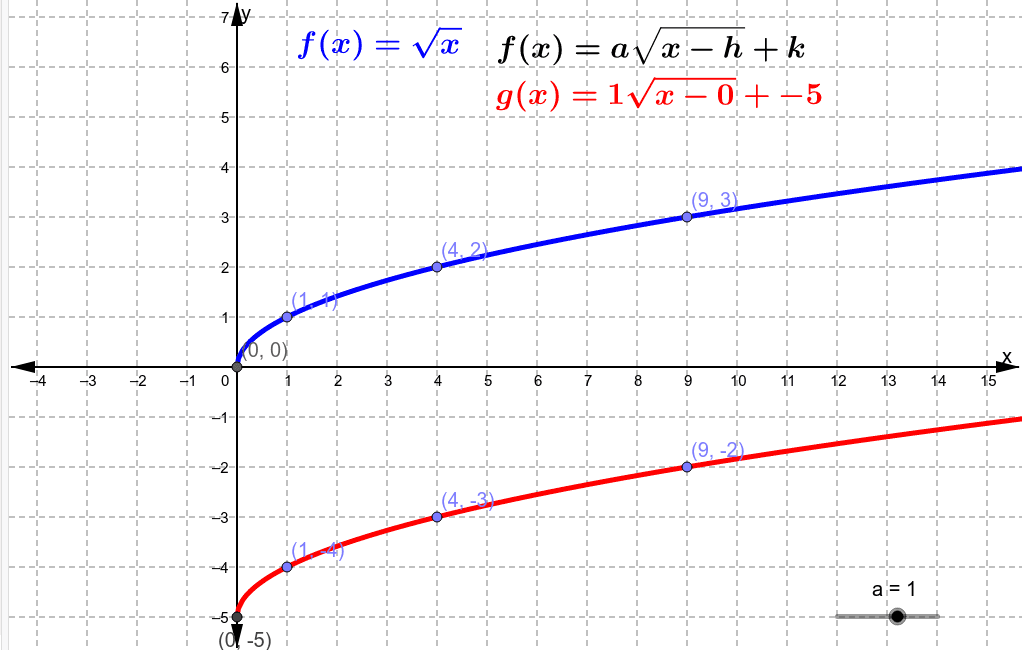
3. Horizontal Shift: \( f(x) = \sqrt{x - h} \)
Subtracting a constant \( h \) shifts the graph horizontally:
\[
f(x) = \sqrt{x - 3}
\]
This shifts the graph of \( \sqrt{x} \) to the right by 3 units. The curve starts at \( x = 3 \):
| \( x \) | \( f(x) = \sqrt{x - 3} \) |
|---|---|
| 3 | 0 |
| 4 | 1 |
| 7 | 2 |
| 12 | 3 |
| 19 | 4 |
4. Vertical Stretch/Compression: \( f(x) = a \sqrt{x} \)
Multiplying by a constant \( a \) stretches or compresses the graph vertically:
\[
f(x) = 2 \sqrt{x}
\]
This stretches the graph by a factor of 2. Each \( y \)-value is twice that of \( \sqrt{x} \):
| \( x \) | \( f(x) = 2 \sqrt{x} \) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 2 |
| 4 | 4 |
| 9 | 6 |
| 16 | 8 |
5. Horizontal Stretch/Compression: \( f(x) = \sqrt{kx} \)
Multiplying the input by a constant \( k \) compresses or stretches the graph horizontally:
\[
f(x) = \sqrt{2x}
\]
This compresses the graph horizontally by a factor of 2:
| \( x \) | \( f(x) = \sqrt{2x} \) |
|---|---|
| 0 | 0 |
| 0.5 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 4.5 | 3 |
| 8 | 4 |
These examples illustrate how the basic graph of \( f(x) = \sqrt{x} \) can be transformed through vertical and horizontal shifts, stretches, and compressions. Experimenting with these transformations helps deepen the understanding of the function’s graphical behavior.
Using Online Graphing Calculators
- : A versatile graphing tool offering real-time graphing, scientific calculator capabilities, and interactive features suitable for educational purposes.
- : Combines geometry, algebra, spreadsheets, graphing, statistics, and calculus in one easy-to-use package, accessible both online and offline.
- : Provides advanced graphing calculator functionalities with step-by-step solutions, making it useful for students learning mathematical concepts.
- : Offers a wide range of calculators including graphing tools for square root functions and other mathematical equations, enhancing problem-solving capabilities.
- : Focuses on providing free graphing tools with customizable settings and a user-friendly interface, suitable for various mathematical tasks.
- : Offers educational resources and graphing tools specifically designed for learning square root graphs and other mathematical topics.
Popular Square Root Graph Calculators
- : Known for its intuitive interface and powerful graphing capabilities, ideal for visualizing square root functions with real-time adjustments.
- : Offers comprehensive tools for graphing square root functions along with other mathematical concepts, suitable for both beginners and advanced users.
- : Provides detailed graphs of square root functions and offers step-by-step solutions to help users understand the process of graphing.
- : Features a user-friendly interface and supports graphing of square root functions with customizable parameters and interactive plotting.
- : Offers free tools for graphing square root functions with clear visuals and options for adjusting scales and viewing different aspects of the graph.
- : Provides educational resources and graphing tools specifically focused on square root functions, designed to aid in learning mathematical concepts visually.
Step-by-Step Guide to Graphing Square Root Functions
- Choose a suitable graphing calculator such as or to begin.
- Identify the function in the form \( y = \sqrt{x} \), where \( x \) represents the input variable.
- Understand the domain restrictions; for square root functions, \( x \geq 0 \).
- Plot points on the graph by substituting different values of \( x \) (e.g., \( x = 0, 1, 4, 9 \)) and calculating \( y \).
- Connect the points smoothly to form the curve of the square root function, ensuring it represents the shape of \( y = \sqrt{x} \).
- Label the axes clearly (x-axis for input values and y-axis for output values).
- Adjust the scale and view of the graph to visualize different portions of the square root function, if necessary.
- Use the graphing calculator's features to analyze the behavior of the function, including its intercepts, asymptotes, and transformations.
- Verify the accuracy of the graph by comparing it with known properties of square root functions.
- Consider exploring advanced features of the graphing calculator to enhance understanding and visualization of square root graphs.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
- Incorrect domain selection: Ensure to use \( x \geq 0 \) for square root functions to avoid undefined values.
- Improper scaling of axes: Always adjust the scale appropriately to avoid misrepresenting the graph.
- Skipping point plotting: Avoid skipping the process of plotting points to ensure accuracy in graphing.
- Ignoring transformations: Understand how transformations affect the graph to accurately plot and interpret the function.
- Not labeling axes and points: Labeling is crucial for clarity; ensure all axes and significant points are clearly marked.
- Overlooking calculator features: Explore all features of the graphing calculator to fully utilize its capabilities for accurate graphing.
- Failing to verify results: Always verify the graph against known properties and calculations to ensure correctness.
- Not using available resources: Utilize tutorials, guides, and online resources to enhance understanding and avoid mistakes.

Advanced Features in Graphing Calculators
- Interactive Graphing: Allows real-time manipulation of graphs, enabling users to explore how changes in parameters affect the square root function.
- Function Analysis: Provides tools to analyze functions such as identifying intercepts, asymptotes, and points of inflection, enhancing understanding of the behavior of square root graphs.
- Multiple Graphs: Supports plotting multiple functions on the same graph, facilitating comparisons and visualizations of different square root functions or transformations.
- Customization: Offers options to customize graphs with different colors, line styles, and labels, making it easier to distinguish between multiple functions or graph elements.
- Export and Share: Allows users to save graphs or share them online, useful for educational purposes or collaborative work.
- Integration with Calculus: Includes features for calculus applications such as finding derivatives and integrals of square root functions directly from the graph.
- Accessibility: Available on various platforms including web-based, desktop, and mobile versions, ensuring accessibility and usability across different devices.
Educational Resources for Learning Square Root Graphs
- : Provides comprehensive tutorials and practice exercises on graphing square root functions, suitable for learners of all levels.
- : Offers clear explanations and interactive examples of square root graphs, making it easy to understand the concepts visually.
- : Includes educational modules specifically dedicated to graphing square root functions, with step-by-step guides and practice problems.
- : Provides dynamic tools for exploring square root graphs interactively, coupled with educational resources for teachers and students.
- : Offers detailed explanations and examples of square root function graphs, along with a graphing calculator for hands-on practice.
Conclusion and Further Reading
In conclusion, graphing square root functions is an essential skill in mathematics, allowing for visual representation and analysis of relationships involving square roots. By utilizing the advanced features of graphing calculators and accessing educational resources, learners can deepen their understanding and proficiency in graphing square root functions.
For further reading and exploration:
- Continue practicing with different square root functions to enhance graphing skills.
- Explore additional graphing calculator functionalities to discover more about mathematical functions.
- Review online tutorials and guides to reinforce understanding of square root graphs.
- Engage in interactive tools and exercises to apply knowledge in graphing square root functions.
Hướng dẫn chi tiết cách vẽ đồ thị hàm căn bậc hai trên máy tính TI-84 Plus CE. Hữu ích cho những ai muốn học cách sử dụng máy tính đồ thị cho phép vẽ đồ thị căn bậc hai.
How to Graph a Square Root Function in the TI-84 Plus CE Calculator | Hướng dẫn vẽ đồ thị hàm căn bậc hai trên máy tính TI-84 Plus CE
READ MORE:
Hướng dẫn chi tiết về cách vẽ đồ thị hàm căn bậc hai. Phù hợp cho những ai muốn học cách đồ thị hóa các hàm căn bậc hai và sử dụng máy tính đồ thị.
Graphing Square Root Functions | Vẽ đồ thị hàm căn bậc hai